New Insights into Functional Roles of the Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PTB Gene Expression
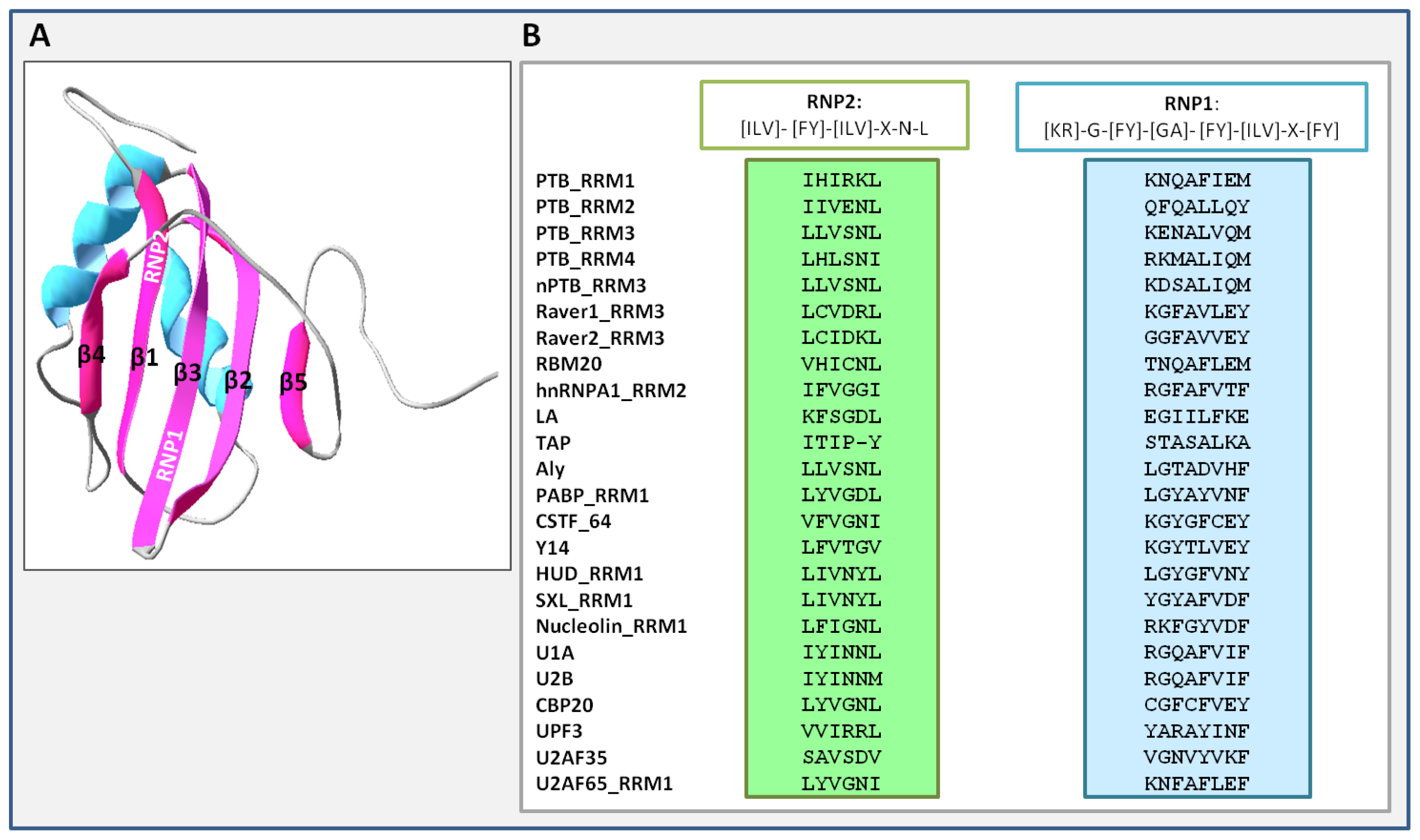
3. Unique Properties of PTB RNA Recognition Motifs
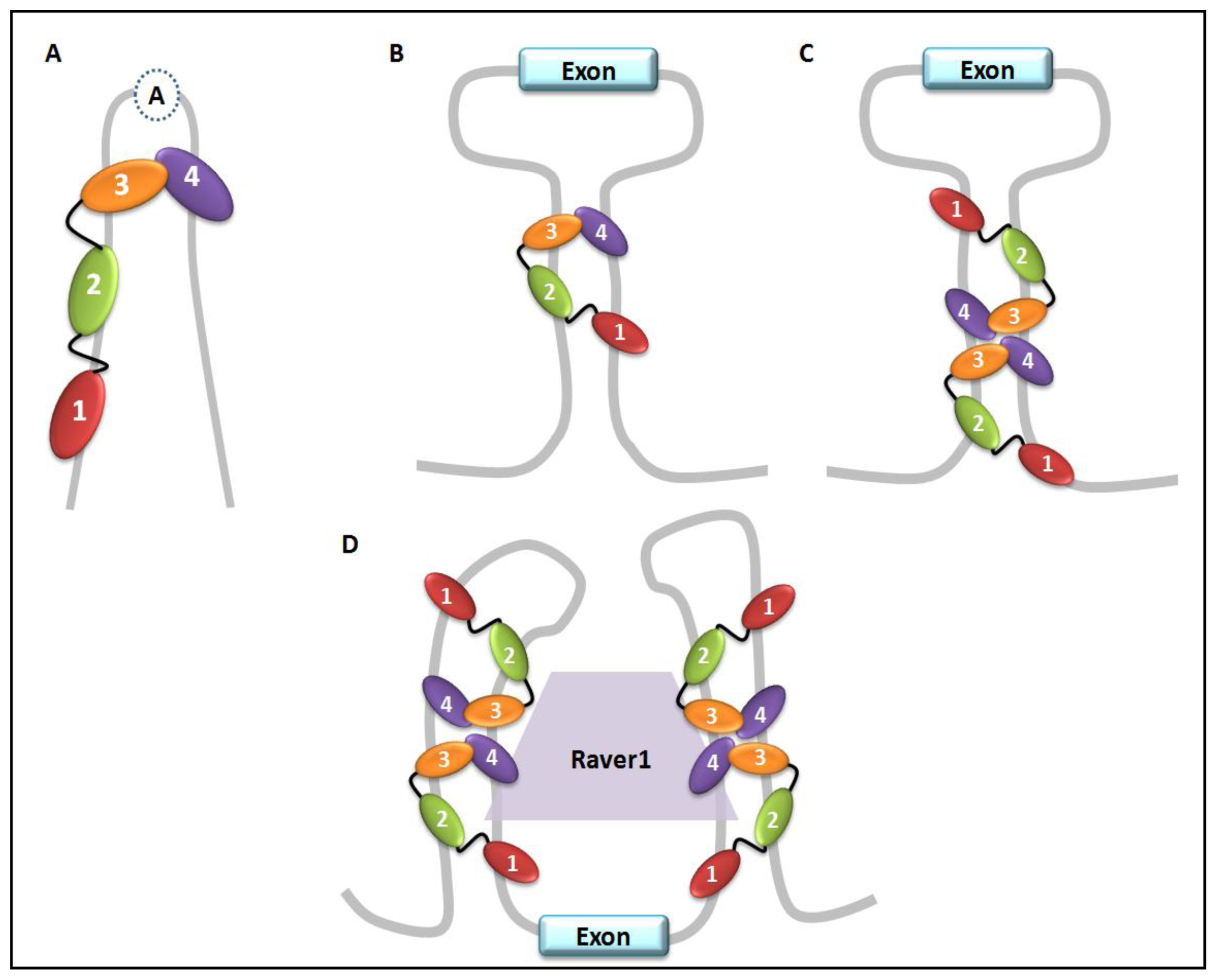
4. PTB Paralogs and Co-Factors
5. PTB Role in Pre-mRNA Splicing
6. PTB Role in Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES)-Mediated Translation Initiation
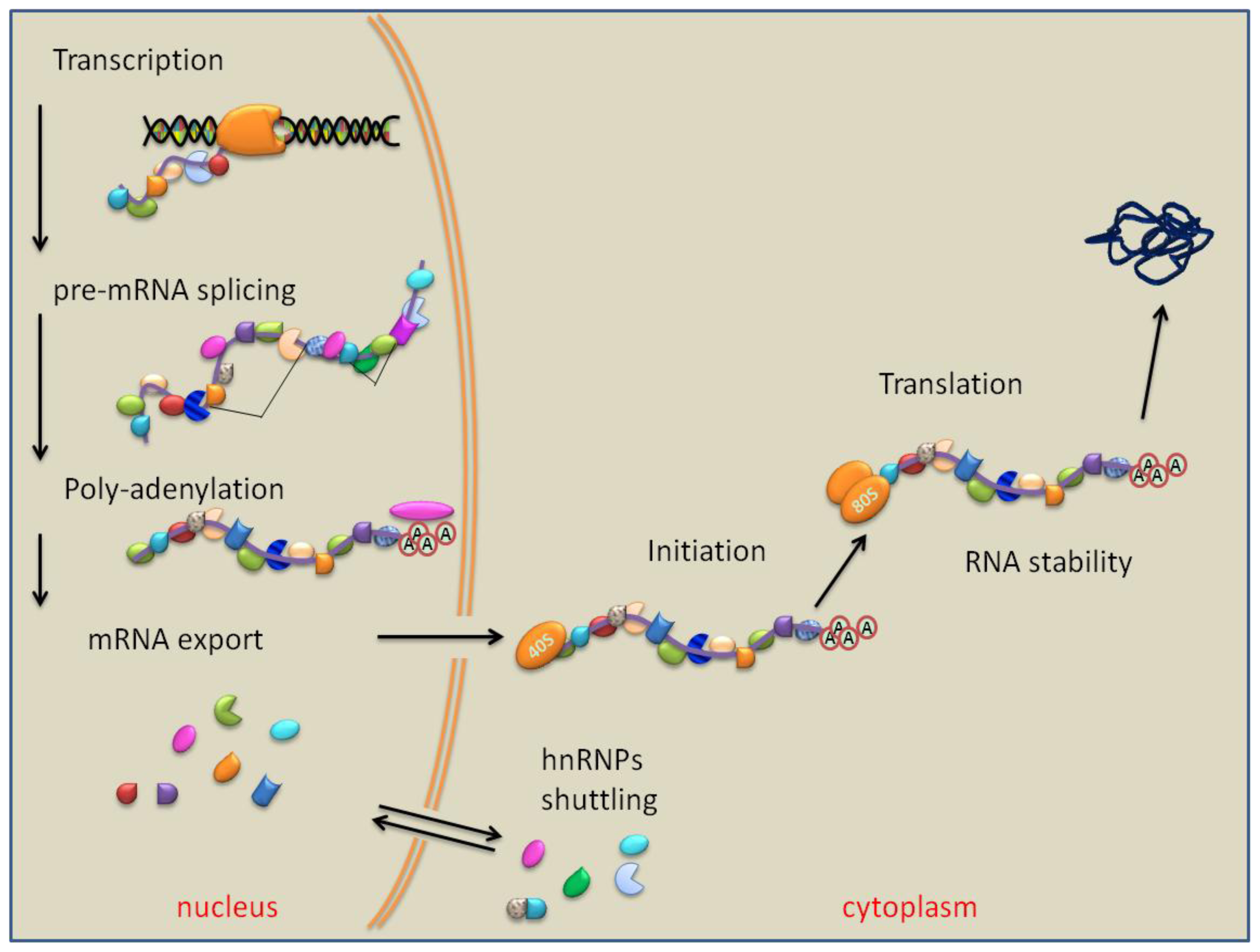
7. PTB Role in RNA Polyadenylation, Transport and Stability
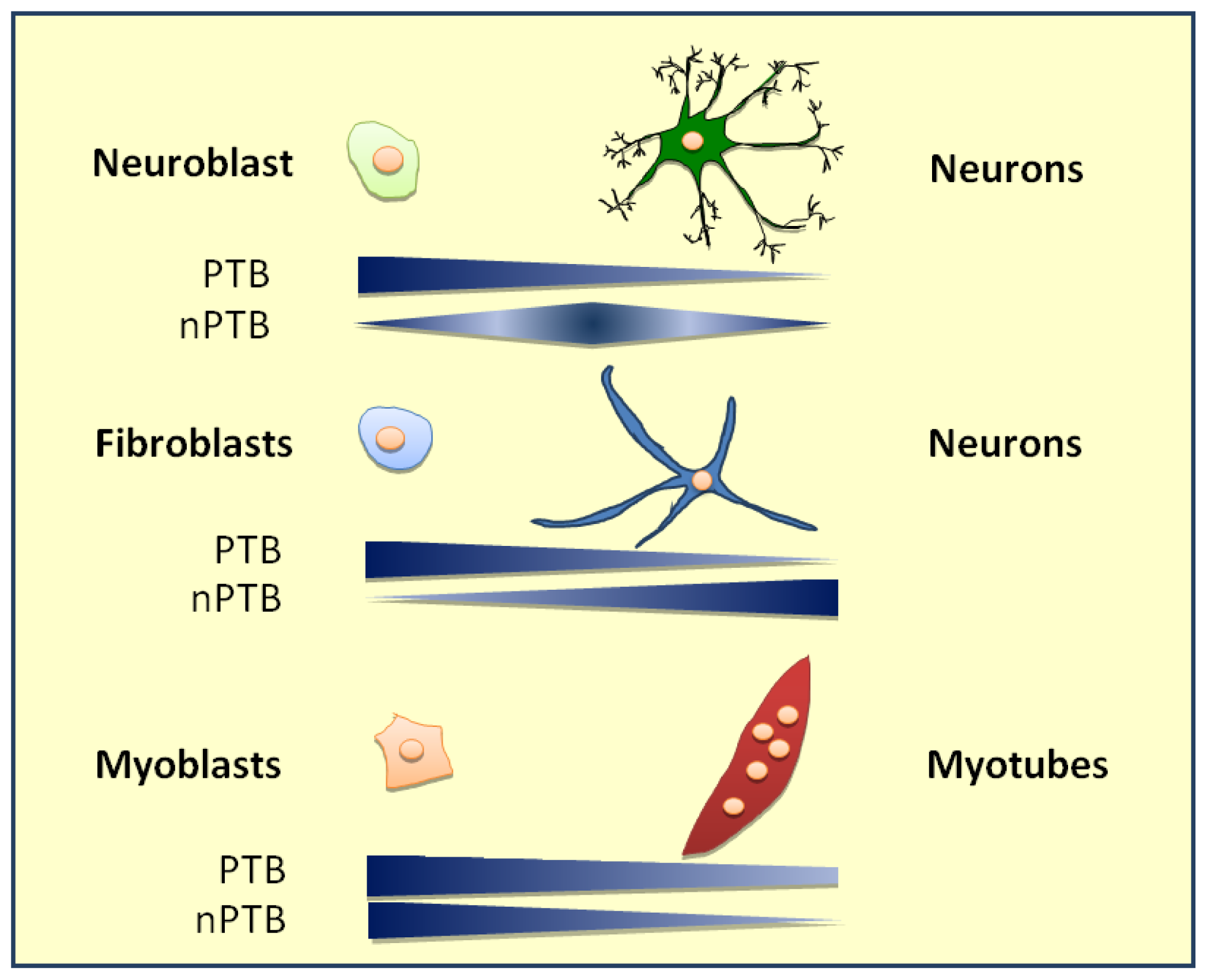
8. PTB Role in Cell Type Differentiation
9. PTB Regulation Mediated by miRNA
10. PTB and Cancer
11. Conclusions
| Gene | Regulated Exon | Exon typology | Position of PTB-cis-acting elements | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-actinin | SM | Mutually exclusive | Upstream | [69,70] |
| α-actinin | NM | Mutually exclusive | Flanking the branch-point | [69,70] |
| α-tropomyosin | 3 | Cassette | Up- and downstream | [71] |
| ATP syntetase γ-subunit | 9 | Cassette | Upstream | [72] |
| β-tropomyosin | 7 | Mutually exclusive | Upstream | [73] |
| c-src tyrosine kinase | N1 | Cassette | Up- and downstream | [74,75] |
| Calcitonin | 4 | Cassette | Downstream | [76] |
| Caspase-2 | 9 | Cassette | Downstream | [77] |
| Cardiac troponin T | 5 | Cassette | Up- and downstream | [78] |
| Clathrin light chain B | EN | Cassette | Upstream | [79] |
| FGF-R1 | α | Cassette | Up- and downstream | [80] |
| FGF-R2 | IIIb | Mutually exclusive | Downstream | [81] |
| GABAAγ2 | 2 | Cassette | Upstream | [79,82] |
| IgM | M1 M2 | Cassette | Exonic | [83] |
| NMDA receptor 1 | 5 | Cassette | Upstream | [79] |
| MEF2 | β | Cassette | Up- and downstream | [84] |
| CaV1.2 calcium channel | 8a-8 | Mutually exclusive | Upstream | [85] |
| PSD-95 | 18 | Cassette | Upstream | [86] |
| PTB | 11 | Cassette | Exonic | [54] |
| mRNA | PTB effect in facilitating translational initiation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| HAV | + | [112] |
| EMCV | + | [42] |
| Poliovirus | + | [113] |
| HVC | + | [108] |
| Norovirus | + | [114] |
| DENV | + | [115] |
| FMDV | + | [116] |
| CVB3 (coxsackievirus B3) | + | [100] |
| CDK11 (p58) | + | [117] |
| EGR2 | + | [118] |
| INSULIN | + | [103] |
| p53 | + | [119] |
| Cat-1 | + | [120] |
| APAF-1 | + | [102] |
| HIF-1alpha | + | [121] |
| p27Kip1 | + | [122] |
| IRF2 | + | [123] |
| Rev-erb α | + | [124] |
| c-myc | + | [125] |
| VEGF | + | [126,127] |
| IGFR1 | n.d. | [128] |
| IR (insulin receptor) | + | [103] |
| UNR | − | [129] |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, M.J. From birth to death: The complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 2005, 309, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Glisovic, T.; Bachorik, J.L.; Yong, J.; Dreyfuss, G. RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation. FEBS Lett 2008, 582, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Halbeisen, R.E.; Galgano, A.; Scherrer, T.; Gerber, A.P. Post-transcriptional gene regulation: From genome-wide studies to principles. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2008, 65, 798–813. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q.; Shai, O.; Lee, L.J.; Frey, B.J.; Blencowe, B.J. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Genet 2008, 40, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.T.; Sandberg, R.; Luo, S.; Khrebtukova, I.; Zhang, L.; Mayr, C.; Kingsmore, S.F.; Schroth, G.P.; Burge, C.B. Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 2008, 456, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen, T.W.; Graveley, B.R. Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature 2010, 463, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Burge, C.B. Splicing regulation: From a parts list of regulatory elements to an integrated splicing code. RNA 2008, 14, 802–813. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Manley, J.L. Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: Insights from molecular and genomics approaches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 10, 741–754. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, M.C.; Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 2009, 136, 701–718. [Google Scholar]
- Tejedor, J.R.; Valcárcel, J. Gene regulation: Breaking the second genetic code. Nature 2010, 465, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Valcárcel, J. Building specificity with nonspecific RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2005, 12, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, A.; Hertel, K.J. Evolution of SR protein and hnRNP splicing regulatory factors. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, K.W. Regulation of alternative splicing by signal transduction pathways. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2007, 623, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.C.; Caceres, J.F. The SR protein family of splicing factors: Master regulators of gene expression. Biochem. J 2009, 417, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Licatalosi, D.D.; Darnell, R.B. RNA processing and its regulation: Global insights into biological networks. Nat. Rev. Genet 2010, 11, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.W.; Valcárcel, J. Alternative pre-mRNA splicing: The logic of combinatorial control. Trends Biochem. Sci 2000, 25, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Auweter, S.D.; Allain, F.H.-T. Structure-function relationships of the polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2008, 65, 516–527. [Google Scholar]
