Effect of Burnable Absorbers on Inert Matrix Fuel Performance and Transuranic Burnup in a Low Power Density Light-Water Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
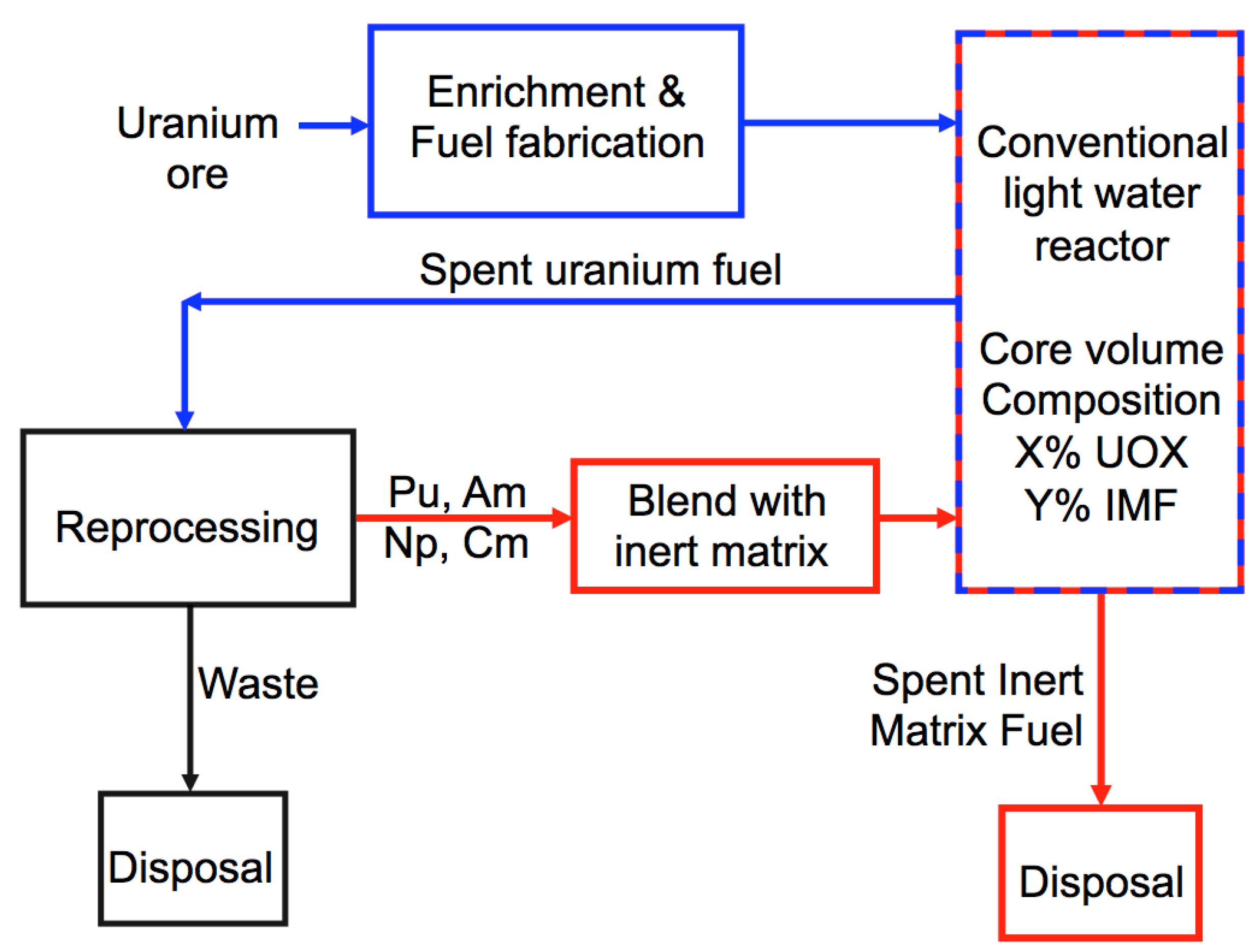
2.1. Overview
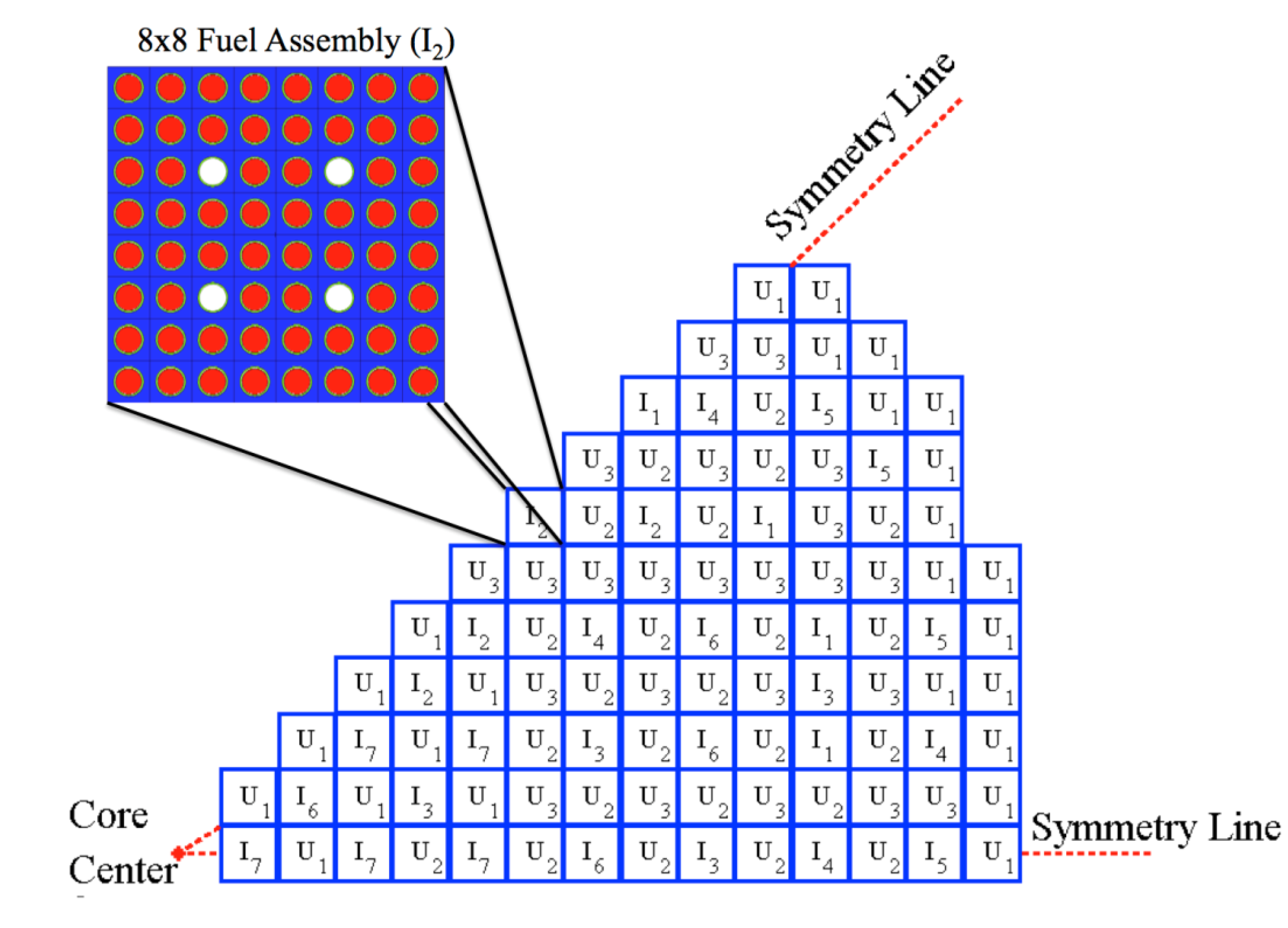
2.2. Monte Carlo Simulations and Fuel Composition
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Fuel pin radius | 0.396cm |
| Pin pitch | 1.3 cm |
| Pin height | 426.7 cm |
