Mesoporous Silica SBA-15 Particles in a Detergent Solution as Abrasive and Coating Material for Household Care Cleaning Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SBA-15 Synthesis and Surface Modification
2.2. Detergent Solutions
2.3. Ergo Ring Testing for Estimation of Primary and Secondary Cleaning Effort
2.4. QCM-D Measurements for Estimation of Detergents Coating Efficiency
2.5. Contact Angle Measurements for Estimation of Substrates Wetting Properties
3. Results
3.1. Primary Cleaning
3.2. Secondary Cleaning
3.3. Coating Efficiency of Neodol 91-5 and SBA-15
3.4. Wettability of Substrates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farn, R.J. Chemistry and Technology of Surfactants; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006; ISBN 1405126965. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, K.; Bo, J.; Kronberg, B. Solution and Polymers in Aqueous Solution, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2002; ISBN 0471498831. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, Ministry of Economic Affairs. Cleaning & Laundry Products Fact Sheet; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Malkin, S.; Guo, C. Handbook of Detergents, 1st ed.; Showell, M.S., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780831132477. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Chen, R. Preparation and polishing properties of spherical porous silica abrasive. Am. J. Nanotechnol. 2010, 1, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissel Pilcher Australian Stainless Steel Development Association. Available online: https://www.assda.asn.au/blog/185-coated-abrasives-for-surface-finishing (accessed on 20 June 2018).
- Canham, L. Mechanical Properties of Porous Silicon. In Handbook of Porous Silicon; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bindzil CC in Waterborne Coating Applications Product Overviews; AkzoNobel: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011.
- Colloidal silica dispersions for Hard Surface Cleaning; EKA Chemocals: Bohus, Sweden, 2011.
- Siriviriyanun, A.; Imae, T. Anti-fingerprint properties of non-fluorinated organosiloxane self-assembled monolayer-coated glass surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, G.; Gao, Y.; An, Y. Surface wettability of (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane self-assembled Monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meynen, V.; Cool, P.; Vansant, E.F. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials Verified syntheses of mesoporous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 125, 170–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, M.C.; Markowitz, M.A.; Spector, M.S.; Gaber, B.P. Direct Synthesis of Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Functional Incorporation by Co-condensation with Organosilanes. J. Phys. Chem. 2001, 105, 9935–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoulia, S.A.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Lemonidou, A.A. Preparation and characterization of vanadia catalysts supported on non-porous, microporous and mesoporous silicates for oxidative dehydrogenation of propane (ODP). Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 110, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Shea, K.J.; Kitagawa, S. Hybrid materials themed issue organosilicas prepared from bridged organosilane precursors w. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.Y.; Zhao, X.S.; Li, X.; Chia, P.A.; Li, J. A Novel Route toward the Synthesis of High-Quality Large-Pore Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas. J. Phys. Chem. 2004, 108, 4684–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giliopoulos, D.I. Development of New Nanocomposite Materials of Epoxy Resins with Advanced Nanostructure of Silica. Ph.D. Thesis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, B.A.; Melde, B.J.; Schroden, R.C. Hybrid Inorganic-Organic Mesoporous Silicates-Nanoscopic Reactors Coming of Age. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.V.; Kulkarni, M.M.; Amalnerkar, D.P.; Seth, T. Surface chemical modification of silica aerogels using various alkyl-alkoxy/chloro silanes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 206, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lian, H.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C. Physicochemical properties of poly (ethylene oxide)-based composite polymer electrolytes with a silane-modified mesoporous silica SBA-15. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3490–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plc, U. Hard-Surface Cleaning Compositions World Intellectual Property Organization. Patent WO1998040452A1, 17 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Garoff, S.; Tilton, R.D. Experimental observations on the scaling of adsorption isotherms for nonionic surfactants at a hydrophobic solid-water interface. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4446–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontturi, K.S.; Tammelin, T.; Johansson, L.S.; Stenius, P. Adsorption of cationic starch on cellulose studied by QCM-D. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4743–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, N.R. Studies on Adsorption and Wetting Phenomena Associated with Solid Surfaces in Aqueous Synthetic and Natural Surfactant Solutions; National Institute of Technology: Odisha, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, D.Y.; Neumann, A.W. Contact angle measurement and contact angle interpretation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 81, 167–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żenkiewicz, M. Methods for the calculation of surface free energy of solids. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 24, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rudawska, A.; Jacniacka, E. Analysis for determining surface free energy uncertainty by the Owen-Wendt method. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2009, 29, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéré, D. Wetting and Roughness. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasaki, G.J. Wettability: Fundamentals and Surface Forces. SPE Form. Eval. 1991, 6, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.N.C. Study of Advancing & Receding Contact Angles and Contact Angle Hysteresis; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Mayer, D.; Offenhäusser, A.; Ingebrandt, S. Surface activation of thin silicon oxides by wet cleaning and silanization. Thin Solid Films 2006, 510, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cras, J.J.; Rowe-Taitt, C.A.; Nivens, D.A.; Ligler, F.S. Comparison of chemical cleaning methods of glass in preparation for silanization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999, 14, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazauskas, A.; Grigaliūnas, V. Float Glass Surface Preparation Methods for Improved Chromium Film Adhesive Bonding. Mater. Sci. 2012, 18, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

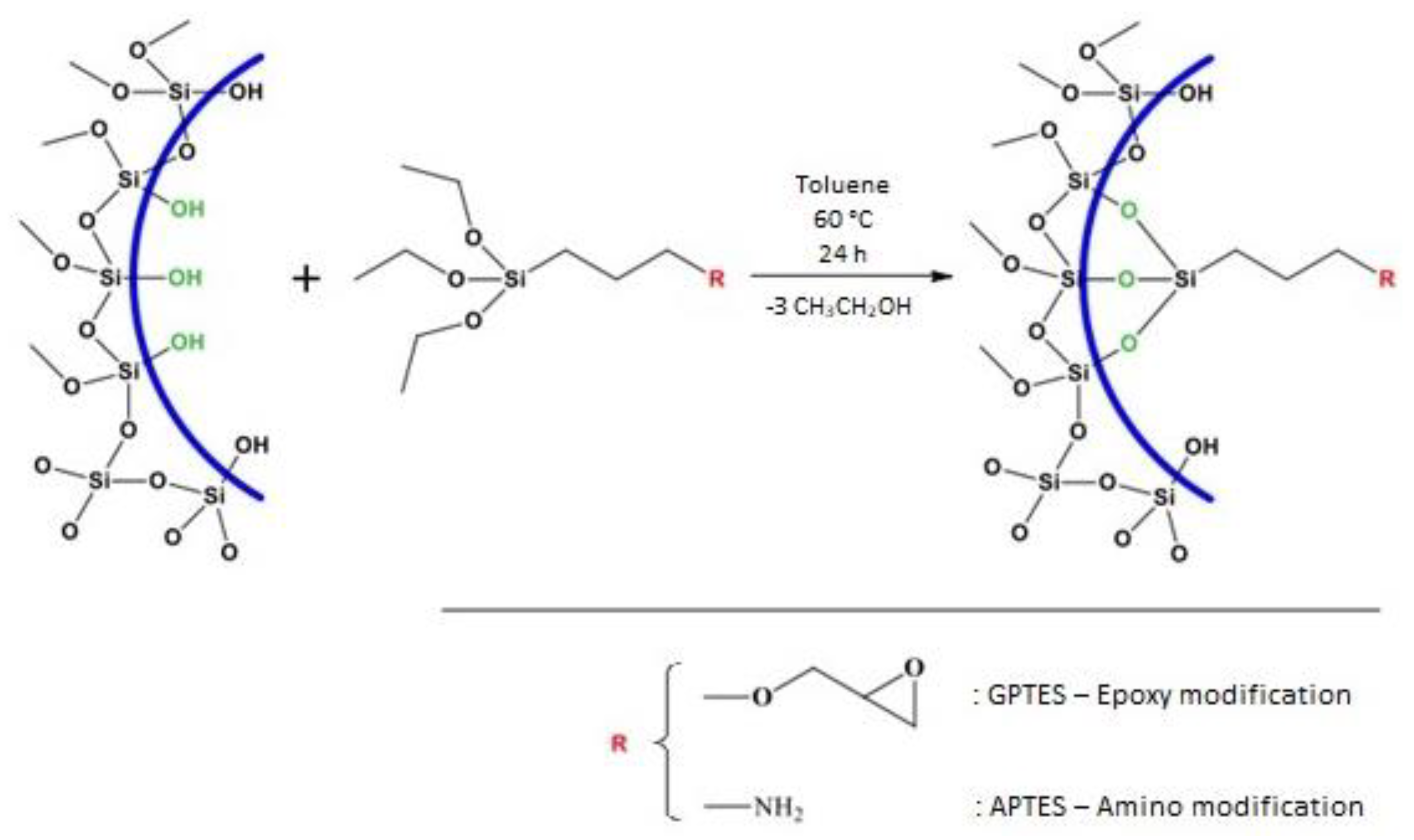




| Material | Description | Synthesis Path |
|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | SBA-15 is a mesoporous silica with hexagonally ordered cylindrical pores. | • Pluronic P123 in aq. HCl, 1.6 (40 °C, stirring for 1 h) • Add TEOS (40 °C, stirring for 24 h) • Aging of the suspension (100 °C, no stirring, 72 h) • Filtration, wash by water, dry at room temperature • Calcination at 550 °C for 6 h, 1 °C/min |
| SBA-15-1 | This material is a SBA silica modified by GPTES, (3-Glycidyloxypropyl) trimethoxysilane. | • Dispersion of SBA-15 in toluene. • Addition of GPTES (60 °C, stirring for 24 h) • Filtration, wash by toluene, ethanol and distilled water • Drying at room temperature for 4 days |
