EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients
Abstract
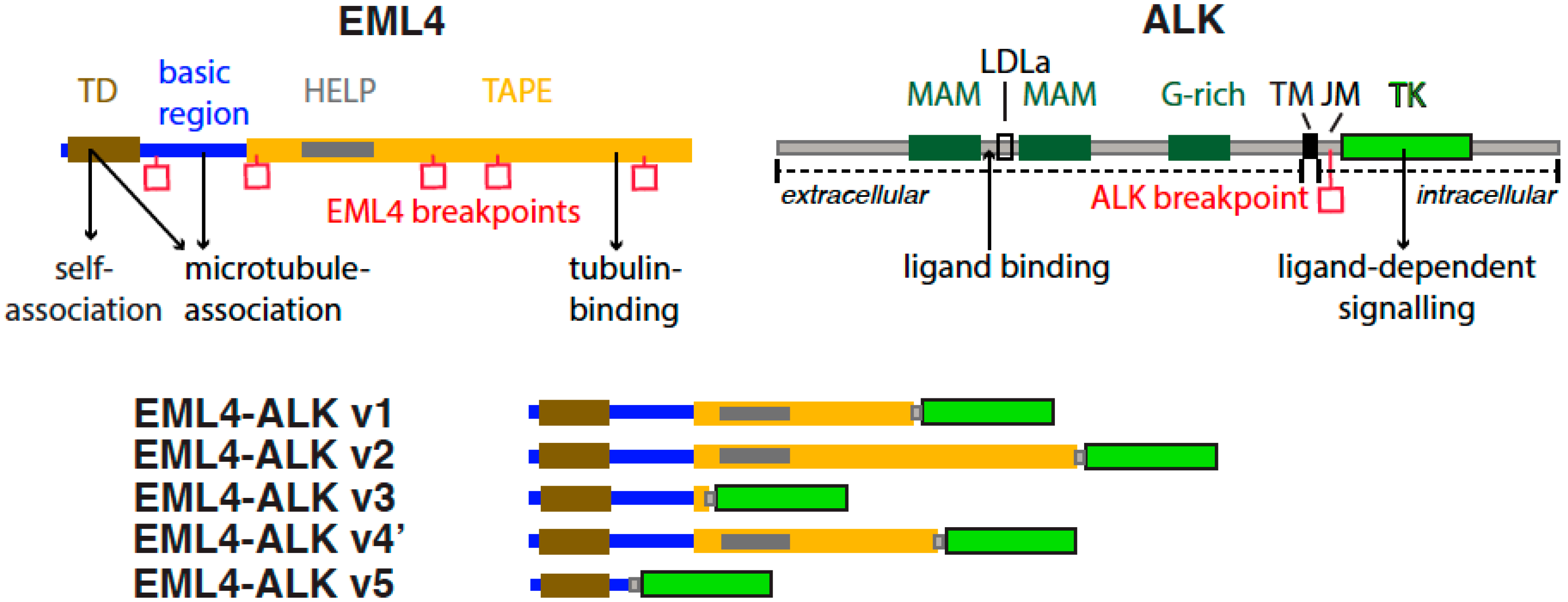
:1. Introduction
2. Human EML Family and EML4
3. EML4-ALK
4. EML4-ALK Variants
4.1. Frequency
4.2. Structure, Stability and Sensitivity
4.3. Localisation and Microtubule Binding
5. Signalling Pathways
6. In the Clinic
6.1. ALK Inhibitors
6.2. Hsp90 Inhibitors
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thun, M.J.; DeLancey, J.O.; Center, M.M.; Jemal, A.; Ward, E.M. The global burden of cancer: Priorities for prevention. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Research UK. Lung Cancer Statistics. Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/lung-cancer (accessed on 28 July 2017).