- Keppetipola, N.; Sharma, S.; Li, Q.; Black, D.L. Neuronal regulation of pre-mRNA splicing by polypyrimidine tract binding proteins, PTBP1 and PTBP2. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol 2012, 47, 360–378. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicka, K.; Bushell, M.; Spriggs, K.A.; Willis, A.E. Polypyrimidine-tract-binding protein: A multifunctional RNA-binding protein. Biochem. Soc. Trans 2008, 36, 641–647. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, J.G.; Mayer, S.A.; Tempst, P.; Nadal-Ginard, B. Characterization and molecular cloning of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein: A component of a complex necessary for pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev 1991, 5, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti, A.; Piñol-Roma, S.; Michael, W.M.; Morandi, C.; Dreyfuss, G. hnRNP I, the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein: Distinct nuclear localization and association with hnRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 1992, 20, 3671–3678. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, R.V.; Leary, D.J.; Huang, S. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein is uncoupled from RNA export. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3808–3820. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, M.G.; Weighardt, F.; Biamonti, G.; Riva, S.; Morandi, C. Sequence determinants for hnRNP I protein nuclear localization. Exp. Cell Res 1997, 235, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, M.G.; Morandi, C. Importin alpha binds to an unusual bipartite nuclear localization signal in the heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein type I. Eur. J. Biochem 2002, 269, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yen, T.S.B. Characterization of the nuclear export signal of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 10306–10314. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, M.G.; Lorenzi, P.; Morandi, C. Organization of the human gene encoding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein type I (hnRNP I) and characterization of hnRNP I related pseudogene. Gene 2000, 255, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Lunde, B.M.; Moore, C.; Varani, G. RNA-binding proteins: Modular design for efficient function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2007, 8, 479–490. [Google Scholar]
- Maris, C.; Dominguez, C.; Allain, F.H.-T. The RNA recognition motif, a plastic RNA-binding platform to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression. FEBS J 2005, 272, 2118–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss, G.; Kim, V.N.; Kataoka, N. Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2002, 3, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Cléry, A.; Blatter, M.; Allain, F.H.-T. RNA recognition motifs: Boring? Not quite. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2008, 18, 290–298. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, M.R.; Grüne, T.; Ghuman, J.; Kelly, G.; Ladas, A.; Matthews, S.; Curry, S. Structure of tandem RNA recognition motifs from polypyrimidine tract binding protein reveals novel features of the RRM fold. EMBO J 2000, 19, 3132–3141. [Google Scholar]
- Vitali, F.; Henning, A.; Oberstrass, F.C.; Hargous, Y.; Auweter, S.D.; Erat, M.; Allain, F.H.-T. Structure of the two most C-terminal RNA recognition motifs of PTB using segmental isotope labeling. EMBO J 2006, 25, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo, J.M.; Majós, N.; Bonnal, S.; Martínez, C.; Castelo, R.; Guigó, R.; Bilbao, D.; Valcárcel, J. Regulation of Fas alternative splicing by antagonistic effects of TIA-1 and PTB on exon definition. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, I.; McAfee, J.G.; Patton, J.G. Multiple RRMs contribute to RNA binding specificity and affinity for polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 11881–11890. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, D.; Kazan, H.; Chan, E.T.; Peña Castillo, L.; Chaudhry, S.; Talukder, S.; Blencowe, B.J.; Morris, Q.; Hughes, T.R. Rapid and systematic analysis of the RNA recognition specificities of RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Biotechnol 2009, 27, 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, D.C.; Chang, B.L.; Gunderson, S.I.; Alpert, L.; Thompson, W.A.; Fairbrother, W.G. Next-generation SELEX identifies sequence and structural determinants of splicing factor binding in human pre-mRNA sequence. RNA 2009, 15, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Oberstrass, F.C.; Auweter, S.D.; Erat, M.; Hargous, Y.; Henning, A.; Wenter, P.; Reymond, L.; Amir-Ahmady, B.; Pitsch, S.; Black, D.L.; et al. Structure of PTB bound to RNA: Specific binding and implications for splicing regulation. Science 2005, 309, 2054–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Lamichhane, R.; Daubner, G.M.; Thomas-Crusells, J.; Auweter, S.D.; Manatschal, C.; Austin, K.S.; Valniuk, O.; Allain, F.H.-T.; Rueda, D. RNA looping by PTB: Evidence using FRET and NMR spectroscopy for a role in splicing repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4105–4110. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, C.M.; Hall, K.B. Interactions between PTB RRMs induce slow motions and increase RNA binding affinity. J. Mol. Biol 2010, 397, 260–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Maris, C.; Allain, F.H.-T.; Black, D.L. U1 snRNA directly interacts with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein during splicing repression. Mol. Cell 2011, 41, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Clerte, C.; Hall, K.B. The domains of polypyrimidine tract binding protein have distinct RNA structural preferences. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Kafasla, P.; Morgner, N.; Pöyry, T.A.A.; Curry, S.; Robinson, C.V.; Jackson, R.J. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein stabilizes the encephalomyocarditis virus IRES structure via binding multiple sites in a unique orientation. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 556–568. [Google Scholar]
