The Contribution of Childhood Parental Rejection and Early Androgen Exposure to Impairments in Socio-Cognitive Skills in Intimate Partner Violence Perpetrators with High Alcohol Consumption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Alcohol Abuse Evaluation
2.4. Psychological Trait Profiles
2.5. Neuropsychological Measures
2.6. Violence-Related Attitudes and Beliefs Scales
2.7. 2D:4D Digit Ratio
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
| High Alcohol (n = 74) | Low Alcohol (n = 71) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 38.34 ± 10.47 | 41.67 ± 11.21 | |
| Right 2D:4D ratio * | 0.95 ± 0.09 | 0.99 ± 0.04 | |
| Left 2D:4D ratio | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 0.99 ± 0.07 | |
| Educational level | Basics | 43 (58%) | 41 (58%) |
| Graduate | 25 (34%) | 23 (32%) | |
| College | 6 (8%) | 7 (10%) | |
| Nationality | Spanish | 57 (77%) | 55 (77%) |
| Latin Americans | 9 (12%) | 6 (8.5%) | |
| Africans | 6 (8%) | 4 (6%) | |
| Russians | 2 (3%) | 6 (8.5%) | |
| Employment status | Working full or part time | 37 (50%) | 39 (55%) |
| Unemployed | 37 (50%) | 32 (45%) | |
| Economic income per year | <1,800 € | 17 (23%) | 14 (20%) |
| 1,800–12,000 € | 40 (54%) | 33 (46%) | |
| 12,000–36,000 € | 17 (23%) | 20 (28%) | |
| >36,000 € | 0 (0%) | 4 (6%) | |
| Marital status * | Single | 20 (27%) | 18 (25%) |
| Married | 19 (26%) | 34 (48%) | |
| Divorced | 35 (47%) | 19 (27%) | |
| IRI perspective taking * | 18.48 ± 7.41 | 23.14 ± 5.43 | |
| IRI empathic concern | 24.21 ± 0.71 | 23.05 ± 0.61 | |
| IRI personal distress ** | 16.00 ± 0.93 | 12.50 ± 0.70 | |
| IRI fantasy | 17.58 ± 0.92 | 18.35 ± 0.82 | |
| STAXI-2 T-Ang * | 18.23 ± 5.24 | 14.13 ± 3.67 | |
| STAXI-2 AEI * | 29.14 ± 10.96 | 22.70 ± 12.30 | |
| Plutchick (impulsivity) * | 30.90 ± 6.49 | 25.28 ± 4.46 | |
| Eyes test * | 21.5 ± 1.37 | 24.89 ± 0.88 | |
| Eyes test (positive emotions) | 4.67 ± 0.36 | 5.11 ± 0.45 | |
| Eyes test (negative emotions) | 7.50 ± 0.82 | 8.63 ± 0.39 | |
| Eyes test (neutral emotions) * | 9.33 ± 0.60 | 11.16 ± 0.51 | |
| WCST total trials ** | 118.28 ± 4.45 | 100.68 ± 4.08 | |
| WCST total mistakes ** | 48.00 ± 5.24 | 17.89 ± 2.15 | |
| WCST perseverative mistakes ** | 13.78 ± 4.37 | 1.95 ± 0.36 | |
| WCST non perseverative mistakes ** | 34.16 ± 4.24 | 16.26 ± 2.03 | |
| WCST perseverative mistakes (%) ** | 16.22 ± 5.79 | 2.05 ± 0.47 | |
| WCST failure to maintain set | 0.97 + 0.34 | 0.79 + 0.34 | |
| WCST trials to complete the first category | 14.57 + 1.81 | 15.05 + 2.17 | |
| WCST number of categories ** | 3.56 + 0.47 | 4.00 + 0.55 | |
| WCST conceptual level | 7.50 + 0.77 | 6.89 + 0.48 | |
| WCST learn to learn | 3.22 + 0.56 | 6.00 + 0.00 | |
3.1. Psychological Trait Profiles
3.2. Neuropsychological Variables
3.3. Violence-Related Attitudes and Beliefs Scales
| High Alcohol (n = 74) | Low Alcohol (n = 71) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| The Spousal Assault Risk Assessment Guide (SARA)Total score * | 11.44 ± 5.99 | 9.16 ± 5.15 | |
| Conflict Tactics Scale CTS | Physical Assault * | 4.61 ± 8.82 | 1.49 ± 4.02 |
| Psychological Aggression * | 18.45 ± 26.60 | 8.63 ± 18.98 | |
| Negotiation | 41.77 ± 42.60 | 32.31 ± 38.18 | |
| Ambivalent Sexism Inventory ASI | Hostile | 2.96 ± 1.17 | 2.27 ± 1.36 |
| Benevolent | 3.29 ± 1.06 | 2.93 ± 1.26 | |
| Parental Acceptance-Rejection Questionnaire Child Version PARQ * | 224.11 ± 39.85 | 215.45 ± 49.17 | |
3.4. Does History of Childhood Parental Rejection Play a Key Role in Adult Violence and Empathy, Mainly in HA IPV Perpetrators? Are Any Cognitive Processes Mediators of This Association?

