Aspergillus Oxylipin Signaling and Quorum Sensing Pathways Depend on G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Oxylipins Exhibit Link to GPCR Signaling
2.1.1. Oxylipins Induce a cAMP Burst in Aspergillus nidulans
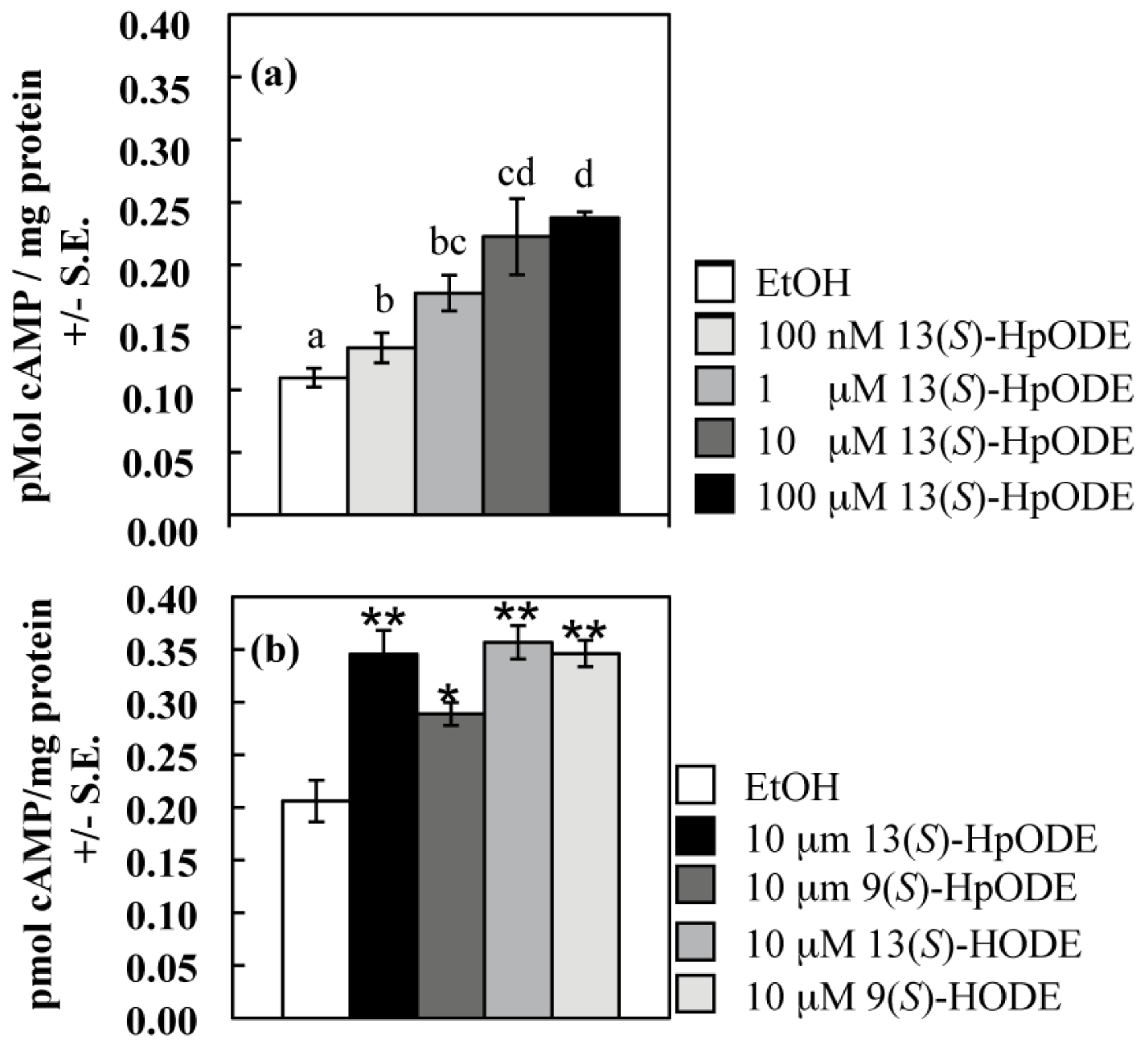
2.1.2. An A. nidulans ∆gprD Mutant Does Not Accumulate cAMP in Response to Oxylipins
| Species | Strain | Genotype | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. nidulans | RDIT9.32 | Wild type ( veA) | [19] |
| A. nidulans | RKIS1 | pabaA1; yA2; veA1 | [44] |
| A. nidulans | RKIS47.1 | pabaA1; yA2; ∆cyaA::pyrG; veA1 | [44] |
| A. nidulans | RDWC2.2 | ∆gprA::argB; veA | This study |
| A. nidulans | RDWC7.2 | ∆gprB::argB; veA | This study |
| A. nidulans | RDWC4.5 | ∆gprC::argB; veA | This study |
| A. nidulans | RDWC5.4 | ∆gprD::argB; veA | This study |
| A. nidulans | rJH12.9 | ∆gprE::argB; veA | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | rJH21.1 | ∆gprF::argB; veA | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | RDWC1.2 | ∆gprG::argB; veA | This study |
| A. nidulans | rJH34.12 | ∆gprH::argB; veA | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | rJH42.14 | ∆gprI::argB; veA | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | RDWC6.5 | ∆gprK::argB; veA | This study |
| A. nidulans | TJAR39 | yA2; pabaA1; ∆gprA::argB; argB2; veA1 | [49] |
| A. nidulans | TKH3.33 | metG1; biA1; ∆gprB::argB; argB2; veA1 | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | RKH68.8 | yA2; pabaA1; ∆gprC::argB; argB2; veA1 | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | RKH57.25 | biA1; ∆gprD::argB; argB2; veA1 | [50] |
| A. nidulans | RKH75.2 | yA2; metG1; pabaA1; biA1; ∆gprG::argB; veA1 | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. nidulans | TJAR13 | ∆gprK::argB; argB2; veA1 | J.-H. Yu, UW-Madison |
| A. flavus | NRRL3357 | Wild type | [51] |
| A. flavus | 3357-5 | pyrG- | [51] |
| A. flavus | TKJA10.1 | ∆gprC::pyrG; pyrG- | This study |
| A. flavus | TKJA8.1 | ∆gprD::pyrG; pyrG- | This study |
| A. flavus | TKJA14.2 | gprC; gprD IRT::pyrG; pyrG- | This study |
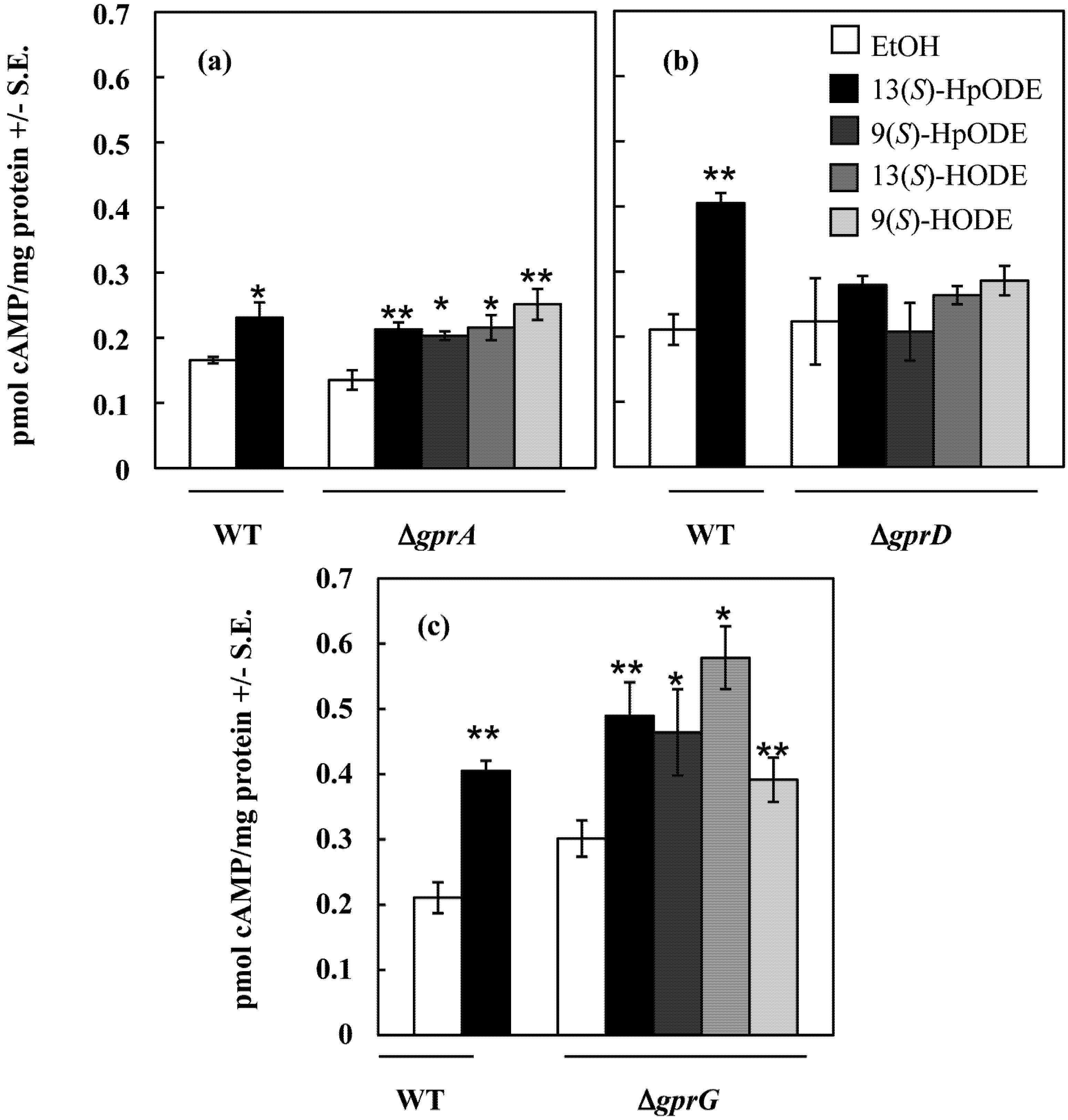
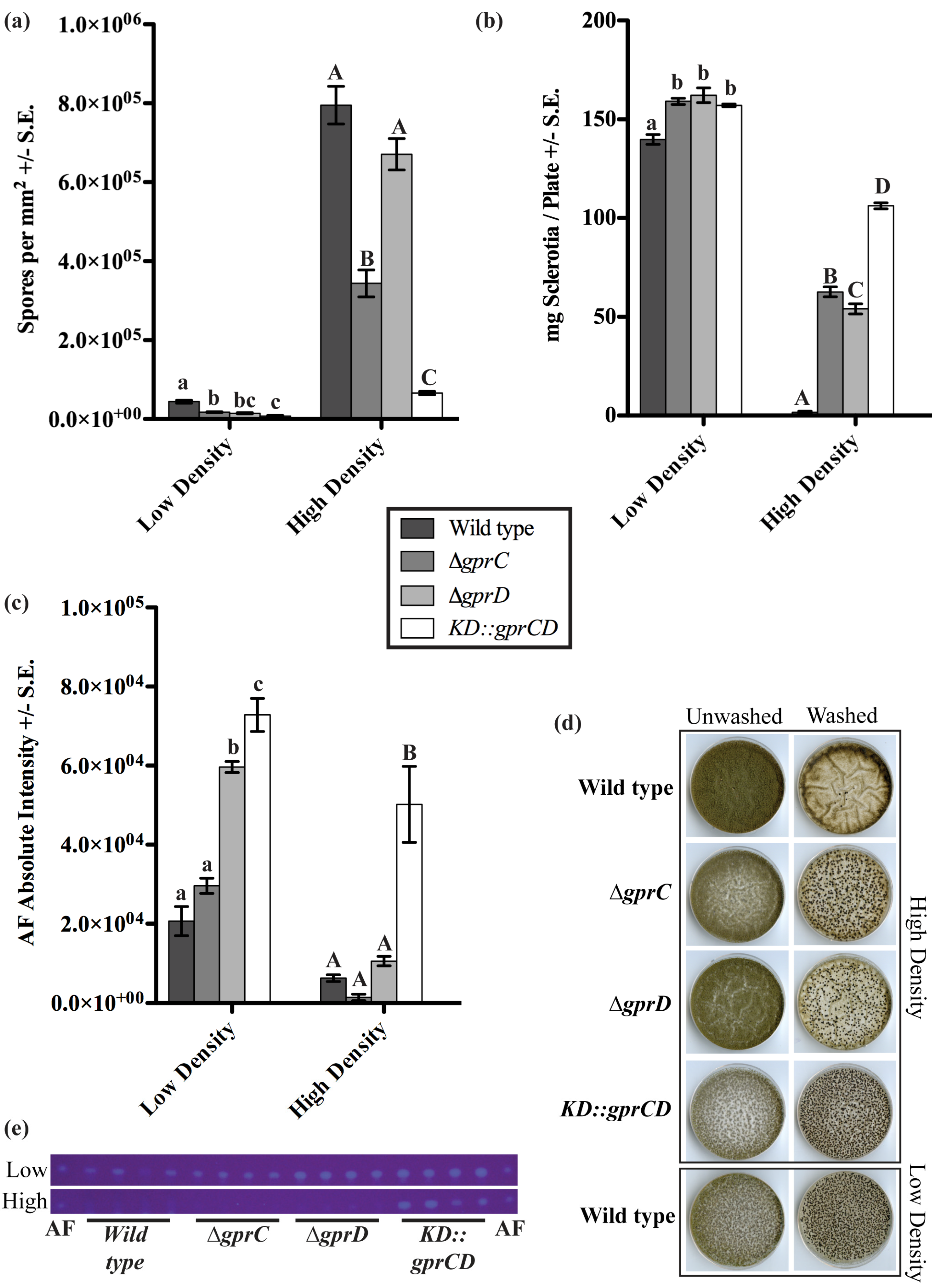
