Scale Effect and Anisotropy Analyzed for Neutrosophic Numbers of Rock Joint Roughness Coefficient Based on Neutrosophic Statistics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Concepts and Neutrosophic Statistical Algorithm of NNs
3. JRC Values and JRC-NNs in an Actual Case
4. Scale Effect Analysis in Different Sample Lengths Based on the Neutrosophic Statistical Algorithm
5. Anisotropic Analysis in Different Measurement Orientations Based on the Neutrosophic Statistical Algorithm
6. Conclusion Remarks
- (1)
- The neutrosophic statistical analysis method without fitting functions is more feasible and more reasonable than the existing method [10].
- (2)
- The neutrosophic statistical analysis method based on the neutrosophic average values and neutrosophic standard deviations of JRC-NNs can retain much more information and reflect the scale effect and anisotropic characteristics of JRC values in detail.
- (3)
- The presented neutrosophic statistical algorithm can analyze the scale effect and the anisotropy of JRC-NNs (JRC values) directly and effectively so as to reduce the information distortion.
- (4)
- The presented neutrosophic statistical algorithm based on the neutrosophic statistical averages and standard deviations of JRC-NNs is more convenient and simpler than the existing curve fitting and derivative analysis of JRC-NN functions in [10].
- (5)
- The presented neutrosophic statistical algorithm can overcome the insufficiencies of the existing method in the fitting and analysis process [10].
- (6)
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barton, N. Review of a new shear-strength criterion for rock joints. Eng. Geol. 1973, 7, 287–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, R.; Cruden, D.M. Estimating joint roughness coefficients. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1979, 16, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.C.; Karakus, M.; Tang, H.M.; Ge, Y.F.; Zhang, L. A new method estimating the 2D joint roughness coefficient for discontinuity surfaces in rock masses. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 72, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Zhu, W.C.; Yu, Q.L.; Liu, X.G. Characterization of anisotropy of joint surface roughness and aperture by variogram approach based on digital image processing technique. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 855–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Zhu, W.C.; Liu, S.X.; Zhang, F.; Guo, L.F. Anisotropy and size effects of surface roughness of rock joints. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2015, 34, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Yong, R.; Liang, Q.F.; Huang, M.; Du, S.G. Neutrosophic functions of the joint roughness coefficient and the shear strength: A case study from the pyroclastic rock mass in Shaoxing City, China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set, and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Smarandache, F. Introduction to Neutrosophic Measure, Neutrosophic Integral, and Neutrosophic Probability; Sitech & Education Publisher: Craiova, Romania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Smarandache, F. Introduction to Neutrosophic Statistics; Sitech & Education Publisher: Craiova, Romania, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Chen, J.Q.; Yong, R.; Du, S.G. Expression and analysis of joint roughness coefficient using neutrosophic number functions. Information 2017, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Ye, J.; Du, S.G.; Yong, R. Expressions of rock joint roughness coefficient using neutrosophic interval statistical numbers. Symmetry 2017, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Neutrosophic number linear programming method and its application under neutrosophic number environments. Soft Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.G.; Hu, Y.J.; Hu, X.F. Measurement of joint roughness coefficient by using profilograph and roughness ruler. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 20, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| L | 10 cm | 20 cm | 30 cm | 40 cm | 50 cm | 60 cm | 70 cm | 80 cm | 90 cm | 100 cm | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | μi1 | σi1 | μi2 | σi2 | μi3 | σi3 | μi4 | σi4 | μi5 | σi5 | μi6 | σi6 | μi7 | σi7 | μi8 | σi8 | μi9 | σi9 | μi10 | σi10 |
