Advanced Surface Coating of Nanoparticles
A topical collection in Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Aspects in Colloid and Interface Science".
Viewed by 70376Editors
2. School of Biological Sciences and Engineering, Yachay TechSan Miguel de Urcuquí, Ecuador
Interests: sonochemistry; colloid and polymers; nanomaterials; rubber technology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
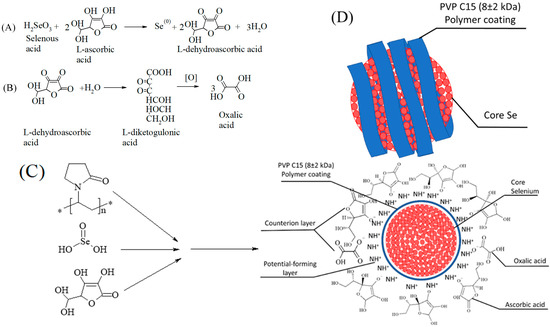
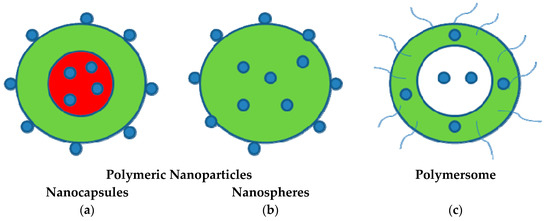
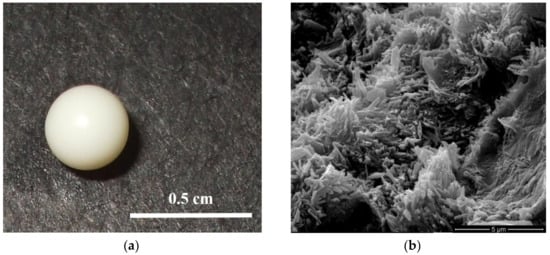
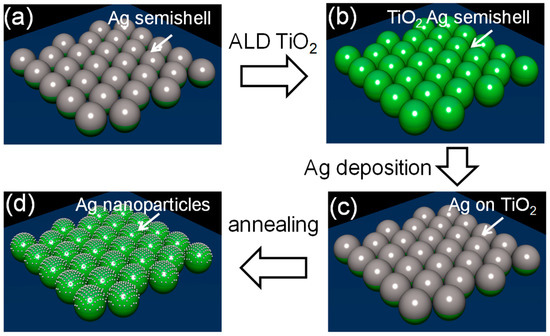
We would like to invite you to submit your work to this Special Issue on "Advanced Surface Coating of Nanoparticles". Generally, surface coatings of nanomaterials are applied in order to selectively change or influence their properties. For this purpose, the surface of a particle (the “core“) can be coated, which, in return, generates single- or multi-layers layer(s) (the “shell”) that can be either complete or incomplete. Surface coating of nanoparticles includes modification, functionalization, or stabilization to enhance their imaging, drug delivery, stability, antireflection, anticorrosion, antifogging, UV resistant, prevent sulfurization, anti microbial, self-cleaning, biological response, biocompatibility, safety, reactivity properties etc. These coated nanomaterials have electronics, military, energy, biomedical, environmental, textile, automotive, and aerospace applications. The aim of this Special Issue is to present the latest developments in the field of coating nanoparticles, through a combination of original research papers and review articles from leading groups around the world.
In particular, the topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Organic/inorganic coating combinations on nanoparticles;
- Single/Multiple layer coatings on nanoparticles;
- Biological coatings on nanoparticles;
- Janus coatings on nanoparticles;
- Manufactoring technologies to coat nanoparticles.
Prof. Dr. Frank Alexis
Dr. Patrick Tang Siah Ying
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Coatings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.