Molecular Study of a Hoxa2 Gain-of-Function in Chondrogenesis: A Model of Idiopathic Proportionate Short Stature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
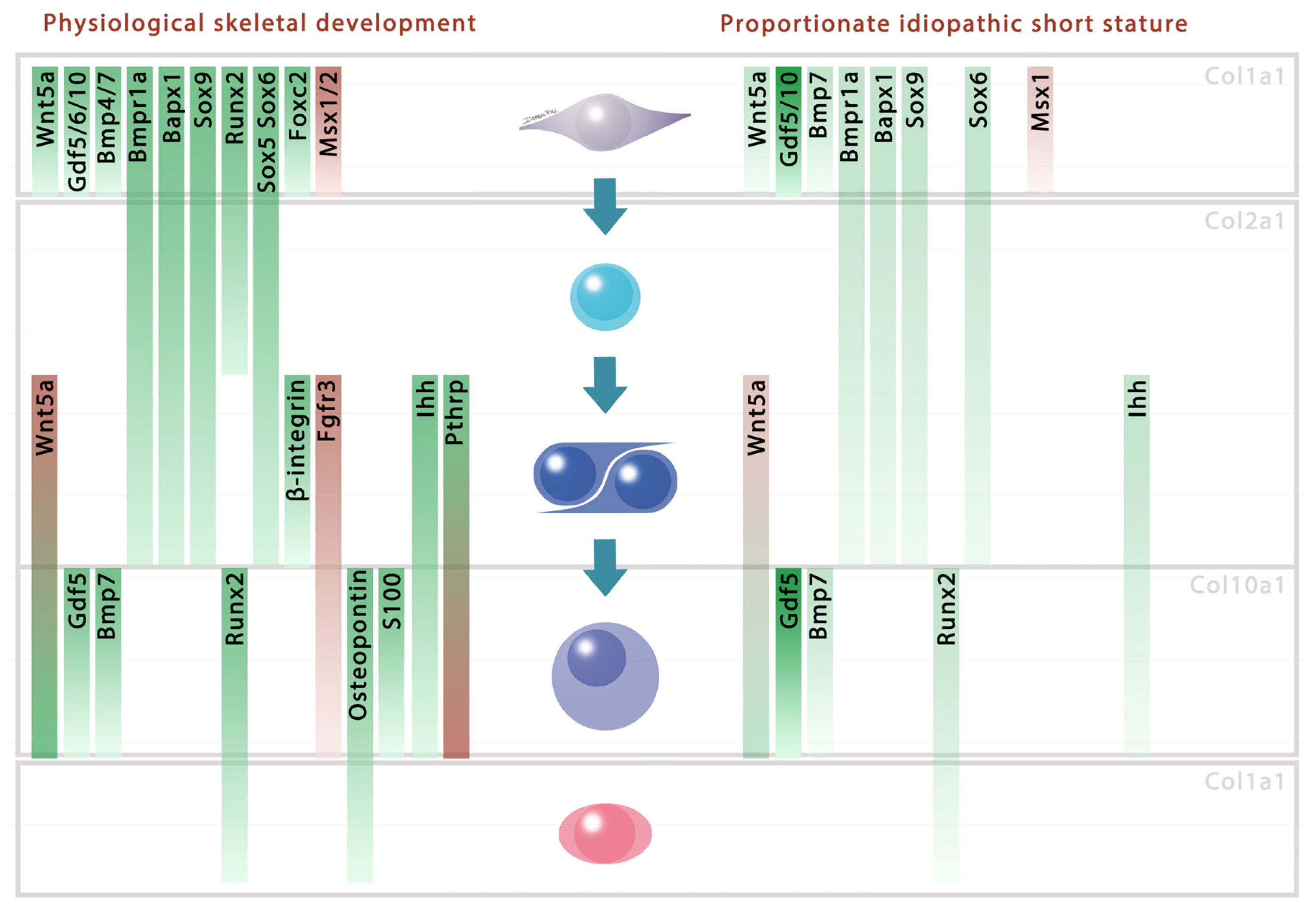
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Transgenic Mice and Embryos