| 0° | 10.5425 | 2.2385 | 9.6532 | 1.7162 | 9.2733 | 1.5227 | 8.9745 | 1.7092 | 8.8222 | 1.6230 | 8.8016 | 1.6069 | 8.6815 | 1.6066 | 8.6009 | 1.5043 | 8.5681 | 1.3465 | 8.4630 | 1.2806 |
| 15° | 10.7111 | 2.2392 | 9.9679 | 1.7379 | 9.3433 | 1.5555 | 9.2708 | 1.2743 | 9.2299 | 1.2850 | 8.9729 | 1.3071 | 8.8332 | 1.1706 | 8.5868 | 0.9413 | 8.3604 | 0.7673 | 8.1404 | 0.6372 |
| 30° | 10.5943 | 2.3528 | 9.9289 | 2.0286 | 9.5715 | 1.6665 | 9.1209 | 1.4207 | 9.0920 | 1.4119 | 8.6006 | 0.9899 | 8.7596 | 1.1489 | 8.5713 | 1.0776 | 8.2927 | 1.0128 | 8.1041 | 0.9664 |
| 45° | 9.9244 | 2.3120 | 9.2005 | 1.7237 | 9.0081 | 1.6464 | 8.5078 | 1.1376 | 8.3336 | 1.431 | 8.6237 | 1.3427 | 8.3262 | 1.2184 | 8.0768 | 1.2717 | 7.8458 | 1.2096 | 7.5734 | 1.1294 |
| 60° | 9.0253 | 2.4592 | 8.4047 | 1.9813 | 7.8836 | 1.8199 | 7.7941 | 1.8829 | 7.1873 | 1.167 | 8.2678 | 1.7830 | 7.3595 | 1.5956 | 7.1381 | 1.4082 | 6.8722 | 1.2178 | 6.7131 | 0.9627 |
| 75° | 7.9352 | 2.1063 | 7.4604 | 1.7756 | 6.7725 | 1.4153 | 6.3056 | 1.0241 | 6.5446 | 1.2140 | 6.4993 | 1.3108 | 6.2440 | 1.1208 | 6.0933 | 0.9171 | 5.9499 | 0.7311 | 5.8317 | 0.5855 |
| 90° | 7.0467 | 2.4054 | 6.6915 | 1.8482 | 6.3378 | 1.4743 | 5.9993 | 1.1700 | 6.1481 | 1.1920 | 6.0893 | 1.1850 | 5.9543 | 1.1021 | 5.8932 | 0.9630 | 5.8259 | 0.9181 | 5.8219 | 0.8355 |
| 105° | 7.7766 | 2.4105 | 7.2221 | 1.7560 | 6.6770 | 1.2608 | 6.2318 | 0.985 | 6.4634 | 1.2288 | 6.4609 | 1.5029 | 6.1670 | 1.3236 | 5.9923 | 1.1016 | 5.8903 | 0.9868 | 5.8359 | 0.8479 |
| 120° | 9.1324 | 2.3250 | 8.5206 | 1.8963 | 8.1998 | 1.5792 | 7.9671 | 1.4094 | 7.3207 | 1.0418 | 7.8245 | 1.1807 | 7.2472 | 1.0637 | 7.0649 | 0.9507 | 6.8537 | 0.8122 | 6.6909 | 0.7715 |
| 135° | 9.2258 | 1.9104 | 8.5670 | 1.5412 | 8.0898 | 1.3452 | 7.8194 | 0.9910 | 7.3735 | 0.9848 | 7.6660 | 1.2845 | 7.3846 | 1.1608 | 7.0872 | 1.1589 | 6.9154 | 1.0345 | 6.7586 | 0.9157 |
| 150° | 10.4673 | 2.4365 | 9.5650 | 1.9065 | 8.9102 | 1.6863 | 8.9059 | 1.4562 | 8.3930 | 1.1855 | 8.8162 | 1.5870 | 8.2064 | 1.3432 | 8.0153 | 1.1287 | 7.6556 | 1.0101 | 7.4443 | 0.9080 |