- Rideau, A.P.; Gooding, C.; Simpson, P.J.; Monie, T.P.; Lorenz, M.; Hüttelmaier, S.; Singer, R.H.; Matthews, S.; Curry, S.; Smith, C.W.J. A peptide motif in Raver1 mediates splicing repression by interaction with the PTB RRM2 domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2006, 13, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, M. Visualizing protein-RNA interactions inside cells by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. RNA 2009, 15, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Henneberg, B.; Swiniarski, S.; Becke, S.; Illenberger, S. A conserved peptide motif in Raver2 mediates its interaction with the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein. Exp. Cell Res 2010, 316, 966–979. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Coelho, M.B.; Kotik-Kogan, O.; Simpson, P.J.; Matthews, S.J.; Smith, C.W.J.; Curry, S. Crystallographic analysis of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-Raver1 interactions involved in regulation of alternative splicing. Structure 2011, 19, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Polydorides, A.D.; Okano, H.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Stefani, G.; Darnell, R.B. A brain-enriched polypyrimidine tract-binding protein antagonizes the ability of Nova to regulate neuron-specific alternative splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6350–6355. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, M.G.; Lorenzi, P.; Morandi, C. Identification and analysis of the human neural polypyrimidine tract binding protein (nPTB) gene promoter region. Gene 2005, 356, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho-Mansfield, G.C.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.-D. PTB/nPTB switch: A post-transcriptional mechanism for programming neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Brazão, T.F.; Demmers, J.; van IJcken, W.; Strouboulis, J.; Fornerod, M.; Romão, L.; Grosveld, F.G. A new function of ROD1 in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. FEBS Lett 2012, 586, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Gooding, C.; Roberts, G.C.; Moreau, G.; Nadal-Ginard, B.; Smith, C.W. Smooth muscle-specific switching of alpha-tropomyosin mutually exclusive exon selection by specific inhibition of the strong default exon. EMBO J 1994, 13, 3861–3872. [Google Scholar]
- Markovtsov, V.; Nikolic, J.M.; Goldman, J.A.; Turck, C.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Black, D.L. Cooperative assembly of an hnRNP complex induced by a tissue-specific homolog of polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol 2000, 20, 7463–7479. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, L.; Bliskovski, V.; Reinhold, W.; Zajac-Kaye, M. Alternative splicing of brain-specific PTB defines a tissue-specific isoform pattern that predicts distinct functional roles. Genomics 2002, 80, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wollerton, M.C.; Gooding, C.; Wagner, E.J.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Smith, C.W.J. Autoregulation of polypyrimidine tract binding protein by alternative splicing leading to nonsense-mediated decay. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, R.; Llorian, M.; Smith, C.W.J. Crossregulation and functional redundancy between the splicing regulator PTB and its paralogs nPTB and ROD1. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 420–434. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.Z.; Grate, L.; Donohue, J.P.; Preston, C.; Nobida, N.; O’Brien, G.; Shiue, L.; Clark, T.A.; Blume, J.E.; Ares, M. Ultraconserved elements are associated with homeostatic control of splicing regulators by alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated decay. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 708–718. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, B.J.; Genin, A.; Cron, R.Q.; Rigby, W.F. Delineation of a novel pathway that regulates CD154 (CD40 ligand) expression. Mol. Cell. Biol 2003, 23, 510–525. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttelmaier, S.; Illenberger, S.; Grosheva, I.; Rüdiger, M.; Singer, R.H.; Jockusch, B.M. Raver1, a dual compartment protein, is a ligand for PTB/hnRNPI and microfilament attachment protein. J. Cell Biol 2001, 155, 775–786. [Google Scholar]
- Gromak, N.; Rideau, A.; Southby, J.; Scadden, A.D.J.; Gooding, C.; Hüttelmaier, S.; Singer, R.H.; Smith, C.W.J. The PTB interacting protein raver1 regulates alpha-tropomyosin alternative splicing. EMBO J 2003, 22, 6356–6364. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhenz, B.; Fabienke, M.; Swiniarski, S.; Wittenmayer, N.; Kirsch, J.; Jockusch, B.M.; Arnold, H.H.; Illenberger, S. Raver2, a new member of the hnRNP family. FEBS Lett 2005, 579, 4254–4258. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, R.; Smith, C.W.J. Novel modes of splicing repression by PTB. Trends Biochem. Sci 2006, 31, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, M.G.; Lorenzi, P.; Avesani, F.; Morandi, C. Functional characterization of the ribonucleoprotein, PTB-binding 1/Raver1 promoter region. Gene 2007, 405, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zieseniss, A.; Schroeder, U.; Buchmeier, S.; Schoenenberger, C.-A.; van den Heuvel, J.; Jockusch, B.M.; Illenberger, S. Raver1 is an integral component of muscle contractile elements. Cell Tissue Res 2007, 327, 583–594. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Rangarajan, E.S.; Yogesha, S.D.; Izard, T. Raver1 interactions with vinculin and RNA suggest a feed-forward pathway in directing mRNA to focal adhesions. Structure 2009, 17, 833–842. [Google Scholar]
- Lahmann, I.; Fabienke, M.; Henneberg, B.; Pabst, O.; Vauti, F.; Minge, D.; Illenberger, S.; Jockusch, B.M.; Korte, M.; Arnold, H.-H. The hnRNP and cytoskeletal protein raver1 contributes to synaptic plasticity. Exp. Cell Res 2008, 314, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ran, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, Y.; Shu, H.-B. RAVER1 is a coactivator of MDA5-mediated cellular antiviral response. J. Mol. Cell Biol 2013, 5, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, M.G.; Lorenzi, P.; Diani, E.; Filippello, A.; Avesani, F.; Morandi, C. Transcriptional regulation of the human Raver2 ribonucleoprotein gene. Gene 2012, 493, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, R.; Rideau, A.; Matlin, A.; Gooding, C.; Robinson, F.; McGlincy, N.; Grellscheid, S.N.; Southby, J.; Wollerton, M.; Smith, C.W.J. Regulation of alternative splicing by PTB and associated factors. Biochem. Soc. Trans 2005, 33, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Southby, J.; Gooding, C.; Smith, C.W.J. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein functions as a repressor to regulate alternative splicing of alpha -actinin mutally exclusive exons. Mol. Cell. Biol 1999, 19, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar]
