Macroautophagy and Cell Responses Related to Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Lipid Metabolism and Unconventional Secretion of Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Autophagy and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
2.1. Molecular Effectors and Mechanisms of Regulation Involved in Mitophagy
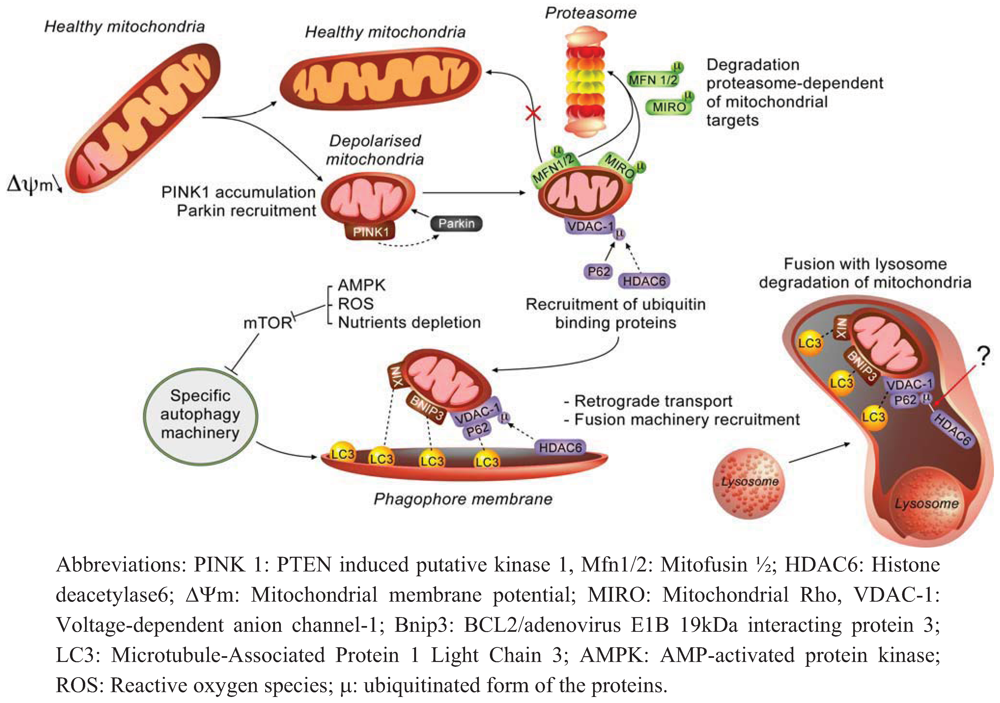
2.2. How does Autophagy Preserve Mitochondria Activity?
2.3. How do Mitochondria Contribute to Autophagy Regulation?
3. Autophagy, Lipid Metabolism and Lipophagy
3.1. Autophagy and Lipids

3.2. Lipids and Autophagy
3.3. Autophagy and Lipid Metabolism Disorders
4. Autophagy and Unconventional Protein Secretion
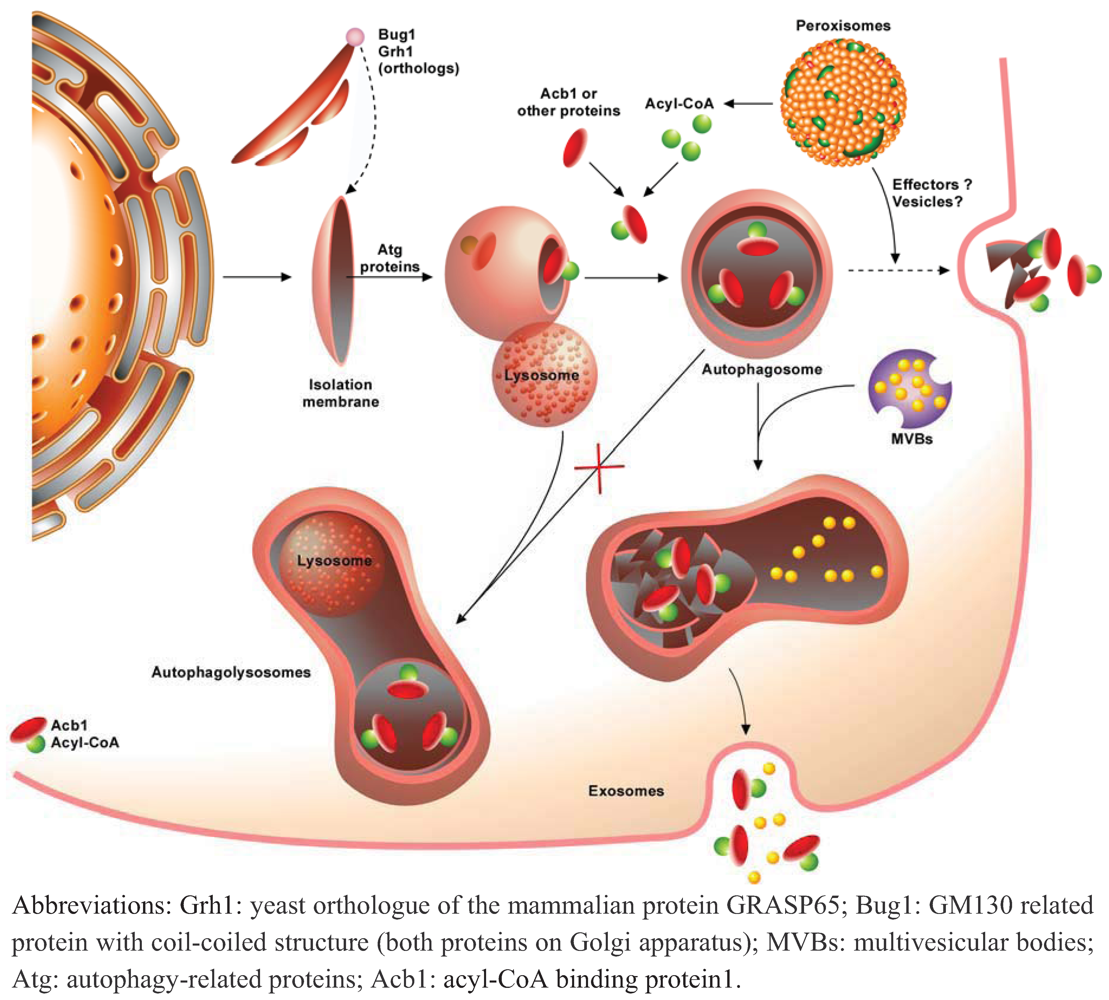
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Li, W.W.; Li, J.; Bao, J.K. Microautophagy: Lesser-known self-eating. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein, S.J.; Cuervo, A.M. Chaperone-mediated autophagy: Molecular mechanisms and physiological relevance. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Peterson, T.R.; Laplante, M.; Oh, S.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 controls fasting-induced ketogenesis and its modulation by ageing. Nature 2010, 468, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Peterson, T.R.; Sabatini, D.M. Regulation of the mTOR complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factors, and stress. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Brumell, J.H.; Chu, C.T.; Codogno, P.; Cuervo, A.M.; Debnath, J.; Deretic, V.; Elazar, Z.; Eskelinen, E.L.; et al. A comprehensive glossary of autophagy-related molecules and processes (2nd edition). Autophagy 2011, 7, 1273–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijaljica, D.; Prescott, M.; Devenish, R.J. The intriguing life of autophagosomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3618–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, B.; Sarkar, S.; Davies, J.E.; Futter, M.; Garcia-Arencibia, M.; Green-Thompson, Z.W.; Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Korolchuk, V.I.; Lichtenberg, M.; Luo, S.; et al. Regulation of mammalian autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1383–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanida, I. Autophagosome formation and molecular mechanism of autophagy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2201–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B. Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2010, 12, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Mizushima, N.; Virgin, H.W. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 2011, 469, 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy and innate immunity ally against bacterial invasion. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3213–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, D.; Nicolson, S.; Kumar, S. Cell death by autophagy: Facts and apparent artefacts. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Kepp, O.; Michaud, M.; Martins, I.; Minoux, H.; Metivier, D.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, R.T.; Kroemer, G. Association and dissociation of autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis by systematic chemical study. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4544–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notte, A.; Leclere, L.; Michiels, C. Autophagy as a mediator of chemotherapy-induced cell death in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Wirawan, E.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Lippens, S.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Autophagy: For better or for worse. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Narendra, D.P. Mechanisms of mitophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebollero, E.; Reggiori, F.; Kraft, C. Reticulophagy and ribophagy: Regulated degradation of protein production factories. Int. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 182834. [Google Scholar]
- Till, A.; Lakhani, R.; Burnett, S.F.; Subramani, S. Pexophagy: The selective degradation of peroxisomes. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 512721. [Google Scholar]
- Weidberg, H.; Shvets, E.; Elazar, Z. Lipophagy: Selective catabolism designed for lipids. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kaushik, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Novak, I.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cuervo, A.M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Cuervo, A.M. Lipophagy: Connecting autophagy and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 282041. [Google Scholar]