3.2. Immunohistochemistry
3.3. Western Blotting
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-14-20386-s001.pdf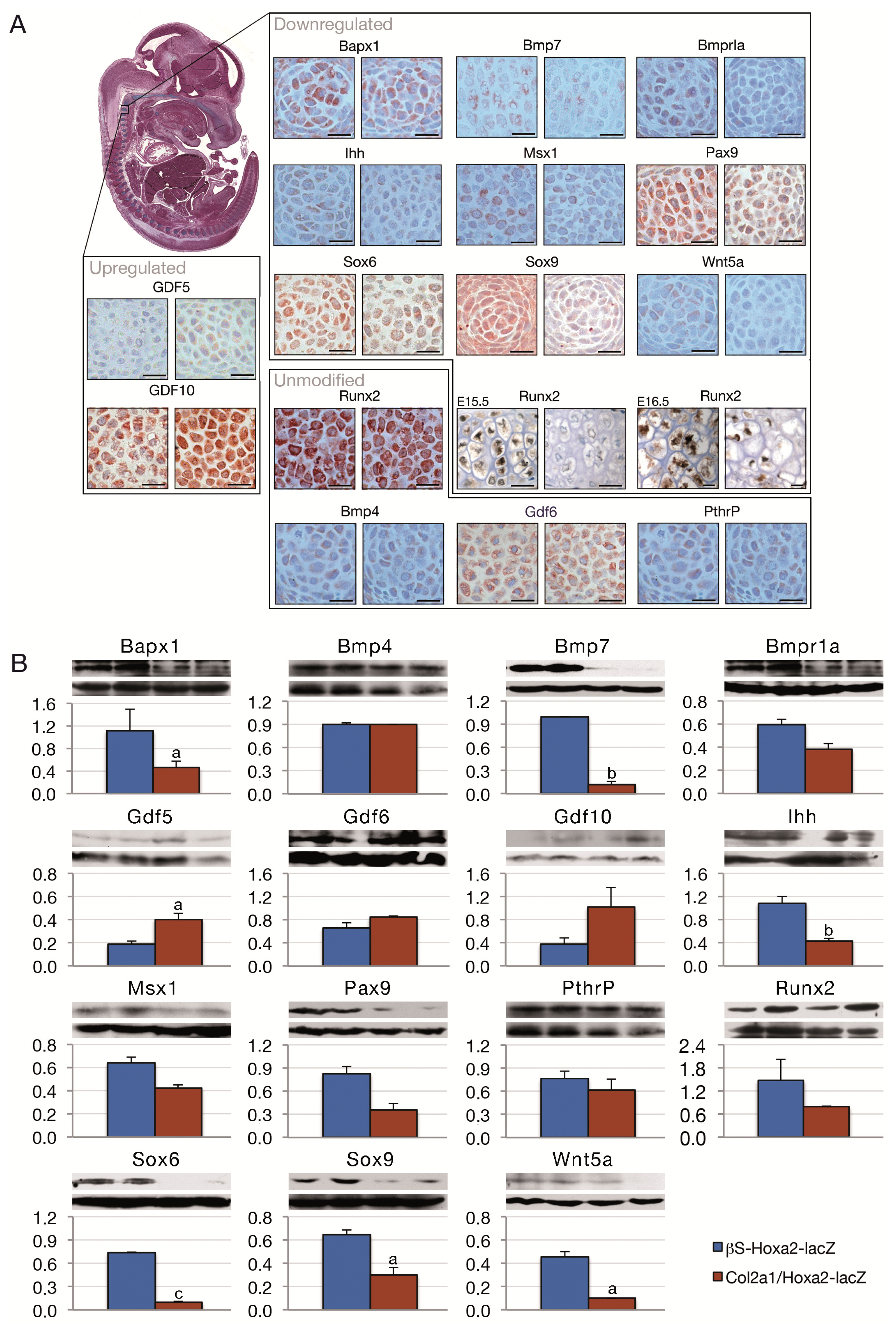
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- POSNA. Short Stature. Available online: http://www.posna.org/ (accessed on 3 February 2013).