2.2. Putative GprD Homologues Are Involved in Density-Dependent Development in A. flavus
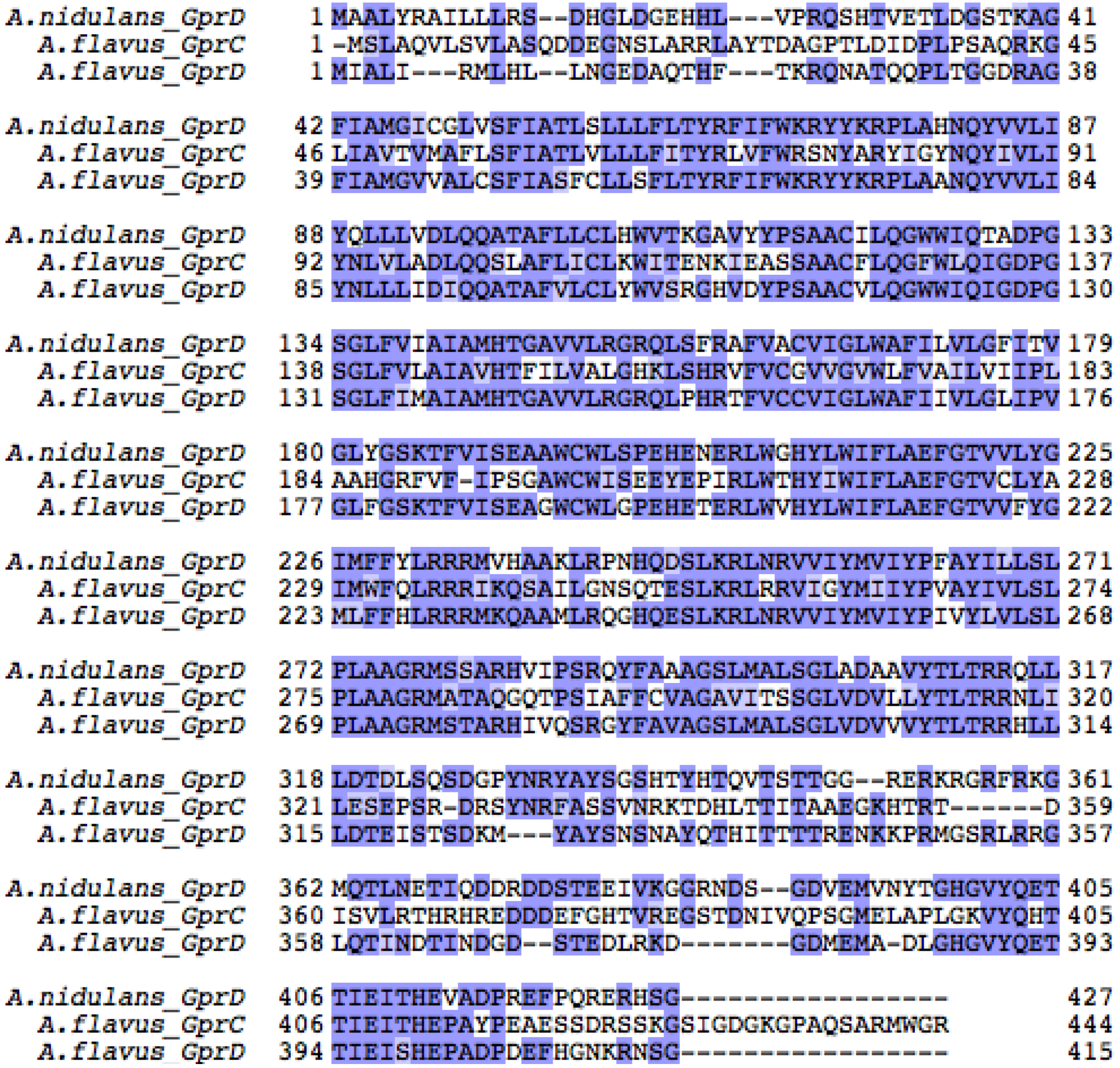
2.2.1. A. flavus Encodes Two Putative Homologues of A. nidulans GprD
2.2.2. gprC and gprD Mutants Exhibit Aberrant Density-Dependent Development
2.3. GprC and GprD Are Required for Proper Responses to Spent Media Extracts
2.3.1. High Density Extracts
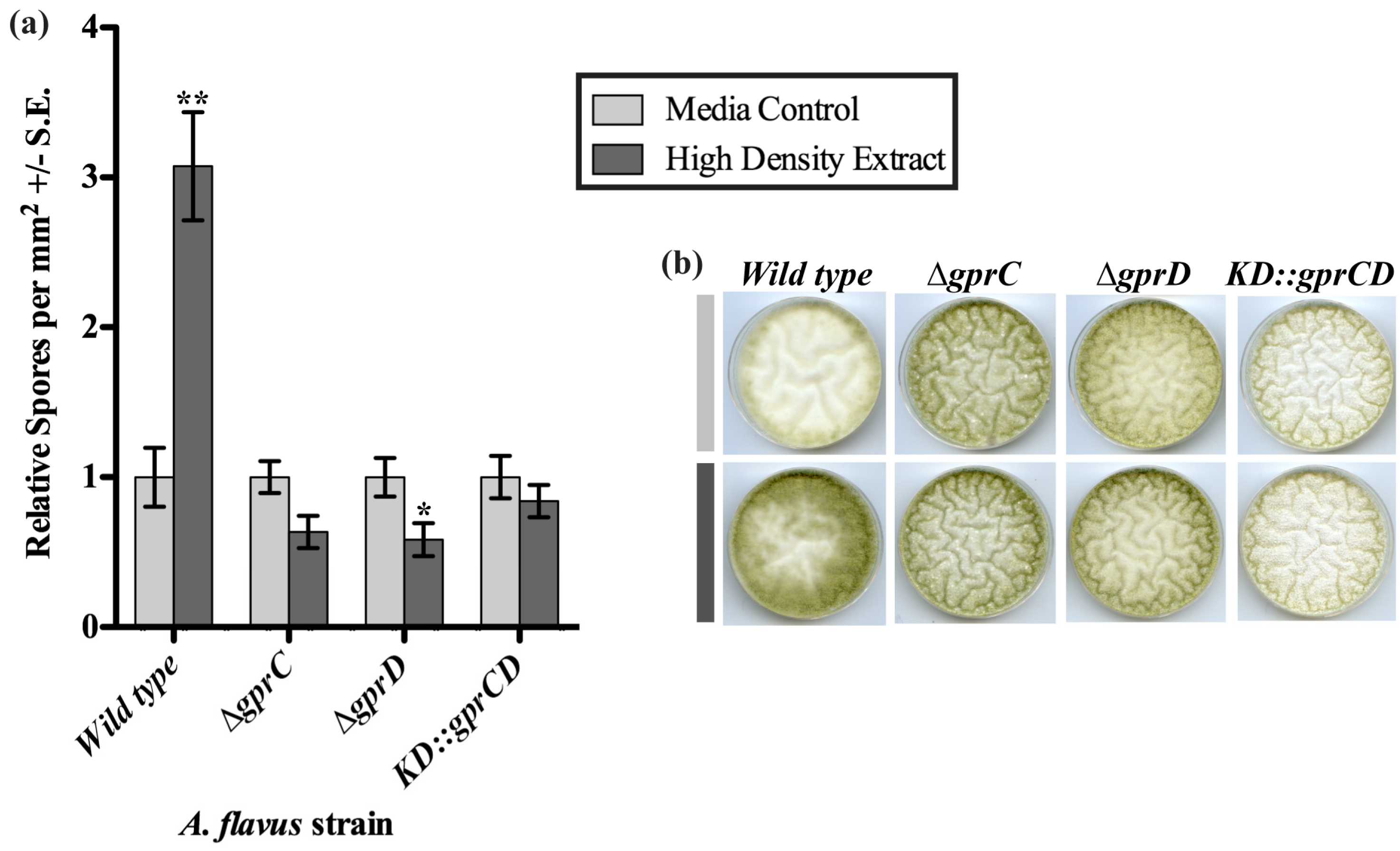
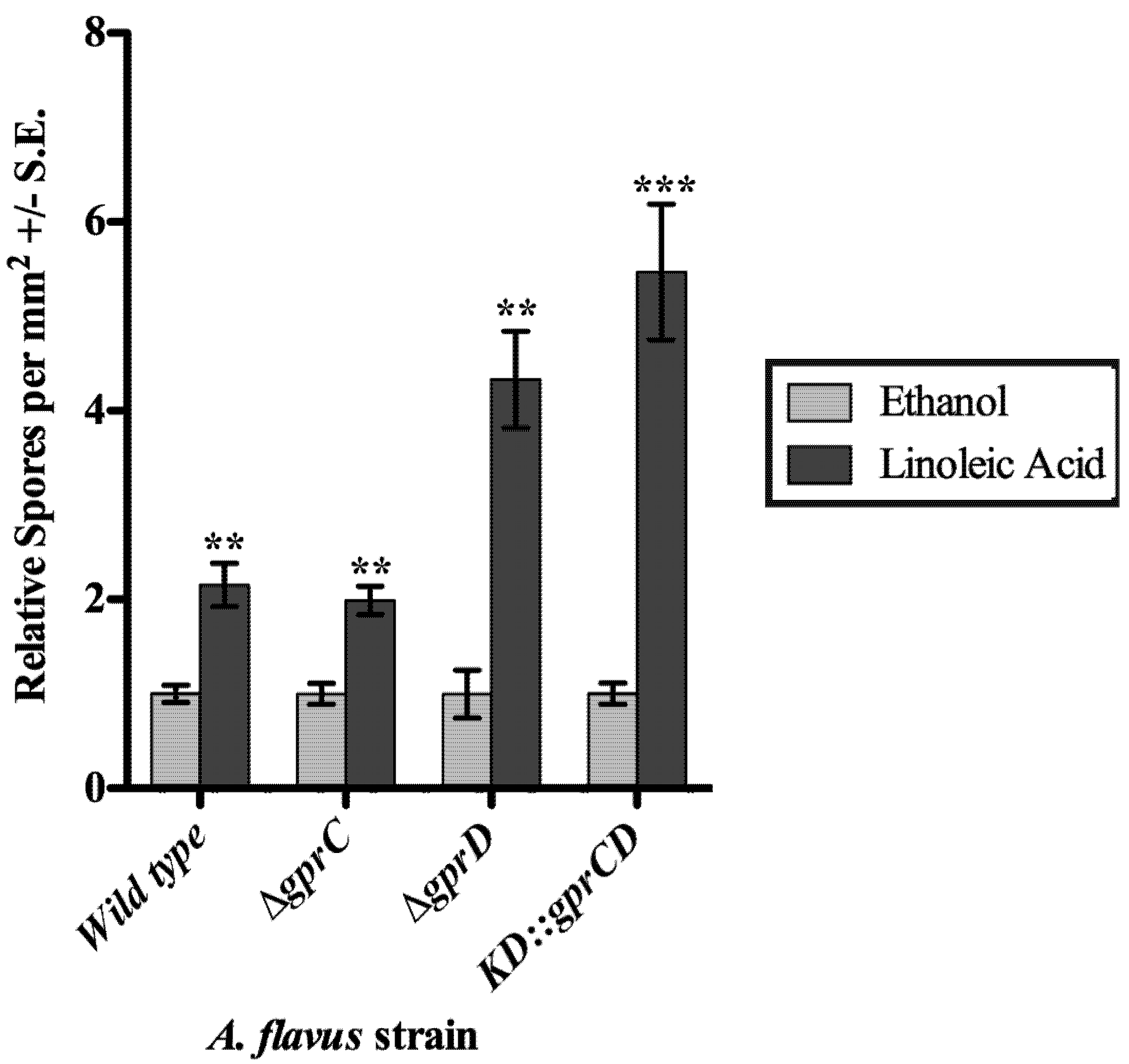
2.3.2. gprC and gprD Mutants Respond to Linoleic Acid
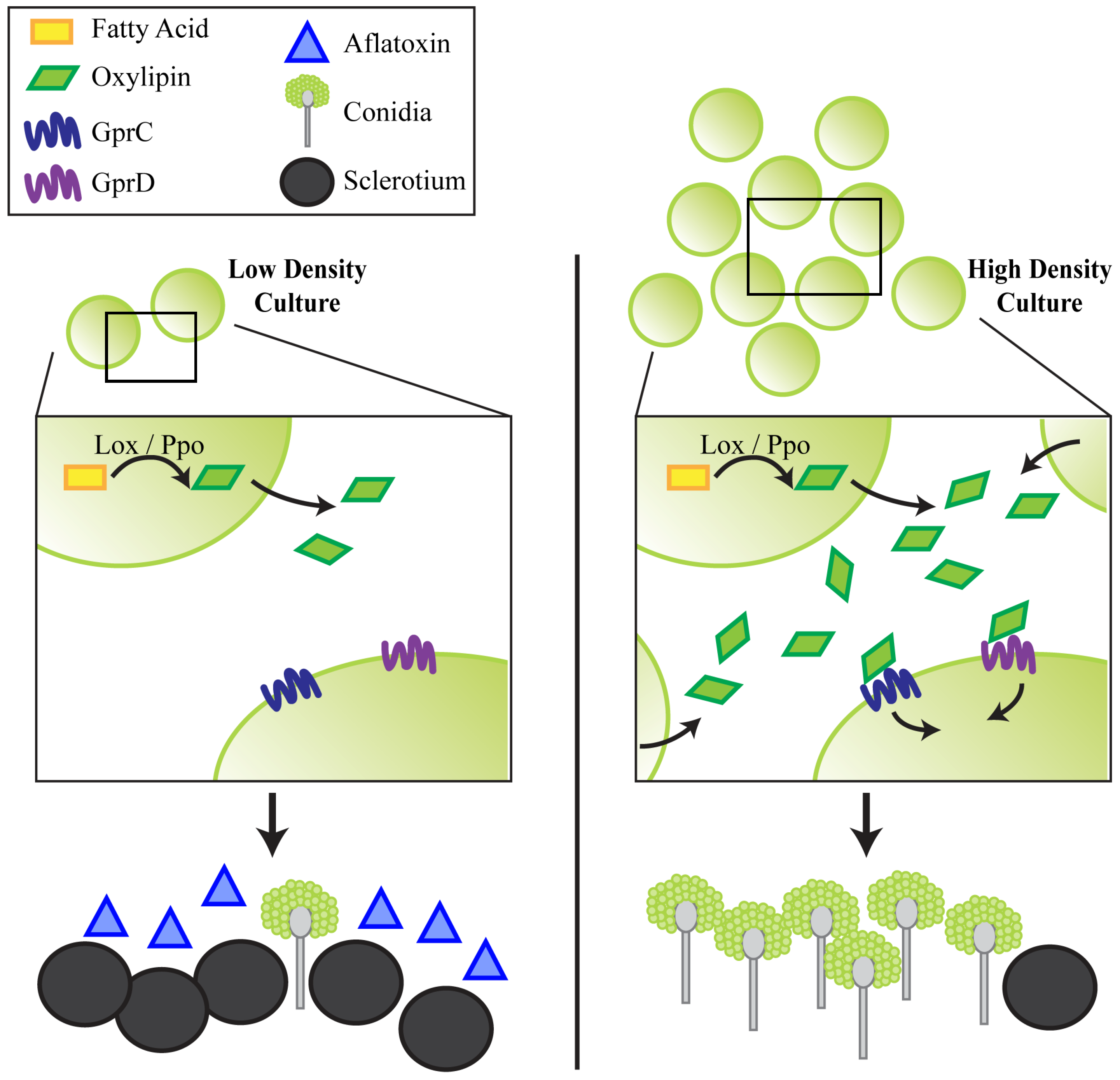
2.4. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Culture Conditions
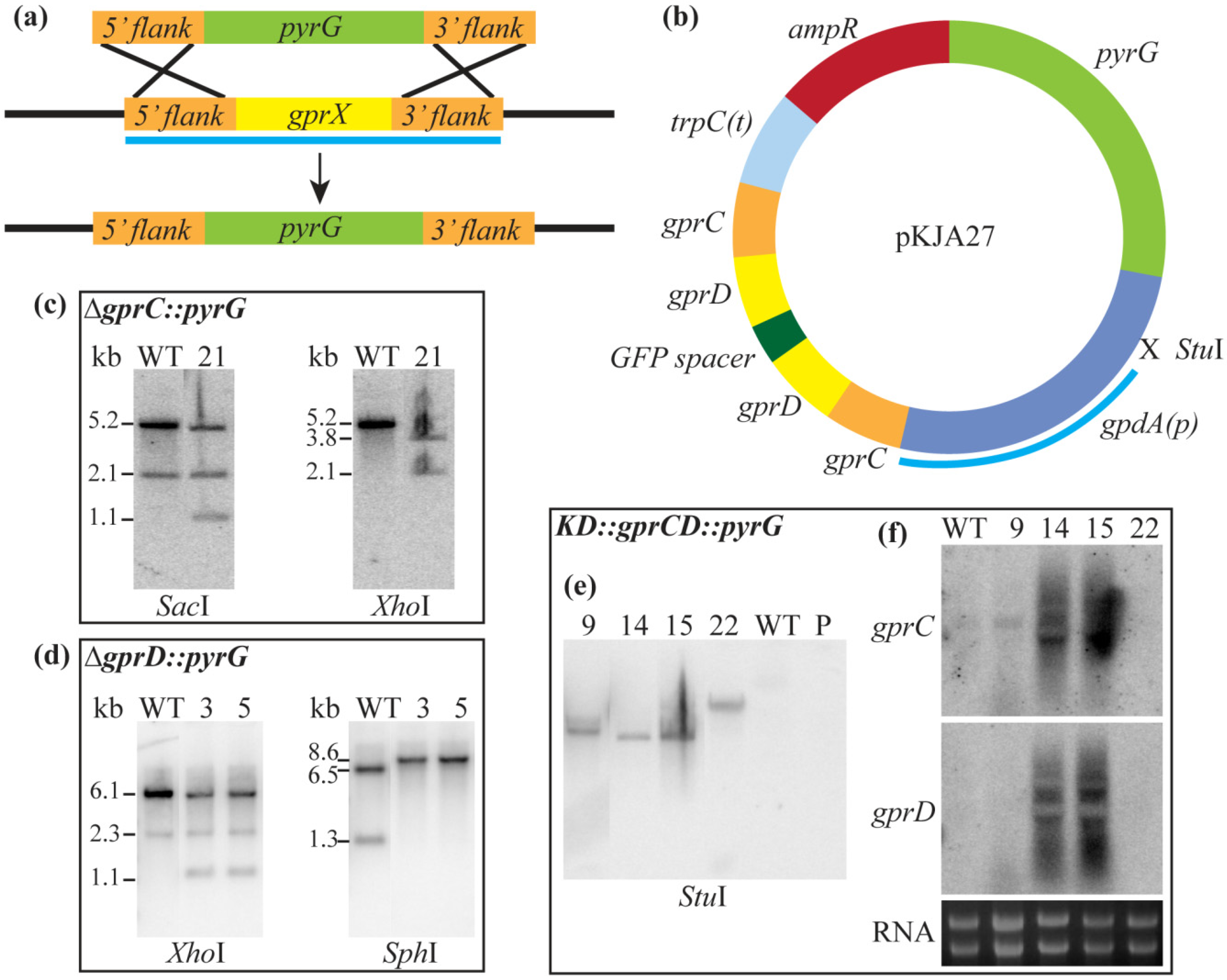
3.2. Strain Construction
| No. | Name | Sequence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | KS AflgprC 5'fk F | ttcctgcggcggttcattcc |
| 2 | KS AflgprC 5'fk+AfupyrG R | cgaagagggtgaagagcattgtttgaggcagtataagccagtcgtcgtgc |
| 3 | KS AfupyrG+AflgprC 3'fk F | gtgacgacaatacctcccgacgatacctggagtgaccggtcgagcaaagg |
| 4 | KS AflgprC 3'fk R | agcggttaagttctgtgtcc |
| 5 | KS Afl gprD 5'fk F | tcatatatccagtcccagtc |
| 6 | KS Afl gprD+AppyrG 5'fk R | ctcgggccatctgttcgtataagctttgttcatctcttgaggtgg |
| 7 | KS AppyrG+Afl gprD 3'fk F | agatccataggatcagcttatcgatgagtgtaccaggagactacg |
| 8 | KS Afl gprD 3'fk R | tgagacggatgtatggcttg |
| 9 | KS Ap pyrG pJMP7 F | agcttatacgaacagatggc |
| 10 | KS Ap pyrG pJMP7 R | tcgataagctgatcctatgg |
| 11 | KS Afu pyrG F | tgcctcaaacaatgctcttc |
| 12 | KS Afu pyrG R | ccaggtatcgtcgggaggt |
| 13 | KS H-N-AflgprD F | tataaagcttccatgggcttaatggtgaggatgctc |
| 14 | KS AflgprD-gprC R2 | catgatggcgtaaaggcagacagtcccgaatcctagcacgataatgaagg |
| 15 | KS AflgprD-gprC F2 | ggactatgggccttcattatcgtgctaggattcgggactgtctgcctttac |
| 16 | KS AflgprC-A-B R2 | tataggatccggcgcgccatcgtcgtcttcacggtgtc |
| 17 | KS AflgprD2 ck F | gcttgacctggaaactttgc |
| 18 | KS AflgprD2 ck R | gatgatacggagacagaatg |
| 19 | KS JP M13 F | gtaaaacgacggccagtg |
| 20 | KS JP M13 R | ggaaacagctatgaccatg |
| 21 | KS AflgprC int F | cctttaccttcagcccaacg |
| 22 | KS AflgprC int R | atcagtccgagtgtgcttgc |
| 23 | KS AflgprD int F | gcttaatggtgaggatgctc |
| 24 | KS AflgprD int R | tgcgttcgagttggagtaag |
3.3. cAMP Quantification
3.3.1. Culture Conditions
3.3.2. Treatment