- Matlin, A.J.; Southby, J.; Gooding, C.; Smith, C.W.J. Repression of α-actinin SM exon splicing by assisted binding of PTB to the polypyrimidine tract. RNA 2007, 13, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Gooding, C.; Roberts, G.C.; Smith, C.W.J. Role of an inhibitory pyrimidine element and polypyrimidine tract binding protein in repression of a regulated alpha-tropomyosin exon. RNA 1998, 4, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Sakashita, E.; Ueno, E.; Tominaga, S.; Hamamoto, T.; Kagawa, Y.; Endo, H. Muscle-specific exonic splicing silencer for exon exclusion in human ATP synthase gamma-subunit pre-mRNA. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 6974–6984. [Google Scholar]
- Saulière, J.; Sureau, A.; Expert-Bezançon, A.; Marie, J. The polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) represses splicing of exon 6B from the beta-tropomyosin pre-mRNA by directly interfering with the binding of the U2AF65 subunit. Mol. Cell. Biol 2006, 26, 8755–8769. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, R.C.; Black, D.L. The polypyrimidine tract binding protein binds upstream of neural cell-specific c-src exon N1 to repress the splicing of the intron downstream. Mol. Cell. Biol 1997, 17, 4667–4676. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, M.Y.; Underwood, J.G.; Nikolic, J.; Luu, M.H.; Black, D.L. Multisite RNA binding and release of polypyrimidine tract binding protein during the regulation of c-src neural-specific splicing. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 949–957. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, H.; Helfman, D.M.; Gagel, R.F.; Berget, S.M. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein positively regulates inclusion of an alternative 3′-terminal exon. Mol. Cell. Biol 1999, 19, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, J.; Dupuis, S.; Wu, J.Y. Polypyrimidine track-binding protein binding downstream of caspase-2 alternative exon 9 represses its inclusion. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 8535–8543. [Google Scholar]
- Charlet-B, N.; Logan, P.; Singh, G.; Cooper, T.A. Dynamic antagonism between ETR-3 and PTB regulates cell type-specific alternative splicing. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Grabowski, P.J. Coordinate repression of a trio of neuron-specific splicing events by the splicing regulator PTB. RNA 1999, 5, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Bruno, I.G.; Xie, T.-X.; Sanger, L.J.; Cote, G.J. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein down-regulates fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 alpha-exon inclusion. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 6154–6157. [Google Scholar]
- Carstens, R.P.; Wagner, E.J.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. An intronic splicing silencer causes skipping of the IIIb exon of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 through involvement of polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol 2000, 20, 7388–7400. [Google Scholar]
- Ashiya, M.; Grabowski, P.J. A neuron-specific splicing switch mediated by an array of pre-mRNA repressor sites: Evidence of a regulatory role for the polypyrimidine tract binding protein and a brain-specific PTB counterpart. RNA 1997, 3, 996–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Kan, J.L.C.; Ghigna, C.; Biamonti, G.; Green, M.R. A single polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) binding site mediates splicing inhibition at mouse IgM exons M1 and M2. RNA 2004, 10, 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Llorian, M.; Cardona, M.; Rongvaux, A.; Moubarak, R.S.; Comella, J.X.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Flavell, R.A.; Olson, E.N.; Smith, C.W.J.; et al. A pathway involving HDAC5, cFLIP and caspases regulates expression of the splicing regulator polypyrimidine tract binding protein in the heart. J. Cell Sci 2013, 126, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.Z.; Sharma, S.; Zheng, S.; Chawla, G.; Nikolic, J.; Black, D.L. Regulation of the mutually exclusive exons 8a and 8 in the CaV1.2 calcium channel transcript by polypyrimidine tract-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 10007–10016. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Gray, E.E.; Chawla, G.; Porse, B.T.; O’Dell, T.J.; Black, D.L. PSD-95 is post-transcriptionally repressed during early neural development by PTBP1 and PTBP2. Nat. Neurosci 2012, 15, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Reed, R.B.; Liu, W.; Grabowski, P.J. Mutations in RRM4 uncouple the splicing repression and RNA-binding activities of polypyrimidine tract binding protein. RNA 2002, 8, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gooding, C.; Edge, C.; Lorenz, M.; Coelho, M.B.; Winters, M.; Kaminski, C.F.; Cherny, D.; Eperon, I.C.; Smith, C.W.J. MBNL1 and PTB cooperate to repress splicing of Tpm1 exon 3. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, 4765–4782. [Google Scholar]
- Boutz, P.L.; Chawla, G.; Stoilov, P.; Black, D.L. MicroRNAs regulate the expression of the alternative splicing factor nPTB during muscle development. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Boutz, P.L.; Stoilov, P.; Li, Q.; Lin, C.-H.; Chawla, G.; Ostrow, K.; Shiue, L.; Ares, M.; Black, D.L. A post-transcriptional regulatory switch in polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins reprograms alternative splicing in developing neurons. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 1636–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Corrionero, A.; Valcárcel, J. RNA processing: Redrawing the map of charted territory. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 918–919. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhu, T.; Ji, X.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Zhang, C.; Yeo, G.; Black, D.L.; Sun, H.; Fu, X.-D.; Zhang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of PTB-RNA interactions reveals a strategy used by the general splicing repressor to modulate exon inclusion or skipping. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 996–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Llorian, M.; Schwartz, S.; Clark, T.A.; Hollander, D.; Tan, L.