Regulation of Mammalian Gene Dosage by Long Noncoding RNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Xist lncRNA and X-Chromosome Inactivation
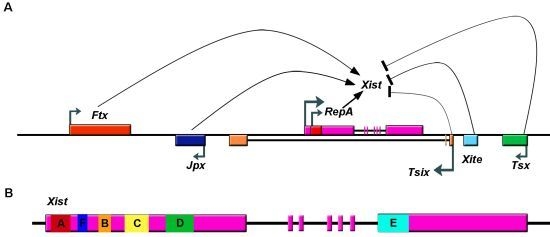
2.1. The X Inactivation Center and Xist lncRNA
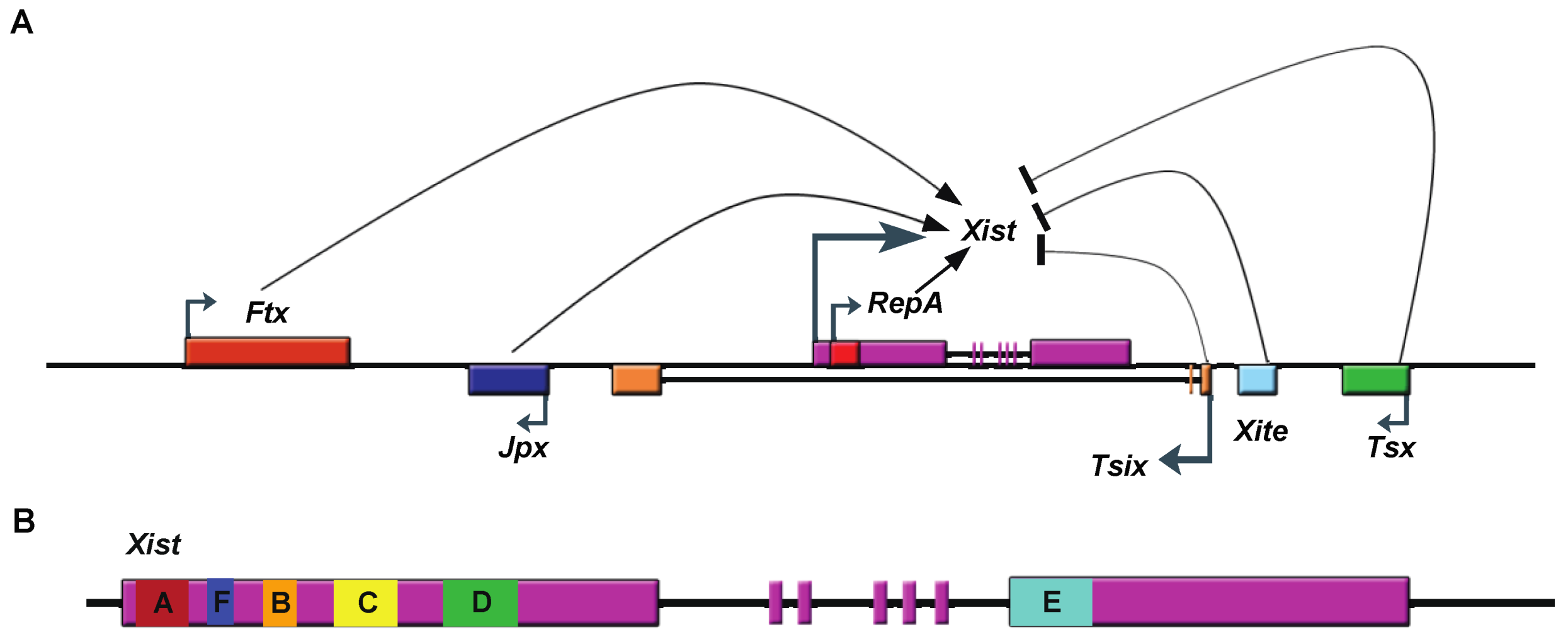
2.2. Xist RNA Contains Multiple Functional Domains
2.3. Upregulation of Xist RNA during XCI Initiation
2.3.1. LncRNAs
2.3.2. Pluripotency Factors
2.4. Loading and Spreading of Xist on the Inactivated X Chromosome
2.5. Xist Promotes Formation of a Heterochromatic Xi
2.6. Perspective
3. Imprinted lncRNA Gtl2
3.1. Discovery of Gtl2

3.2. Gtl2 Function
3.2.1. Gtl2 Regulates Genomic Imprinting
3.2.2. Gtl2 Regulates Cellular Reprogramming
3.2.3. Gtl2 Functions in Tumorigenesis
3.3. Molecular Mechanisms Potentially Underlying Gtl2 Regulation of the Dlk1-Dio3 Locus
3.3.1. Gtl2 Maintains Dlk1-Dio3 Imprinting By Protecting the Maternal IG-DMR from Methylation
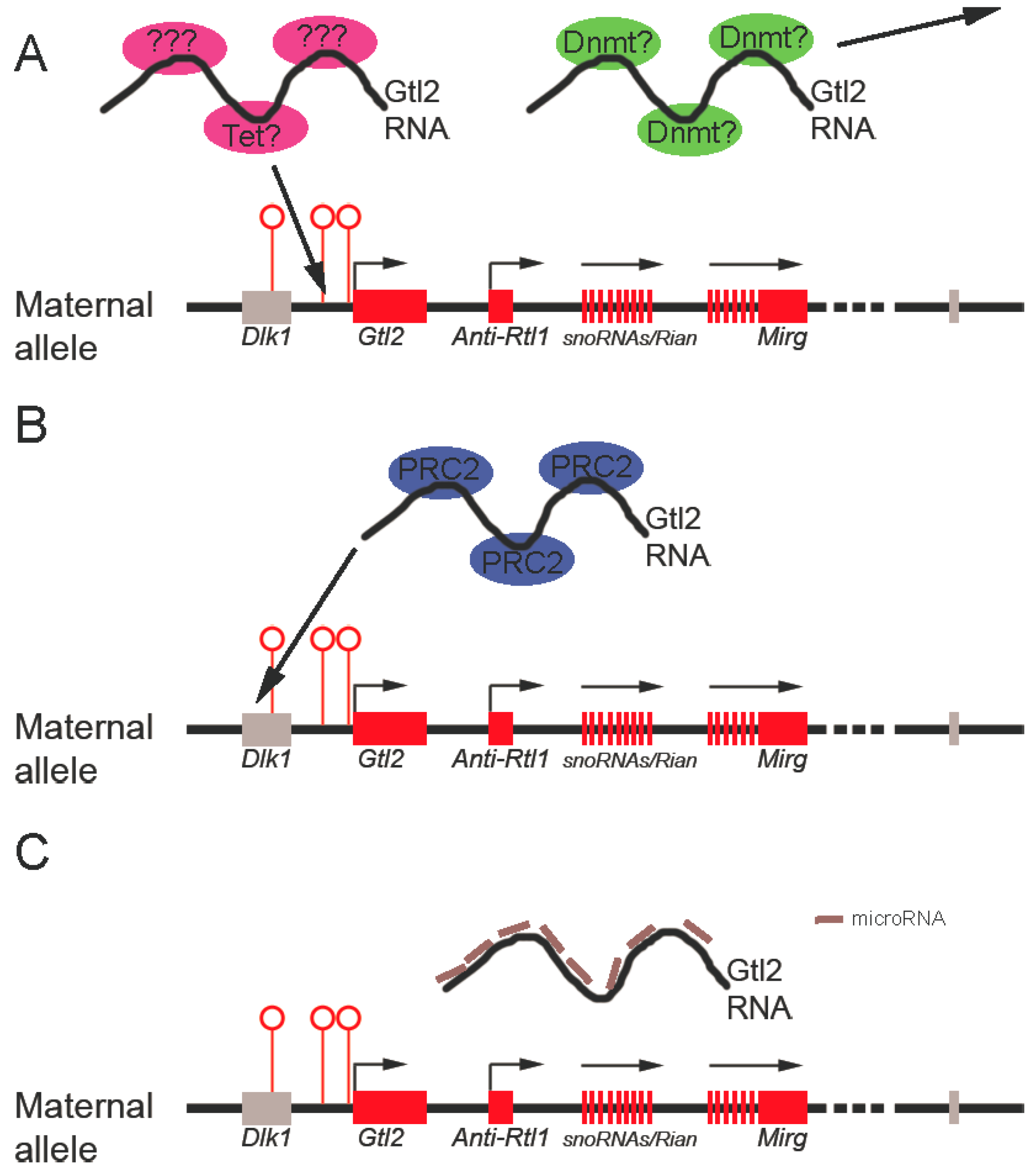
3.3.2. Gtl2 silences Gene Expression through Recruitment of Chromatin Modifying Machinery
3.3.3. Gtl2 Acts as a ceRNA to Maintain Expression of Maternally-Expressed ncRNAs
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Okazaki, Y.; Furuno, M.; Kasukawa, T.; Adachi, J.; Bono, H.; Kondo, S.; Nikaido, I.; Osato, N.; Saito, R.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cdnas. Nature 2002, 420, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, M.L.; Bertram, E.G. A morphological distinction between neurones of the male and female, and the behaviour of the nucleolar satellite during accelerated nucleoprotein synthesis. Nature 1949, 163, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, M.F. Gene action in the x-chromosome of the mouse (mus musculus l). Nature 1961, 190, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, T.S.; Gribnau, J. X chromosome inactivation in the cycle of life. Development 2012, 139, 2085–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribnau, J.; Grootegoed, J.A. Origin and evolution of x chromosome inactivation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T. Gracefully ageing at 50, x-chromosome inactivation becomes a paradigm for rna and chromatin control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendrel, A.V.; Heard, E. Fifty years of x-inactivation research. Development 2011, 138, 5049–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrelo, R.; Wutz, A. Cancer progenitors and epigenetic contexts: An xisting connection. Epigenetics: Official J. DNA Methyl. Soc. 2009, 4, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastan, S. Non-random x-chromosome inactivation in mouse x-autosome translocation embryos--location of the inactivation centre. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1983, 78, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rastan, S.; Robertson, E.J. X-chromosome deletions in embryo-derived (ek) cell lines associated with lack of x-chromosome inactivation. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1985, 90, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.J.; Lafreniere, R.G.; Powers, V.E.; Sebastio, G.; Ballabio, A.; Pettigrew, A.L.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Levy, E.; Craig, I.W.; Willard, H.F. Localization of the x inactivation centre on the human x chromosome in xq13. Nature 1991, 349, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.J.; Ballabio, A.; Rupert, J.L.; Lafreniere, R.G.; Grompe, M.; Tonlorenzi, R.; Willard, H.F. A gene from the region of the human x inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive x chromosome. Nature 1991, 349, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Borsani, G.; Tonlorenzi, R.; Simmler, M.C.; Dandolo, L.; Arnaud, D.; Capra, V.; Grompe, M.; Pizzuti, A.; Muzny, D.; Lawrence, C.; et al. Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive x chromosome. Nature 1991, 351, 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff, N.; Ashworth, A.; Kay, G.F.; Cooper, P.; Smith, S.; McCabe, V.M.; Norris, D.P.; Penny, G.D.; Patel, D.; Rastan, S. Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse xist from the inactive x chromosome. Nature 1991, 351, 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.J.; Willard, H.F. The human x-inactivation centre is not required for maintenance of x-chromosome inactivation. Nature 1994, 368, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Csankovszki, G.; Panning, B.; Bates, B.; Pehrson, J.R.; Jaenisch, R. Conditional deletion of xist disrupts histone macroh2a localization but not maintenance of x inactivation. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutz, A.; Jaenisch, R. A shift from reversible to irreversible x inactivation is triggered during es cell differentiation. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 695–705. [Google Scholar]
- Wutz, A. Gene silencing in x-chromosome inactivation: Advances in understanding facultative heterochromatin formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutz, A.; Rasmussen, T.P.; Jaenisch, R. Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of xist rna. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hoki, Y.; Kimura, N.; Kanbayashi, M.; Amakawa, Y.; Ohhata, T.; Sasaki, H.; Sado, T. A proximal conserved repeat in the xist gene is essential as a genomic element for x-inactivation in mouse. Development 2009, 136, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Royce-Tolland, M.E.; Andersen, A.A.; Koyfman, H.R.; Talbot, D.J.; Wutz, A.; Tonks, I.D.; Kay, G.F.; Panning, B. The a-repeat links asf/sf2-dependent xist rna processing with random choice during x inactivation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, B.K.; Erwin, J.A.; Song, J.J.; Lee, J.T. Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat rna to the mouse x chromosome. Science 2008, 322, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszczyk, M.M.; Zanier, K.; Sattler, M. A nmr strategy to unambiguously distinguish nucleic acid hairpin and duplex conformations applied to a xist rna a-repeat. NucleicAcids Res. 2008, 36, 7068–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszczyk, M.M.; Sattler, M. (1)h, (1)(3)c, (1)(5)n and (3)(1)p chemical shift assignments of a human xist rna a-repeat tetraloop hairpin essential for x-chromosome inactivation. Biomolecular NMRAssign. 2012, 6, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenner, S.; Blaud, M.; Fouillen, L.; Savoye, A.; Marchand, V.; Dubois, A.; Sanglier-Cianferani, S.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Clerc, P.; Avner, P.; et al. 2-d structure of the a region of xist rna and its implication for prc2 association. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Lee, J.T. Yy1 tethers xist rna to the inactive x nucleation center. Cell 2011, 146, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletskii, A.; Hong, Y.K.; Pehrson, J.; Egholm, M.; Strauss, W.M. Pna interference mapping demonstrates functional domains in the noncoding rna xist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9215–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, K.; Levasseur, P.; Aristarkhov, A.; Lee, J.T. Locked nucleic acids (lnas) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of xist rna localization to the x chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22196–22201. [Google Scholar]
