Covalent Immobilization of Bacillus licheniformis γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase on Aldehyde-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
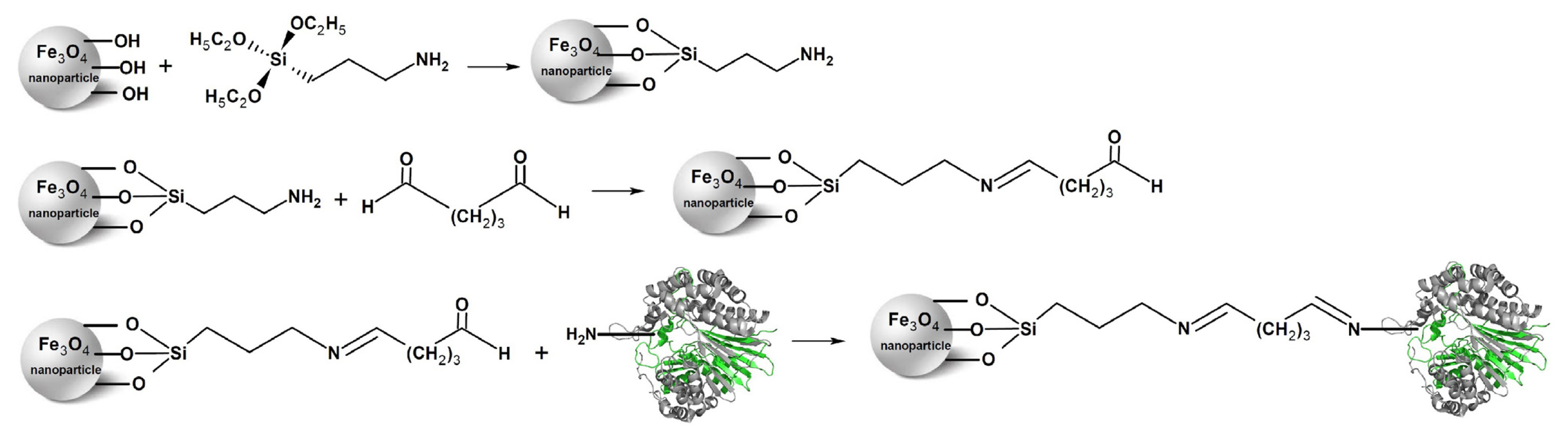
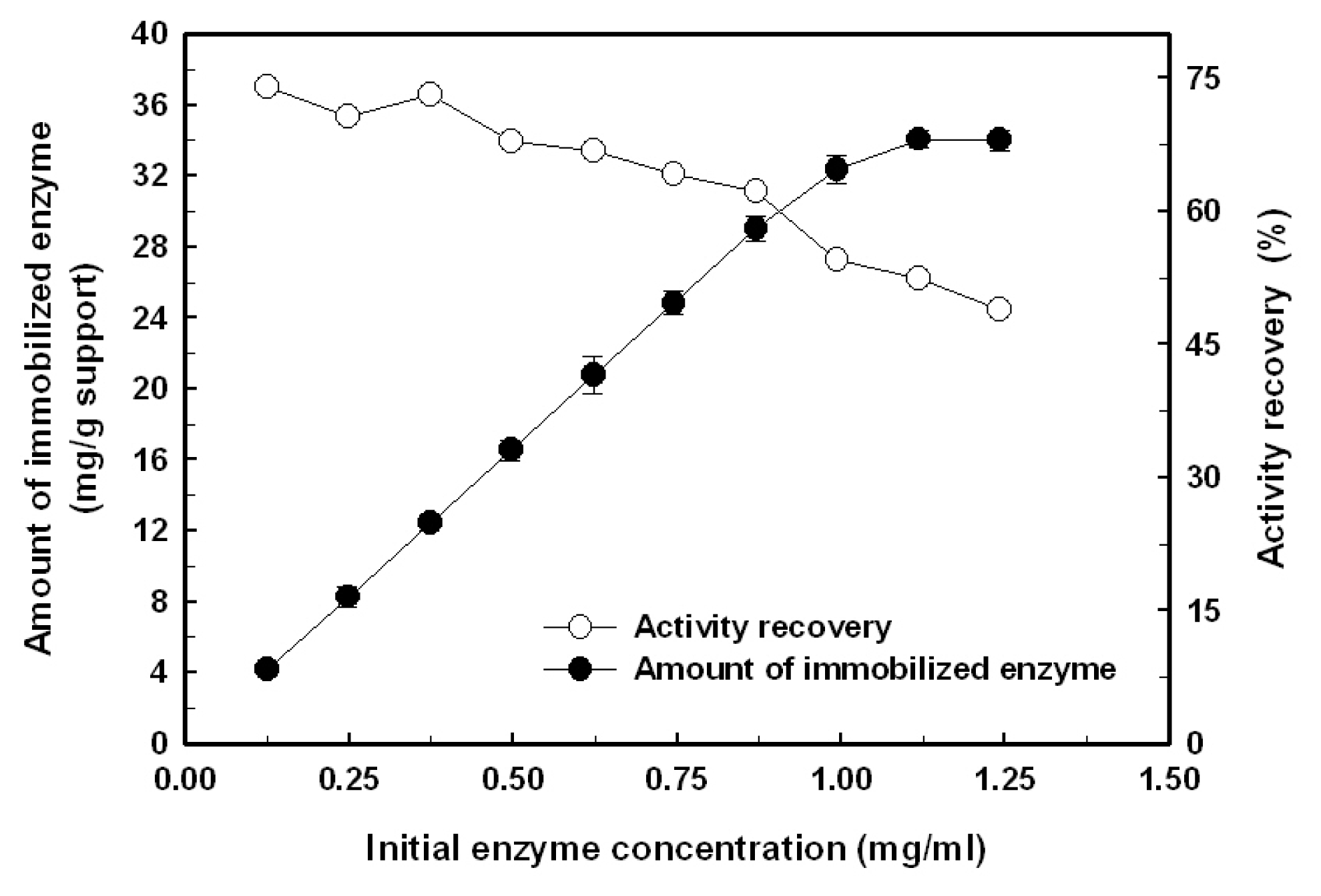
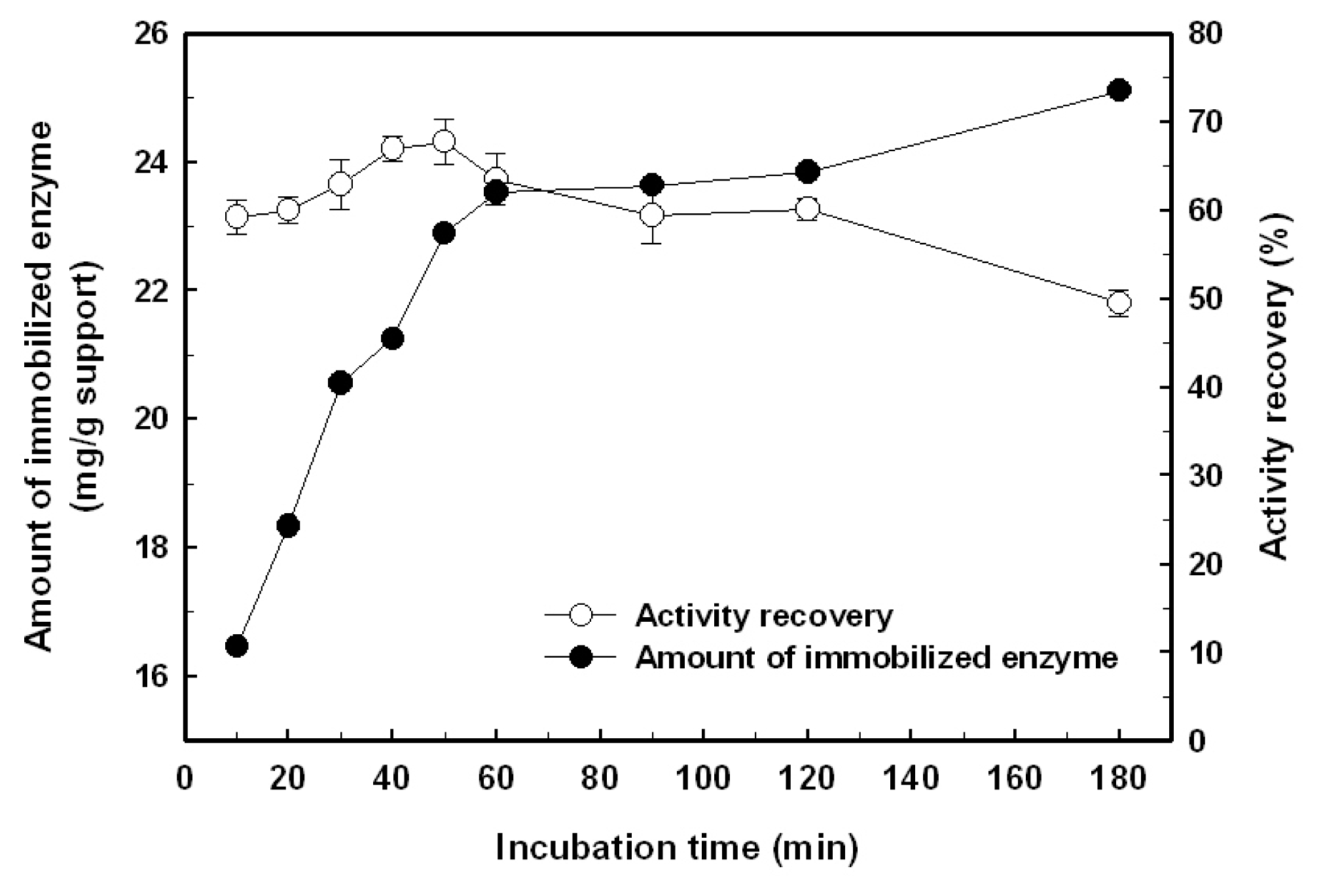
2.1. Immobilization of the Recombinant Enzyme
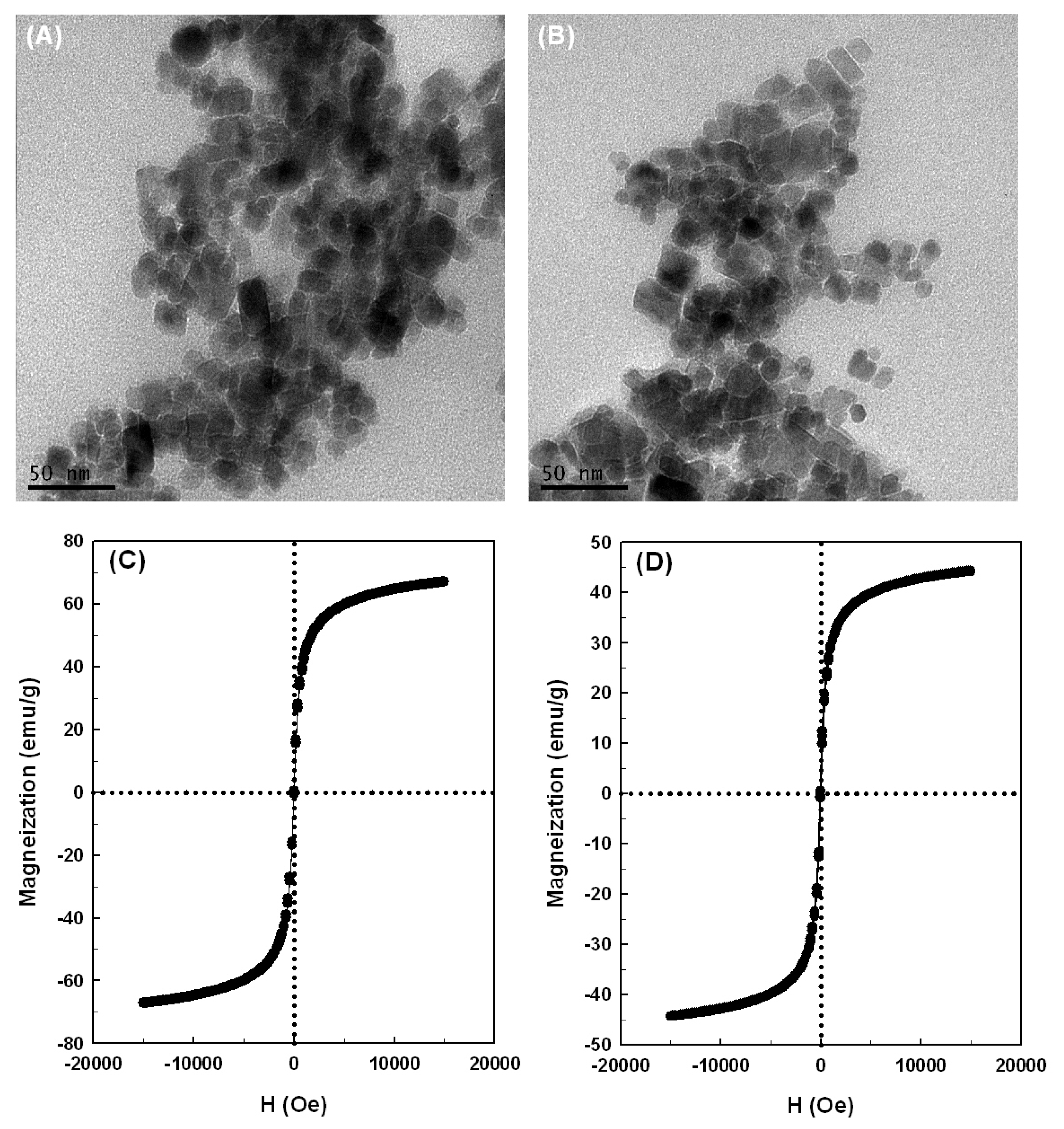
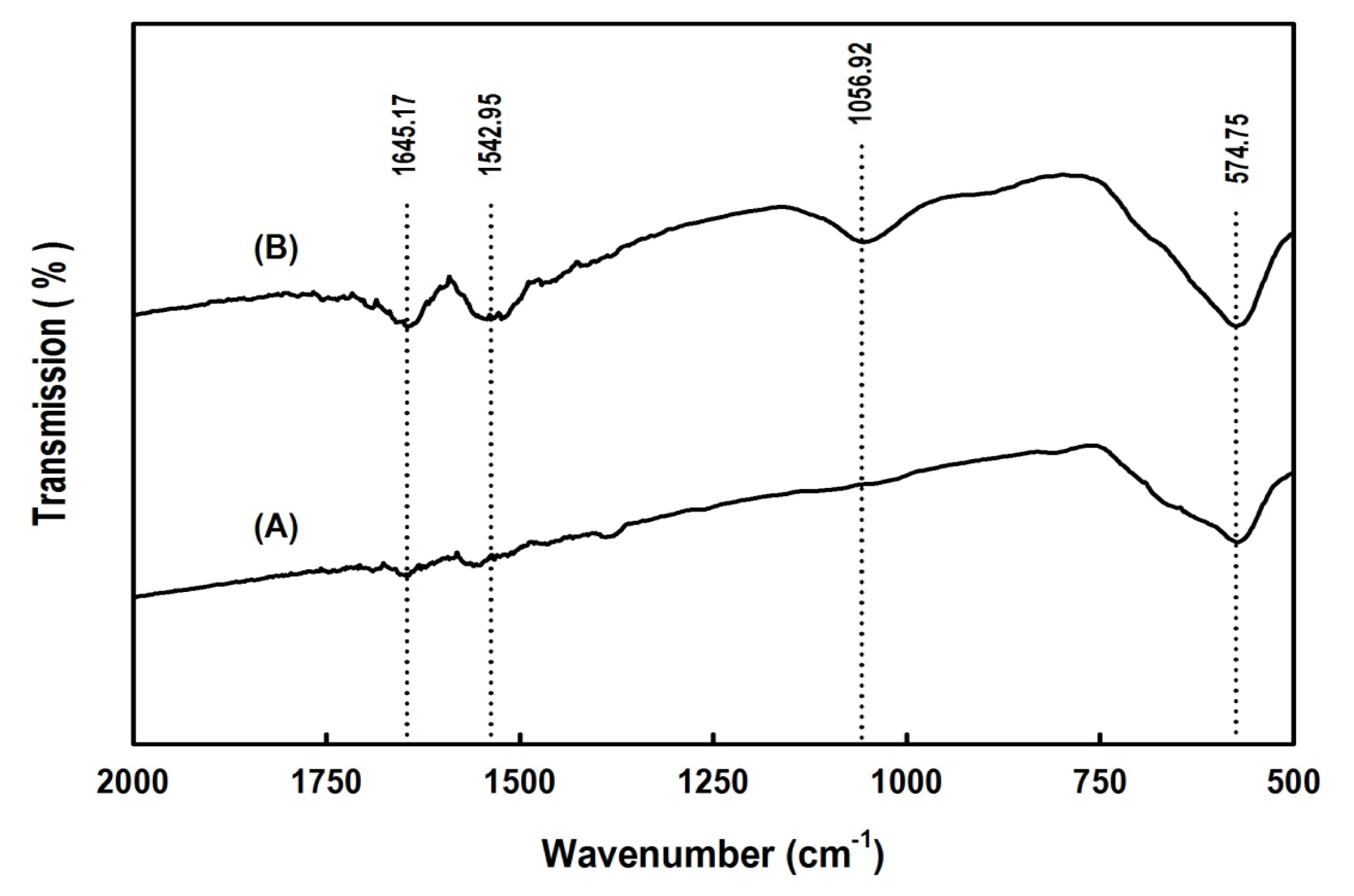
2.2. Properties of the Magnetic Nanoparticles
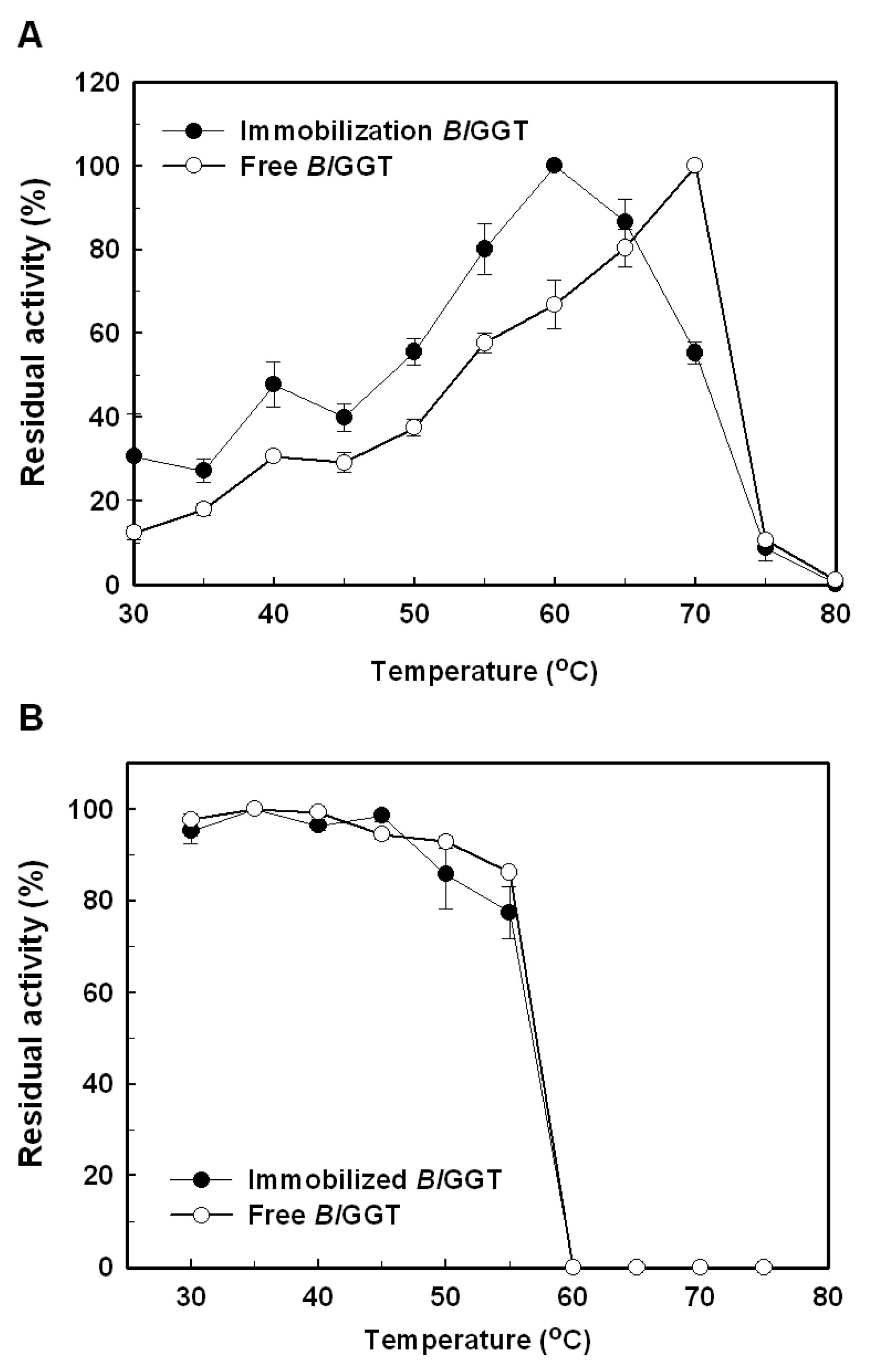
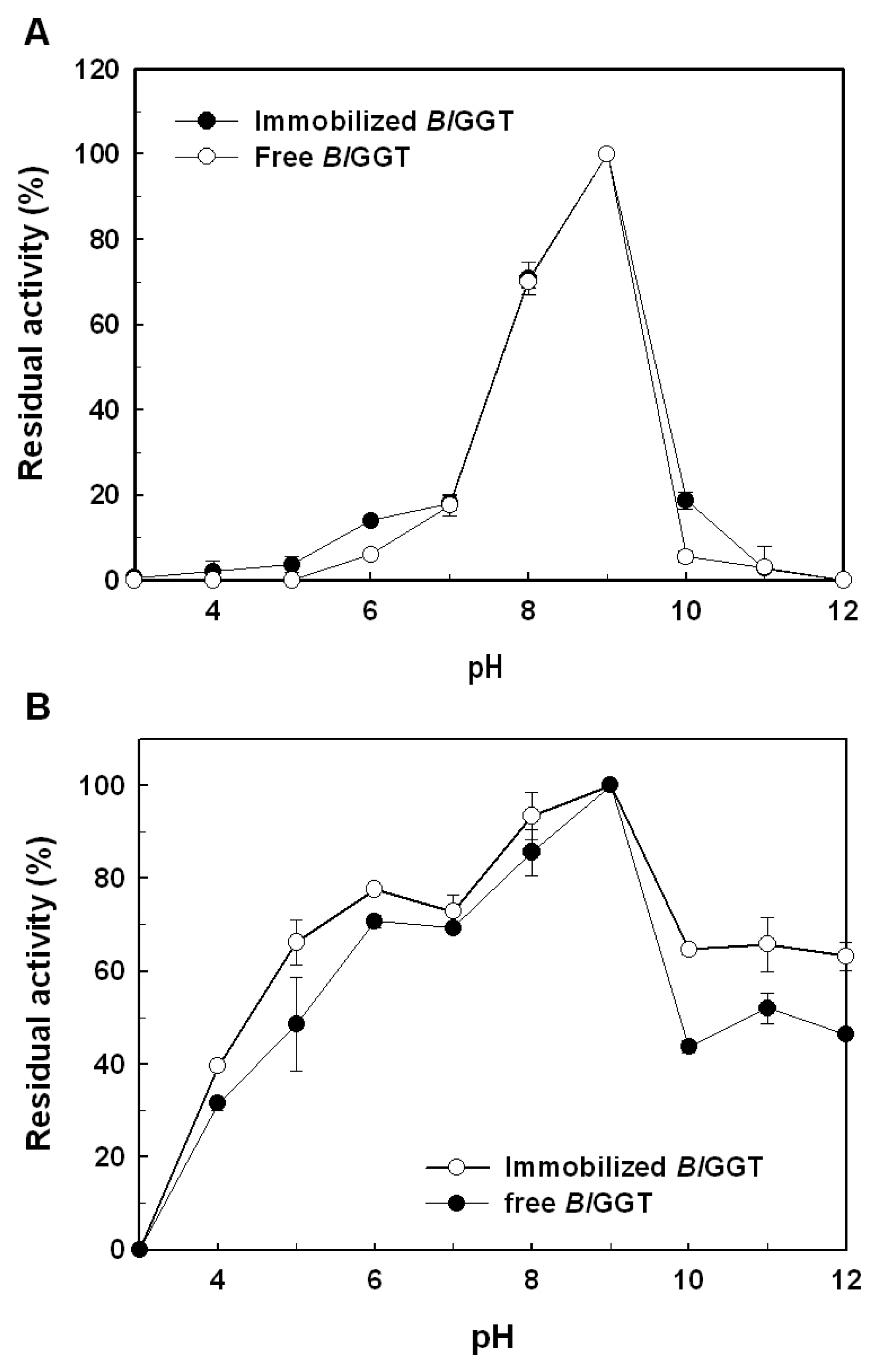
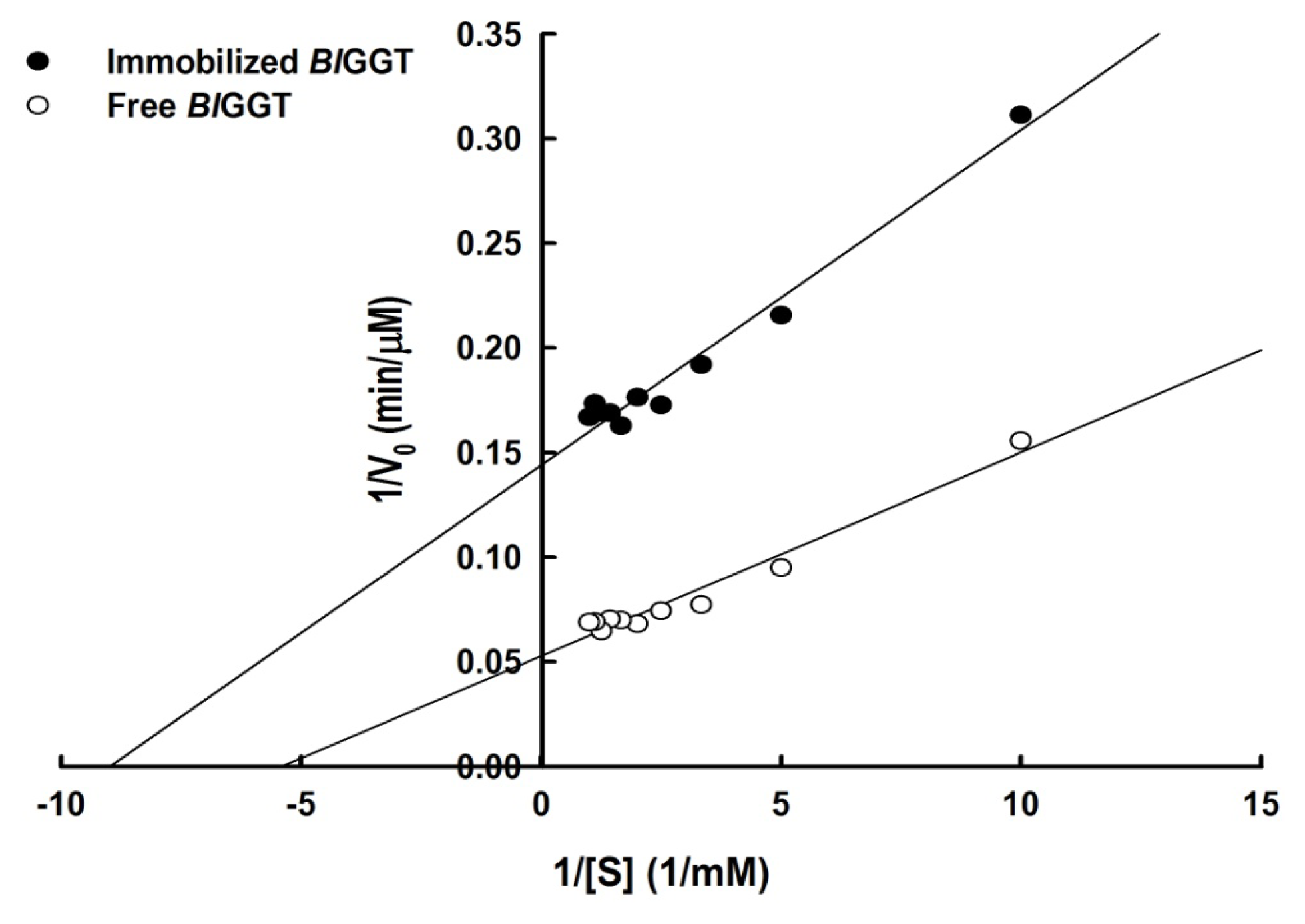
2.3. Characterization of Free and Immobilized Enzymes
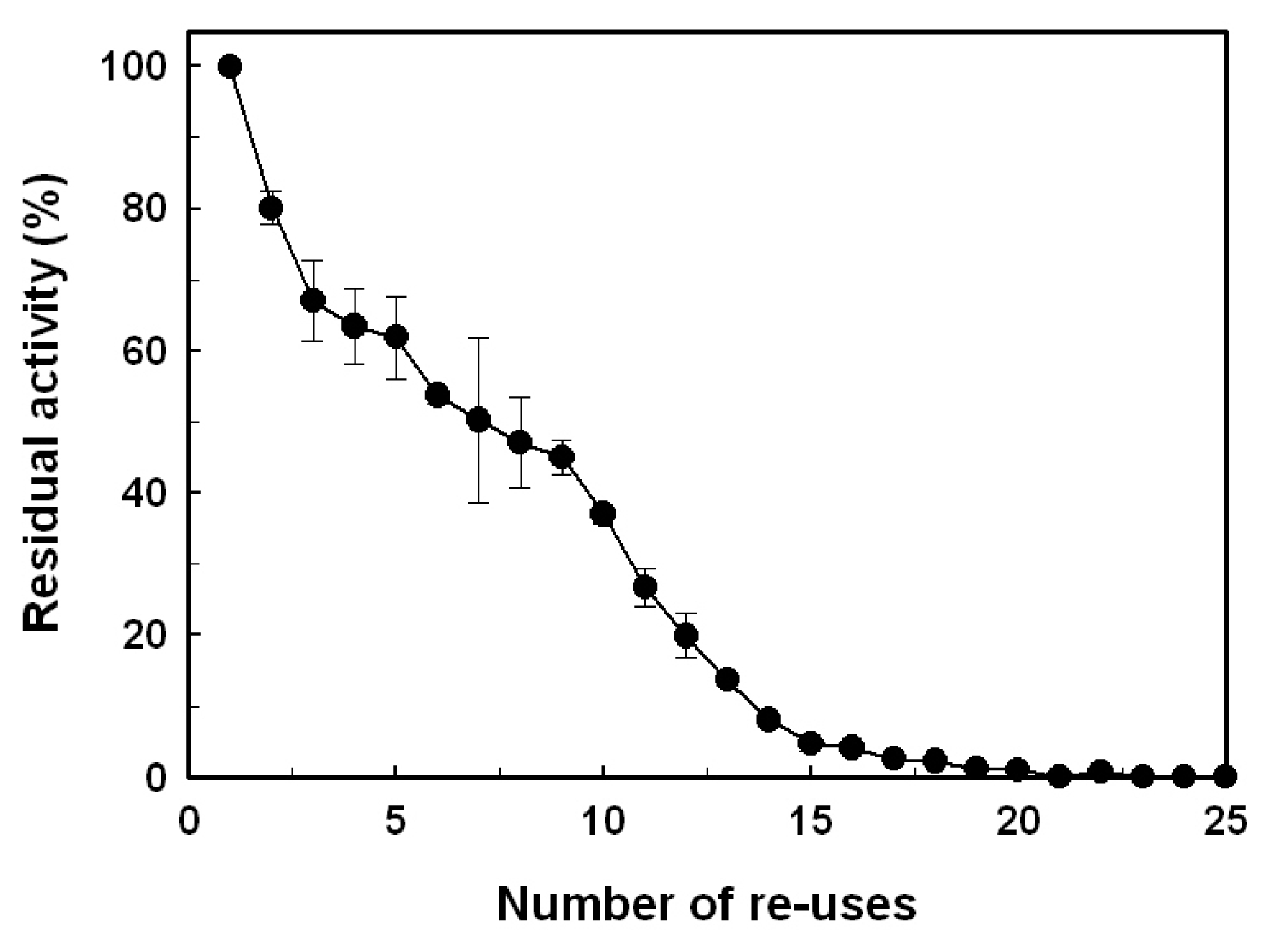
2.4. Reusability
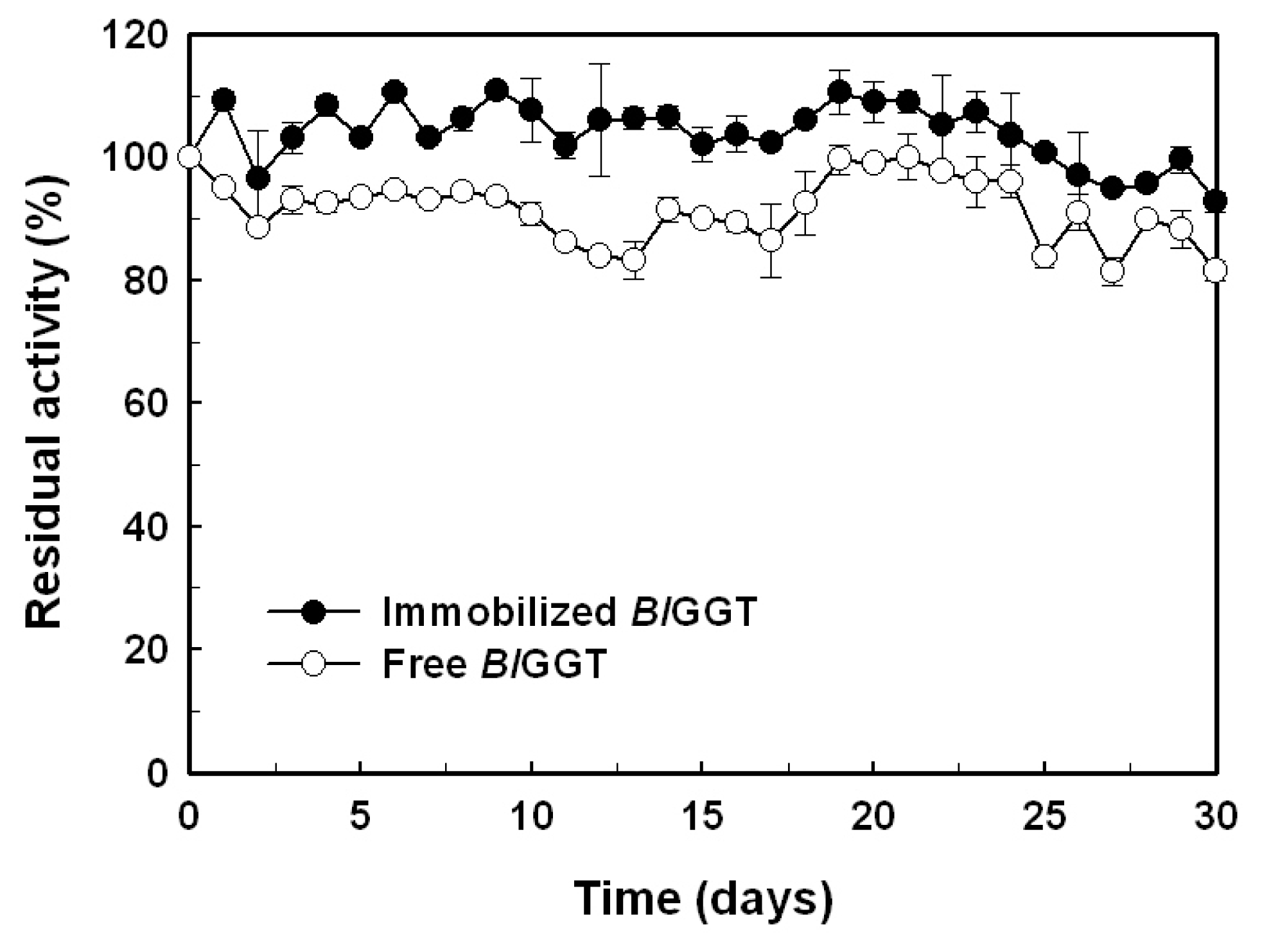
2.5. Storage Stability of Free and Immobilized Enzymes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant GGT
3.3. Determination of GGT Activity
3.4. Preparation of Aldehyde-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles and Enzyme Immobilization
3.5. Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.6. Effects of Temperature and pH
3.7. Reusability of the Immobilized Enzyme
3.8. Storage Stability of the Immobilized Enzyme
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Vellard, M. The enzyme as drug: Application of enzymes as pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2003, 14, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Kim, S.K. Application of marine microbial enzymes in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Adv. Food Nutr. Res 2012, 65, 423–435. [Google Scholar]