-Y.; Spellman, R.; Gordon, A.; Schweitzer, A.C.; de la Grange, P.; Ast, G.; et al. Position-dependent alternative splicing activity revealed by global profiling of alternative splicing events regulated by PTB. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2010, 17, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, C.; Cloutier, P.; Shkreta, L.; Toutant, J.; Klarskov, K.; Chabot, B. hnRNP I/PTB can antagonize the splicing repressor activity of SRp30c. RNA 2007, 13, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Kafasla, P.; Mickleburgh, I.; Llorian, M.; Coelho, M.; Gooding, C.; Cherny, D.; Joshi, A.; Kotik-Kogan, O.; Curry, S.; Eperon, I.C.; et al. Defining the roles and interactions of PTB. Biochem. Soc. Trans 2012, 40, 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Stoilov, P.; Kapur, K.; Han, A.; Jiang, H.; Shen, S.; Black, D.L.; Wong, W.H. MADS: A new and improved method for analysis of differential alternative splicing by exon-tiling microarrays. RNA 2008, 14, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Chen, Z.; Cai, X. A biophysical model for identifying splicing regulatory elements and their interactions. PLoS One 2013, 8, e54885. [Google Scholar]
- Stoneley, M.; Willis, A.E. Cellular internal ribosome entry segments: Structures, trans-acting factors and regulation of gene expression. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3200–3207. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Salas, E.; Pacheco, A.; Serrano, P.; Fernandez, N. New insights into internal ribosome entry site elements relevant for viral gene expression. J. Gen. Virol 2008, 89, 611–626. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, B.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, S. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein interacts with coxsackievirus B3 RNA and influences its translation. J. Gen. Virol 2010, 91, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Vashist, S.; Urena, L.; Chaudhry, Y.; Goodfellow, I. Identification of RNA-protein interaction networks involved in the norovirus life cycle. J. Virol 2012, 86, 11977–11990. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.A.; Spriggs, K.A.; Coldwell, M.J.; Jackson, R.J.; Willis, A.E. The Apaf-1 internal ribosome entry segment attains the correct structural conformation for function via interactions with PTB and unr. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 757–771. [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs, K.A.; Cobbold, L.C.; Ridley, S.H.; Coldwell, M.; Bottley, A.; Bushell, M.; Willis, A.E.; Siddle, K. The human insulin receptor mRNA contains a functional internal ribosome entry segment. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 5881–5893. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Tzima, E.; Ochs, K.; Bassili, G.; Trusheim, H.; Linder, M.; Preissner, K.T.; Niepmann, M. Evidence for an RNA chaperone function of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein in picornavirus translation. RNA 2005, 11, 1809–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Back, S.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, W.J.; Cho, S.; Oh, H.R.; Kim, J.-E.; Jang, S.K. Translation of polioviral mRNA is inhibited by cleavage of polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins executed by polioviral 3C(pro). J. Virol 2002, 76, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Florez, P.M.; Sessions, O.M.; Wagner, E.J.; Gromeier, M.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. The polypyrimidine tract binding protein is required for efficient picornavirus gene expression and propagation. J. Virol 2005, 79, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, N.; Wimmer, E.; Mueller, S. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein-1 (PTB1) is a determinant of the tissue and host tropism of a human rhinovirus/poliovirus chimera PV1(RIPO). PLoS One 2013, 8, e60791. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.-S.; Luo, G. The polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTB) is required for efficient replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA. Virus Res 2006, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Agis-Juárez, R.A.; Galván, I.; Medina, F.; Daikoku, T.; Padmanabhan, R.; Ludert, J.E.; del Angel, R.M. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein is relocated to the cytoplasm and is required during dengue virus infection in Vero cells. J. Gen. Virol 2009, 90, 2893–2901. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, H.; Duan, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein influences negative strand RNA synthesis of dengue virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2009, 385, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kanda, T.; Gauss-Müller, V.; Cordes, S.; Tamura, R.; Okitsu, K.; Shuang, W.; Nakamoto, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Imazeki, F.; Yokosuka, O. Hepatitis A virus (HAV) proteinase 3C inhibits HAV IRES-dependent translation and cleaves the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein. J. Viral Hepat 2010, 17, 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatramana, M.; Ray, P.S.; Chadda, A.; Das, S. A 25 kDa cleavage product of polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) present in mouse tissues prevents PTB binding to the 5′ untranslated region and inhibits translation of hepatitis A virus RNA. Virus Res 2003, 98, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kafasla, P.; Morgner, N.; Robinson, C.V.; Jackson, R.J. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein stimulates the poliovirus IRES by modulating eIF4G binding. EMBO J 2010, 29, 3710–3722. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, D.; Karakasiliotis, I.; Vashist, S.; Chung, L.M.W.; Rees, J.; Reese, J.; McFadden, N.; Benson, A.; Yarovinsky, F.; Simmonds, P.; et al. Functional analysis of RNA structures present at the 3′ extremity of the murine norovirus genome: The variable polypyrimidine tract plays a role in viral virulence. J. Virol 2010, 84, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, A.; Leong, K.M.; Ng, M.L.; Chu, J.J.H.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. The polypyrimidine tract-binding protein is required for efficient dengue virus propagation and associates with the viral replication machinery. J. Biol. Chem 2009, 284, 17021–17029. [Google Scholar]