- Knodler, L.A.; Celli, J. Eating the strangers within: Host control of intracellular bacteria via xenophagy. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambold, A.S.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Mechanisms of mitochondria and autophagy crosstalk. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 4032–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.E.; Dodson, M.W.; Jiang, C.; Cao, J.H.; Huh, J.R.; Seol, J.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Hay, B.A.; Guo, M. Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature 2006, 441, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Song, S.; Kim, S.; Bae, E.; Kim, J.; Shong, M.; Kim, J.M.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Drosophila PINK1 mutants is complemented by parkin. Nature 2006, 441, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Narendra, D.; Tanaka, A.; Suen, D.F.; Youle, R.J. Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawajiri, S.; Saiki, S.; Sato, S.; Sato, F.; Hatano, T.; Eguchi, H.; Hattori, N. PINK1 is recruited to mitochondria with parkin and associates with LC3 in mitophagy. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, N.; Sato, S.; Shiba, K.; Okatsu, K.; Saisho, K.; Gautier, C.A.; Sou, Y.S.; Saiki, S.; Kawajiri, S.; Sato, F.; et al. PINK1 stabilized by mitochondrial depolarization recruits Parkin to damaged mitochondria and activates latent Parkin for mitophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, C.; Lorenz, H.; Weihofen, A.; Selkoe, D.J.; Lemberg, M.K. The mitochondrial intramembrane protease PARL cleaves human Pink1 to regulate Pink1 trafficking. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.W.; Grenier, K.; Aguileta, M.A.; Muise, S.; Farazifard, R.; Haque, M.E.; McBride, H.M.; Park, D.S.; Fon, E.A. Mitochondrial processing peptidase regulates PINK1 processing, import and Parkin recruitment. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.M.; Lazarou, M.; Wang, C.; Kane, L.A.; Narendra, D.P.; Youle, R.J. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates PINK1 import and proteolytic destabilization by PARL. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, D.P.; Jin, S.M.; Tanaka, A.; Suen, D.F.; Gautier, C.A.; Shen, J.; Cookson, M.R.; Youle, R.J. PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.; Holmstrom, K.M.; Skujat, D.; Fiesel, F.C.; Rothfuss, O.C.; Kahle, P.J.; Springer, W. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is dependent on VDAC1 and p62/SQSTM1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: An update and review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1757, 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Poburko, D.; Demaurex, N. Regulation of the mitochondrial proton gradient by cytosolic Ca(2+) signals. Pflugers Arch. 2012.
- Lee, J.Y.; Nagano, Y.; Taylor, J.P.; Lim, K.L.; Yao, T.P. Disease-causing mutations in parkin impair mitochondrial ubiquitination, aggregation, and HDAC6-dependent mitophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, D.; Kane, L.A.; Hauser, D.N.; Fearnley, I.M.; Youle, R.J. p62/SQSTM1 is required for Parkin-induced mitochondrial clustering but not mitophagy; VDAC1 is dispensable for both. Autophagy 2010, 6, 1090–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppins, S.; Nunnari, J. The molecular mechanism of mitochondrial fusion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Cleland, M.M.; Xu, S.; Narendra, D.P.; Suen, D.F.; Karbowski, M.; Youle, R.J. Proteasome and p97 mediate mitophagy and degradation of mitofusins induced by Parkin. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twig, G.; Elorza, A.; Molina, A.J.; Mohamed, H.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Walzer, G.; Stiles, L.; Haigh, S.E.; Katz, S.; Las, G.; et al. Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and elimination by autophagy. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.C.; Salazar, A.M.; Pham, A.H.; Sweredoski, M.J.; Kolawa, N.J.; Graham, R.L.; Hess, S.; Chan, D.C. Broad activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by Parkin is critical for mitophagy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sawada, T.; Lee, S.; Yu, W.; Silverio, G.; Alapatt, P.; Millan, I.; Shen, A.; Saxton, W.; Kanao, T.; et al. Parkinson's disease-associated kinase PINK1 regulates Miro protein level and axonal transport of mitochondria. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Winter, D.; Ashrafi, G.; Schlehe, J.; Wong, Y.L.; Selkoe, D.; Rice, S.; Steen, J.; Lavoie, M.J.; Schwarz, T.L. PINK1 and Parkin Target Miro for Phosphorylation and Degradation to Arrest Mitochondrial Motility. Cell 2011, 147, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Koga, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tang, W.; Wong, E.; Gao, Y.S.; Pandey, U.B.; Kaushik, S.; Tresse, E.; Lu, J.; et al. HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective quality-control autophagy. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, H.; Thiagarajan, P.; Dasgupta, S.K.; Schumacher, A.; Prchal, J.T.