3.5. Is Prenatal Masculinization Involved in Violence and Empathy during Adulthood, Mainly in HA IPV Perpetrators? Which Psychological or Cognitive Characteristics Mediate This Association?
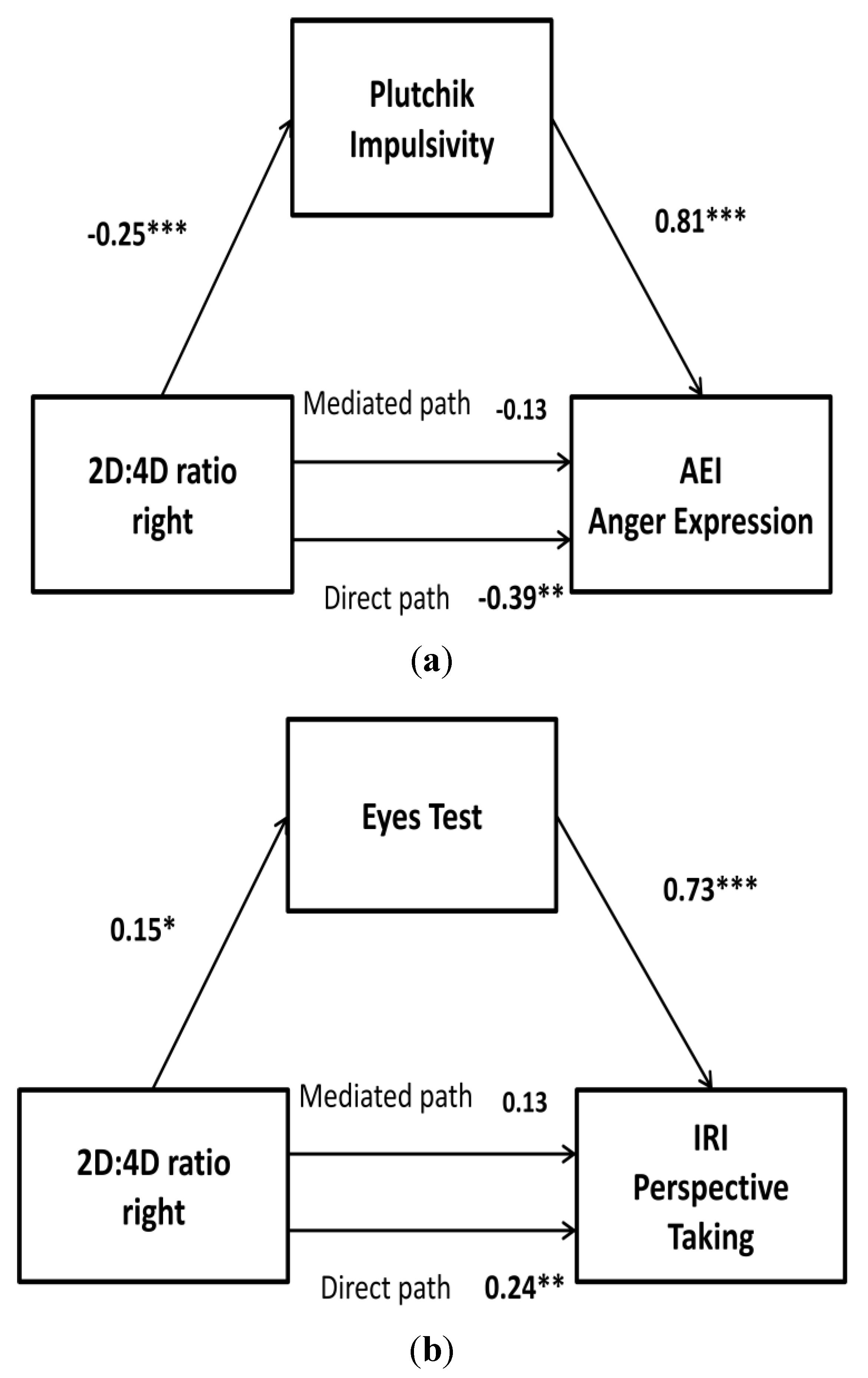
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinto, L.A.; Sullivan, E.L.; Ronsebaum, A.; Wyngarden, N.; Umhau, J.C.; Miller, M.W.; Taft, C.T. Biological correlates of intimate partner violence perpetration. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2010, 15, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fals-Stewart, W. The occurrence of partner physical aggression on days of alcohol consumption: A longitudinal diary study. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2003, 71, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, D.A.; Douglas, E.M. Alcohol and drug abuse in men who sustain intimate partner violence. Aggress. Behav. 2011, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, G.L. Improving violence intervention outcomes by integrating alcohol treatment. J. Interpers. Violence 2005, 20, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, J.S.; Gaher, R.M.; Jacobs, G.A.; Meyer, D.; Johnson-Jiménez, E. Associations between alcohol and PTSD symptoms among American Red Cross disaster relief workers responding to the 9/11/2001 attacks. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2005, 31, 347–364. [Google Scholar]
- Walling, S.M.; Meehan, J.C.; Marshall, A.D.; Holtzworth-Munroe, A.; Taft, C.T. The relationship of intimate partner aggression to head injury, executive functioning, and intelligence. J. Marital Fam. Ther. 2012, 38, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.; Josephs, R. Alcohol myopia: Its prized and dangerous effects. Am. Psychol. 1990, 45, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancola, P.R.; Duke, A.A.; Ritz, K.Z. Alcohol, violence, and the alcohol myopia model: Preliminary findings and implications for prevention. Addict. Behav. 2011, 36, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookstein, F.L.; Streissguth, A.P.; Sampson, P.D.; Connor, P.D.; Barr, H.M. Corpus callosum shape and neuropsychological deficits in adult males with heavy fetal alcohol exposure. Neuroimage 2002, 15, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Frias, M.; de la fe Fernandez, M.; Planells, E.; Miranda, M.T.; Mataix, J.; Llopis, J. Alcohol consumption and academic performance in a population of Spanish high school students. J. Stud. Alcohol 2001, 62, 741–744. [Google Scholar]
- Stout, J.C.; Rock, S.L.; Campbell, M.C.; Busemeyer, J.R.; Finn, P.R. Psychological processes underlying risky decisions in drug abusers. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2005, 19, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, W.; Tivis, R.; Scott, H.; Nixon, S.; Parsons, O. Neuropsychological déficits in sober alcoholics: Influences of chronicity and recent alcohol consumption. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Paraskevaides, T.; Morgan, C.J.; Leits, J.R.; Bisby, J.A.; Rendell, P.G.; Curran, V. Drinking and future thinking: Acute effects of alcohol on prospective memory and future simulation. Psychopharmacology 2010, 208, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurage, P.; Grynberg, D.; Noël, X.; Joassin, F.D.R.; Hanak, C.; Verbanck, P.; Luminet, O.; Timary, P.; Campanella, S.; Philippot, P. The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” test as a new way to explore complex emotions decoding in alcohol dependence. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 190, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, P.; Friedmann, C.; Suchan, B. Empathy and social problem solving in alcohol dependence, mood disorders and selected personality disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 448–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekermann, J.; Daum, I. Social cognition in alcoholism: A link to prefrontal cortex dysfunction? Addiction 2008, 103, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancola, P.R. The moderating effects of dispositional empathy on alcohol related aggression in men and women. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2003, 112, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisco, C.G.; Parrott, D.J.; Tharp, A.T. The role of heavy episodic drinking and hostile sexism in men’s sexual aggression toward female intimate partners. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, D.; Toth, S.L. Child maltreatment. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 1, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa-Gresa, P.; Moya-Albiol, L. Neurobiology of child abuse: The “cycle of violence”. (in Spanish). Rev. Neurol. 2011, 52, 489–503. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Martínez, A.; Moya-Albiol, L. Neuropsychology of perpetrators of domestic violence: The role of traumatic brain injury and alcohol abuse and/or dependence. Rev. Neurol. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kornhuber, J.; Erhard, G.; Lenz, B.; Kraus, K.; Sperling, W.; Bayerlein, K.; Biermann, T.; Stoessel, C. Low digit ratio 2D:4D in alcohol dependent patients. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, J.T.; Fink, B. Digit ratio, nicotine and alcohol intake and national rates of smoking and alcohol consumption. Pers. Ind. Diff. 2011, 50, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.C.; Dreber, A.; Apicella, C.L.; Eisenberg, D.T.; Gray, P.B.; Little, A.C.; Garcia, J.R.; Zamore, R.S.; Lum, J.K. Testosterone exposure, dopaminergic reward, and sensation-seeking in young men. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 99, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.A.; Hurd, P.L. Finger length ratio (2D:4D) correlates with physical aggression in men but not in women. Biol. Psychol. 2005, 68, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, J.T.; Peters, M. Digit ratio (2D:4D) and hand preference for writing in the BBC internet study. Laterality 2009, 14, 528–540. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlmeier, M.D.; Peters, K.; te Wildt, B.T.; Zedler, M.; Ziegenbein, M.; Wiese, B.; Emrich, H.M.; Schneider, U. Comorbidity of alcohol and substance dependence with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Alcohol Alcohol. 2008, 43, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, B.; Jacob, C.; Frieling, H.; Jacobi, A.; Hillemacher, T.; Muschler, M.; Watson, K.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Polymorphism of the long polyglutamine tract in the human androgen receptor influences craving of men in alcoholwithdrawal. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowska, B.; Pawlowski, B. Alcohol and nicotine intake and prenatal level of androgens measured by digit ratio. Pers. Ind. Diff. 2013, 55, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, C.J.; Sacco, K.A.; Neavins, T.M.; Wupperman, P.; George, T.P. Neurocognitive performance among alcohol dependent men with and without physical violence toward their partners: A preliminary report. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2008, 34, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá-Miñana, A.; Lila, M.; Oliver, A. Consumo de alcohol en hombres penados por violencia contra la pareja: Factores individuales y contextuales. (in Spanish). Adicciones 2013, 25, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fulwiler, C.; Eckstine, J.; Kalsy, S. Impulsive-aggressive traits, serotonin function, and alcohol-enhanced aggression. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Martínez, A.; Lila, M.; Sariñana-González, P.; González-Bono, E.; Moya-Albiol, L. High testosterone levels and sensitivity to acute stress in perpetrators of domestic violence with low cognitive flexibility and impairments in their emotional decoding process: A preliminary study. Aggress. Behav. 2013, 39, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lila, M.; Oliver, A.; Galiana, L.; Gracia, E. Predicting success indicators of an intervention programme for convicted intimate-partner violence offenders: The Contexto programme. Eur. J. Psychol. Appl. Legal Context 2013, 5, 73–95. [Google Scholar]
