Sustainable Innovation in Organizations for Improving Decisions
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Amparo Cervera-Taulet
Prof. Dr. Amparo Cervera-Taulet
 Prof. Dr. Amparo Cervera-Taulet
Prof. Dr. Amparo Cervera-Taulet
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Marketing, University of Valencia, 46022 Valencia, Spain
Interests: strategic resources and capabilities for innovation; sustainable entrepreneurship; service research, co-creation
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The search for sustainability has recognized the importance of balancing competing priorities of environmental protection, economic growth and social equity. However, academics have noticed that this “triple bottom line approach” is far from being the dominant business model for companies.
Classification schemas, lists, and frameworks have been proposed in the literature as roadmaps for firms to identify potential sustainable innovation opportunities. However, definitions of sustainable innovation have traditionally been limited to products and to its environmental dimension. Considering sustainable innovation as the result of a learning process that changes the company generating knowledge for the modification or introduction of new products / services / processes in the market that are sustainable in economic, environmental and social terms, potential areas for academic research emerge.
The studies of this Topical Collection are expected to address:
- Sustainable innovation construct operationalizations,
- External and internal drivers of sustainable innovation, moderating factors,
- Management of sustainable innovation,
- Sustainable innovation orientation,
- Performance outcomes of sustainable innovation: value co-creation,
- Marketing aspects of sustainable innovation,
- Consumer aspects of sustainable innovation,
- Sustainable innovation ecosystems,
- Market-oriented sustainable innovations
- Economic, social, and environmental aspects in sustainable innovation activities,
- Sustainable innovation in public and nonprofit organizations,
- Education for sustainable innovation,
- Sectorial applications of sustainable innovation.
Prof. Dr. Domingo Enrique Ribeiro-Soriano
Prof. Dr. Amparo Cervera-Taulet
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- sustainable innovation
- performance
- models
- value
- ecosystems
- environmental
- social
- economic
Published Papers (27 papers)
Open AccessArticle
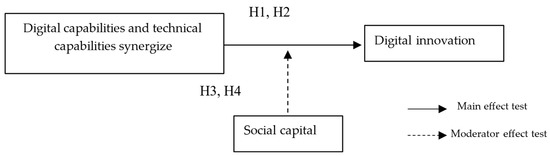
Research on the Synergic Influences of Digital Capabilities and Technological Capabilities on Digital Innovation
by
Hongyang Wang and Baizhou Li
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1909
Abstract
Digital innovation is the key for enterprises to obtain core competitiveness in today’s increasingly fierce market environment. Based on a sample of high-tech manufacturing companies listed in the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-shares from 2011 to 2020, this paper empirically tests the impact mechanism
[...] Read more.
Digital innovation is the key for enterprises to obtain core competitiveness in today’s increasingly fierce market environment. Based on a sample of high-tech manufacturing companies listed in the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-shares from 2011 to 2020, this paper empirically tests the impact mechanism of the synergic influence of digital capabilities and technological capabilities of enterprises on digital innovation by using static panel regression, dynamic panel regression, and the moderation of social capital on their relationship. The results show that the synergic influence of digital capability and technology absorptive capability has a positive correlation with enterprise digital innovation. The synergy of digital capabilities and technological innovation capabilities has a positive correlation with enterprise digital innovation. Social capital plays a positive moderating role in the impact of the two synergic influences on digital innovation. The results imply that strengthening the coordinated development of digital capabilities and technological capabilities is essential for enterprises to carry out digital innovation, which is of great significance for the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
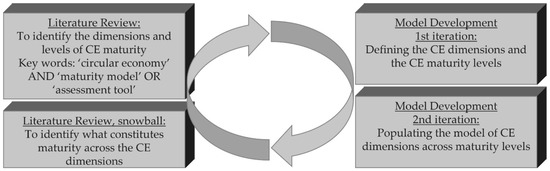
Maturity Model as a Driver for Circular Economy Transformation
by
Jonas Nygaard Uhrenholt, Jesper Hemdrup Kristensen, Maria Camila Rincón, Sofie Adamsen, Steffen Foldager Jensen and Brian Vejrum Waehrens
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2856
Abstract
The movement of manufacturing organisations towards a circular economy sets the scene for extensive industrial change. This change is not simply a continuation of current business; instead, it brings up multiple questions concerning ways of thinking, modes of operation, and the very foundation
[...] Read more.