- Clerc, P.; Avner, P. Role of the region 3' to xist exon 6 in the counting process of x-chromosome inactivation. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Davidow, L.S.; Warshawsky, D. Tsix, a gene antisense to xist at the x-inactivation centre. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, T.; Wang, Z.; Sasaki, H.; Li, E. Regulation of imprinted x-chromosome inactivation in mice by tsix. Development 2001, 128, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Morey, C.; Arnaud, D.; Avner, P.; Clerc, P. Tsix-mediated repression of xist accumulation is not sufficient for normal random x inactivation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar]
- Morey, C.; Navarro, P.; Debrand, E.; Avner, P.; Rougeulle, C.; Clerc, P. The region 3' to xist mediates x chromosome counting and h3 lys-4 dimethylation within the xist gene. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 594–604. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, P.; Page, D.R.; Avner, P.; Rougeulle, C. Tsix-mediated epigenetic switch of a ctcf-flanked region of the xist promoter determines the xist transcription program. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2787–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.K.; Deaton, A.M.; Lee, J.T. A transient heterochromatic state in xist preempts x inactivation choice without rna stabilization. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Pichard, S.; Ciaudo, C.; Avner, P.; Rougeulle, C. Tsix transcription across the xist gene alters chromatin conformation without affecting xist transcription: Implications for x-chromosome inactivation. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohhata, T.; Hoki, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Sado, T. Crucial role of antisense transcription across the xist promoter in tsix-mediated xist chromatin modification. Development 2008, 135, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, Y.; Sun, B.K.; Lee, J.T. Intersection of the rna interference and x-inactivation pathways. Science 2008, 320, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, P.; Oldfield, A.; Legoupi, J.; Festuccia, N.; Dubois, A.; Attia, M.; Schoorlemmer, J.; Rougeulle, C.; Chambers, I.; Avner, P. Molecular coupling of tsix regulation and pluripotency. Nature 2010, 468, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, Y.; Lee, J.T. Xite, x-inactivation intergenic transcription elements that regulate the probability of choice. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, M.C.; Ma, W.; Clift, D.; Namekawa, S.; Kelleher, R.J., 3rd; Lee, J.T. Tsx produces a long noncoding rna and has general functions in the germline, stem cells, and brain. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Sun, S.; Lee, J.T. The long noncoding rna, jpx, is a molecular switch for x chromosome inactivation. Cell 2010, 143, 390–403. [Google Scholar]