- Contell-Guillamón, C.; Gual-Solé, A.; Colom-Farran, J. Test para la identificación de transtornos por uso de alcohol (AUDIT): Traducción y validación del AUDIT al catalán y castellano. (in Spanish). Adicciones 1999, 11, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Babor, T.E.; Grant, M.G. From clinical research to secondary prevention: International collaboration in the development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). Alcohol Health Res. World 1989, 13, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Martos, A; Navarro, R.; Vecino, C.; Pérez, R. Validación de los cuestionarios KFA (CBA) y CAGE para diagnóstico del alcoholism. (in Spanish). Drogalcohol 1986, 11, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield, D.; McLeod, G.; Hall, P. The CAGE Questionnaire: Validation of a new alcoholism screening instrument. Am. J.Psychiatry 1974, 131, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Millon, T.; Davis, R.; Millon, C. Inventario Clínico Multiaxial de Millon-III (MCMI-III); (in Spanish). Tea Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Millon, T. MCMI-III Manual; National Computer Systems, Inc.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.H. Measuring individual differences in empathy: Evidence for a multidimensional approach. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1983, 44, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, V.; Frías, M.D.; Samper, P. La medida de la empatía: Análisis del interpersonal reactivity index. (in Spanish). Psichotema 2004, 16, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel-Tobal, J.J.; Casado, M.; Cano-Vindel, A.; Spielberger, C.D. Adaptación española del Inventario de Expresión de Ira Estado-Rasgo STAXI-II; Tea Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger, C.D. Manual for the State-Trait Anger ExpressionInventory-2; Psychological Assessment Resources Odessa: Lutz, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Páez, F.; Jiménez, A.; López, A.; Raull, J.P.; Ortega, H.; Nicolini, H. Estudio de validez de la traducción al castellano de la Escala de Impulsividad de Plutchik. (in Spanish). Salud Mental. 1996, 19, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Plutchik, R.; van Praag, H.M. The measurement of suicidality and impulsivity. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 13, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Hill, J.; Raste, Y.; Plumb, I. The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2001, 42, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, R.K.; Chelune, G.J.; Talley, J.L.; Kay, G.G.; Curtis, G. Test de Clasificación de Tarjetas de Wisconsin; (in Spainish). TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Heaton, R.K. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test Manual; Psychological Assessment Resources Odessa: Lutz, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Andrés Pueyo, A.; López, S.; Álvarez, E. Valoración del riesgo de violencia contra la pareja por media de la SARA. (in Spanish). Pap. Psicól. 2008, 29, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kropp, P.R.; Hart, S.D. The Spousal Assault Risk Assessment (SARA) guide: Reliability and validity in adult male offenders. Law Hum. Behav. 2000, 24, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rivas, M.J.; Andreu Rodríguez, J.M.; Graña Gómez, J.L.; O’Leary, D.K.; González Mdel, P. Validation of the modified version of the Conflict Tactics Scale (M-CTS) in a Spanish population of youths. Psicothema 2007, 19, 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Straus, M.A.; Hamby, S.L.; Boney-McCoy, S.; Sugarman, D.B. The revised conflict tactics scales (CTS2): Development and preliminary psychometric data. J. Fam. Issues 1996, 17, 283–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expósito, F.; Moya, M.; Glick, P. Sexismo ambivalente: Medición y correlates. (in Spanish). Rev. Psicol. Soc. 1998, 13, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, P.; Fiske, S.T. The ambivalent sexism inventory: Differentiating hostil and benevolent sexism. (in Spanish). J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1996, 70, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, R.O.; Saavedra, J.; Granum, E.O. Development and validation of the parental acceptance rejection questionnaire: Test manual. JSAS Cat. Sel. Doc. Psyhol. 