| 165° | 10.6035 | 2.2090 | 9.9647 | 1.6606 | 9.5320 | 1.5695 | 8.8760 | 1.5994 | 8.6121 | 1.4899 | 8.6463 | 1.5942 | 8.3931 | 1.3637 | 8.1107 | 1.2203 | 7.9051 | 1.0893 | 7.7175 | 1.0050 |
| 180° | 9.8501 | 2.1439 | 9.0984 | 1.8556 | 8.7574 | 1.7300 | 8.6002 | 1.6753 | 8.2973 | 1.5862 | 8.1266 | 1.6278 | 7.9647 | 1.4864 | 7.8981 | 1.3395 | 7.8338 | 1.1935 | 7.8291 | 1.0616 |
| 195° | 9.9383 | 2.2254 | 9.2299 | 1.8331 | 8.6781 | 1.6791 | 8.7993 | 1.4556 | 8.5308 | 1.5551 | 8.1016 | 1.5598 | 7.9219 | 1.2559 | 7.6562 | 0.9674 | 7.4610 | 0.8060 | 7.3131 | 0.7402 |
| 210° | 9.5903 | 1.9444 | 8.9414 | 1.5298 | 8.6532 | 1.6227 | 8.2601 | 1.5626 | 8.2065 | 1.5438 | 7.3828 | 1.2507 | 7.7527 | 1.2989 | 7.5050 | 1.1484 | 7.2495 | 1.0876 | 7.0479 | 0.9558 |
| 225° | 8.9167 | 1.9764 | 8.2550 | 1.4256 | 8.1330 | 1.4751 | 7.7012 | 1.2124 | 7.6798 | 1.4502 | 7.4365 | 1.1748 | 7.3183 | 1.2086 | 7.1309 | 1.2749 | 6.8652 | 1.2190 | 6.6742 | 1.1571 |
| 240° | 7.8582 | 1.8456 | 7.3032 | 1.4385 | 6.8241 | 1.1626 | 6.7427 | 1.2022 | 6.3250 | 0.8971 | 6.8181 | 1.1123 | 6.3526 | 1.0430 | 6.1521 | 0.9953 | 5.9138 | 0.8906 | 5.7515 | 0.7329 |
| 255° | 7.2166 | 1.9341 | 6.8638 | 1.3901 | 6.3349 | 1.2705 | 6.1050 | 1.0350 | 6.0333 | 0.9671 | 6.0693 | 1.1394 | 5.8924 | 0.9417 | 5.7122 | 0.8153 | 5.7803 | 0.8598 | 5.3946 | 0.5627 |
| 270° | 6.8025 | 2.1165 | 6.3123 | 1.6374 | 6.0061 | 1.3786 | 5.8815 | 1.3700 | 5.7871 | 1.1783 | 5.9707 | 1.2858 | 5.8530 | 1.2711 | 5.7376 | 1.1886 | 5.8259 | 0.9181 | 5.5856 | 1.0273 |
| 285° | 7.0061 | 1.5474 | 6.4941 | 1.1183 | 6.1107 | 0.9586 | 5.8455 | 0.9821 | 5.7563 | 0.9033 | 6.0606 | 1.3603 | 5.8403 | 1.2714 | 5.6386 | 1.1359 | 5.4716 | 1.0374 | 5.3629 | 0.9501 |
| 300° | 8.4720 | 1.7448 | 7.8124 | 1.3531 | 7.5303 | 1.2127 | 7.2813 | 1.0247 | 6.9533 | 1.1089 | 7.0673 | 0.8880 | 6.8002 | 0.9202 | 6.6414 | 0.8727 | 6.4460 | 0.8434 | 6.3104 | 0.7904 |
| 315° | 10.1428 | 2.4790 | 9.4554 | 2.1149 | 8.9644 | 1.7308 | 8.5698 | 1.4949 | 8.1224 | 1.4089 | 8.6863 | 1.5162 | 8.3659 | 1.5934 | 7.6582 | 1.3811 | 7.4641 | 1.1563 | 7.3537 | 1.0960 |