| Cladding thickness | 0.05 cm |
| Cladding | Zircalloy |
| Gap thickness | 0.02 cm |
| Lattice size | 8 pin × 8 pin |
| Number of fuel pins per assembly | 60 |
| Number of guide tubes per assembly | 4 |
| Active Core diameter | 325 cm |
| Uranium fuel density | 11g/cm3 |
| Inert matrix fuel density | 5.75 g/cm3 (doped) |
| Pressure vessel inner diameter | 401.6 cm |
| Pressure vessel thickness | 20 cm |
2.3. Thermal Transport

| Property | Location | Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | Uranium dioxide fuel | 2.9 W/m-K | [28], SI |
| Inert matrix fuel | 1.8 W/m-K | [29], SI | |
| Cladding | 20.0 W/m-K | [27] | |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient | Air gap | 5,679 W/m2-K | [27] |
| Moderator | 16,600 W/m2-K | SI | |
| Coolant flow rate | Per channel | 0.384 kg/sec | * |
| Temperature | Inlet | 550 K | * |
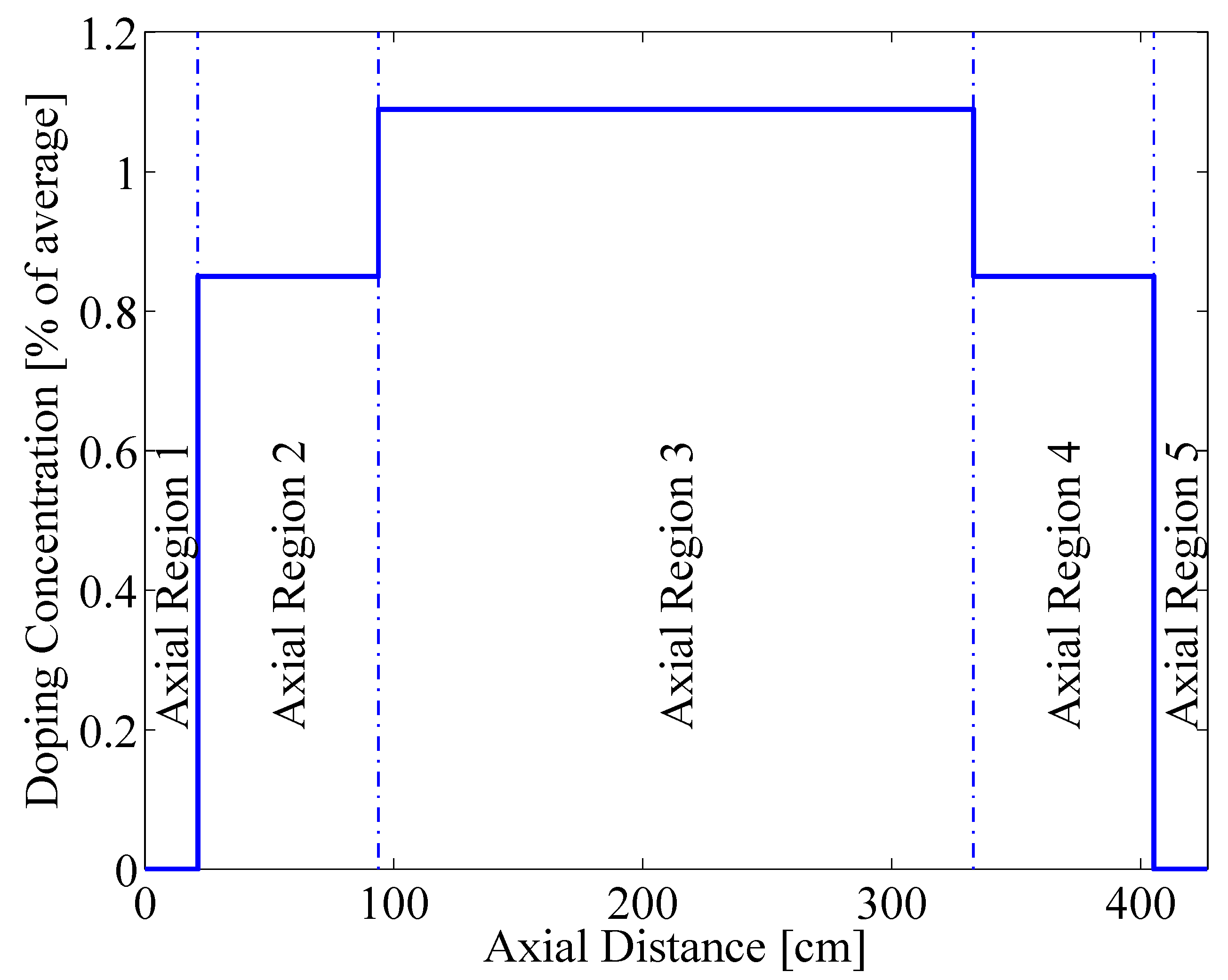