3.3.3. Extraction
3.3.4. Quantification of cAMP
3.3.5. Protein Quantification
3.4. Oxylipins and Fatty Acids
3.5. Density-Dependent Physiology
3.6. Spent Media Bioassay
3.6.1. Extract Collection
3.6.2. Bioassay
3.7. Linoleic Acid Disk Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary

Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Squire, R.A. Ranking animal carcinogens: A proposed regulatory approach. Science 1981, 214, 877–880. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, M. p53 mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma after aflatoxin exposure. Lancet 1991, 338, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouas, D.; Shi, H.; Hainaut, P. The aflatoxin-induced TP53 mutation at codon 249 (R249S): Biomarker of exposure, early detection and target for therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009, 286, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cleveland, T.E.; Nierman, W.C.; Bennett, J.W. Aspergillus flavus genomics: Gateway to human and animal health, food safety, and crop resistance to disease. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2005, 22, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.; Onsongo, M.; Njapau, H.; Schurz-Rogers, H.; Luber, G.; Kieszak, S.; Nyamongo, J.; Backer, L.; Dahiye, A.M.; Misore, A.; et al. Aflatoxin contamination of commercial maize products during an outbreak of acute aflatoxicosis in eastern and central Kenya. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, J.A. Mast cells and eicosanoid mediators: A system of reciprocal paracrine and autocrine regulation. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 217, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affeldt, K.J.; Keller, N.P. Oxylipins in Fungal-Mammalian. Interactions. In Biocommunications of Fungi; Witzany, G., Ed.; Springer: Houten, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, S.A.; Kolomiets, M.V. The lipid language of plant-fungal interactions. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Morcillo, R.J.; Angel, J.; Martín-Rodríguez; Vierheilig, H.; Ocampo, J.A.; García-Garrido, J.M. Late activation of the 9-oxylipin pathway during arbuscular mycorrhiza formation in tomato and its regulation by jasmonate signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3545–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Kunze, S.; Willis, D.K.; Feussner, I.