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Essential role for Nix in autophagic maturation of erythroid cells. Nature 2008, 454, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Schweers, R.L.; Zhang, J.; Randall, M.S.; Loyd, M.R.; Li, W.; Dorsey, F.C.; Kundu, M.; Opferman, J.T.; Cleveland, J.L.; Miller, J.L.; et al. NIX is required for programmed mitochondrial clearance during reticulocyte maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19500–19505. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, I.; Kirkin, V.; McEwan, D.G.; Zhang, J.; Wild, P.; Rozenknop, A.; Rogov, V.; Lohr, F.; Popovic, D.; Occhipinti, A.; et al. Nix is a selective autophagy receptor for mitochondrial clearance. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanki, T. Nix, a receptor protein for mitophagy in mammals. Autophagy 2010, 6, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bosch-Marce, M.; Shimoda, L.A.; Tan, Y.S.; Baek, J.H.; Wesley, J.B.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Semenza, G.L. Mitochondrial autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10892–10903. [Google Scholar]
- Rikka, S.; Quinsay, M.N.; Thomas, R.L.; Kubli, D.A.; Zhang, X.; Murphy, A.N.; Gustafsson, A.B. Bnip3 impairs mitochondrial bioenergetics and stimulates mitochondrial turnover. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.X.; Ni, H.M.; Li, M.; Liao, Y.; Chen, X.; Stolz, D.B.; Dorn, G.W., 2nd; Yin, X.M. Nix is critical to two distinct phases of mitophagy, reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagy induction and Parkin-ubiquitin-p62-mediated mitochondrial priming. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27879–27890. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, L.C.; Scorrano, L. High levels of Fis1, a pro-fission mitochondrial protein, trigger autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1777, 860–866. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, L.C.; Di Benedetto, G.; Scorrano, L. During autophagy mitochondria elongate, are spared from degradation and sustain cell viability. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusdon, A.M.; Zhu, J.; Van Houten, B.; Chu, C.T. ATP13A2 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics through macroautophagy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settembre, C.; Fraldi, A.; Jahreiss, L.; Spampanato, C.; Venturi, C.; Medina, D.; de Pablo, R.; Tacchetti, C.; Rubinsztein, D.C.; Ballabio, A. A block of autophagy in lysosomal storage disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- De Pablo-Latorre, R.; Saide, A.; Polishhuck, E.V.; Nusco, E.; Fraldi, A.; Ballabio, A. Impaired parkin-mediated mitochondrial targeting to autophagosomes differentially contributes to tissue pathology in lysosomal storage diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1770–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselyov, K.; Jennigs, J.J., Jr.; Rbaibi, Y.; Chu, C.T. Autophagy, mitochondria and cell death in lysosomal storage diseases. Autophagy 2007, 3, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, L.; Schlierf, A.; Lutz, A.K.; Shan, J.; Deinlein, A.; Kast, J.; Galehdar, Z.; Palmisano, V.; Patenge, N.; Berg, D.; et al. Parkin is transcriptionally regulated by ATF4: Evidence for an interconnection between mitochondrial stress and ER stress. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.R.; Lackner, L.L.; West, M.; DiBenedetto, J.R.; Nunnari, J.; Voeltz, G.K. ER tubules mark sites of mitochondrial division. Science 2011, 334, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Hailey, D.W.; Rambold, A.S.; Satpute-Krishnan, P.; Mitra, K.; Sougrat, R.; Kim, P.K.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation. Cell 2010, 141, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, M.; Ferguson, D.J.; Edelmann, M.; Kessler, B.; Morten, K.J.; Komatsu, M.; Simon, A.K. Loss of autophagy in erythroid cells leads to defective removal of mitochondria and severe anemia in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 832–837. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.J.; Quijano, C.; Chen, E.; Liu, H.; Cao, L.; Fergusson, M.M.; Rovira, II; Gutkind, S.; Daniels, M.P.; Komatsu, M.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress mediate the physiological impairment induced by the disruption of autophagy. Aging (Albany NY) 2009, 1, 425–437. [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, M.; Waguri, S.; Ueno, T.; Iwata, J.; Murata, S.; Tanida, I.; Ezaki, J.; Mizushima, N.; Ohsumi, Y.; Uchiyama, Y.; et al. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, L.M.; Miller, B.C.; Ng, A.; Eisenberg, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cadwell, K.; Graham, D.B.; Mizushima, N.N.; Xavier, R.; Virgin, H.W.; et al. Identification of Atg5-dependent transcriptional changes and increases in mitochondrial mass in Atg5-deficient T lymphocytes. Autophagy 2009, 5, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, M.; Lindsten, T.; Yang, C.