2.4. Reactivity Coefficients




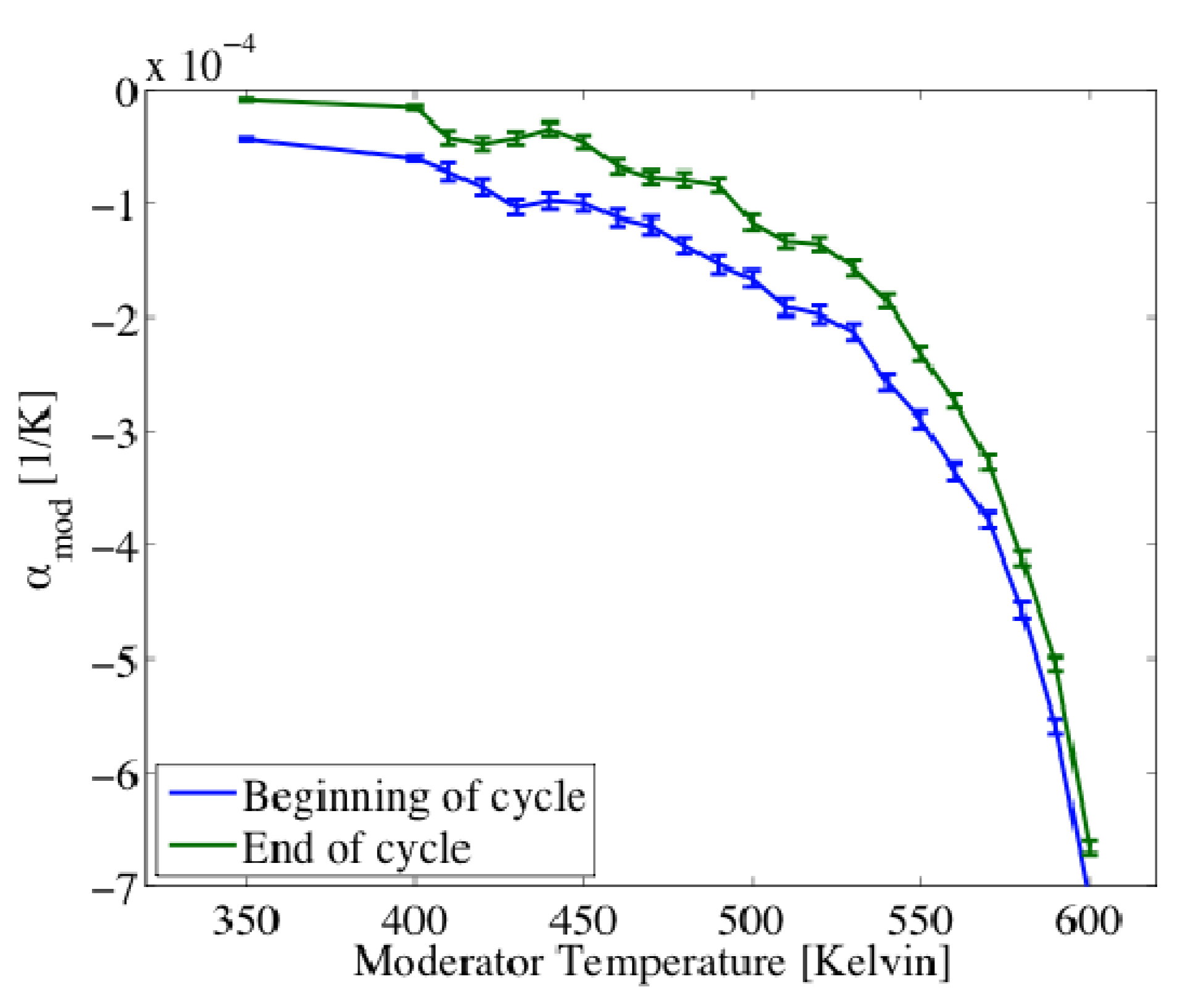
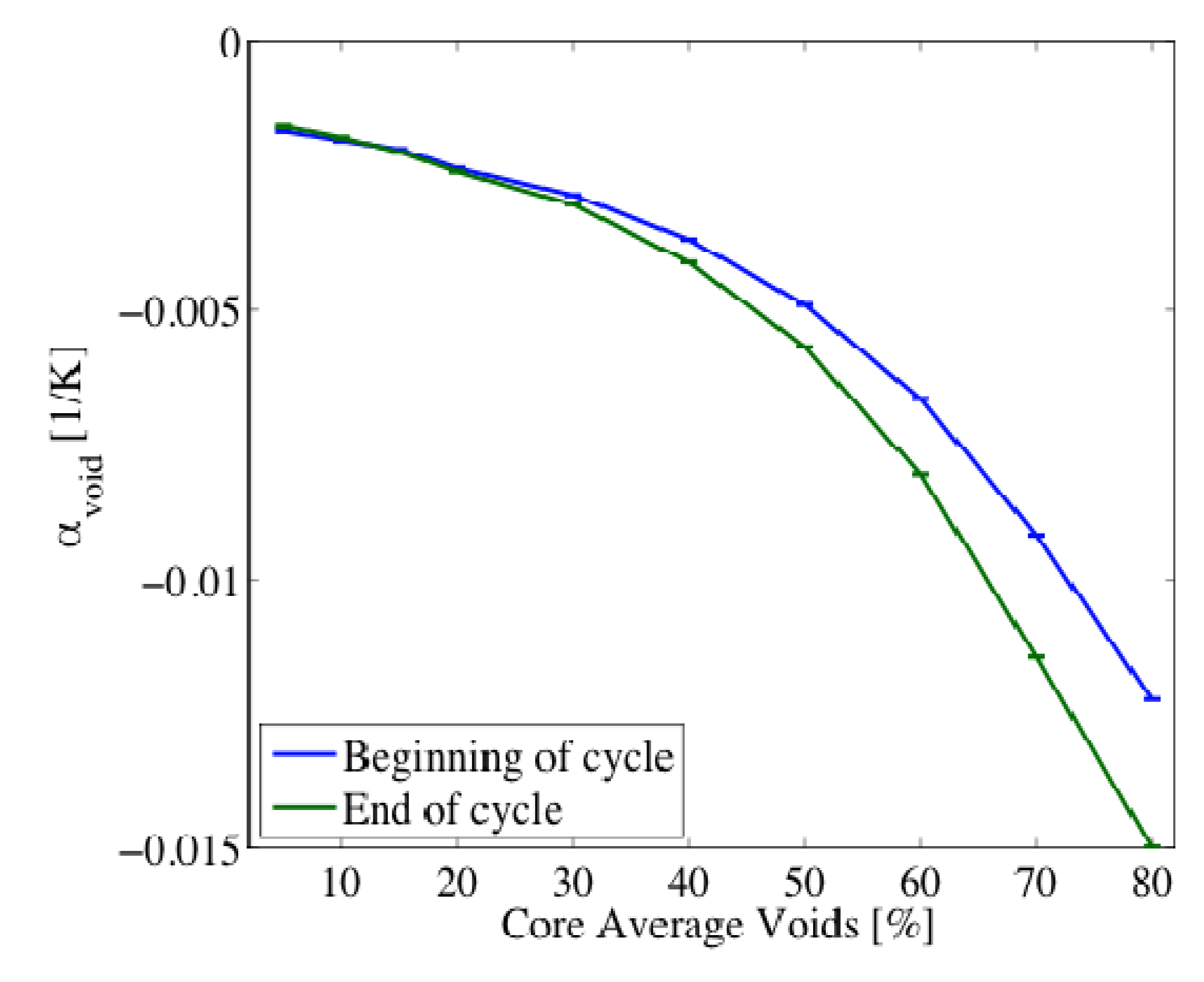
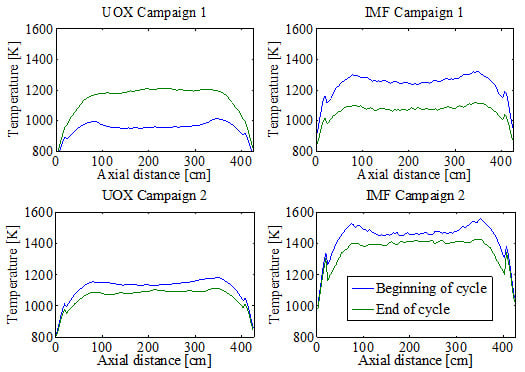
3. Results and Discussion
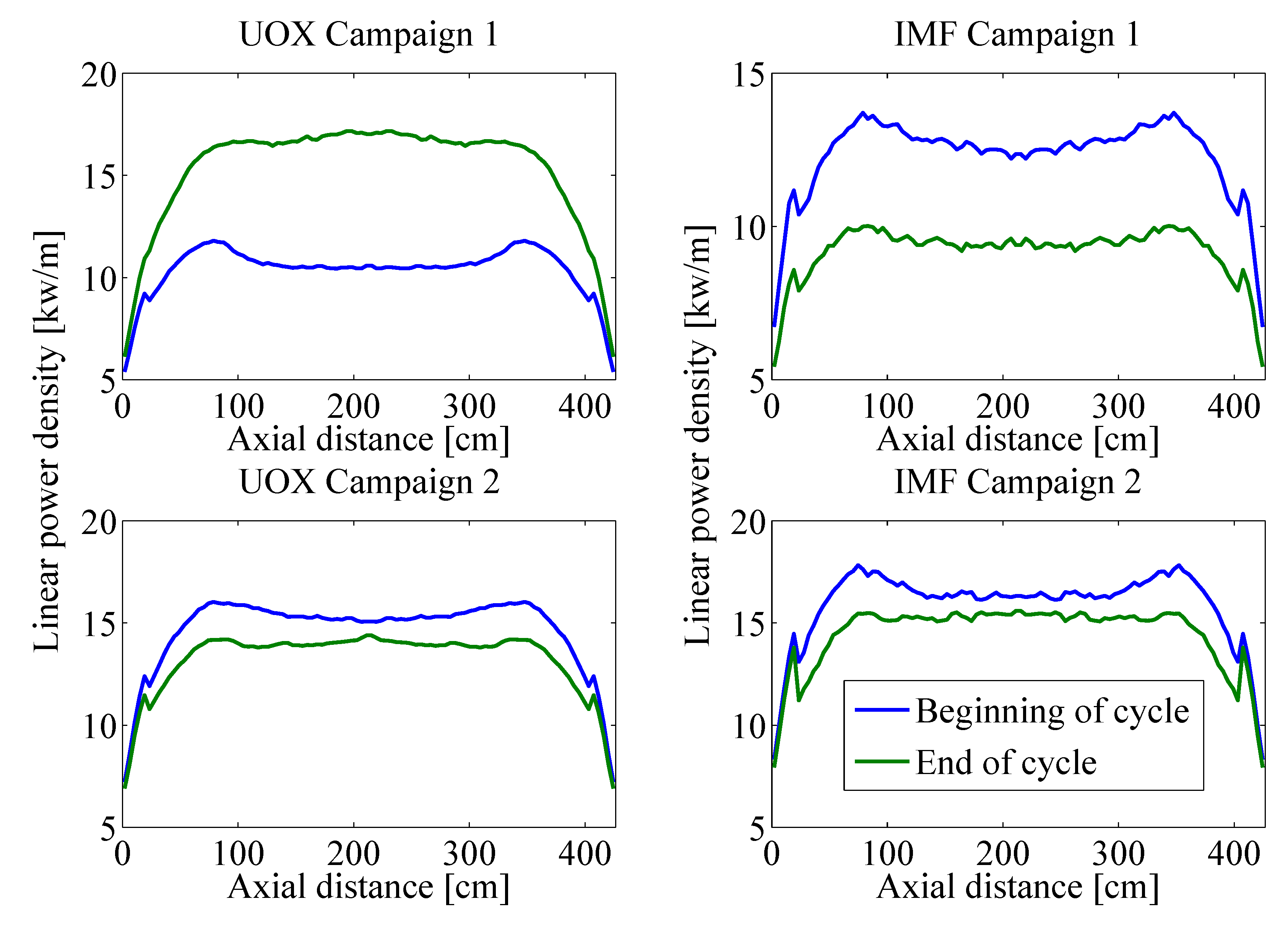
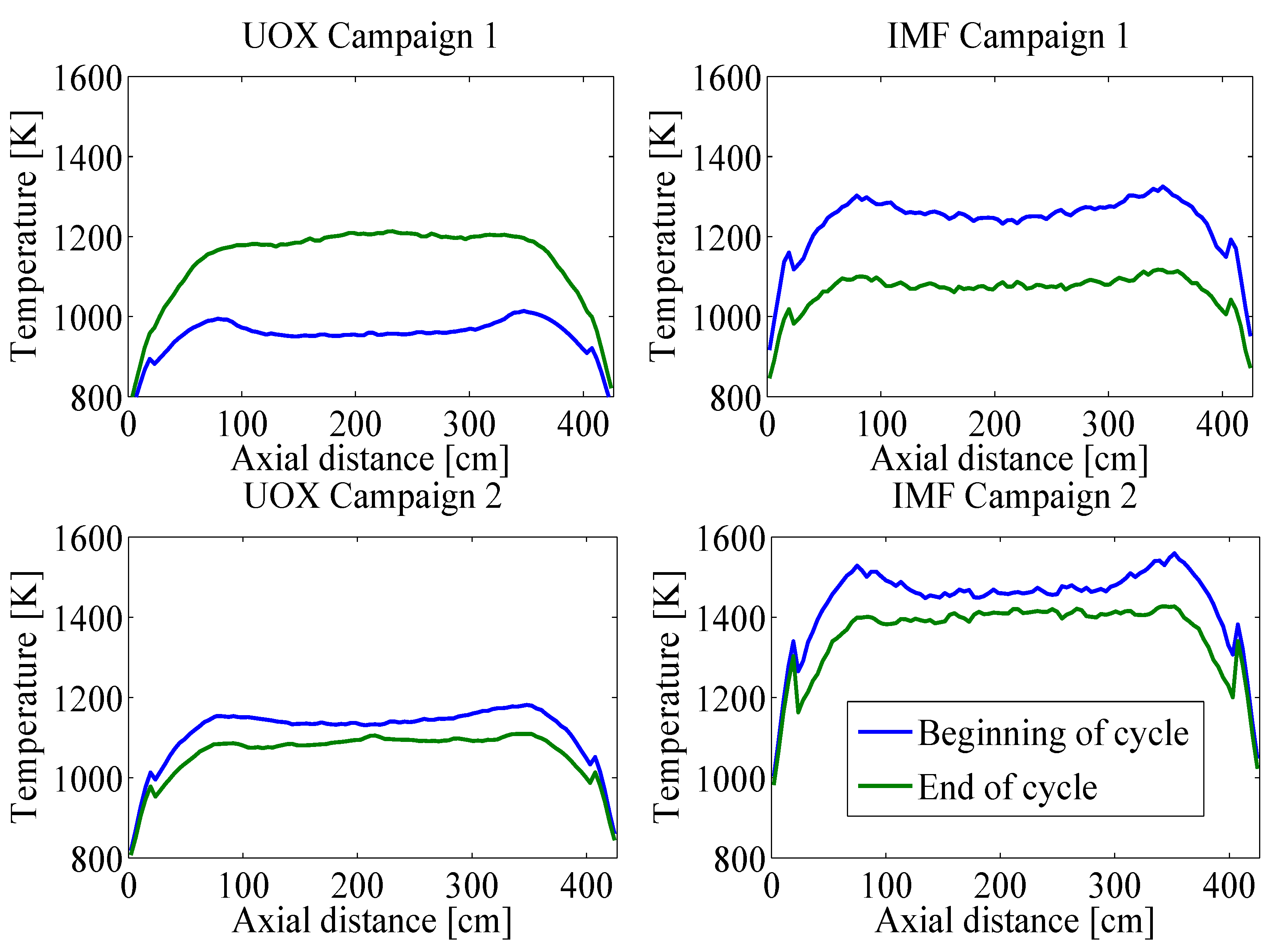
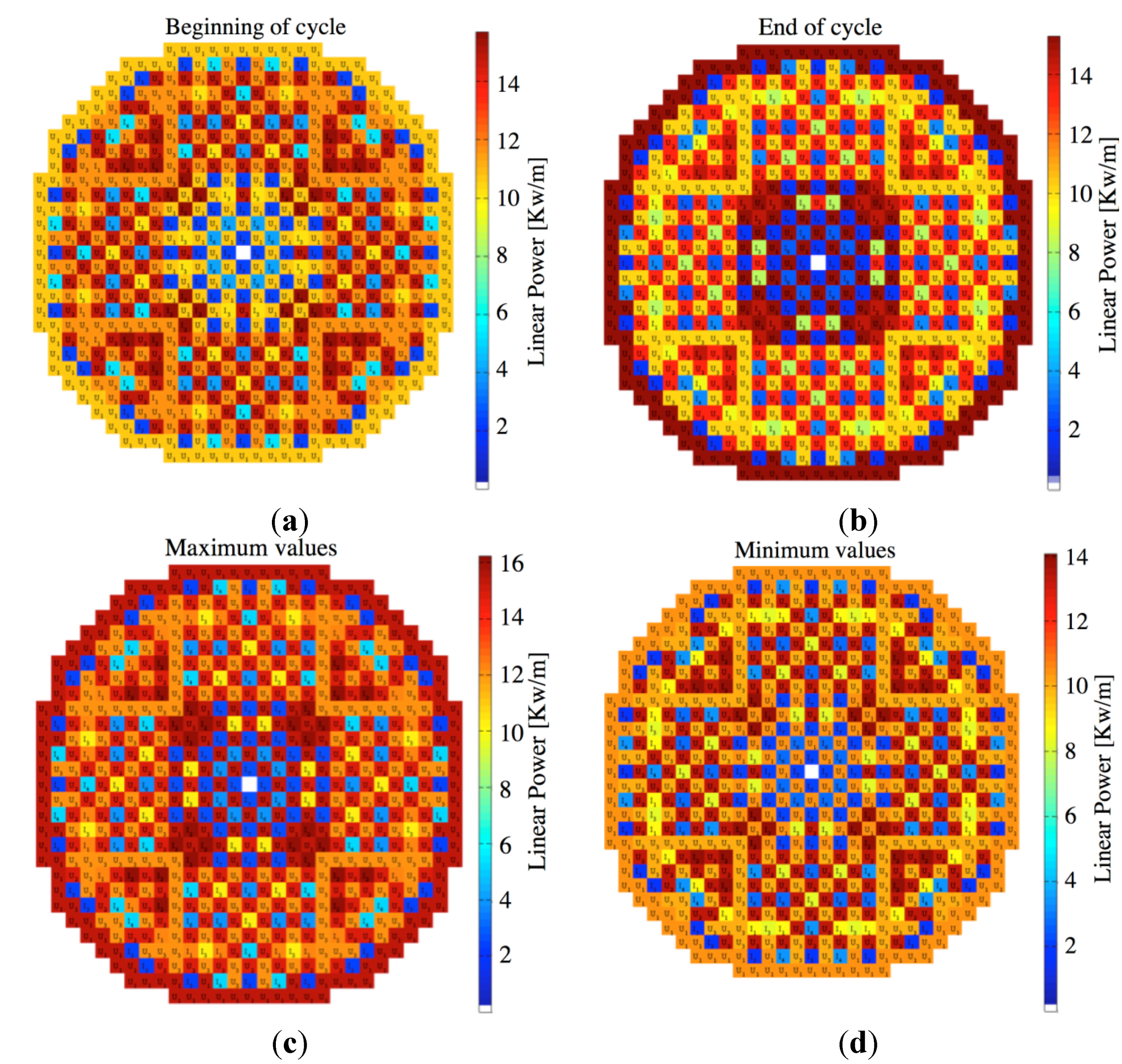
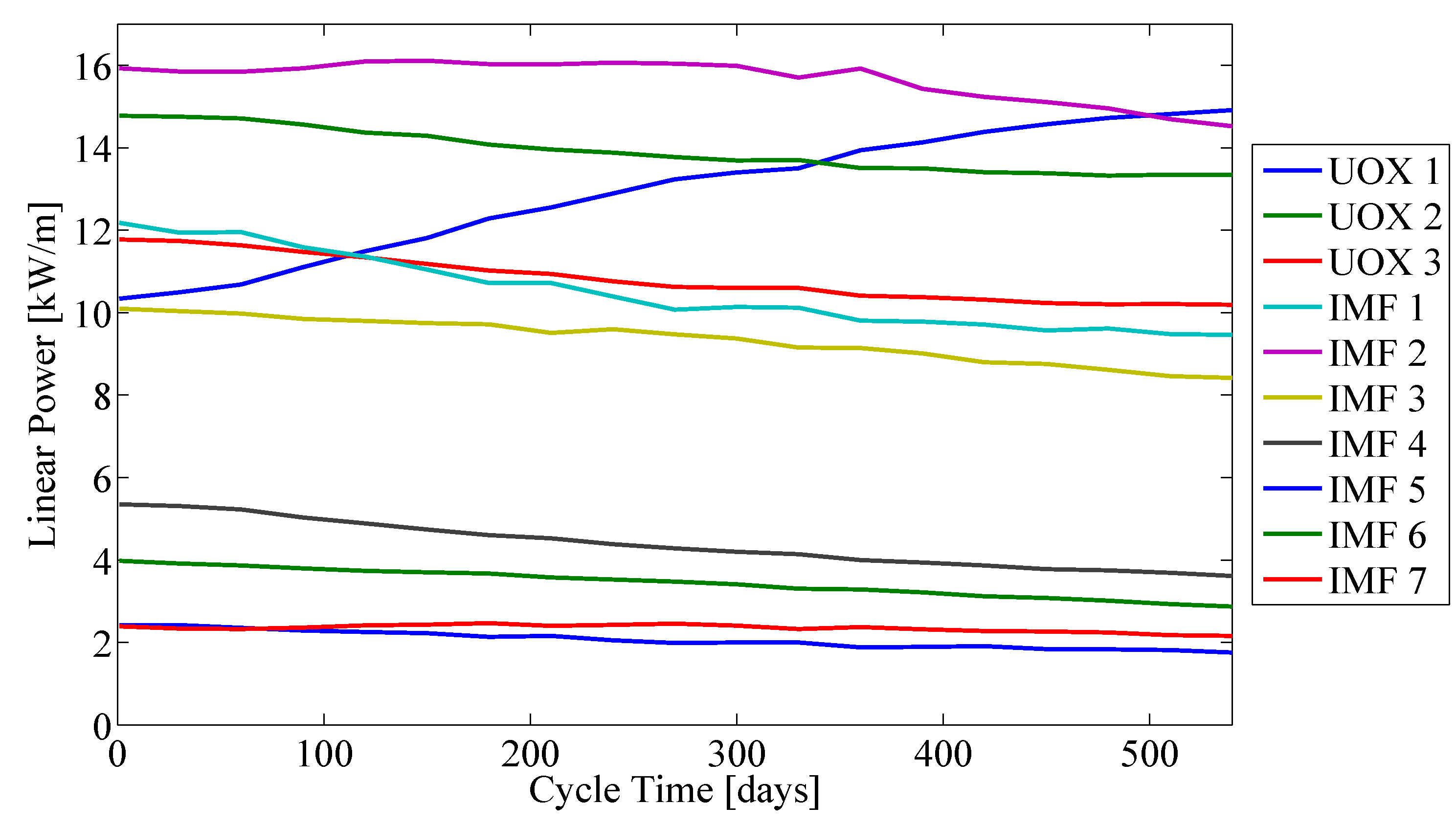
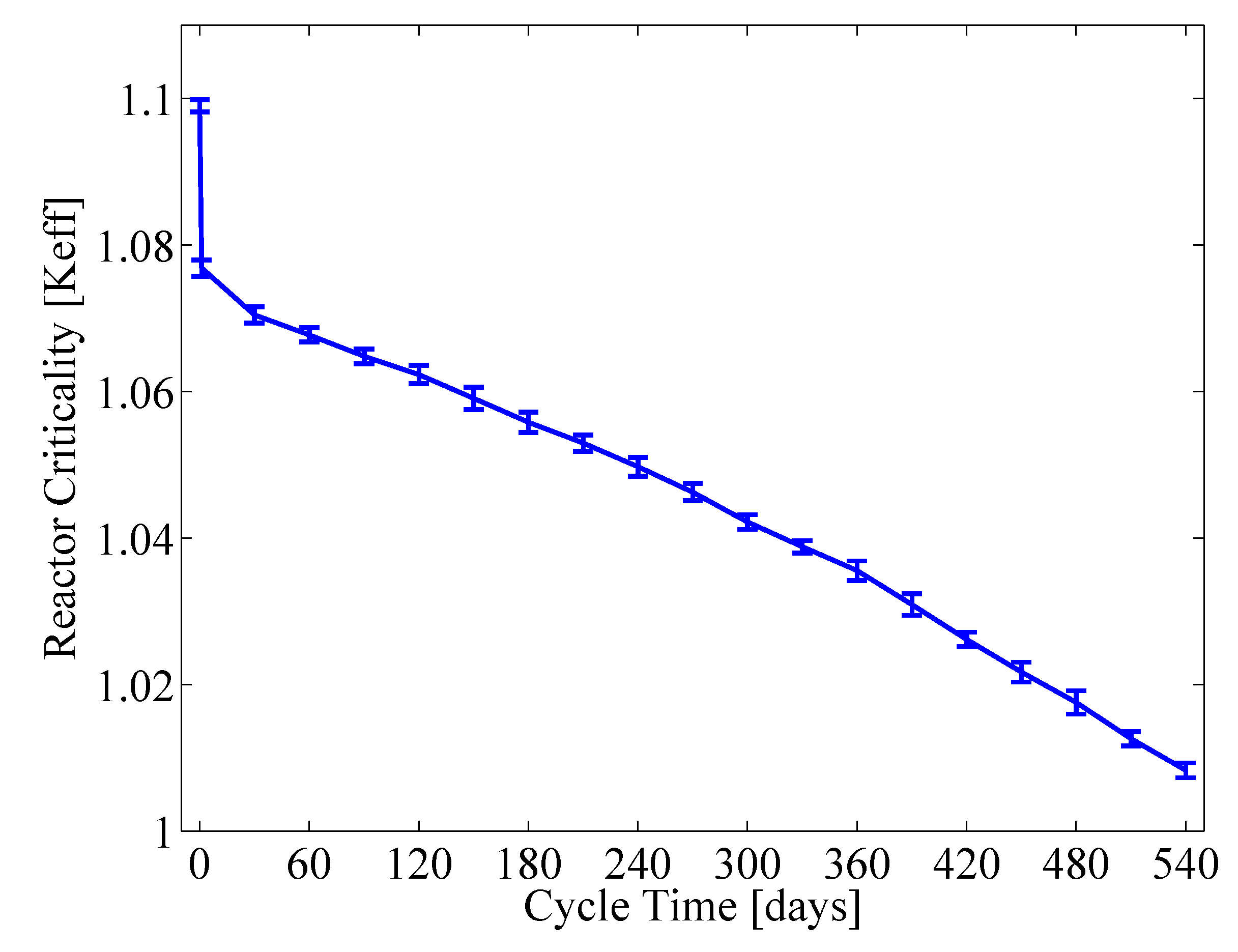
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Von Hippel, F.N. Energy—Plutonium and reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel. Science 2001, 293, 2397–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.; Hoffman, D.C.; Mtingwa, S.K.; Omberg, R.P.; Pillon, S.; Rempe, J.L. Report of Advanced Nuclear Transformation Technology Subcommittee of the Nuclear Energy Research Advisory Committee; Technical Reprot; Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Herring, J.S.; MacDonald, P.E.; Weaver, K.D. Thorium-based transmuter fuels for light water reactors. Nucl. Technol. 2004, 147, 84–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kasemeyer, U.; Hellwig, C.; Lebenhaft, J.; Chawla, R. Comparison of various partial light water reactor core loadings with inert matrix and mixed-oxide fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2003, 319, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.A.; Deinert, M.R.; Cady, K.B. Burnup simulations and spent fuel characteristics of ZrO2 based inert matrix fuels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 361, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulenko, J.S.; Wang, J.; Acosta, C. The Optimum Plutonium Inert Matrix Fuel Form for Reactor-Based Plutonium Disposition. In Proceedings of the ANES/SENA 2004 Symposium, American Nuclear Society, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 3–6 October 2004.