- Niepmann, M.; Petersen, A.; Meyer, K.; Beck, E. Functional involvement of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein in translation initiation complexes with the internal ribosome entry site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J. Virol 1997, 71, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, S.; Shibayama, M.; Sato, M.; Tokunaga, A.; Yoshida, N. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein regulates the cell cycle through IRES-dependent translation of CDK11(p58) in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3706–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen, D.; Blees, J.S.; Schulz, K.; Döring, C.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Heide, H.; Weigert, A.; Schmid, T.; Brüne, B. IRES-dependent translation of egr2 is induced under inflammatory conditions. RNA 2012, 18, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, R.; Ray, P.S.; Das, S. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein regulates IRES-mediated translation of p53 isoforms. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, M.; Yaman, I.; Gaccioli, F.; Zeenko, V.V.; Wang, C.; Caprara, M.G.; Venema, R.C.; Komar, A.A.; Snider, M.D.; Hatzoglou, M. The hnRNA-binding proteins hnRNP L and PTB are required for efficient translation of the Cat-1 arginine/lysine transporter mRNA during amino acid starvation. Mol. Cell. Biol 2009, 29, 2899–2912. [Google Scholar]
- Schepens, B.; Tinton, S.A.; Bruynooghe, Y.; Beyaert, R.; Cornelis, S. The polypyrimidine tract-binding protein stimulates HIF-1alpha IRES-mediated translation during hypoxia. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 6884–6894. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.; Kim, J.H.; Back, S.H.; Jang, S.K. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein enhances the internal ribosomal entry site-dependent translation of p27Kip1 mRNA and modulates transition from G1 to S phase. Mol. Cell. Biol 2005, 25, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, D.; Venkataramana, M.; Ponnuswamy, A.; Das, S. Role of polypyrimidine tract binding protein in mediating internal initiation of translation of interferon regulatory factor 2 RNA. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7049. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Woo, K.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, T.-D.; Kim, K.-T. hnRNP Q and PTB modulate the circadian oscillation of mouse Rev-erb alpha via IRES-mediated translation. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 7068–7078. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold, L.C.; Spriggs, K.A.; Haines, S.J.; Dobbyn, H.C.; Hayes, C.; de Moor, C.H.; Lilley, K.S.; Bushell, M.; Willis, A.E. Identification of internal ribosome entry segment (IRES)-trans-acting factors for the Myc family of IRESs. Mol. Cell. Biol 2008, 28, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, L.S.; Bartley, M.A.; Bert, A.; Hunter, J.; Polyak, S.; Diamond, P.; Vadas, M.A.; Goodall, G.J. A multi-protein complex containing cold shock domain (Y-box) and polypyrimidine tract binding proteins forms on the vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA. Potential role in mRNA stabilization. Eur. J. Biochem 2004, 271, 648–660. [Google Scholar]
- Huez, I.; Créancier, L.; Audigier, S.; Gensac, M.C.; Prats, A.C.; Prats, H. Two independent internal ribosome entry sites are involved in translation initiation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol 1998, 18, 6178–6190. [Google Scholar]
- Giraud, S.; Greco, A.; Brink, M.; Diaz, J.J.; Delafontaine, P. Translation initiation of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor mRNA is mediated by an internal ribosome entry site. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 5668–5675. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis, S.; Tinton, S.A.; Schepens, B.; Bruynooghe, Y.; Beyaert, R. UNR translation can be driven by an IRES element that is negatively regulated by polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 3095–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Fred, R.G.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Grunnet, L.G.; Welsh, N. High glucose suppresses human islet insulin biosynthesis by inducing miR-133a leading to decreased polypyrimidine tract binding protein-expression. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10843. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.A.; Spriggs, K.A.; Bushell, M.; Evans, J.R.; Stoneley, M.; Le Quesne, J.P.C.; Spriggs, R.V.; Willis, A.E. Identification of a motif that mediates polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-dependent internal ribosome entry. Genes Dev 2005, 19, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Bushell, M.; Stoneley, M.; Kong, Y.W.; Hamilton, T.L.; Spriggs, K.A.; Dobbyn, H.C.; Qin, X.; Sarnow, P.; Willis, A.E. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein regulates IRES-mediated gene expression during apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbyn, H.C.; Hill, K.; Hamilton, T.L.; Spriggs, K.A.; Pickering, B.M.; Coldwell, M.J.; de Moor, C.H.; Bushell, M.; Willis, A.E. Regulation of BAG-1 IRES-mediated translation following chemotoxic stress. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Castelo-Branco, P.; Furger, A.; Wollerton, M.; Smith, C.; Moreira, A.; Proudfoot, N. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein modulates efficiency of polyadenylation. Mol. Cell. Biol 2004, 24, 4174–4183. [Google Scholar]
- Pautz, A.; Linker, K.; Hubrich, T.; Korhonen, R.; Altenhöfer, S.; Kleinert, H. The polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTB) is involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of human inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 32294–32302. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Liu, G.; Sun, Y.; Xie, J. Relocalization of the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein during PKA-induced neurite growth. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 912–923. [Google Scholar]