| 330° | 9.8295 | 2.2844 | 9.0011 | 1.6139 | 8.3261 | 1.6005 | 8.3290 | 1.3232 | 7.8712 | 1.2376 | 8.0526 | 1.2755 | 7.9134 | 1.1209 | 7.6498 | 1.0157 | 7.3466 | 0.9740 | 7.0927 | 0.9342 |
| 345° | 9.6831 | 2.0192 | 9.1761 | 1.6305 | 8.7732 | 1.1686 | 8.4741 | 1.1887 | 7.8597 | 1.1436 | 7.8485 | 1.0332 | 7.7270 | 1.0174 | 7.4667 | 0.9254 | 7.1781 | 0.821 | 7.0038 | 0.7346 |
| L | 10 cm | 20 cm | 30 cm | 40 cm | 50 cm | 60 cm | 70 cm | 80 cm | 90 cm | 100 cm | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | ai1 | bi1 | ai2 | bi2 | ai3 | bi3 | ai4 | bi4 | ai5 | bi5 | ai6 | bi6 | ai7 | bi7 | ai8 | bi8 | ai9 | bi9 | ai10 | bi10 |
| 0° | 8.3040 | 4.4771 | 7.9370 | 3.4325 | 7.7506 | 3.0454 | 7.2653 | 3.4184 | 7.1992 | 3.2459 | 7.1947 | 3.2138 | 7.0750 | 3.2132 | 7.0966 | 3.0085 | 7.2216 | 2.6930 | 7.1824 | 2.5612 |
| 15° | 8.4719 | 4.4784 | 8.2300 | 3.4759 | 7.7878 | 3.1110 | 7.9964 | 2.5487 | 7.9449 | 2.5700 | 7.6657 | 2.6142 | 7.6627 | 2.3412 | 7.6456 | 1.8825 | 7.5931 | 1.5347 | 7.5032 | 1.2745 |
| 30° | 8.2415 | 4.7057 | 7.9003 | 4.0572 | 7.9051 | 3.3330 | 7.7002 | 2.8414 | 7.6801 | 2.8239 | 7.6107 | 1.9798 | 7.6107 | 2.2977 | 7.4938 | 2.1552 | 7.2799 | 2.0256 | 7.1377 | 1.9328 |
| 45° | 7.6124 | 4.6240 | 7.4768 | 3.4474 | 7.3616 | 3.2929 | 7.3701 | 2.2753 | 6.9018 | 2.8636 | 7.2810 | 2.6853 | 7.1078 | 2.4369 | 6.8051 | 2.5434 | 6.6362 | 2.4192 | 6.4440 | 2.2589 |
| 60° | 6.5660 | 4.9185 | 6.4234 | 3.9627 | 6.0638 | 3.6397 | 5.9112 | 3.7658 | 6.0203 | 2.3341 | 6.4848 | 3.5660 | 5.7639 | 3.1912 | 5.7299 | 2.8163 | 5.6544 | 2.4355 | 5.7504 | 1.9253 |
| 75° | 5.8289 | 4.2126 | 5.6847 | 3.5513 | 5.3573 | 2.8306 | 5.2815 | 2.0483 | 5.3307 | 2.4279 | 5.1885 | 2.6216 | 5.1232 | 2.2416 | 5.1762 | 1.8342 | 5.2188 | 1.4622 | 5.2462 | 1.1710 |
| 90° | 4.6413 | 4.8108 | 4.8432 | 3.6965 | 4.8635 | 2.9486 | 4.8293 | 2.3399 | 4.9561 | 2.3841 | 4.9043 | 2.3701 | 4.8522 | 2.2043 | 4.9302 | 1.9260 | 4.9078 | 1.8362 | 4.9865 | 1.6709 |
| 105° | 5.3661 | 4.821 | 5.4661 | 3.5119 | 5.4162 | 2.5216 | 5.2460 | 1.9717 | 5.2346 | 2.4576 | 4.9580 | 3.0058 | 3.0054 | 2.6472 | 4.8907 | 2.2031 | 4.9034 | 1.9737 | 4.9881 | 1.6957 |