- Recktenwald, G.R.; Deinert, M.R. A cost probability analysis of reprocessing spent nuclear fuel in the us. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.A.; Deinert, M.R.; Cady, B. The cost impact of delaying the us spent nuclear fuel reprocessing facility. Energy Econ. 2009, 31, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.A.; Deinert, M.R.; Cady, K.B. Burnup Simulations of an Inert Matrix Fuel Using a Two Region, Multi-Group Reactor Physics Model, the Physics of Advanced Fuel Cycles. In Proceedings of PHYSOR 2006, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 September 2006.
- Herring, J.S.; MacDonald, P.E.; Weaver, K.D.; Kullberg, C. Low cost, proliferation resistant, uranium-thorium dioxide fuels for light water reactors. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2001, 203, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, C.; Cerrai, E. Buring Weapon-Grade in Ad Hoc Designed Reactors? In Proceedings of International Symposium on Conversion of Nuclear Warheads for Peaceful Purposes, Rome, Italy, 15–17 June 1992.
- Lombardi, C.; Mazzola, A. Exploiting the plutonium stockpiles in pwrs by using inert matrix fuel. Ann. Nucl. Energy 1996, 23, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Hellwig, C. Study of a zirconia based inert matrix fuel under irradiation. J. Nucl. Mater. 2003, 320, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, C.; Kasemeyer, U. Inert matrix fuel performance during the first two irradiation cycles in a test reactor: Comparison with modeling results. J. Nucl. Mater. 2003, 319, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, C.; Kasemeyer, U.; Ledergerber, G.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Chawla, R. Interpretation of experimental results from moderate-power in-pile testing of a pu-er-zr-oxide inert matrix fuel. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2003, 30, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, C.; Pouchon, M.; Restani, R.; Ingold, F.; Bart, G. Fabrication and microstructure characterization of inert matrix fuel based on yttria stabilized zirconia. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2005, 340, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, N.; Ait-Amar, H.; Taouinet, M.; Benazzouz, C.; Kamel, Z.; Fodil-Cherif, H.; Telmoune, S.; Slimani, R.; Zahri, A.; Sahel, D. Comparative study of simulated zirconia inert matrix fuel stabilized with yttrium, lanthanum or praseodymium: Synthesis and leaching tests. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2006, 48, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemeyer, U.; Paratte, J.M.; Grimm, P.; Chawla, R. Comparison of pressurized water reactor core characteristics for 100% plutonium-containing loadings. Nucl. Technol. 1998, 122, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Recktenwald, G.; Deinert, M.R. Actinide transmutation using with deep burn in an inert matrix fuel. Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 2010, 102, 145–146. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, E.A.; Deinert, M.R. A Practical Limit for Actinide Transmutation in Intert Matrix Fuels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Physics of Reactors 2008 PHYSOR, Interlaken, Switzerland, 14–19 September 2008.
- Medvedev, P.G.; Frank, S.M.; O’Holleran, T.P.; Meyer, M.K. Dual phase MgO-ZrO2 ceramics for use in lwr inert matrix fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 342, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.; Lemehov, S. Modelling heat capacity, thermal expansion, and thermal conductivity of dioxide components of inert matrix fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 352, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segrev, M. Use of axially graded burnable boron for hot-spot temperature reduction in a pressurized water reactor core. J. Nucl. Mater. 2000, 135, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- O’Leary, P.M.; Pitts, M.L. Effects of Burnable Absorbers on PWR Spent Nuclear Fuel. In Proceedings of Waste Management 2001 Conference, Tucson, AZ, USA, 25 Febuary–1 March 2001.
- The Westinghouse AP1000 Advanced Nuclear Plant; Westinghouse Electric Company LLC: Butler, PA, USA, 2003; p. 17.
- Pelowitz, D.B.; Durkee, J.W.; Elson, J.S.; Fensin, M.L.; James, M.R.; Johns, R.C.; McKinney, G.W.; Mashnik, S.G.; Wasters, L.S.; Wilcox, T.A.; et al. Mcnpx User's Manual Version 2.7.0; LA-CP-11-00438; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lamarsh, J.R. Introduction to Nuclear Engineering, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.G.; Carbajo, J.J.; Ivanov, V.K.; Yoder, G.L. Thermophysical Properties of Inert Matrix Fuels for Actinide Transmutation; Technical Report ORNL/TM-2000/351; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ronochi, C.; Ottaviani, J.P.; Degueldre, C.; Calabrese, R. Thermophysical properties of inert matrix fuels for actinide transmutation. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 320, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Power Plant Engineering Course Manual; United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission Technical Training Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. Available online: http://pbadupws.nrc.gov/docs/ML0230/ML023020604.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2013).
- Hellwig, C.; Streit, M.; Blair, P.; Tverberg, T.; Klaassen, F.C.; Schram, R.P.C.; Vettraino, F.; Yamashita, T. Inert matrix fuel behavior in test irradiations. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 352, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Recktenwald, G.; Deinert, M. Effect of Burnable Absorbers on Inert Matrix Fuel Performance and Transuranic Burnup in a Low Power Density Light-Water Reactor. Energies 2013, 6, 2291-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042291
Recktenwald G, Deinert M. Effect of Burnable Absorbers on Inert Matrix Fuel Performance and Transuranic Burnup in a Low Power Density Light-Water Reactor. Energies. 2013; 6(4):2291-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042291
Chicago/Turabian StyleRecktenwald, Geoff, and Mark Deinert. 2013. "Effect of Burnable Absorbers on Inert Matrix Fuel Performance and Transuranic Burnup in a Low Power Density Light-Water Reactor" Energies 6, no. 4: 2291-2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042291