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus infection inhibits the expression of peanut 13S-HPODE-forming seed lipoxygenases. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2005, 18, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Keller, N.P. Oxylipins act as determinants of natural product biosynthesis and seed colonization in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodhagen, M.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Hornung, E.; Goebel, C.; Feussner, I.; Keller, N.P. Reciprocal oxylipin-mediated cross-talk in the Aspergillus-seed pathosystem. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 378–391. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Brodhagen, M.; Isakeit, T.; Brown, S.H.; Göbel, C.; Betran, J.; Feussner, I.; Keller, N.P.; Kolomiets, M.V. Inactivation of the lipoxygenase ZmLOX3 increases susceptibility of maize to Aspergillus spp. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2009, 22, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.C.; Ogg, C.; Nickerson, K.W. Lipoxygenase inhibitors shift the yeast/mycelium dimorphism in Ceratocystis ulmi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Keller, N.P. Oxylipins as developmental and host-fungal communication signals. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz Brown, S.; Zarnowski, R.; Sharpee, W.C.; Keller, N.P. Morphological transitions governed by density dependence and lipoxygenase activity in Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.H.; Scott, J.B.; Bhaheetharan, J.; Sharpee, W.C.; Milde, L.; Wilson, R.A.; Keller, N.P. Oxygenase coordination is required for morphological transition and the host-fungus interaction of Aspergillus flavus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2009, 22, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodhun, F.; Feussner, I. Oxylipins in fungi. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. The lipid body protein, PpoA, coordinates sexual and asexual sporulation in Aspergillus nidulan. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11344–11353. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Kowieski, T.M.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. Endogenous lipogenic regulators of spore balance in Aspergillus nidulans. Euk. Cell 2004, 3, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Kowieski, T.M.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. Three putative oxylipin biosynthetic genes integrate sexual and asexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Bok, J.-W.; Andes, D.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frisvad, J.C.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus cyclooxygenase-like enzymes are associated with prostaglandin production and virulence. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 4548–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, T.R.T.; Chung, D.; Giles, S.S.; Hull, C.M.; Andes, D.; Keller, N.P. Defects in conidiophore development and conidium-macrophage interactions in a dioxygenase mutant of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, L.M.; Ovchinnikova, E.S.; Meijler, M.M.; Krom, B.P. Microbial spy games and host response: Roles of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa small molecule in communication with other species. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.; Casadevall, A. Quorum sensing in fungi—A review. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; del Poeta, M. Lipid signalling in pathogenic fungi. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Garcia, E.; Garzia, A.; Cordobés, S.; Espeso, E.A.; Ugalde, U. 8-Carbon oxylipins inhibit germination and growth, and stimulate aerial conidiation in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burow, G.B.; Nesbitt, T.C.; Dunlap, J.; Keller, N.P. Seed lipoxygenase products modulate Aspergillus mycotoxin biosynthesis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1997, 10, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, A.M.; Hinze, L.L.; Gardner, H.W.; Keller, N.P. Sporogenic effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on development of Aspergillus spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3668–3673. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciotti, E.; Fitzgerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Gupta, S.; Dastidar, S.; Ray, A. Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors: Molecular and functional characteristics. Pharmacology 2010, 85, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folcik, V.A.; Cathcart, M.K. Predominance of esterified hydroperoxy-linoleic acid in human monocyte-oxidized LDL. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn, H. Biosynthesis, metabolization and biological importance of the primary 15-lipoxygenase metabolites 15-hydro(pero)xy-5Z,8Z,11Z,13E-eicosatetraenoic acid and 13-hydro(pero)xy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid. Prog. Lipid Res. 1996, 35, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Obinata, H.; Ogawa, A.; Kishi, M.; Tatei, K.; Ishikawa, O.; Izumi, T. G2A plays proinflammatory roles in human keratinocytes under oxidative stress as a receptor for 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2007, 128, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Obinata, H.; Hattori, T.; Nakane, S.; Tatei, K.; Izumi, T. Identification of 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid and other oxidized free fatty acids as ligands of the G protein-coupled receptor G2A. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40676–40683. [Google Scholar]
- Obinata, H.; Izumi, T. G2A as a receptor for oxidized free fatty acids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009, 89, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.D.; Thon, M.R.; Pan, H.; Dean, R.A. Novel G-protein-coupled receptor-like proteins in the plant pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafon, A.; Han, K.-H.; Seo, J.-A.; Yu, J.-H.; d’Enfert, C. G-protein and cAMP-mediated signaling in aspergilli: A genomic perspective. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2006, 43, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhou, L.; Dou, T.; Han, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhan, X.; Tang, C.