- Koeller, K.M.; Wong, C.H. Enzymes for chemical synthesis. Nature 2001, 409, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, A.; Dordick, J.S.; Hauer, B.; Kiener, A.; Wubbolt, M.; Witholt, B. Industrial biocatalysts today and tomorrow. Nature 2001, 409, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Toscano, M.D.; Woycechowsky, K.J.; Hilvert, D. Minimalist active-site redesign: Teaching old enzymes new tricks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2007, 46, 3212–3236. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Alzohairy, M.A. Recent advances and applications of immobilized enzyme technologies: A review. Res. J. Biol. Sci 2010, 5, 565–575. [Google Scholar]
- Polizzi, K.M.; Bommarius, A.S.; Broering, J.M.; Chaparro-Riggers, J.F. Stability of biocatalysts. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2007, 11, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Hanefeld, U.; Gardossi, L.; Magner, E. Understanding enzyme immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev 2009, 38, 453–468. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo, C.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2007, 40, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L. Immobilized enzymes: Science or art? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2005, 9, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, D.; Jordaan, J. Advances in enzyme immobilization. Biotechnol. Lett 2009, 31, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Straathof, A.J.; Panke, S.; Schmid, A. The production of fine chemicals by biotransformations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2002, 13, 548–556. [Google Scholar]
- Spahn, C.; Minteer, S.D. Enzyme immobilization in biotechnology. Recent Pat. Eng 2008, 2, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Tischer, W.; Wedekind, F. Immobilized enzymes: Methods and applications. Top. Curr. Chem 1999, 200, 95–126. [Google Scholar]