- Oostdijk, W.; Grote, F.K.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.; Wit, J.M. Diagnostic approach in children with short stature. Horm. Res 2009, 72, 206–217. [Google Scholar]
- Massip, L.; Ectors, F.; Deprez, P.; Maleki, M.; Behets, C.; Lengele, B.; Delahaut, P.; Picard, J.; Rezsohazy, R. Expression of Hoxa2 in cells entering chondrogenesis impairs overall cartilage development. Differentiation 2007, 75, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Deprez, P.M.; Nichane, M.G.; Rousseaux, P.; Devogelaer, J.P.; Chappard, D.; Lengele, B.G.; Rezsohazy, R.; Nyssen-Behets, C. Postnatal growth defect in mice upon persistent Hoxa2 expression in the chondrogenic cell lineage. Differentiation 2012, 83, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Baek, W.Y.; Kim, J.E. Transcriptional regulation of bone formation. Front. Biosci 2011, 3, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Marie, P.J. Transcription factors controlling osteoblastogenesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2008, 473, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Eames, B.F.; de la Fuente, L.; Helms, J.A. Molecular ontogeny of the skeleton. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2003, 69, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda, R.; Castagnola, P.; Cancedda, F.D.; Dozin, B.; Quarto, R. Developmental control of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol 2000, 44, 707–714. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, V.; Smits, P. Transcriptional control of chondrocyte fate and differentiation. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2005, 75, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, I.; Hill, R.E.; Balling, R.; Munsterberg, A.; Imai, K. Pax1 and Pax9 activate Bapx1 to induce chondrogenic differentiation in the sclerotome. Development 2003, 130, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Church, V.; Nohno, T.; Linker, C.; Marcelle, C.; Francis-West, P. Wnt regulation of chondrocyte differentiation. J. Cell Sci 2002, 115, 4809–4818. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Z.; Qi, Y.Y.; Zou, X.H.; Wang, L.L.; Ouyang, H.W. Comparison the effects of BMP-4 and BMP-7 on articular cartilage repair with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. IFMBE Proc 2009, 23, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Monsoro-Burq, A.H.; Bontoux, M.; Teillet, M.A.; le Douarin, N.M. Heterogeneity in the development of the vertebra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10435–10439. [Google Scholar]
- Monsoro-Burq, A.H.; Duprez, D.; Watanabe, Y.; Bontoux, M.; Vincent, C.; Brickell, P.; le Douarin, N. The role of bone morphogenetic proteins in vertebral development. Development 1996, 122, 3607–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Kempf, H.; Murtaugh, L.C.; Sato, M.E.; Lassar, A.B. Shh establishes an Nkx3.2/Sox9 autoregulatory loop that is maintained by BMP signals to induce somitic chondrogenesis. Genes Dev 2002, 16, 1990–2005. [Google Scholar]
- Minina, E.; Wenzel, H.M.; Kreschel, C.; Karp, S.; Gaffield, W.; McMahon, A.P.; Vortkamp, A. BMP and Ihh/PTHrP signaling interact to coordinate chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Development 2001, 128, 4523–4534. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, B.S.; Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Yoshii, I.; Mishina, Y.; Behringer, R.R.; Lyons, K.M. Bmpr1a and Bmpr1b have overlapping functions and are essential for chondrogenesis in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5062–5067. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Topol, L.; Lee, H.; Wu, J. Wnt5a and Wnt5b exhibit distinct activities in coordinating chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Development 2003, 130, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, B.S.; Pogue, R.; Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Yoshii, I.; Mishina, Y.; Behringer, R.R.; Lyons, K.M. BMPs regulate multiple aspects of growth-plate chondrogenesis through opposing actions on FGF pathways. Development 2006, 133, 4667–4678. [Google Scholar]
- Komori, T. Regulation of skeletal development by the Runx family of transcription factors. J. Cell Biochem 2005, 95, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Amano, K.; Ichida, F.; Sugita, A.; Hata, K.; Wada, M.; Takigawa, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Kogo, M.; Nishimura, R.; Yoneda, T. MSX2 stimulates chondrocyte maturation by controlling Ihh expression. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 29513–29521. [Google Scholar]
- Kempf, H.; Ionescu, A.; Udager, A.M.; Lassar, A.B. Prochondrogenic signals induce a competence for Runx2 to activate hypertrophic chondrocyte gene expression. Dev. Dyn 2007, 236, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, S.; Andoh, M.; Ueno-Kudoh, H.; Sato, T.; Miyaki, S.; Asahara, H. Sox9 directly promotes Bapx1 gene expression to repress Runx2 in chondrocytes. Exp. Cell Res 2009, 315, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Deng, J.M.; Ogunrinu, G.; Behringer, R.R. Col2a1-directed expression of Cre recombinase in differentiating chondrocytes in transgenic mice. Genesis 2000, 26, 145–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kanzler, B.; Kuschert, S.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Mallo, M. Hoxa-2 restricts the chondrogenic domain and inhibits bone formation during development of the branchial area. Development 1998, 125, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar]