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q. Genome-wide prediction of G protein-coupled receptors in Verticillium spp. Fungal Biol 2010, 114, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wright, S.J.; Krystofova, S.; Park, G.; Borkovich, K.A. Heterotrimeric G protein signaling in filamentous fungi. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 423–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Hsueh, Y.; Heitman, J. Magnificent seven: Roles of G protein-coupled receptors in extracellular sensing in fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 1010–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Keller, N.P. Genetic involvement of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase in a G protein signaling pathway regulating morphological and chemical transitions in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 2001, 157, 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K.; Hicks, J.K.; Huang, T.-P.; Keller, N.P. Pka, Ras and RGS protein interactions regulate activity of AflR, a Zn(II)2Cys6 transcription factor in Aspergillus nidulan. Genetics 2003, 165, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Fillinger, S.; Chaveroche, M.-K.; Shimizu, K.; Keller, N.; d’Enfert, C. cAMP and ras signalling independently control spore germination in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roze, L.V.; Beaudry, R.M.; Keller, N.P.; Linz, J.E. Regulation of aflatoxin synthesis by FadA/cAMP/protein kinase A signaling in Aspergillus parasiticus. Mycopathologia 2004, 158, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, A.; Seo, J.-A.; Han, K.-H.; Yu, J.-H.; d’Enfert, C. The heterotrimeric G-protein GanB(α)-SfaD(β)-GpgA(γ) is a carbon source sensor involved in early cAMP-dependent germination in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 2005, 171, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liavonchanka, A.; Feussner, I. Lipoxygenases: Occurrence, functions and catalysis. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 163, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.; Heydeck, D.; Hofheinz, K.; Roffeis, J.; O’Donnell, V.B.; Kuhn, H.; Walther, M. Molecular enzymology of lipoxygenases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 503, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-A.; Han, K.-H.; Yu, J.