- Chureau, C.; Chantalat, S.; Romito, A.; Galvani, A.; Duret, L.; Avner, P.; Rougeulle, C. Ftx is a non-coding rna which affects xist expression and chromatin structure within the x-inactivation center region. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Chambers, I.; Karwacki-Neisius, V.; Chureau, C.; Morey, C.; Rougeulle, C.; Avner, P. Molecular coupling of xist regulation and pluripotency. Science 2008, 321, 1693–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, M.E.; Silva, S.S.; Pinter, S.F.; Xu, N.; Lee, J.T. The pluripotency factor oct4 interacts with ctcf and also controls x-chromosome pairing and counting. Nature 2009, 460, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Swigut, T.; Valouev, A.; Rada-Iglesias, A.; Wysocka, J. Sequence-specific regulator prdm14 safeguards mouse escs from entering extraembryonic endoderm fates. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, A.; Levine, S.S.; Cole, M.F.; Frampton, G.M.; Brambrink, T.; Johnstone, S.; Guenther, M.G.; Johnston, W.K.; Wernig, M.; Newman, J.; et al. Connecting microrna genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Cell 2008, 134, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, T.B.; Senner, C.E.; Schneider, J.; Alcayna-Stevens, T.; Tattermusch, A.; Hemberger, M.; Brockdorff, N. Pluripotency factor binding and tsix expression act synergistically to repress xist in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Epigenet. Chromatin 2011, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkers, I.; Barakat, T.S.; Achame, E.M.; Monkhorst, K.; Kenter, A.; Rentmeester, E.; Grosveld, F.; Grootegoed, J.A.; Gribnau, J. Rnf12 is an x-encoded dose-dependent activator of x chromosome inactivation. Cell 2009, 139, 999–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Bossenz, M.; Chung, Y.; Ma, H.; Byron, M.; Taniguchi-Ishigaki, N.; Zhu, X.; Jiao, B.; Hall, L.L.; Green, M.R.; et al. Maternal rnf12/rlim is required for imprinted x-chromosome inactivation in mice. Nature 2010, 467, 977–981. [Google Scholar]
- Surralles, J.; Natarajan, A.T. Position effect of translocations involving the inactive x chromosome: Physical linkage to xic/xist does not lead to long-range de novo inactivation in human differentiated cells. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1998, 82, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, B.C.; Tada, T.; Takagi, N.; Brockdorff, N.; Nesterova, T.B. Attenuated spread of x-inactivation in an x;autosome translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7706–7711. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, M.F. X-chromosome inactivation: A repeat hypothesis. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1998, 80, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ciaudo, C.; Fazzari, M.J.; Mise, N.; Servant, N.; Glass, J.L.; Attreed, M.; Avner, P.; Wutz, A.; Barillot, E.; et al. Line-1 activity in facultative heterochromatin formation during x chromosome inactivation. Cell 2010, 141, 956–969. [Google Scholar]
- Helbig, R.; Fackelmayer, F.O. Scaffold attachment factor a (saf-a) is concentrated in inactive x chromosome territories through its rgg domain. Chromosoma 2003, 112, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Brockdorff, N.; Kawano, S.; Tsutui, K.; Nakagawa, S. The matrix protein hnrnp u is required for chromosomal localization of xist rna. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullirsch, D.; Hartel, R.; Kishimoto, H.; Leeb, M.; Steiner, G.; Wutz, A. The trithorax group protein ash2l and saf-a are recruited to the inactive x chromosome at the onset of stable x inactivation. Development 2010, 137, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchesi, J.C.; Kelly, W.G.; Panning, B. Chromatin remodeling in dosage compensation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 615–651. [Google Scholar]