- Lettice, L.A.; Purdie, L.A.; Carlson, G.J.; Kilanowski, F.; Dorin, J.; Hill, R.E. The mouse bagpipe gene controls development of axial skeleton, skull, and spleen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9695–9700. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, N.; Martin-Seisdedos, C.; McCue, P.; Croce, C.M. BMP7 null mutation in mice: Developmental defects in skeleton, kidney, and eye. Exp. Cell Res 1997, 230, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tribioli, C.; Lufkin, T. The murine Bapx1 homeobox gene plays a critical role in embryonic development of the axial skeleton and spleen. Development 1999, 126, 5699–5711. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, L.C.; Mallein-Gerin, F.; Lee, J.C. Differential effects of osteogenic protein-1 (BMP-7) on gene expression of BMP and GDF family members during differentiation of the mouse MC615 chondrocyte cells. J. Cell Physiol 2002, 191, 298–309. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, B.S.; Lyons, K.M. Multiple functions of BMPs in chondrogenesis. J. Cell Biochem 2004, 93, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bendall, A.J.; Abate-Shen, C. Roles for Msx and Dlx homeoproteins in vertebrate development. Gene 2000, 247, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, F.; Lubbert, M.; Stock, M. Upstream and downstream targets of RUNX proteins. J. Cell Biochem 2003, 89, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama, Y.; Tuan, R.S.; Shum, L. Distinct functions of BMP4 and GDF5 in the regulation of chondrogenesis. J. Cell Biochem 2004, 91, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Bhargav, D.; Wei, A.; Williams, L.A.; Tao, H.; Ma, D.D.; Diwan, A.D. BMP-13 emerges as a potential inhibitor of bone formation. Int. J. Biol. Sci 2009, 5, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Marsell, R.; Einhorn, T.A. The role of endogenous bone morphogenetic proteins in normal skeletal repair. Injury 2009, 40, S4–S7. [Google Scholar]
- Meech, R.; Edelman, D.B.; Jones, F.S.; Makarenkova, H.P. The homeobox transcription factor Barx2 regulates chondrogenesis during limb development. Development 2005, 132, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg, H.M. Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 2003, 423, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, H. Control of chondrogenesis by the transcription factor Sox9. Mod. Rheumatol 2008, 18, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, C.D.; Maity, S.N.; Lu, J.F.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Coustry, F.; de Crombrugghe, B.; Yasuda, H. Identification of SOX9 interaction sites in the genome of chondrocytes. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10113. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, E.W.; Drissi, M.H. WNT5A regulates chondrocyte differentiation through differential use of the CaN/NFAT and IKK/NF-kappaB pathways. Mol. Endocrinol 2010, 24, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Lanske, B.; Amling, M.; Neff, L.; Guiducci, J.; Baron, R.; Kronenberg, H.M. Ablation of the PTHrP gene or the PTH/PTHrP receptor gene leads to distinct abnormalities in bone development. J. Clin. Invest 1999, 104, 399–407. [Google Scholar]
- Karaplis, A.C.; Luz, A.; Glowacki, J.; Bronson, R.T.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Kronenberg, H.M.; Mulligan, R.C. Lethal skeletal dysplasia from targeted disruption of the parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene. Genes Dev 1994, 8, 277–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ducy, P.; Starbuck, M.; Priemel, M.; Shen, J.; Pinero, G.; Geoffroy, V.; Amling, M.; Karsenty, G. A Cbfa1-dependent genetic pathway controls bone formation beyond embryonic development. Genes Dev 1999, 13, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.P.; Bradley, A.; McMahon, A.P.; Jones, S. A Wnt5a pathway underlies outgrowth of multiple structures in the vertebrate embryo. Development 1999, 126, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Akazawa, H.; Komuro, I.; Sugitani, Y.; Yazaki, Y.; Nagai, R.; Noda, T. Targeted disruption of the homeobox transcription factor Bapx1 results in lethal skeletal dysplasia with asplenia and gastroduodenal malformation. Genes Cells 2000, 5, 499–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Selever, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Mishina, Y.; Martin, J.F.; Behringer, R.R. BMP receptor type IA in limb bud mesenchyme regulates distal outgrowth and patterning. Dev. Biol 2006, 295, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- St-Jacques, B.; Hammerschmidt, M.; McMahon, A.P. Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev 1999, 13, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, H.; Lyons, J.P.; Mori-Akiyama, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, J.M.; Taketo, M.M.; Nakamura, T.; Behringer, R.R.; et al. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev 2004, 18, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, H.; Neubuser, A.; Kratochwil, K.; Balling, R. Pax9-deficient mice lack pharyngeal pouch derivatives and teeth and exhibit craniofacial and limb abnormalities. Genes Dev 1998, 12, 2735–2747. [Google Scholar]