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Selak, M.A.; Ney, P.A.; Thompson, C.B. Ulk1 plays a critical role in the autophagic clearance of mitochondria and ribosomes during reticulocyte maturation. Blood 2008, 112, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.L.; Ng, X.H.; Grace, L.G.; Yao, T.P. Mitochondrial dynamics and Parkinson' s disease: Focus on parkin. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 935–949. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, M.K.; Cookson, M.R. Mitochondrial quality control and dynamics in Parkinson's disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deas, E.; Wood, N.W.; Plun-Favreau, H. Mitophagy and Parkinson's disease: The PINK1-parkin link. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.X.; Correia, S.C.; Wang, X.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Moreira, P.I.; Zhu, X. A synergistic dysfunction of mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics and mitophagy in Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20 Suppl. 2, S401–412. [Google Scholar]
- De la Mata, M.; Garrido-Maraver, J.; Cotan, D.; Cordero, M.D.; Oropesa-Avila, M.; Izquierdo, L.G.; De Miguel, M.; Lorite, J.B.; Infante, E.R.; Ybot, P.; et al. Recovery of MERRF Fibroblasts and Cybrids Pathophysiology by Coenzyme Q(10). Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotan, D.; Cordero, M.D.; Garrido-Maraver, J.; Oropesa-Avila, M.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Gomez Izquierdo, L.; De la Mata, M.; De Miguel, M.; Lorite, J.B.; Infante, E.R.; et al. Secondary coenzyme Q10 deficiency triggers mitochondria degradation by mitophagy in MELAS fibroblasts. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2669–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkerson, R.W.; De Vries, R.L.; Lebot, P.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Torgyekes, E.; Shirihai, O.S.; Przedborski, S.; Schon, E.A. Mitochondrial autophagy in cells with mtDNA mutations results from synergistic loss of transmembrane potential and mTORC1 inhibition. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H.; Lin, Z.; Flomenberg, N.; Pestell, R.G.; Howell, A.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E. Glutamine fuels a vicious cycle of autophagy in the tumor stroma and oxidative mitochondrial metabolism in epithelial cancer cells: Implications for preventing chemotherapy resistance. Cancer. Biol. Ther. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahira, K.; Haspel, J.A.; Rathinam, V.A.; Lee, S.J.; Dolinay, T.; Lam, H.C.; Englert, J.A.; Rabinovitch, M.; Cernadas, M.; Kim, H.P.; et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlides, S.; Tsirigos, A.; Migneco, G.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Chiavarina, B.; Flomenberg, N.; Frank, P.G.; Casimiro, M.C.; Wang, C.; Pestell, R.G.; et al. The autophagic tumor stroma model of cancer: Role of oxidative stress and ketone production in fueling tumor cell metabolism. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3485–3505. [Google Scholar]
- Castello-Cros, R.; Bonuccelli, G.; Molchansky, A.; Capozza, F.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Birbe, R.C.; Howell, A.; Pestell, R.G.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Sotgia, F.; et al. Matrix remodeling stimulates stromal autophagy, "fueling" cancer cell mitochondrial metabolism and metastasis. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2021–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Weidberg, H.; Shvets, E.; Elazar, Z. Biogenesis and cargo selectivity of autophagosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strappazzon, F.; Vietri-Rudan, M.; Campello, S.; Nazio, F.; Florenzano, F.; Fimia, G.M.; Piacentini, M.; Levine, B.; Cecconi, F. Mitochondrial BCL-2 inhibits AMBRA1-induced autophagy. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Humbeeck, C.; Cornelissen, T.; Hofkens, H.; Mandemakers, W.; Gevaert, K.; De Strooper, B.; Vandenberghe, W. Parkin interacts with Ambra1 to induce mitophagy. J. Neurosci 2011, 31, 10249–10261. [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli, E. The fateful encounter of mitochondria with calcium: How did it happen? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1797, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, J.M.; Perocchi, F.; Girgis, H.S.; Plovanich, M.; Belcher-Timme, C.A.; Sancak, Y.; Bao, X.R.; Strittmatter, L.; Goldberger, O.; Bogorad, R.L.; et al. Integrative genomics identifies MCU as an essential component of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Nature 2011, 476, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Csordas, G.; Renken, C.; Varnai, P.; Walter, L.; Weaver, D.; Buttle, K.F.; Balla, T.; Mannella, C.A.; Hajnoczky, G. Structural and functional features and significance of the physical linkage between ER and mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordas, G.; Thomas, A.P.; Hajnoczky, G. Quasi-synaptic calcium signal transmission between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glancy, B.; Balaban, R.S. Role of mitochondrial ca(2+) in the regulation of cellular energetics. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2959–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meley, D.; Bauvy, C.; Houben-Weerts, J.H.; Dubbelhuis, P.F.; Helmond, M.T.; Codogno, P.; Meijer, A.J. AMP-activated protein kinase and the regulation of autophagic proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34870–34879. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Giordano, S.; Zhang, J. Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: Cross-talk and redox signalling. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherz-Shouval, R.; Shvets, E.; Fass, E.; Shorer, H.; Gil, L.; Elazar, Z. Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Azad, M.B.; Gibson, S.B. Superoxide is the major reactive oxygen species regulating autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; McMillan-Ward, E.; Kong, J.; Israels, S.J.; Gibson, S.B. Mitochondrial electron-transport-chain inhibitors of complexes I and II induce autophagic cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. J. Cell. Sci. 2007, 120, 4155–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baregamian, N.; Song, J.; Bailey, C.E.; Papaconstantinou, J.; Evers, B.M.; Chung, D.H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 control reactive oxygen species release, mitochondrial autophagy, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 phosphorylation during necrotizing enterocolitis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Maeda, A.; Ji, J.; Baty, C.J.; Watkins, S.C.; Greenberger, J.S.; Kagan, V.E. Are mitochondrial reactive oxygen species required for autophagy? Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2011, 412, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, S.; Foncea, R.; Guerrero, J.; Leighton, F. Oxidative stress and upregulation of mitochondrial biogenesis genes in mitochondrial DNA-depleted HeLa cells. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 1999, 258, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauen, M.; Spitkovsky, D.; Schubert, J.; Fischer, J.H.; Hayashi, J.; Wiesner, R.J. Respiratory chain deficiency slows down cell-cycle progression via reduced ROS generation and is associated with a reduction of p21CIP1/WAF1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 209, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Spitkovsky, D.; Radicella, J.P.; Epe, B.; Wiesner, R.J. Reactive oxygen species derived from the mitochondrial respiratory chain are not responsible for the basal levels of oxidative base modifications observed in nuclear DNA of Mammalian cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lee, J.Y.; Wei, H.; Tanabe, O.; Engel, J.D.; Morrison, S.J.; Guan, J.L. FIP200 is required for the cell-autonomous maintenance of fetal hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2010, 116, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.L.; Chou, A.H.; Wu, A.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Weng, Y.H.; Kao, Y.C.; Yeh, T.H.; Chu, P.J.; Lu, C.S. PARK6 PINK1 mutants are defective in maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential and inhibiting ROS formation of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1812, 674–684. [Google Scholar]
- Alemi, M.; Prigione, A.; Wong, A.; Schoenfeld, R.; DiMauro, S.; Hirano, M.; Taroni, F.; Cortopassi, G. Mitochondrial DNA deletions inhibit proteasomal activity and stimulate an autophagic transcript. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoshevich, L.; Murrow, L.; Chen, N.; Fernandez, E.; Roy, S.; Fung, C.; Debnath, J. ATG12 conjugation to ATG3 regulates mitochondrial homeostasis and cell death. Cell 2010, 142, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, A.D.; Eisenstein, M.; Ber, Y.; Bialik, S.; Kimchi, A. The autophagy protein Atg12 associates with antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members to promote mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.X.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Ni, H.M.; Lin, C.W.; Gao, W.; Lu, B.; Stolz, D.B.; Clemens, D.L.; Yin, X.M. Autophagy reduces acute ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity and steatosis in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1740–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchi-Sato, K.; Ozeki, S.; Houjou, T.; Taguchi, R.; Fujimoto, T. The surface of lipid droplets is a phospholipid monolayer with a unique Fatty Acid composition. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44507–44512. [Google Scholar]