- Millevoi, S.; Decorsière, A.; Loulergue, C.; Iacovoni, J.; Bernat, S.; Antoniou, M.; Vagner, S. A physical and functional link between splicing factors promotes pre-mRNA 3′ end processing. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 4672–4683. [Google Scholar]
- Gama-Carvalho, M.; Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Brodsky, A.S.; Silver, P.A.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Genome-wide identification of functionally distinct subsets of cellular mRNAs associated with two nucleocytoplasmic-shuttling mammalian splicing factors. Genome Biol 2006, 7, R113. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, W.Q.; Li, B.; Huang, P.Y.; Lai, M.M.; Yen, T.S. Role of polypyrimidine tract binding protein in the function of the hepatitis B virus posttranscriptional regulatory element. J. Virol 2001, 75, 10779–10786. [Google Scholar]
- Fred, R.G.; Welsh, N. The importance of RNA binding proteins in preproinsulin mRNA stability. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol 2009, 297, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Knoch, K.-P.; Bergert, H.; Borgonovo, B.; Saeger, H.-D.; Altkrüger, A.; Verkade, P.; Solimena, M. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein promotes insulin secretory granule biogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol 2004, 6, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Galbán, S.; Kuwano, Y.; Pullmann, R.; Martindale, J.L.; Kim, H.H.; LaI, A.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Yang, X.; Dang, Y.; Liu, J.O.; Lewis, S.M.; et al. RNA-binding proteins HuR and PTB promote the translation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol. Cell. Biol 2008, 28, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J.; Lin, S. A region within the 5′-untranslated region of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha mRNA mediates its turnover in lung adenocarcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem 2009, 284, 36500–36510. [Google Scholar]
- Gorospe, M.; Tominaga, K.; Wu, X.; Fähling, M.; Ivan, M. Post-transcriptional control of the hypoxic response by RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs. Front. Mol. Neurosci 2011, 4, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kosinski, P.A.; Laughlin, J.; Singh, K.; Covey, L.R. A complex containing polypyrimidine tract-binding protein is involved in regulating the stability of CD40 ligand (CD154) mRNA. J. Immunol 2003, 170, 979–988. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, J.F.; Vavassori, S.; Covey, L.R. A polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-dependent pathway of mRNA stability initiates with CpG activation of primary B cells. J. Immunol 2008, 181, 3336–3345. [Google Scholar]
- Vavassori, S.; Covey, L.R. Post-transcriptional regulation in lymphocytes: The case of CD154. RNA Biol 2009, 6, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Matus-Nicodemos, R.; Vavassori, S.; Castro-Faix, M.; Valentin-Acevedo, A.; Singh, K.; Marcelli, V.; Covey, L.R. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein is critical for the turnover and subcellular distribution of CD40 ligand mRNA in CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol 2011, 186, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, R.; Izquierdo, J.M. The RNA-binding protein PTB exerts translational control on 3′-untranslated region of the mRNA for the ATP synthase beta-subunit. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2007, 357, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, A.; Takagaki, Y.; Brackenridge, S.; Wollerton, M.; Manley, J.L.; Proudfoot, N.J. The upstream sequence element of the C2 complement poly(A) signal activates mRNA 3′ end formation by two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev 1998, 12, 2522–2534. [Google Scholar]
- Danckwardt, S.; Kaufmann, I.; Gentzel, M.; Foerstner, K.U.; Gantzert, A.-S.; Gehring, N.H.; Neu-Yilik, G.; Bork, P.; Keller, W.; Wilm, M.; et al. Splicing factors stimulate polyadenylation via USEs at non-canonical 3′ end formation signals. EMBO J 2007, 26, 2658–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Pogar, T.; Liang, S.; Hague, L.K.; Lutz, C.S. Specific trans-acting proteins interact with auxiliary RNA polyadenylation elements in the COX-2 3′-UTR. RNA 2007, 13, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, K.-C.; Kim, T.-D.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, K.-T. Mouse period 2 mRNA circadian oscillation is modulated by PTB-mediated rhythmic mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Besse, F.; López de Quinto, S.; Marchand, V.; Trucco, A.; Ephrussi, A. Drosophila PTB promotes formation of high-order RNP particles and represses oskar translation. Genes Dev 2009, 23, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.A.; Gagnon, J.A.; Mowry, K.L. PTB/hnRNP I is required for RNP remodeling during RNA localization in Xenopus oocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol 2008, 28, 678–686. [Google Scholar]
- Shibayama, M.; Ohno, S.; Osaka, T.; Sakamoto, R.; Tokunaga, A.; Nakatake, Y.; Sato, M.; Yoshida, N. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein is essential for early mouse development and embryonic stem cell proliferation. FEBS J 2009, 276, 6658–6668. [Google Scholar]
- Llorian, M.; Smith, C.W.J. Decoding muscle alternative splicing. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 2011, 21, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.P.; Nagel, R.J.; Fagg, W.S.; Shiue, L.; Cline, M.S.; Perriman, R.J.; Donohue, J.P.; Ares, M. Quaking and PTB control overlapping splicing regulatory networks during muscle cell differentiation. RNA 2013, 19, 627–638. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-C.; Tarn, W.-Y. Exon selection in alpha-tropomyosin mRNA is regulated by the antagonistic action of RBM4 and PTB. Mol. Cell. Biol 2005, 25, 10111–10121. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-C.; Tarn, W.-Y. RBM4 down-regulates PTB and antagonizes its activity in muscle cell-specific alternative splicing. J. Cell Biol 2011, 193, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Bahi, N.; Llovera, M.; Comella, J.X.; Sanchis, D. Polypyrimidine tract binding proteins (PTB) regulate the expression of apoptotic genes and susceptibility to caspase-dependent apoptosis in differentiating cardiomyocytes. Cell Death Differ 2009, 16, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Makeyev, E.V.; Zhang, J.; Carrasco, M.A.; Maniatis, T. The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 435–448. [Google Scholar]