The movement of manufacturing organisations towards a circular economy sets the scene for extensive industrial change. This change is not simply a continuation of current business; instead, it brings up multiple questions concerning ways of thinking, modes of operation, and the very foundation of a business. Manufacturing organisations are experiencing uncertainty regarding how to address this transformation due to its multi-faceted nature. Maturity models are seen by some as a tool for assessing and guiding manufacturing organisations when it comes to complex and multi-faceted agendas, such as that of the circular economy (CE). Maturity models provide scaffolding in the form of presentation of a desired evolution path from which manufacturing organisations can define reasonable and desirable plans for engagement with the circular economy. This study adopts the cumulative capability perspective in developing a CE maturity reference model that explicates the circular transformation by noting six discrete maturity levels across six organisational dimensions: value creation, governance, people and skills, supply chain and partnership, operations and technology, and product and material. The progression of circular maturity is explained by the principles of expertise and the systems perspective. The explication of CE transformation across dimensions and levels provides a boundary object for organisations, i.e., a scaffolding for moving from its current zone of development to its proximal zone of development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
CSR Strategy in Tourism during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Maria Johann
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 5395
Abstract
Travel and tourism is one of the most affected sectors due to the COVID-19 pandemic, impacting economies, enterprises, and livelihoods worldwide. The pandemic has heavily damaged businesses across the tourism industry, including airlines, transportation, hotels, cruises, and others. Numerous tourism companies went bankrupt
[...] Read more.
Travel and tourism is one of the most affected sectors due to the COVID-19 pandemic, impacting economies, enterprises, and livelihoods worldwide. The pandemic has heavily damaged businesses across the tourism industry, including airlines, transportation, hotels, cruises, and others. Numerous tourism companies went bankrupt or had been struggling to survive, yet other ones have adapted their strategy and seized the crisis to transform their business for the post-pandemic future. This study aims at investigating the TUI Group’s CSR strategic adaptability during the COVID-19 pandemic. The case study is based on a documentary analysis including such documents as annual reports, sustainability strategy, sustainability reports, and financial statements. The findings show that the pandemic crisis moved forward the company’s transformation into a digital platform and its sustainability transformation. Moreover, the CSR strategy has been constantly adapted to the evolving COVID-19 environment. The company’s efforts aimed at maintaining sustainable value have been primarily focused on supporting and engaging employees, ensuring safe holiday packages for customers, and supporting local communities and partners. Several implications are provided based on the study results.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
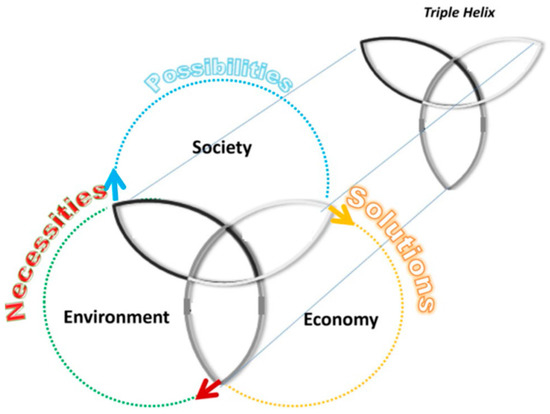
Analysis of the Impact of the Triple Helix on Sustainable Innovation Targets in Spanish Technology Companies
by
María-Jesús Luengo-Valderrey, Julián Pando-García, Iñaki Periáñez-Cañadillas and Amparo Cervera-Taulet
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3555
Abstract
The establishment of broad-based networks, such as the Triple Helix, for innovation and sustainability is sufficiently corroborated. In this work we suggest that the information received from the Triple Helix has a significant and different impact on the objectives of sustainable innovation, depending
[...] Read more.
The establishment of broad-based networks, such as the Triple Helix, for innovation and sustainability is sufficiently corroborated. In this work we suggest that the information received from the Triple Helix has a significant and different impact on the objectives of sustainable innovation, depending on whether companies cooperate or not. To this end, an empirical analysis of a stratified sample of more than 5000 Spanish medium and high technology companies in 2010-2014-2015 was carried out. The results confirm that companies that do not cooperate place more importance on the information received from the Triple Helix to establish their sustainable innovation targets.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
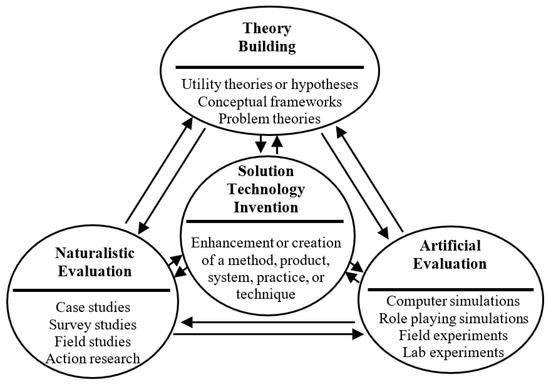
Carving out New Business Models in a Small Company through Contextual Ambidexterity: The Case of a Sustainable Company
by
Vinicius Minatogawa, Matheus Franco, Orlando Durán, Ruy Quadros, Maria Holgado and Antonio Batocchio
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 5097
Abstract
Business model innovation (BMI) and organizational ambidexterity have been pointed out as mechanisms for companies achieving sustainability. However, especially considering small and medium enterprises (SMEs), there is a lack of studies demonstrating how to combine these mechanisms. Tackling such a gap, this study
[...] Read more.