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crino, L.; Ahn, M.J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Shaw, A.T.; Khan, T.M.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Solomon, B.J.; Halmos, B.; Jessop, N.A.; Wain, J.C.; Yeo, A.T.; Benes, C.; et al. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 120ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprenant, K.A.; Dean, K.; McKee, J.; Hake, S. EMAP, an echinoderm microtubule-associated protein found in microtubule-ribosome complexes. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suprenant, K.A.; Tuxhorn, J.A.; Daggett, M.A.; Ahrens, D.P.; Hostetler, A.; Palange, J.M.; VanWinkle, C.E.; Livingston, B.T. Conservation of the WD-repeat, microtubule-binding protein, EMAP, in sea urchins, humans, and the nematode C. elegans. Dev. Genes Evol. 2000, 210, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenmuller, B.; Everley, P.; Palange, J.; Lepley, D.; Suprenant, K.A. The human EMAP-like protein-70 (ELP70) is a microtubule destabilizer that localizes to the mitotic apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulinski, J.C.; Borisy, G.G. Self-assembly of microtubules in extracts of cultured hela-cells and the identification of hela microtubule-associated proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidebrecht, H.J.; Buck, F.; Pollmann, M.; Siebert, R.; Parwaresch, R. Cloning and localization of C2orf2(ropp120), a previously unknown WD repeat protein. Genomics 2000, 68, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.W.; Law, E.W.; Rennalls, L.P.; Busacca, S.; O’Regan, L.; Fry, A.M.; Fennell, D.A.; Bayliss, R. Crystal structure of EML1 reveals the basis for Hsp90 dependence of oncogenic EML4-ALK by disruption of an atypical beta-propeller domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.W.; O’Regan, L.; Roth, D.; Montgomery, J.M.; Straube, A.; Fry, A.M.; Bayliss, R. Microtubule association of EML proteins and the EML4-ALK variant 3 oncoprotein require an N-terminal trimerization domain. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, A.M.; O’Regan, L.; Montgomery, J.; Adib, R.; Bayliss, R. EML proteins in microtubule regulation and human disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Costa, D.B.; Heist, R.S.; Solomon, B.; Stubbs, H.; Admane, S.; McDermott, U.; et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4247–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Takada, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Ueno, T.; Haruta, H.; Hamada, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; et al. A mouse model for EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19893–19897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, E.L.; Bang, Y.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.; Maki, R.G.; Ou, S.H.I.; Dezube, B.J.; Janne, P.A.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, H.R.; Li, H.R.; Bruey, J.M.; Scheerle, J.A.; Meloni-Ehrig, A.M.; Kelly, J.C.; Novick, C.; Albitar, M. Exon scanning by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for detection of known and novel EML4-ALK fusion variants in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Li, L.; Guan, Y.; Soriano, R.; Rivers, C.S.; Mohan, S.; Pandita, A.; Tang, J.; Modrusan, Z. Exon array profiling detects EML4-ALK fusion in breast, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.L.; Takeuchi, K.; Soda, M.; Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Enomoto, M.; Hamada, T.; Haruta, H.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Identification of novel isoforms of the EML4-ALK transforming gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4971–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Soda, M.; Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Satoh, Y.; et al. Multiplex reverse transcription-PCR screening for EML4-ALK fusion transcripts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6618–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.; Pao, W. EML4-ALK: Honing in on a new target in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4232–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Togashi, Y.; Soda, M.; Hatano, S.; Inamura, K.; Takada, S.; Ueno, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Satoh, Y.; et al. KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Rodig, S.J.; Chirieac, L.R.; Janne, P.A. The biology and treatment of EML4-ALK non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuckmann, J.M.; Balke-Want, H.; Malchers, F.; Peifer, M.; Sos, M.L.; Koker, M.; Meder, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Pao, W.; et al. Differential protein stability and ALK inhibitor sensitivity of EML4-ALK fusion variants. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4682–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Isobe, K.; Inoue, A.; Maemondo, M.; Oizumi, S.; Fujita, Y.; Gemma, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Ueno, T.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. A prospective PCR-based screening for the EML4-ALK oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5682–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.L.; Soda, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Ueno, T.; Takashima, J.; Nakajima, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Hamada, T.; Haruta, H.; et al. EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, C.G.; Seo, S.; Kim, S.W.; Jang, S.J.; Park, K.S.