- Lilleväli, K.; Kulla, A.; Ord, T. Comparative expression analysis of the genes encoding polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) and its neural homologue (brPTB) in prenatal and postnatal mouse brain. Mech. Dev 2001, 101, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Bitel, C.L.; Perrone-Bizzozero, N.I.; Frederikse, P.H. HuB/C/D, nPTB, REST4, and miR-124 regulators of neuronal cell identity are also utilized in the lens. Mol. Vis 2010, 16, 2301–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Ouyang, K.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; Wu, Q.; Wei, C.; Bi, Y.; et al. Direct conversion of fibroblasts to neurons by reprogramming PTB-regulated microRNA circuits. Cell 2013, 152, 82–96. [Google Scholar]
- Fred, R.G.; Sandberg, M.; Pelletier, J.; Welsh, N. The human insulin mRNA is partly translated via a cap- and eIF4A-independent mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2011, 412, 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Engels, B.; Jannot, G.; Remenyi, J.; Simard, M.J.; Hutvagner, G. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein (hnRNP I) is possibly a conserved modulator of miRNA-mediated gene regulation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33144. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Pool, M.; Darcy, K.M.; Lim, S.B.; Auersperg, N.; Coon, J.S.; Beck, W.T. Knockdown of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein suppresses ovarian tumor cell growth and invasiveness in vitro. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Norton, J.T.; Ghosh, S.; Kim, J.; Fushimi, K.; Wu, J.Y.; Stack, M.S.; Huang, S. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTB) differentially affects malignancy in a cell line-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 20277–20287. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, C.; Daily, K.; Nguyen, V.T.; Wang, C.; Lewandowska, M.A.; Bensaude, O.; Huang, S. Characterization of MRP RNA-protein interactions within the perinucleolar compartment. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 858–867. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Arslan, A.D.; Pool, M.D.; Ho, T.-T.; Darcy, K.M.; Coon, J.S.; Beck, W.T. Knockdown of splicing factor SRp20 causes apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and its expression is associated with malignancy of epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 356–365. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, D.; Sharathchandra, A.; Ponnuswamy, A.; Grover, R.; Das, S. Effect of a natural mutation in the 5′ untranslated region on the translational control of p53 mRNA. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4148–4159. [Google Scholar]
- De Hoog, C.L.; Foster, L.J.; Mann, M. RNA and RNA binding proteins participate in early stages of cell spreading through spreading initiation centers. Cell 2004, 117, 649–662. [Google Scholar]
- Babic, I.; Sharma, S.; Black, D.L. A role for polypyrimidine tract binding protein in the establishment of focal adhesions. Mol. Cell. Biol 2009, 29, 5564–5577. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, H.C.; Hai, T.; Zhu, W.; Baggerly, K.A.; Tsavachidis, S.; Krahe, R.; Cote, G.J. Splicing factors PTBP1 and PTBP2 promote proliferation and migration of glioma cell lines. Brain 2009, 132, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Manley, J.L. Turning on a fuel switch of cancer: hnRNP proteins regulate alternative splicing of pyruvate kinase mRNA. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 8977–8980. [Google Scholar]
- Clower, C.V.; Chatterjee, D.; Wang, Z.; Cantley, L.C.; vander Heiden, M.G.; Krainer, A.R. The alternative splicing repressors hnRNP A1/A2 and PTB influence pyruvate kinase isoform expression and cell metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar]
- David, C.J.; Chen, M.; Assanah, M.; Canoll, P.; Manley, J.L. HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature 2010, 463, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Wang, M.J.; Tseng, K.-Y. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein induces p19(Ink4d) expression and inhibits the proliferation of H1299 cells. PLoS One 2013, 8, e58227. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold, L.C.; Wilson, L.A.; Sawicka, K.; King, H.A.; Kondrashov, A.V.; Spriggs, K.A.; Bushell, M.; Willis, A.E. Upregulated c-myc expression in multiple myeloma by internal ribosome entry results from increased interactions with and expression of PTB-1 and YB-1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2884–2891. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, A.D.; He, X.; Wang, M.; Rumschlag-Booms, E.; Rong, L.; Beck, W.T. A high-throughput assay to identify small-molecule modulators of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. J. Biomol. Screen 2013, 18, 180–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Masuda, A.; Matsuura, T.; Ito, M.; Okushin, K.; Engel, A.G.; Ohno, K. Tannic acid facilitates expression of the polypyrimidine tract binding protein and alleviates deleterious inclusion of CHRNA1 exon P3A due to an hnRNP H-disrupting mutation in congenital myasthenic syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet 2009, 18, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanelli, M.G.; Diani, E.; Lievens, P.M.-J. New Insights into Functional Roles of the Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22906-22932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122906
Romanelli MG, Diani E, Lievens PM-J. New Insights into Functional Roles of the Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(11):22906-22932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122906
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanelli, Maria Grazia, Erica Diani, and Patricia Marie-Jeanne Lievens. 2013. "New Insights into Functional Roles of the Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 11: 22906-22932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122906