| 120° | 6.8074 | 4.6500 | 6.6243 | 3.7926 | 6.6206 | 3.1584 | 6.5577 | 2.8188 | 6.2789 | 2.0837 | 6.6438 | 2.3614 | 6.1834 | 2.1274 | 6.1142 | 1.9014 | 6.0415 | 1.6243 | 5.9194 | 1.5430 |
| 135° | 7.3153 | 3.8208 | 7.0258 | 3.0824 | 6.7446 | 2.6904 | 6.8283 | 1.9821 | 6.3887 | 1.9696 | 6.3815 | 2.5690 | 6.2238 | 2.3216 | 5.9283 | 2.3178 | 5.8810 | 2.0689 | 5.8429 | 1.8314 |
| 150° | 8.0308 | 4.8731 | 7.6585 | 3.8130 | 7.2240 | 3.3725 | 7.4497 | 2.9125 | 7.2075 | 2.3710 | 7.2292 | 7.2291 | 6.8633 | 2.6863 | 6.8866 | 2.2573 | 6.6454 | 2.0203 | 6.5363 | 1.8161 |
| 165° | 8.3945 | 4.4180 | 8.3040 | 3.3213 | 7.9625 | 3.1391 | 7.2766 | 3.1988 | 7.1222 | 2.9799 | 7.0521 | 3.1884 | 7.0294 | 2.7274 | 6.8904 | 2.4406 | 6.8158 | 2.1787 | 6.7124 | 2.0101 |
| 180° | 7.7062 | 4.2877 | 7.2427 | 3.7113 | 7.0273 | 3.4601 | 6.9249 | 3.3506 | 6.7111 | 3.1724 | 6.4988 | 3.2556 | 6.4782 | 2.9729 | 6.5586 | 2.6790 | 6.6403 | 2.3871 | 6.7675 | 2.1232 |
| 195° | 7.7130 | 4.4507 | 7.3968 | 3.6661 | 6.9990 | 3.3583 | 7.3437 | 2.9113 | 6.9757 | 3.1102 | 6.5419 | 3.1195 | 6.6660 | 2.5119 | 6.6888 | 1.9348 | 6.6550 | 1.6120 | 6.5729 | 1.4803 |
| 210° | 7.6459 | 3.8887 | 7.4116 | 3.0596 | 7.0305 | 3.2453 | 6.6975 | 3.1252 | 6.6628 | 3.0875 | 6.1321 | 2.5014 | 6.4538 | 2.5977 | 6.3566 | 2.2967 | 6.1619 | 2.1752 | 6.0921 | 1.9116 |
| 225° | 6.9402 | 3.9529 | 6.8294 | 2.8512 | 6.6580 | 2.9502 | 6.4888 | 2.4248 | 6.2296 | 2.9004 | 6.2617 | 2.3495 | 6.1097 | 2.4172 | 5.8560 | 2.5498 | 5.6462 | 2.4379 | 5.5170 | 2.3143 |
| 240° | 6.0125 | 3.6913 | 5.8648 | 2.8769 | 5.6615 | 2.3252 | 5.5405 | 2.4044 | 5.4280 | 1.7941 | 5.7058 | 2.2246 | 5.3096 | 2.0861 | 5.1568 | 1.9906 | 5.0231 | 1.7812 | 5.0186 | 1.4658 |
| 255° | 5.2825 | 3.8683 | 5.4738 | 2.7801 | 5.0644 | 2.5410 | 5.0700 | 2.0701 | 5.0662 | 1.9343 | 4.9300 | 2.2788 | 4.9507 | 1.8834 | 4.8968 | 1.6307 | 4.9204 | 1.7197 | 4.8319 | 1.1253 |
| 270° | 4.6859 | 4.2330 | 4.6748 | 3.2749 | 4.6275 | 2.7571 | 4.5115 | 2.7401 | 4.6088 | 2.3565 | 4.6849 | 2.5716 | 4.5820 | 2.5422 | 4.5490 | 2.3772 | 4.9078 | 1.8362 | 4.5584 | 2.0545 |