- Bickel, P.E.; Tansey, J.T.; Welte, M.A. PAT proteins, an ancient family of lipid droplet proteins that regulate cellular lipid stores. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1791, 419–440. [Google Scholar]
- Minnaard, R.; Schrauwen, P.; Schaart, G.; Jorgensen, J.A.; Lenaers, E.; Mensink, M.; Hesselink, M.K. Adipocyte differentiation-related protein and OXPAT in rat and human skeletal muscle: involvement in lipid accumulation and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4077–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. The life of lipid droplets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Debeer, L.J.; Thomas, J.; De Schepper, P.J.; Mannaerts, G.P. Lysosomal triacylglycerol lipase and lipolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 8841–8846. [Google Scholar]
- de Duve, C.; de Barsy, T.; Poole, B.; Trouet, A.; Tulkens, P.; Van Hoof, F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1974, 23, 2495–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Boya, P.; Gonzalez-Polo, R.A.; Casares, N.; Perfettini, J.L.; Dessen, P.; Larochette, N.; Metivier, D.; Meley, D.; Souquere, S.; Yoshimori, T.; et al. Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Duee, P.H.; Pegorier, J.P.; el Manoubi, L.; Herbin, C.; Kohl, C.; Girard, J. Hepatic triglyceride hydrolysis and development of ketogenesis in rabbits. Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 249, E478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.T.; Tan, H.L.; Shui, G.; Bauvy, C.; Huang, Q.; Wenk, M.R.; Ong, C.N.; Codogno, P.; Shen, H.M. Dual role of 3-methyladenine in modulation of autophagy via different temporal patterns of inhibition on class I and III phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10850–10861. [Google Scholar]
- Czaja, M.J.; Cuervo, A.M. Lipases in lysosomes, what for? Autophagy 2009, 5, 866–867. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Goldman, S.; Baerga, R.; Zhao, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Jin, S. Adipose-specific deletion of autophagy-related gene 7 (atg7) in mice reveals a role in adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19860–19865. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X. Rab32 is important for autophagy and lipid storage in Drosophila. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32086. [Google Scholar]
- Baerga, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.H.; Goldman, S.; Jin, S. Targeted deletion of autophagy-related 5 (atg5) impairs adipogenesis in a cellular model and in mice. Autophagy 2009, 5, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Franklin, V.; Mak, E.; Liao, X.; Tabas, I.; Marcel, Y.L. Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Lay, S.; Briand, N.; Blouin, C.M.; Chateau, D.; Prado, C.; Lasnier, F.; Le Liepvre, X.; Hajduch, E.; Dugail, I. The lipoatrophic caveolin-1 deficient mouse model reveals autophagy in mature adipocytes. Autophagy 2010, 6, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ost, A.; Svensson, K.; Ruishalme, I.; Brannmark, C.; Franck, N.; Krook, H.; Sandstrom, P.; Kjolhede, P.; Stralfors, P. Attenuated mTOR signaling and enhanced autophagy in adipocytes from obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Furuya, N.; Koike, M.; Ueno, T.; Komatsu, M.; Arai, H.; Tanaka, K.; Kominami, E.; Uchiyama, Y. The MAP1-LC3 conjugation system is involved in lipid droplet formation. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2009, 382, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Driessen, K.; Nixon, S.J.; Zerial, M.; Parton, R.G. Regulated localization of Rab18 to lipid droplets: effects of lipolytic stimulation and inhibition of lipid droplet catabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42325–42335. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Watkins, J.W.; Bermudez, M.; Gray, R.; Gaban, A.; Portie, K.; Grace, S.; Kleve, M.; Craciun, G. A life-span extending form of autophagy employs the vacuole-vacuole fusion machinery. Autophagy 2008, 4, 874–886. [Google Scholar]
- Kovsan, J.; Bashan, N.; Greenberg, A.S.; Rudich, A. Potential role of autophagy in modulation of lipid metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyombo, A.A.; Tjon-Kon-Sang, S.; Rbaibi, Y.; Bashllari, E.; Bisceglia, J.; Muallem, S.; Kiselyov, K. TRP-ML1 regulates lysosomal pH and acidic lysosomal lipid hydrolytic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 7294–7301. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.H.; Shui, G.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.J.; Bay, B.H.; Wenk, M.R.; Shen, H.M. Induction of autophagy by palmitic acid via a PKC-mediated signalling pathway independent of mTOR. J. Biol. Chem. 2012.