| SBA-15-2 | This material is a SBA-15 silica modified by APTES, (3-Aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane. | • Dispersion of SBA-15 in toluene. • Addition of APTES (60 °C, stirring for 24 h) • Filtration, wash by toluene, ethanol and distilled water • Dry at room temperature for 4 days |
| Material | Δm (ng/cm2) |
|---|---|
| SBA-15 | 62.59 |
| SBA-15-1 | 24.85 |
| SBA-15-2 | 9.45 |
| Neodol 91-5 | 43.68 |
| Neodol 91-5 with SBA-15 | 91.01 |
| Neodol 91-5 with SBA-15-1 | 74.52 |
| Neodol 91-5 with SBA-15-2 | 52.51 |
| Water | Dodecane | Diiodomethane | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | MeOH:HCl | Clean | MeOH:HCl | Clean | MeOH:HCl | |||||||||
| s | a | r | S | a | R | s | a | r | s | A | r | s | s | |
| Glass | 31° (±2) | 36° (±1) | 9° (±2) | 18° (±1) | 25° (±1) | 8° (±4) | <3° | 6° (±1) | n. | <3° | 6° (±1) | n. | 48° (±4) | 51° (±6) |
| Melamine | 50° (±2) | 65° (±4) | 50° (±2) | 96° (±2) | 97° (±2) | 54° (±2) | <3° | 6° (±1) | n. | <3° | 6° (±1) | n. | 39° (±3) | 38° (±2) |
| Teflon | 115° (±2) | 123° (±1) | 90° (±2) | 115° (±2) | 127° (±2) | 91° (±2) | 29° (±2) | 36° (±1) | 8° (±2) | 39° (±3) | 36° (±1) | 8° (±2) | 83° (±3) | 75° (±6) |
| Substrate | Preparation Method | SFE Calculation Method: Owens–Wendt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dispersive Component (mN/m) | Polar Component (mN/m) | Total SFE (mN/m) | ||
| Glass | Clean | 35.38 (±2.20) | 31.10 (±1.69) | 66.49 (±3.89) |
| MeOH:HCl | 33.71 (±3.37) | 37.80 (±2.36) | 71.52 (±5.72) | |
| Melamine | Clean | 40.11 | 17.92 | 58.03 |
| MeOH:HCl | 40.60 | 0.16 | 40.76 | |
| Teflon | Clean | 15.98 | 0.11 | 16.09 |
| MeOH:HCl | 20.12 | 0.00 | 20.12 | |
| Substrate | Water | Dodecane | Diiodomethane | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | a | r | s | a | r | s | |
| Glass | 8° (±1) | 16° (±2) | 8° (±2) | n. | n. | n. | 39° (±5) |
| Melamine | 6° (±2) | 12° (±3) | 10° (±3) | n. | n. | n. | 31° (±6) |
| Teflon | 54° (±4) | 64° (±4) | 13° (±4) | 32° (±2) | 40° (±2) | 14° (±2) | 76° (±9) |
| Substrate | Coating | SFE Calculation Method: Owens–Wendt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dispersive Component (mN/m) | Polar Component (mN/m) | Total SFE (mN/m) | ||
| Glass | Neodol 91-5 & SBA-15 | 40.11 | 36.05 | 76.16 |
| Melamine | Neodol 91-5 & SBA-15 | 43.8 | 34.09 | 77.9 |
| Teflon | Neodol 91-5 & SBA-15 | 19.59 | 27.03 | 46.62 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plomaritis, A.; Giliopoulos, D.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Kostoglou, M.; Karapantsios, T.D. Mesoporous Silica SBA-15 Particles in a Detergent Solution as Abrasive and Coating Material for Household Care Cleaning Products. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010012
Plomaritis A, Giliopoulos D, Triantafyllidis K, Kostoglou M, Karapantsios TD. Mesoporous Silica SBA-15 Particles in a Detergent Solution as Abrasive and Coating Material for Household Care Cleaning Products. Colloids and Interfaces. 2019; 3(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010012
Chicago/Turabian StylePlomaritis, Athanasios, Dimitris Giliopoulos, Konstantinos Triantafyllidis, Margaritis Kostoglou, and Thodoris D. Karapantsios. 2019. "Mesoporous Silica SBA-15 Particles in a Detergent Solution as Abrasive and Coating Material for Household Care Cleaning Products" Colloids and Interfaces 3, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010012
APA StylePlomaritis, A., Giliopoulos, D., Triantafyllidis, K., Kostoglou, M., & Karapantsios, T. D. (2019). Mesoporous Silica SBA-15 Particles in a Detergent Solution as Abrasive and Coating Material for Household Care Cleaning Products. Colloids and Interfaces, 3(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010012