-H. The gprA and gprB genes encode putative G protein-coupled receptors required for self-fertilization in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Seo, J.; Yu, J. A putative G protein-coupled receptor negatively controls sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-M.; Price, M.S.; Obrian, G.R.; Georgianna, D.R.; Payne, G.A. Improved protocols for functional analysis in the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus flavus. BMC Microbiol 2007, 7. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, T.; Brown, D.; Keller, N.P.; Hammond, T.M. RNA silencing of mycotoxin production in Aspergillus and Fusarium species. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2005, 18, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, E.; Nayak, T.; Oakley, C.E.; Edgerton, H.; Xiong, Y.; Taheri-Talesh, N.; Osmani, S.A.; Oakley, B.R.; Oakley, B. Fusion PCR and gene targeting in Aspergillus nidulans. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar]
- Drews, J. Drug discovery: A historical perspective. Science 2000, 287, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goujon, M.; McWilliam, H.; Li, W.; Valentin, F.; Squizzato, S.; Paern, J.; Lopez, R. A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W695–W699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Clamp, M.; Cuff, J.; Searle, S.M.; Barton, G.J. The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Affeldt, K.J.; Brodhagen, M.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus Oxylipin Signaling and Quorum Sensing Pathways Depend on G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Toxins 2012, 4, 695-717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4090695
Affeldt KJ, Brodhagen M, Keller NP. Aspergillus Oxylipin Signaling and Quorum Sensing Pathways Depend on G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Toxins. 2012; 4(9):695-717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4090695
Chicago/Turabian StyleAffeldt, Katharyn J., Marion Brodhagen, and Nancy P. Keller. 2012. "Aspergillus Oxylipin Signaling and Quorum Sensing Pathways Depend on G Protein-Coupled Receptors" Toxins 4, no. 9: 695-717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4090695