- Smits, P.; Li, P.; Mandel, J.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, J.M.; Behringer, R.R.; de Crombrugghe, B.; Lefebvre, V. The transcription factors L-Sox5 and Sox6 are essential for cartilage formation. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, H.; Wilm, B.; Sakai, N.; Imai, K.; Maas, R.; Balling, R. Pax1 and Pax9 synergistically regulate vertebral column development. Development 1999, 126, 5399–5408. [Google Scholar]
- Smits, P.; Dy, P.; Mitra, S.; Lefebvre, V. Sox5 and Sox6 are needed to develop and maintain source, columnar, and hypertrophic chondrocytes in the cartilage growth plate. J. Cell Biol 2004, 164, 747–758. [Google Scholar]
- Abzhanov, A.; Rodda, S.J.; McMahon, A.P.; Tabin, C.J. Regulation of skeletogenic differentiation in cranial dermal bone. Development 2007, 134, 3133–3144. [Google Scholar]
- Franz-Odendaal, T.A. Induction and patterning of intramembranous bone. Front. Biosci 2012, 17, 3734–3746. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, B.K. Development of the clavicles in birds and mammals. J. Exp. Zool 2001, 289, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.F.; Fukai, N.; Selby, P.B.; Olsen, B.R.; Mundlos, S. Mouse clavicular development: Analysis of wild-type and cleidocranial dysplasia mutant mice. Dev. Dyn 1997, 210, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, J.; Klinger, M.; Kruse, C.; Faza, M.; Hargus, G.; Rohwedel, J. Ultrastructural analysis of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived chondrocytes. Anat. Embryol 2005, 210, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Buxton, P.; Edwards, C.; Archer, C.W.; Francis-West, P. Growth/differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) and skeletal development. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am 2001, 83, S23–S30. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, T.J.; Gerstenfeld, L.C.; Einhorn, T.A. Differential temporal expression of members of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily during murine fracture healing. J. Bone Miner Res 2002, 17, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Dehne, T.; Schenk, R.; Perka, C.; Morawietz, L.; Pruss, A.; Sittinger, M.; Kaps, C.; Ringe, J. Gene expression profiling of primary human articular chondrocytes in high-density micromasses reveals patterns of recovery, maintenance, re- and dedifferentiation. Gene 2010, 462, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, H.; Chaboissier, M.C.; Martin, J.F.; Schedl, A.; de Crombrugghe, B. The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev 2002, 16, 2813–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, X.; Joeng, K.S.; Long, F. Indian hedgehog requires additional effectors besides Runx2 to induce osteoblast differentiation. Dev. Biol 2012, 362, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yueh, Y.G.; Gardner, D.P.; Kappen, C. Evidence for regulation of cartilage differentiation by the homeobox gene Hoxc-8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9956–9961. [Google Scholar]
- Kruger, C.; Kappen, C. Expression of cartilage developmental genes in Hoxc8- and Hoxd4- transgenic mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8978. [Google Scholar]
- Gerard, A.C.; Many, M.C.; Daumerie, C.; Costagliola, S.; Miot, F.; DeVijlder, J.J.; Colin, I.M.; Denef, J.F. Structural changes in the angiofollicular units between active and hypofunctioning follicles align with differences in the epithelial expression of newly discovered proteins involved in iodine transport and organification. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 2002, 87, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, L.W.; Stubbs, J.T., 3rd; Young, M.F. Antisera and cDNA probes to human and certain animal model bone matrix noncollagenous proteins. Acta Orthop. Scand. Suppl 1995, 266, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Stevens, A. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 4th ed; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, Scotland, 1996; p. 766. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Deprez, P.M.L.; Nichane, M.G.; Lengelé, B.G.; Rezsöhazy, R.; Nyssen-Behets, C. Molecular Study of a Hoxa2 Gain-of-Function in Chondrogenesis: A Model of Idiopathic Proportionate Short Stature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20386-20398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141020386
Deprez PML, Nichane MG, Lengelé BG, Rezsöhazy R, Nyssen-Behets C. Molecular Study of a Hoxa2 Gain-of-Function in Chondrogenesis: A Model of Idiopathic Proportionate Short Stature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(10):20386-20398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141020386
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeprez, Pierre M. L., Miloud G. Nichane, Benoît G. Lengelé, René Rezsöhazy, and Catherine Nyssen-Behets. 2013. "Molecular Study of a Hoxa2 Gain-of-Function in Chondrogenesis: A Model of Idiopathic Proportionate Short Stature" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 10: 20386-20398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141020386