- Plath, K.; Fang, J.; Mlynarczyk-Evans, S.K.; Cao, R.; Worringer, K.A.; Wang, H.; de la Cruz, C.C.; Otte, A.P.; Panning, B.; Zhang, Y. Role of histone h3 lysine 27 methylation in x inactivation. Science 2003, 300, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.; Mak, W.; Zvetkova, I.; Appanah, R.; Nesterova, T.B.; Webster, Z.; Peters, A.H.; Jenuwein, T.; Otte, A.P.; Brockdorff, N. Establishment of histone h3 methylation on the inactive x chromosome requires transient recruitment of eed-enx1 polycomb group complexes. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 481–495. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Chen, T.; Chadwick, B.; Li, E.; Zhang, Y. Ring1b-mediated h2a ubiquitination associates with inactive x chromosomes and is involved in initiation of x inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52812–52815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Napoles, M.; Mermoud, J.E.; Wakao, R.; Tang, Y.A.; Endoh, M.; Appanah, R.; Nesterova, T.B.; Silva, J.; Otte, A.P.; Vidal, M.; et al. Polycomb group proteins ring1a/b link ubiquitylation of histone h2a to heritable gene silencing and x inactivation. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 663–676. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, I.; Otte, A.P.; Allis, C.D.; Reinberg, D.; Heard, E. Epigenetic dynamics of imprinted x inactivation during early mouse development. Science 2004, 303, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantry, S.; Mills, K.C.; Yee, D.; Otte, A.P.; Panning, B.; Magnuson, T. The polycomb group protein eed protects the inactive x-chromosome from differentiation-induced reactivation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantry, S.; Magnuson, T. The polycomb group protein eed is dispensable for the initiation of random x-chromosome inactivation. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margueron, R.; Reinberg, D. The polycomb complex prc2 and its mark in life. Nature 2011, 469, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmaier, A.; Savarese, F.; Lachner, M.; Martens, J.; Jenuwein, T.; Wutz, A. A chromosomal memory triggered by xist regulates histone methylation in x inactivation. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, E171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoeftner, S.; Sengupta, A.K.; Kubicek, S.; Mechtler, K.; Spahn, L.; Koseki, H.; Jenuwein, T.; Wutz, A. Recruitment of prc1 function at the initiation of x inactivation independent of prc2 and silencing. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3110–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhere, A.; Viiri, K.; Araujo, C.C.; Rasaiyaah, J.; Bouwman, R.D.; Whyte, W.A.; Pereira, C.F.; Brookes, E.; Walker, K.; Bell, G.W.; et al. Short rnas are transcribed from repressed polycomb target genes and interact with polycomb repressive complex-2. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 675–688. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, S.; Li, G.; Son, J.; Xu, C.F.; Margueron, R.; Neubert, T.A.; Reinberg, D. Phosphorylation of the prc2 component ezh2 is cell cycle-regulated and up-regulates its binding to ncrna. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, L.; Dimitrova, E.; Oxley, D.; Webster, J.; Poot, R.; Demmers, J.; Bezstarosti, K.; Taylor, S.; Ura, H.; Koide, H.; et al. Rybp-prc1 complexes mediate h2a ubiquitylation at polycomb target sites independently of prc2 and h3k27me3. Cell 2012, 148, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Genomic imprinting: The emergence of an epigenetic paradigm. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.; Mondal, T.; Kanduri, C. Epigenetics of imprinted long noncoding rnas. Epigenetics 2009, 4, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Mitchell, J.A.; Sanz, L.A.; Pauler, F.M.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Feil, R.; Fraser, P. The air noncoding rna epigenetically silences transcription by targeting g9a to chromatin. Science 2008, 322, 1717–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostowski, L.; Sedlak, N.; Engel, N. The kcnq1ot1 long non-coding rna affects chromatin conformation and expression of kcnq1, but does not regulate its imprinting in the developing heart. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.R.; Mondal, T.; Mohammad, F.; Enroth, S.; Redrup, L.; Komorowski, J.; Nagano, T.; Mancini-Dinardo, D.; Kanduri, C. Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding rna mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 232–246. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster-Gossler, K.; Simon-Chazottes, D.; Guenet, J.L.; Zachgo, J.; Gossler, A. Gtl2lacz, an insertional mutation on mouse chromosome 12 with parental origin-dependent phenotype. Mammal. Genome : Official J. Int. Mammal. Genome Soc. 1996, 7, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster-Gossler, K.; Bilinski, P.; Sado, T.; Ferguson-Smith, A.; Gossler, A. The mouse gtl2 gene is differentially expressed during embryonic development, encodes multiple alternatively spliced transcripts, and may act as an rna. Dev. Dyn. 1998, 212, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattanach, B.M.; Rasberry, C. Evidence of imprinting involving the distal region of chr. 12. Mouse Genome 1994, 91, 858. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.V.; Matteson, P.G.; Jones, B.K.; Guan, X.J.; Tilghman, S.M. The dlk1 and gtl2 genes are linked and reciprocally imprinted. GenesDevelop. 2000, 14, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, N.; Wagatsuma, H.; Wakana, S.; Shiroishi, T.; Nomura, M.; Aisaka, K.; Kohda, T.; Surani, M.A.; Kaneko-Ishino, T.; Ishino, F. Identification of an imprinted gene, meg3/gtl2 and its human homologue meg3, first mapped on mouse distal chromosome 12 and human chromosome 14q. Genes Cells 2000, 5, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, S.; Tevendale, M.; Baker, J.; Georgiades, P.; Campbell, E.; Freeman, T.; Johnson, M.H.; Paulsen, M.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Delta-like and gtl2 are reciprocally expressed, differentially methylated linked imprinted genes on mouse chromosome 12. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekita, Y.; Wagatsuma, H.; Irie, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Kohda, T.; Matsuda, J.; Yokoyama, M.; Ogura, A.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Gossler, A.; et al. Aberrant regulation of imprinted gene expression in gtl2lacz mice. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2006, 113, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steshina, E.Y.; Carr, M.S.; Glick, E.A.; Yevtodiyenko, A.; Appelbe, O.K.; Schmidt, J.V. Loss of imprinting at the dlk1-gtl2 locus caused by insertional mutagenesis in the gtl2 5' region. BMC Genet. 2006, 7, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, H.; Youngson, N.; Lin, S.P.; Dalbert, S.; Paulsen, M.; Bachellerie, J.P.