- Las, G.; Serada, S.B.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Twig, G.; Shirihai, O.S. Fatty acids suppress autophagic turnover in beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42534–42544. [Google Scholar]
- Masini, M.; Bugliani, M.; Lupi, R.; del Guerra, S.; Boggi, U.; Filipponi, F.; Marselli, L.; Masiello, P.; Marchetti, P. Autophagy in human type 2 diabetes pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Kaushik, S.; Cuervo, A.M. Altered lipid content inhibits autophagic vesicular fusion. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3052–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, L.R.; Gelino, S.; Melendez, A.; Hansen, M. Autophagy and lipid metabolism coordinately modulate life span in germline-less C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; O'Rourke, E.J.; Ruvkun, G. Fat metabolism links germline stem cells and longevity in C. elegans. Science 2008, 322, 957–960. [Google Scholar]
- Minor, L.K.; Mahlberg, F.H.; Jerome, W.G.; Lewis, J.C.; Rothblat, G.H.; Glick, J.M. Lysosomal hydrolysis of lipids in a cell culture model of smooth muscle foam cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1991, 54, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Tamura, H.; Ueno, T.; Nishimura, T.; Inoue, T.; Sasaki, M.; Koike, M.; Arai, H.; Kominami, E.; et al. LC3, a microtubule-associated protein1A/B light chain3, is involved in cytoplasmic lipid droplet formation. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2010, 393, 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Purohit, V.; Gao, B.; Song, B.J. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholic fatty liver. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, C.L.; Song, F.Y.; Zhao, X.L.; Yu, L.H.; Zhu, Z.P.; Xie, K.Q. PI3K/Akt pathway activation was involved in acute ethanol-induced fatty liver in mice. Toxicology 2012, 296, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- De Ferranti, S.; Mozaffarian, D. The perfect storm: Obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic consequences. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, P.; Fu, S.; Calay, E.S.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovsan, J.; Bluher, M.; Tarnovscki, T.; Kloting, N.; Kirshtein, B.; Madar, L.; Shai, I.; Golan, R.; Harman-Boehm, I.; Schon, M.R.; et al. Altered autophagy in human adipose tissues in obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Dong, L.Q.; Liu, F. DsbA-L alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced adiponectin downregulation. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.B.; Rao, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liang, W.B.; Li, C.; Xue, H.; Zhou, B.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Lv, M.L.; et al. The association of interleukin-16 polymorphisms with IL-16 serum levels and risk of colorectal and gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Calder, P.C.; Ahluwalia, N.; Brouns, F.; Buetler, T.; Clement, K.; Cunningham, K.; Esposito, K.; Jonsson, L.S.; Kolb, H.; Lansink, M.; et al. Dietary factors and low-grade inflammation in relation to overweight and obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106 Suppl. 3, S5–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jenkins, J.R.; Trayhurn, P. Expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines by human adipocytes differentiated in culture: Integrated response to TNF-alpha. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E731–E740. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki, T.; Kusunoki, C.; Kondo, M.; Yasuda, M.; Kume, S.; Morino, K.; Sekine, O.; Ugi, S.; Uzu, T.; Nishio, Y.; et al. Autophagy regulates inflammation in adipocytes. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2012, 417, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, S.; Arias, E.; Kwon, H.; Lopez, N.M.; Athonvarangkul, D.; Sahu, S.; Schwartz, G.J.; Pessin, J.E.; Singh, R. Loss of autophagy in hypothalamic POMC neurons impairs lipolysis. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Schatz, G.; Dobberstein, B. Common principles of protein translocation across membranes. Science 1996, 271, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Lafon-Cazal, M.; Adjali, O.; Galeotti, N.; Poncet, J.; Jouin, P.; Homburger, V.; Bockaert, J.; Marin, P. Proteomic analysis of astrocytic secretion in the mouse. Comparison with the cerebrospinal fluid proteome. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24438–24448. [Google Scholar]
- Nickel, W.; Rabouille, C. Mechanisms of regulated unconventional protein secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 10, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Seelenmeyer, C.; Stegmayer, C.; Nickel, W. Unconventional secretion of fibroblast growth factor 2 and galectin-1 does not require shedding of plasma membrane-derived vesicles. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Nickel, W. Pathways of unconventional protein secretion. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Leissring, M.A. Insulin-degrading enzyme is exported via an unconventional protein secretion pathway. Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, U.; Abel, K.J.; Bohn, H.; Lobermann, H.; Lottspeich, F.; Kupper, H. Characterization of cDNA encoding human placental anticoagulant protein (PP4): Homology with the lipocortin family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3708–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Lutomski, D.; Fouillit, M.; Bourin, P.; Mellottee, D.; Denize, N.; Pontet, M.; Bladier, D.; Caron, M.; Joubert-Caron, R. Externalization and binding of galectin-1 on cell surface of K562 cells upon erythroid differentiation. Glycobiology 1997, 7, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joliot, A.; Maizel, A.; Rosenberg, D.; Trembleau, A.; Dupas, S.; Volovitch, M.; Prochiantz, A. Identification of a signal sequence necessary for the unconventional secretion of Engrailed homeoprotein. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.P.; Hughes, R.C. Determinants in the N-terminal domains of galectin-3 for secretion by a novel pathway circumventing the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi complex. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, O.; Engling, A.; Bucala, R.; Lue, H.; Nickel, W.; Bernhagen, J. Regulated secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is mediated by a non-classical pathway involving an ABC transporter. FEBS Lett. 2003, 551, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinseth, M.A.; Anjard, C.; Fuller, D.; Guizzunti, G.; Loomis, W.F.; Malhotra, V. The Golgi-associated protein GRASP is required for unconventional protein secretion during development. Cell 2007, 130, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, W.; Seedorf, M. Unconventional mechanisms of protein transport to the cell surface of eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2008, 24, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Ruegg, A.; Werner, S.; Beer, H.D. Active caspase-1 is a regulator of unconventional protein secretion. Cell 2008, 132, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchler, K.; Sterne, R.E.; Thorner, J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE6 gene product: a novel pathway for protein export in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3973–3984. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, J.P.; Varshavsky, A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature 1989, 340, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjithaya, R.; Subramani, S. Autophagy: A broad role in unconventional protein secretion? Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.L.; Wang, Y.; Ong, Y.S.; Hong, W. COPII and exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1744, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.; Schekman, R. COPII-mediated vesicle formation at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2011, 124, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.; Adolf, F.; Weimer, C.; Bruegger, B.; Wieland, F.T. ArfGAP1 activity and COPI vesicle biogenesis. Traffic 2009, 10, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.E.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, M.G.; Tang, B.L. Non-classical membrane trafficking processes galore. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duran, J.M.; Anjard, C.; Stefan, C.; Loomis, W.F.; Malhotra, V. Unconventional secretion of Acb1 is mediated by autophagosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjithaya, R.; Anjard, C.; Loomis, W.F.; Subramani, S. Unconventional secretion of Pichia pastoris Acb1 is dependent on GRASP protein, peroxisomal functions, and autophagosome formation. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.; Anjard, C.; Malhotra, V.; Loomis, W.F.; Kuspa, A. Unconventional secretion of AcbA in Dictyostelium discoideum through a vesicular intermediate. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, W.F.; Behrens, M.M.; Williams, M.E.; Anjard, C. Pregnenolone sulfate and cortisol induce secretion of acyl-CoA-binding protein and its conversion into endozepines from astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21359–21365. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsen, H.; Stenmark, H. Protein secretion: Unconventional exit by exophagy. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, C.; McCaffery, J.M.; Curwin, A.J.; Duran, J.M.; Malhotra, V. Biogenesis of a novel compartment for autophagosome-mediated unconventional protein secretion. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 195, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, N.; Jiang, S.; Pilli, M.; Ornatowski, W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Deretic, V. Autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway for extracellular delivery of IL-1beta. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4701–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiori, F. 1. Membrane origin for autophagy. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2006, 74, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Demine, S.; Michel, S.; Vannuvel, K.; Wanet, A.; Renard, P.; Arnould, T. Macroautophagy and Cell Responses Related to Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Lipid Metabolism and Unconventional Secretion of Proteins. Cells 2012, 1, 168-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells1020168
Demine S, Michel S, Vannuvel K, Wanet A, Renard P, Arnould T. Macroautophagy and Cell Responses Related to Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Lipid Metabolism and Unconventional Secretion of Proteins. Cells. 2012; 1(2):168-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells1020168
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemine, Stéphane, Sébastien Michel, Kayleen Vannuvel, Anaïs Wanet, Patricia Renard, and Thierry Arnould. 2012. "Macroautophagy and Cell Responses Related to Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Lipid Metabolism and Unconventional Secretion of Proteins" Cells 1, no. 2: 168-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells1020168