- Varavinit, S.; Chaokasem, N. Covalent immobilization of a glucoamylase to bagasse dialdehyde cellulose. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2001, 17, 721–725. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, S.J.; Thies, J.C.; Dureault, A.; Cameron, N.R.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Carette, N.; Michon, T.; Weberslcirch, R. Covalent enzyme immobilization onto photopolymerized highly porous monliths. Adv. Mater 2006, 18, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.R.; Pundir, C.S. Covalent immobilization of lipase onto onion membrane affixed on plastic surface: Kinetic properties and application in milk fat hydrolysis. Indian J. Biotechnol 2007, 6, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Tasso, M.; Cordeiro, A.L.; Salchert, K. Covalent immobilization of subtilisin A onto thin films of maleic anhydride copolymers. Macromol. Biosci 2009, 9, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.G.; Wan, L.S.; Liu, Z.M.; Huang, X.J.; Xu, Z.K. Enzyme immobilization on electronspun polymer nanofibers: An overview. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym 2009, 56, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Lin, X.Q. Covalent immobilization of single-walled carbon nanotubes and single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid nanocomposites on glassy carbon electrode: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Talanta 2008, 77, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, J.; Kumar, C.; Chandra, T. Preparation and characterization of cellulose-bound magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym 2011, 68, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Tan, B.; Zhou, F.; Qin, Y.; Yang, R. Covalent immobilization of Kluyveromyces fragilis β-galactosidase on magnetic nanosized epoxy support for synthesis of galacto-oligosaccharide. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng 2012, 35, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Brannigan, J.A.; Dodson, G.; Duggleby, H.J.; Moody, P.C.; Smith, J.L.; Tomchick, D.R.; Murzin, A.G. A protein catalytic framework with an N-terminal nucleophile is capable of self-activation. Nature 1995, 90, 416–419. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, S.S.; Meister, A. γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase from kidney. Meth. Enzymol 1985, 113, 400–419. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Kumagai, H. Autocatalytic processing of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 43536–43543. [Google Scholar]
- Boanca, G.; Sand, A.; Barycki, J.J. Uncoupling the enzymatic and autoprocessing activities of Helicobacter pylori γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 19029–19037. [Google Scholar]
- Castellano, I.; Merlino, A.; Rossi, M.; La Cara, F. Biochemical and structural properties of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans: An enzyme specialized in hydrolase activity. Biochimie 2010, 92, 464–474. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Hashimoto, W.; Kumagai, H. Glutathione metabolism in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym 1999, 6, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, D.A.; Forman, H.J. Glutathione in defense and signaling: Lessons from a small thiol. Ann. NY Acad. Sci 2002, 973, 488–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ubiyvovk, V.M.; Blazhenko, O.V.; Gigot, D.; Penninckx, M.; Sibirny, A.A. Role of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase in detoxification of xenobiotics in the yests Hansenula polymorpha and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. Biol. Int 2006, 30, 665–671. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Yamada, C.; Kato, K. γ-Glutamyl compounds and enzymatic production using bacterial γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.L.; Chou, P.R.; Hua, Y.W.; Hsu, W.H. Overexpression, one-step purification, and biochemical characterization of a recombinant γ-glutamyl transpeptidase from Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2006, 73, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Lo, H.F. Influence of N-terminal truncations on the functional expression of Bacillus licheniformis γ-glutamyl transpeptidase in recombinant Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol 2008, 57, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.P.; Liang, W.C.; Lyu, R.C.; Chi, M.C.; Wang, T.Z.; Su, K.L.; Hung, H.C.; Lin, L.L. Effects of C-terminal truncation on autocatalytic processing of Bacillus licheniformis γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochemistry (Mos. ) 2010, 75, 919–929. [Google Scholar]
- Koneracká, M.; Kopčanský, P.; Timko, M.; Ramchand, C.N.; de Sequeira, A.; Treven, M. Direct binding procedure of proteins and enzymes to fine magnetic particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2002, 252, 409–411. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.H.; Liao, M.H.; Chen, D.H. Direct binding and characterization of lipase onto magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Prog 2003, 19, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, S.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Ou, J.J.; Ho, L. Preparation and characterization of Pseudomonas putida esterase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2006, 39, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, H.; Matsunaga, T. Amino-silane modified superparamagnetic particles with surface-immobilized enzyme. J. Colloid Interface Sci 1991, 141, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.W.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, W.C. Protein and enzyme immobilization on non-porous microspheres of polystyrene. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem 1998, 27, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ikediobi, C.O.; Stevens, M.; Latinwo, L. Immobilization of linamarase on non-porous glass beads. Process Biochem 1998, 33, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, W.; Caruntu, D.; Yu, M.H.; Martin, A.; Chen, J.F.; O’Connor, C.J.; Zhou, W.L. Synthesis of porous magnetic hollow silica nanospheres for nanomedicine application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 17473–17477. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, S.C.; Yu, C.H.; Gao, X.; Tam, K. Silica-encapsulated nanomagnetic particle as a new recoverable biocatalyst carrier. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16914–16922. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.C.; Kuo, Y.Y.; Liang, C.F.; Chien, W.T.; Wu, H.T.; Chang, T.C.; Jan, F.D.; Lin, C.C. Site-specific immobilization of enzymes on magnetic nanoparticles and their use in organic synthesis. Bioconjugate Chem 2012, 23, 714–724. [Google Scholar]
- Kouassi, G.K.; Irudayaraj, J.; McCarty, G. Examination of cholesterol oxidase attachment to magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Rivera, J.G.; He, L.; Kulkarni, H.; Lee, D.K.; Messersmith, P.B. Facile, high efficiency immobilization of lipase enzyme on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via a biomimetic coating. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.H.; Chen, D.H. Immobilization of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase on magnetic nanoparticles for improving its stability. Biotechnol. Lett 2001, 23, 3234–3241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.H.; Liao, M.H. Preparation and characterization of YADH-bound magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym 2002, 16, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.L.; Cheng, W.C.; Yang, J.C.; Chi, M.C.; Chen, J.H.; Lin, H.P.; Lin, L.L. Preparation of carboxylated magnetic particles for the efficient immobilization of C-terminally lysine-tagged Bacillus stearothermophilus aminopeptidase II. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2010, 37, 717–725. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, R.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Guisan, J.M. Immobilization stabilization of enzymes: Variables that control the intensity of the trypsin (amine)–agarose (aldehyde) multipoint attachment. Enzyme Microb. Technol 1989, 11, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.L.; Li, X.C.; Yi, B.; Deng, L. The preparation and catalytically active characterization of papain immobilized on magnetic composite microspheres. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2004, 35, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pedroche, J.; del Mar Yust, M.; Mateo, C.; Fernadez-Lafuente, R.; Girón-Calle, J.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque, J.; Guisán, J.M.; Francisco, M. Effect of the support and experimental conditions in the intensity of the multipoint covalent attachment of proteins on glyoxylagarose supports: Correlation between enzyme-support linkages and thermal stability. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2007, 40, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Sato, S.; Mukataka, S. Production of chitosan oligosaccharides using chitosanase immobilized on amylase-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Process Biochem 2008, 43, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski, M.; Meister, A. γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase: A new convenient substrate for determination and study of l- and d-glutamyl transpeptidase activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1963, 73, 679–681. [Google Scholar]
- Khalafalla, S.E.; Reimers, G.W. Preparation of dilution-stable aqueous magnetic fluids. IEEE Trans. Magn 1980, 16, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-Y.; Tsai, M.-G.; Chi, M.-C.; Wang, T.-F.; Lin, L.-L. Covalent Immobilization of Bacillus licheniformis γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase on Aldehyde-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4613-4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14034613
Chen Y-Y, Tsai M-G, Chi M-C, Wang T-F, Lin L-L. Covalent Immobilization of Bacillus licheniformis γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase on Aldehyde-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(3):4613-4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14034613
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Yu, Ming-Gen Tsai, Meng-Chun Chi, Tzu-Fan Wang, and Long-Liu Lin. 2013. "Covalent Immobilization of Bacillus licheniformis γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase on Aldehyde-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 3: 4613-4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14034613