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Cavaille, J. Imprinted microrna genes transcribed antisense to a reciprocally imprinted retrotransposon-like gene. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.E.; Lin, S.P.; Ito, M.; Takagi, N.; Takada, S.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Genomic imprinting contributes to thyroid hormone metabolism in the mouse embryo. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Yevtodiyenko, A.; Carr, M.S.; Patel, N.; Schmidt, J.V. Analysis of candidate imprinted genes linked to dlk1-gtl2 using a congenic mouse line. Mammal. Genome: Official J. Int. Mammal. Genome Soc. 2002, 13, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaille, J.; Seitz, H.; Paulsen, M.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Bachellerie, J.P. Identification of tandemly-repeated c/d snorna genes at the imprinted human 14q32 domain reminiscent of those at the prader-willi/angelman syndrome region. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Tierling, S.; Dalbert, S.; Schoppenhorst, S.; Tsai, C.E.; Oliger, S.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Paulsen, M.; Walter, J. High-resolution map and imprinting analysis of the gtl2-dnchc1 domain on mouse chromosome 12. Genomics 2006, 87, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Geuns, E.; De Temmerman, N.; Hilven, P.; Van Steirteghem, A.; Liebaers, I.; De Rycke, M. Methylation analysis of the intergenic differentially methylated region of dlk1-gtl2 in human. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 15, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheunsuchon, P.; Nakayama, Y.; Lawlor, M.W.; Zhong, Y.; Rice, K.A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Gordon, F.E.; Lidov, H.G.; et al. Activation of paternally expressed genes and perinatal death caused by deletion of the gtl2 gene. Development 2010, 137, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.P.; Youngson, N.; Takada, S.; Seitz, H.; Reik, W.; Paulsen, M.; Cavaille, J.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Asymmetric regulation of imprinting on the maternal and paternal chromosomes at the dlk1-gtl2 imprinted cluster on mouse chromosome 12. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Okamoto, A.; Kobayashi, R.; Shirai, M.; Obata, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Sotomaru, Y.; Kono, T. Deletion of gtl2, imprinted non-coding rna, with its differentially methylated region induces lethal parent-origin-dependent defects in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Stadtfeld, M.; Apostolou, E.; Akutsu, H.; Fukuda, A.; Follett, P.; Natesan, S.; Kono, T.; Shioda, T.; Hochedlinger, K. Aberrant silencing of imprinted genes on chromosome 12qf1 in mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2010, 465, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Stadtfeld, M.; Apostolou, E.; Ferrari, F.; Choi, J.; Walsh, R.M.; Chen, T.; Ooi, S.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Bestor, T.H.; Shioda, T.; et al. Ascorbic acid prevents loss of dlk1-dio3 imprinting and facilitates generation of all-ips cell mice from terminally differentiated b cells. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 398-405, S391-S392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempiainen, H.; Couttet, P.; Bolognani, F.; Muller, A.; Dubost, V.; Luisier, R.; Del Rio Espinola, A.; Vitry, V.; Unterberger, E.; Thomson, J.P.; et al. Identification of dlk1-dio3 imprinted gene cluster non-coding rnas as novel candidate biomarkers for liver tumor promotion. Toxicol. Sci.: Official J. Soc. Toxicol. 