| 285° | 5.4587 | 3.0948 | 5.3757 | 2.2367 | 5.1521 | 1.9172 | 4.8634 | 1.9642 | 4.8530 | 1.8066 | 4.7003 | 2.7205 | 4.5688 | 2.5429 | 4.5027 | 2.2719 | 4.4341 | 2.0749 | 4.4128 | 1.9002 |
| 300° | 6.7272 | 3.4897 | 6.4594 | 2.7061 | 6.3176 | 2.4254 | 6.2566 | 2.0494 | 5.8444 | 2.2178 | 6.1793 | 1.7760 | 5.8800 | 1.8404 | 5.7687 | 1.7453 | 5.6025 | 1.6869 | 5.5200 | 1.5808 |
| 315° | 7.6638 | 4.9579 | 7.3405 | 4.2297 | 7.2336 | 3.4616 | 7.0749 | 2.9898 | 6.7135 | 2.8178 | 7.1701 | 3.0324 | 6.7725 | 3.1868 | 6.2771 | 2.7622 | 6.3079 | 2.3125 | 6.2577 | 2.1921 |
| 330° | 7.5450 | 4.5689 | 7.3872 | 3.2277 | 6.7256 | 3.2009 | 7.0058 | 2.6464 | 6.6335 | 2.4751 | 6.7770 | 2.5510 | 6.7925 | 2.2418 | 6.6340 | 2.0314 | 6.3726 | 1.9480 | 6.1586 | 1.8684 |
| 345° | 7.6639 | 4.0383 | 7.5456 | 3.2610 | 7.6046 | 2.3372 | 7.2854 | 2.3774 | 6.7161 | 2.2872 | 6.8153 | 2.0664 | 6.7096 | 2.0348 | 6.5413 | 1.8508 | 6.3570 | 1.6421 | 6.2692 | 1.4692 |
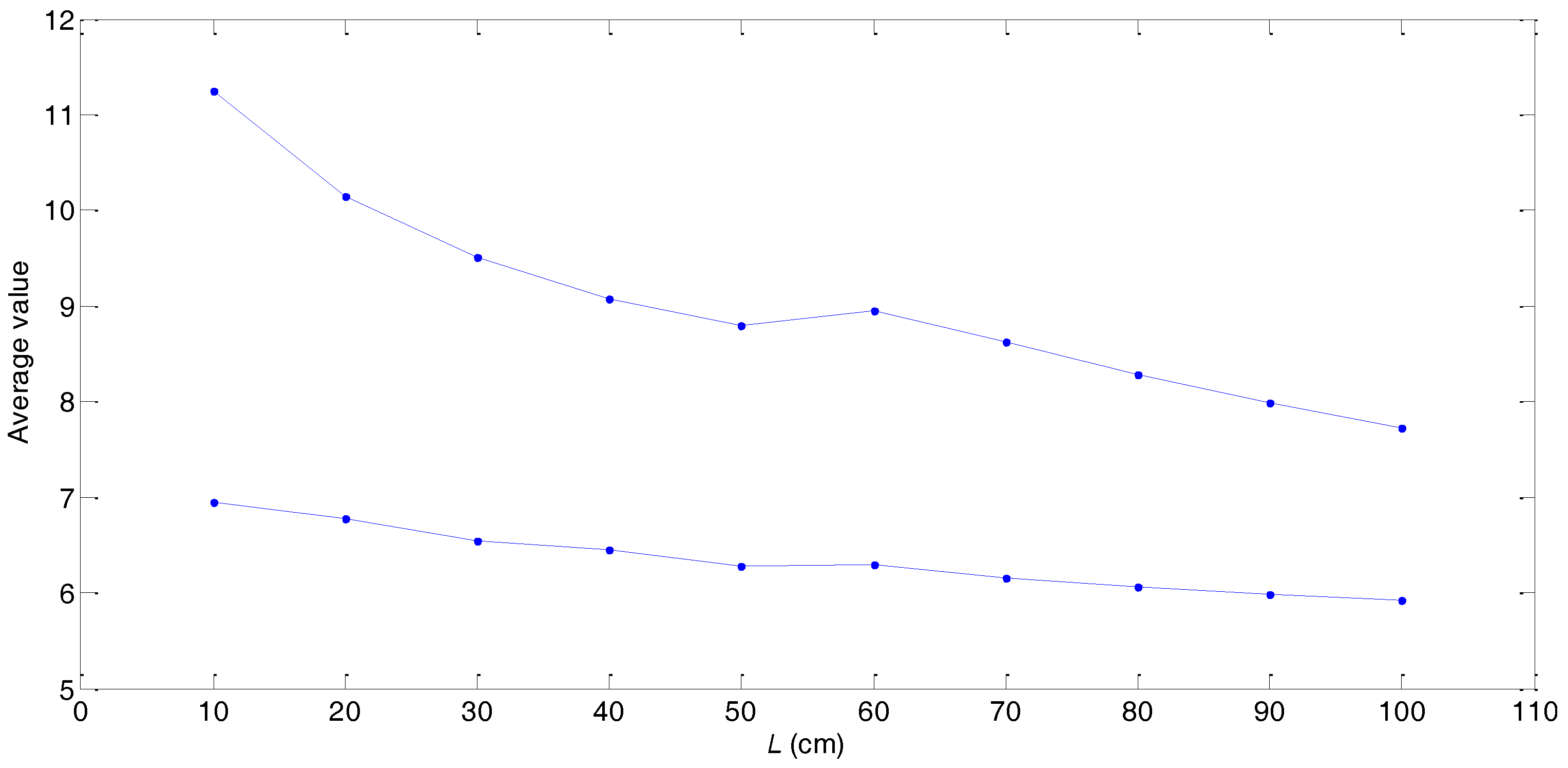
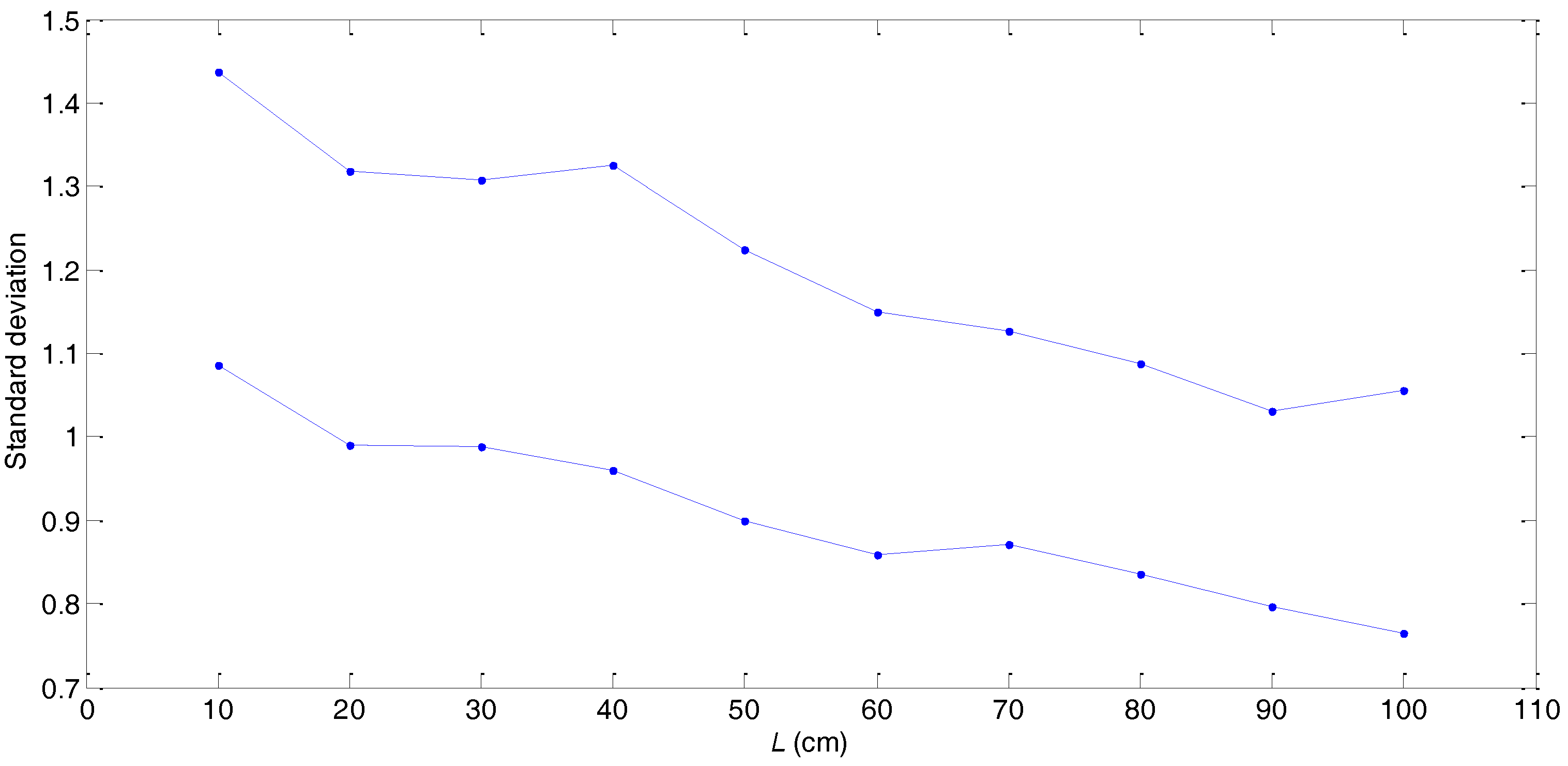
| Sample Length L | Average Value | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I [0, 1]) | ||||
| 10 cm | 6.9427 | 4.3055 | [6.9427, 11.2482] | [1.0866, 1.4375] |
| 20 cm | 6.7740 | 3.3761 | [6.7740, 10.1501] | [0.9894, 1.3176] |
| 30 cm | 6.5483 | 2.9609 | [6.5483, 9.5092] | [0.9878, 1.3073] |
| 40 cm | 6.4490 | 2.6322 | [6.4490, 9.0812] | [0.9607, 1.3257] |
| 50 cm | 6.2795 | 2.5196 | [6.2795, 8.7991] | [0.8988, 1.2243] |
| 60 cm | 6.2913 | 2.6582 | [6.2913, 8.9495] | [0.8594, 1.1493] |
| 70 cm | 6.1505 | 2.4706 | [6.1505, 8.6211] | [0.8711, 1.1260] |
| 80 cm | 6.0573 | 2.2253 | [6.0573, 8.2826] | [0.8352, 1.0883] |
| 90 cm | 5.9928 | 1.9952 | [5.9928, 7.9880] | [0.7960, 1.0300] |
| 100 cm | 5.9261 | 1.7990 | [5.9261, 7.7251] | [0.7644, 1.0553] |
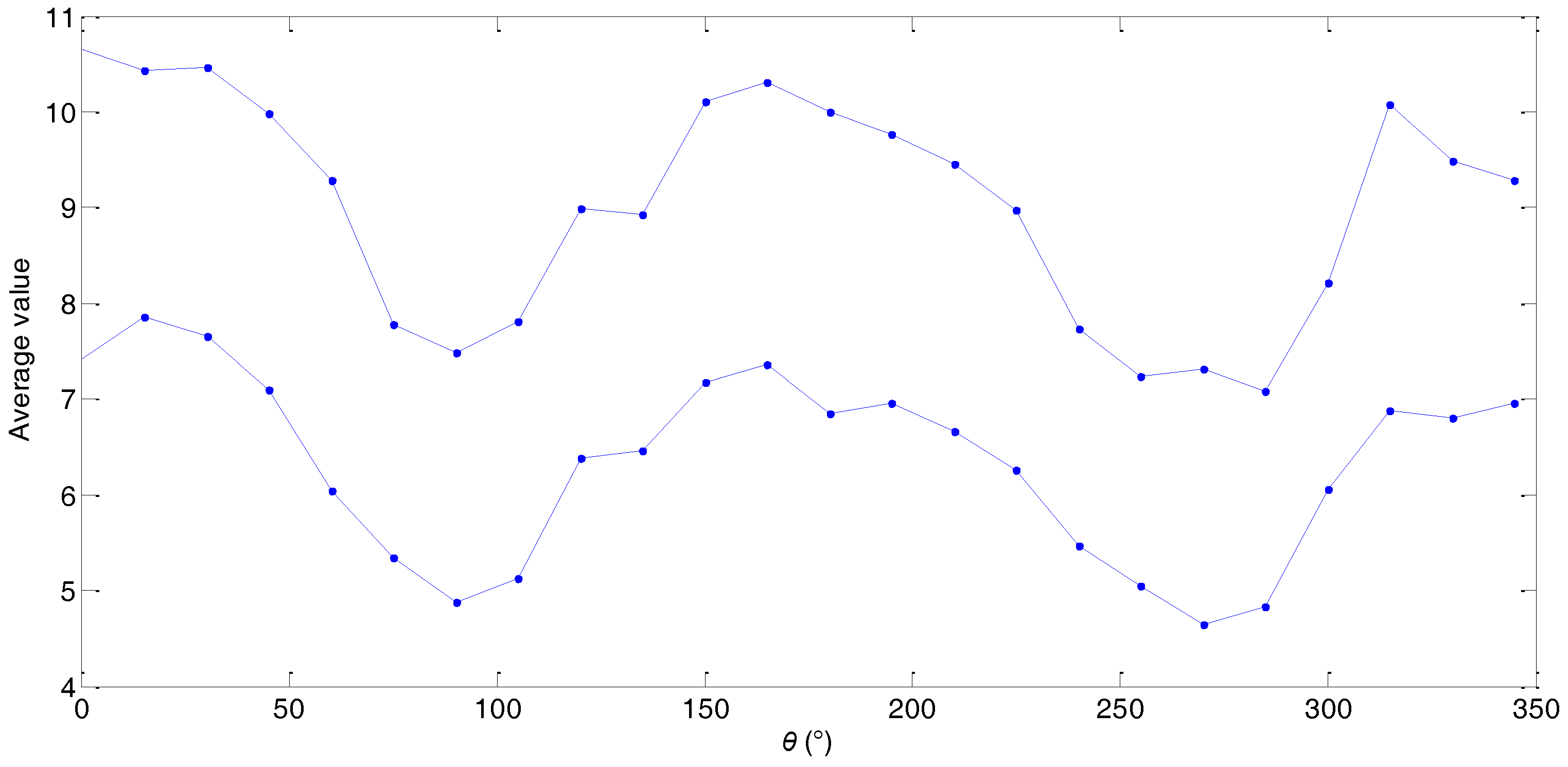
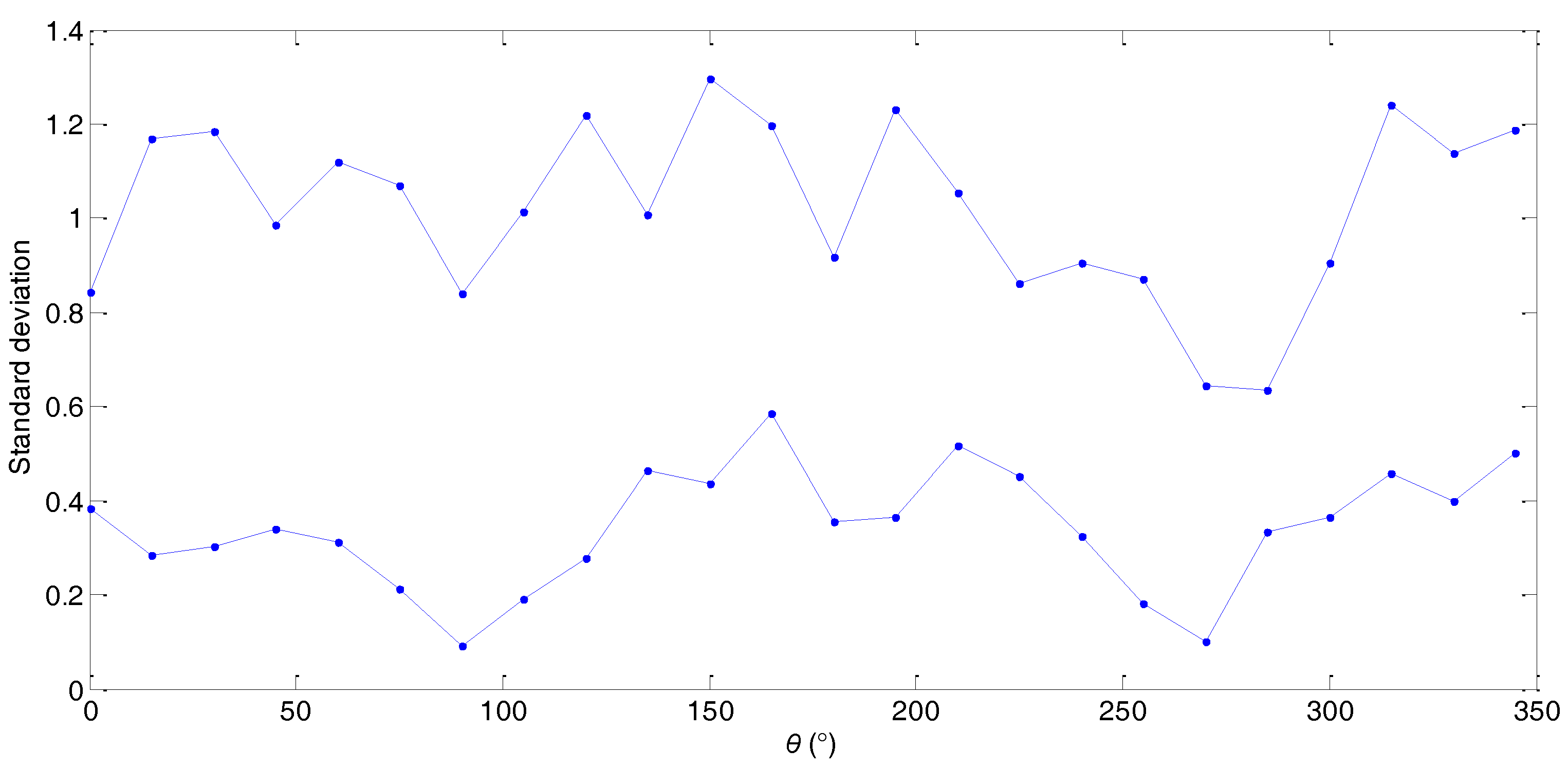
| Orientation θ | Average Value | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I [0, 1]) | ||||
| 0° | 7.4226 | 3.2309 | [7.4226, 10.6535] | [0.3844, 0.8420] |
| 15° | 7.8501 | 2.5831 | [7.8501, 10.4332] | [0.2843, 1.1698] |
| 30° | 7.6560 | 2.8152 | [7.6560, 10.4712] | [0.3013, 1.1842] |
| 45° | 7.0997 | 2.8847 | [7.0997, 9.9844] | [0.3385, 0.9850] |