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, B.; Richards, M.W.; Bayliss, R.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Differential protein stability and clinical responses of EML4-ALK fusion variants to various ALK inhibitors in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunen, J.P.; Mermel, C.; Zejnullahu, K.; Murphy, C.; Lifshits, E.; Holmes, A.J.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.; Chiang, D.; Thomas, R.; et al. EML4-ALK fusion gene and efficacy of an ALK kinase inhibitor in lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4275–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. The role of the ALK receptor in cancer biology. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, iii4–iii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Scarborough, H.; Kim, J.; Rozhok, A.I.; Chen, Y.A.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Bai, Y.; Fang, B.; Liu, R.Z.; et al. Coupling an EML4-ALK-centric interactome with RNA interference identifies sensitizers to ALK inhibitors. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, rs12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Khan, T.M.; Benes, C.; Lifshits, E.; Ebi, H.; Rivera, V.M.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Iafrate, A.J.; Engelman, J.A.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic strategies to overcome crizotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancers harboring the fusion oncogene EML4-ALK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7535–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ma, S. Recent development in the discovery of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 590–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Zhou, C.; Shreeve, S.M.; Selaru, P.; Polli, A.; et al. Clinical experience with crizotinib in patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Bang, Y.J.; Kwak, E.L.; Iafrate, A.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Fox, S.B.; Riely, G.J.; Solomon, B.; Ou, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated results from a phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Gainor, J.; Engelman, J.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; Ou, S.H.; Butaney, M.; et al. Effect of crizotinib on overall survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring ALK gene rearrangement: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.; Shepherd, F.A.; Fossella, F.V.; Pereira, J.R.; De Marinis, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gatzemeier, U.; Tsao, T.C.; Pless, M.; Muller, T.; et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.J.; Kim, H.R.; Shim, H.S. Clinical outcomes in ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas according to ALK fusion variants. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Oya, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Shimizu, J.; Horio, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Sakao, Y.; Hida, T.; Yatabe, Y. Differential crizotinib response duration among ALK fusion variants in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhong, W.Z.; Zhou, Q.; Tu, H.Y.; Tian, H.X.; Guo, W.B.; Yang, L.L.; Yan, H.H.; et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase variants and the percentage of ALK-positive tumor cells and the efficacy of crizotinib in advanced NSCLC. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Gettinger, S.; Senzer, N.N.; Martins, R.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lilenbaum, R.; Gray, J.E.; Iafrate, A.J.; Katayama, R.; Hafeez, N.; et al. Activity of IPI-504, a novel heat-shock protein 90 inhibitor, in patients with molecularly defined non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| EML4-ALK Variant | Gene Fusion Points | Frequency | TAPE Domain | Inhibitor Sensitivity | Localisation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant 1 | E13; A20 | 33% | Partial TAPE | ALK- mid HSP90- high | Cytoplasm | [7,15,27,28] |
| Variant 2 | E20; A20 | 10% | Partial TAPE | ALK- high HSP90- high | Cytoplasm | [7,15,27,28] |
| Variant 3a/b | E6a; A20 | 29% | No TAPE | ALK- low HSP90- low | Microtubules, cytoplasm and nucleus | [15,27,28] |
| Variant 4’ | E14; ins11del49A20 | 3% | Partial TAPE | Not known | Not known | [24,27] |
| Variant 5a | E2; A20 | 2% | No TAPE | ALK- low HSP90- low | Cytoplasm | [15,24,27] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabir, S.R.; Yeoh, S.; Jackson, G.; Bayliss, R. EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients. Cancers 2017, 9, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090118
Sabir SR, Yeoh S, Jackson G, Bayliss R. EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients. Cancers. 2017; 9(9):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090118
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabir, Sarah R., Sharon Yeoh, George Jackson, and Richard Bayliss. 2017. "EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients" Cancers 9, no. 9: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090118
APA StyleSabir, S. R., Yeoh, S., Jackson, G., & Bayliss, R. (2017). EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients. Cancers, 9(9), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090118