2012, 131, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Mehta, K.R.; Danila, D.C.; Scolavino, S.; Johnson, S.R.; Klibanski, A. A pituitary-derived meg3 isoform functions as a growth suppressor in tumor cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2003, 88, 5119–5126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Ren, Z.; Sun, P. Overexpression of the long non-coding rna meg3 impairs in vitro glioma cell proliferation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gejman, R.; Mahta, A.; Zhong, Y.; Rice, K.A.; Zhou, Y.; Cheunsuchon, P.; Louis, D.N.; Klibanski, A. Maternally expressed gene 3, an imprinted noncoding rna gene, is associated with meningioma pathogenesis and progression. CancerRes. 2010, 70, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Batista, D.L.; Gejman, R.; Ansell, P.J.; Zhao, J.; Weng, C.; Klibanski, A. Activation of p53 by meg3 non-coding rna. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24731–24742. [Google Scholar]
- Braconi, C.; Kogure, T.; Valeri, N.; Huang, N.; Nuovo, G.; Costinean, S.; Negrini, M.; Miotto, E.; Croce, C.M.; Patel, T. Microrna-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding rna gene meg3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4750–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, F.E.; Nutt, C.L.; Cheunsuchon, P.; Nakayama, Y.; Provencher, K.A.; Rice, K.A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Klibanski, A. Increased expression of angiogenic genes in the brains of mouse meg3-null embryos. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding rnas. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, M.S.; Yevtodiyenko, A.; Schmidt, C.L.; Schmidt, J.V. Allele-specific histone modifications regulate expression of the dlk1-gtl2 imprinted domain. Genomics 2007, 89, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, E.N.; Schmidt, J.V. Identification of imprinting regulators at the meg3 differentially methylated region. Genomics 2012, 100, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ohsumi, T.K.; Kung, J.T.; Ogawa, Y.; Grau, D.J.; Sarma, K.; Song, J.J.; Kingston, R.E.; Borowsky, M.; Lee, J.T. Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated rnas by rip-seq. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H. Redefining microrna targets. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Sarnow, P.; Kay, M.A. Biological basis for restriction of microrna targets to the 3' untranslated region in mammalian mrnas. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cesana, M.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Santini, T.; Sthandier, O.; Chinappi, M.; Tramontano, A.; Bozzoni, I. A long noncoding rna controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous rna. Cell 2011, 147, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, K.-H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.C. Regulation of Mammalian Gene Dosage by Long Noncoding RNAs. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 124-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010124
Hung K-H, Wang Y, Zhao JC. Regulation of Mammalian Gene Dosage by Long Noncoding RNAs. Biomolecules. 2013; 3(1):124-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010124
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Ko-Hsuan, Yang Wang, and Jing Crystal Zhao. 2013. "Regulation of Mammalian Gene Dosage by Long Noncoding RNAs" Biomolecules 3, no. 1: 124-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010124