| 60° | 6.0368 | 3.2555 | [6.0368, 9.2923] | [0.3130, 1.1182] |
| 75° | 5.3436 | 2.4401 | [5.3436, 7.7837] | [0.2130, 1.0704] |
| 90° | 4.8714 | 2.6187 | [4.8714, 7.4901] | [0.0907, 0.8406] |
| 105° | 5.1312 | 2.6809 | [5.1312, 7.8121] | [0.1902, 1.0122] |
| 120° | 6.3791 | 2.6061 | [6.3791, 8.9852] | [0.2789, 1.2189] |
| 135° | 6.4560 | 2.4654 | [6.4560, 8.9214] | [0.4636, 1.0067] |
| 150° | 7.1731 | 2.9296 | [7.1731, 10.1027] | [0.4368, 1.2946] |
| 165° | 7.3560 | 2.9602 | [7.3560, 10.3162] | [0.5843, 1.1961] |
| 180° | 6.8556 | 3.1400 | [6.8556, 9.9956] | [0.3554, 0.9170] |
| 195° | 6.9553 | 2.8155 | [6.9553, 9.7708] | [0.3640, 1.2298] |
| 210° | 6.6645 | 2.7889 | [6.6645, 9.4534] | [0.5157, 1.0531] |
| 225° | 6.2537 | 2.7148 | [6.2537, 8.9685] | [0.4522, 0.8612] |
| 240° | 5.4721 | 2.2640 | [5.4721, 7.7361] | [0.3255, 0.9058] |
| 255° | 5.0487 | 2.1831 | [5.0487, 7.2318] | [0.1818, 0.8701] |
| 270° | 4.6391 | 2.6743 | [4.6391, 7.3134] | [0.1003, 0.6426] |
| 285° | 4.8322 | 2.2530 | [4.8322, 7.0852] | [0.3335, 0.6340] |
| 300° | 6.0556 | 2.1518 | [6.0556, 8.2074] | [0.3653, 0.9042] |
| 315° | 6.8812 | 3.1943 | [6.8812, 10.0755] | [0.4565, 1.2396] |
| 330° | 6.8032 | 2.6760 | [6.8032, 9.4792] | [0.3983, 1.1377] |
| 345° | 6.9508 | 2.3364 | [6.9508, 9.2872] | [0.5018, 1.1878] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Du, S. Scale Effect and Anisotropy Analyzed for Neutrosophic Numbers of Rock Joint Roughness Coefficient Based on Neutrosophic Statistics. Symmetry 2017, 9, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym9100208
Chen J, Ye J, Du S. Scale Effect and Anisotropy Analyzed for Neutrosophic Numbers of Rock Joint Roughness Coefficient Based on Neutrosophic Statistics. Symmetry. 2017; 9(10):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym9100208
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiqian, Jun Ye, and Shigui Du. 2017. "Scale Effect and Anisotropy Analyzed for Neutrosophic Numbers of Rock Joint Roughness Coefficient Based on Neutrosophic Statistics" Symmetry 9, no. 10: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym9100208