1978, 8, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lila, M.; Gracia, E. Determinantes de la aceptación-rechazo parental. Psicothema 2005, 17, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Martínez, A.; De Andrés-García, S.; Sariñana-González, P.; Sanchis-Calatayud, M.V.; Roa, J.M.; González-Bono, E.; Moya-Albiol, L. The 2D:4D ratio and its relationship with other androgenization parameters in parents of individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Ann. Psychol. 2013, 29, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Aldenderfer, M.S.; Blashfield, R.K. Cluster Analysis; Sage: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Preacher, K.J.; Rucker, D.D.; Hayes, A.F. Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2007, 42, 185–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapu-Ustárroz, J.; Pérez-Sayes, G.; Erekatxo-Bilbao, M.; Pelegrín-Valero, C. What is theory of mind? Rev. Neurol. 2007, 44, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Holtzworth-Munroe, A.; Smutzler, N. Comparing the emotional reactions and behavioral intentions of violent and nonviolent husbands to aggressive, distressed, and other wife behaviors. Violence Vict. 1996, 11, 319–339. [Google Scholar]
- Covell, C.N.; Huss, M.T.; Langhinrichsen-Rohling, J. Empathic deficits among male batterers: A multidimensional approach. J. Fam. Violence 2007, 22, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, N.; Fernández-Montalvo, J.; Tirapu-Ustárroz, J. Alteraciones neuropsicológicas en el alcoholismo: Una revisión sobre la afectación de la memoria y las funciones ejecutivas. (in Spanish). Adicciones 2004, 1, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shorey, R.C.; Brasfield, H.; Febres, J.; Stuart, G.L. The association between impulsivity, trait anger, and the perpetration of intimate partner and general violence among women arrested for domestic violence. J. Interpers Violence 2011, 26, 2681–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Martínez, A.; González-Bono, E.; Lila, M.; Moya-Albiol, L. Testosterone/cortisol ratio in response to acute stress: A possible marker of risk for marital violence. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Martínez, Á.; Lila, M.; Catalá-Miñana, A.; Williams, R.K.; Moya-Albiol, L. The Contribution of Childhood Parental Rejection and Early Androgen Exposure to Impairments in Socio-Cognitive Skills in Intimate Partner Violence Perpetrators with High Alcohol Consumption. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 3753-3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10083753
Romero-Martínez Á, Lila M, Catalá-Miñana A, Williams RK, Moya-Albiol L. The Contribution of Childhood Parental Rejection and Early Androgen Exposure to Impairments in Socio-Cognitive Skills in Intimate Partner Violence Perpetrators with High Alcohol Consumption. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013; 10(8):3753-3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10083753
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Martínez, Ángel, Marisol Lila, Alba Catalá-Miñana, Ryan K. Williams, and Luis Moya-Albiol. 2013. "The Contribution of Childhood Parental Rejection and Early Androgen Exposure to Impairments in Socio-Cognitive Skills in Intimate Partner Violence Perpetrators with High Alcohol Consumption" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, no. 8: 3753-3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10083753