Business model innovation (BMI) and organizational ambidexterity have been pointed out as mechanisms for companies achieving sustainability. However, especially considering small and medium enterprises (SMEs), there is a lack of studies demonstrating how to combine these mechanisms. Tackling such a gap, this study seeks to understand how SMEs can ambidextrously manage BMI. Our aim is to provide a practical artifact, accessible to SMEs, to operationalize BMI through organizational ambidexterity. To this end, we conducted our study under the design science research to, first, build an artifact for operationalizing contextual ambidexterity for business model innovation. Then, we used an in-depth case study with a vegan fashion small e-commerce to evaluate the practical outcomes of the artifact. Our findings show that the company improves its business model while, at the same time, designs a new business model and monetizes it. Thus, our approach was able to take the first steps in the direction of operationalizing contextual ambidexterity for business model innovation in small and medium enterprises, democratizing the concept. We contribute to theory by connecting different literature strands and to practice by creating an artifact to assist management.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
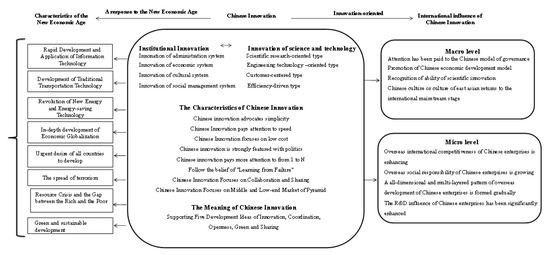
Chinese-Style Innovation and Its International Repercussions in the New Economic Times
by
Zhifeng Shen, Ahsan Siraj, Hongbing Jiang, Yongming Zhu and Junjie Li
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 4416
Abstract
Innovation is the powerful headspring that makes the economy and society continue with sustainable development, and how to innovate is a current research issue all over the world. The purposes of this research are to examine Chinese-style innovations and to analyze the influence
[...] Read more.
Innovation is the powerful headspring that makes the economy and society continue with sustainable development, and how to innovate is a current research issue all over the world. The purposes of this research are to examine Chinese-style innovations and to analyze the influence of Chinese-style innovation on the international market in the current economic times. From multiple perspectives of institutional innovation as well as scientific and technological innovation, the content, characteristics and connotation of Chinese-style innovation are comprehensively expounded and analyzed through the collection, combination and exploration of innovation, especially in Chinese-style innovation literature and interviews with relevant scholars, experts and enterprises. Then, the fit of Chinese-style innovation and characteristics of the new economic era are systematically described. Based on the exploration of international repercussions of Chinese-style innovation from both macro and micro aspects, the mechanism of Chinese-style innovation’s influence on China’s international market is also analyzed. In China, the underlying concept has not been well investigated before, therefore there is a gap in which to do research in this area. In accordance with the current research, a conceptual model for the new economic era, Chinese-style innovation and China’s international repercussions is established. This study finds that the influence of Chinese companies in research and development has significantly improved, the all-round and multi-domain pattern of Chinese enterprises’ overseas development has gradually taken shape, Chinese companies’ overseas social responsibility is growing, the overseas competitiveness of Chinese companies has gradually increased, the overall strength of China’s science and technology has gradually gained international recognition and its international repercussions have improved significantly.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
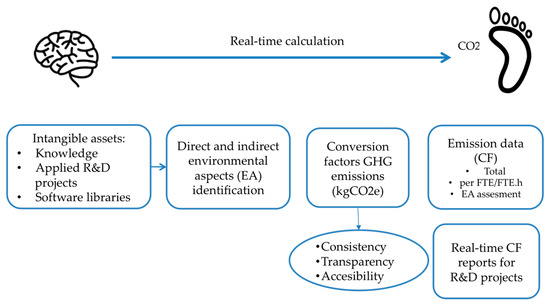
Methodology for Carbon Footprint Calculation Towards Sustainable Innovation in Intangible Assets
by
Edurne Loyarte-López, Mario Barral and Juan Carlos Morla
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 12698
Abstract
Calculating the carbon footprint is fundamental to understand how an organization’s activities impact global sustainability. The main challenge is how to calculate it when environmental aspects are intangible assets. The present paper investigates in what ways the environmental effects of 13 aspects in
[...] Read more.
Calculating the carbon footprint is fundamental to understand how an organization’s activities impact global sustainability. The main challenge is how to calculate it when environmental aspects are intangible assets. The present paper investigates in what ways the environmental effects of 13 aspects in relation with R&D activities in an applied research center could contribute to sustainable development. For this purpose, we described methodology to routinely measure greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and calculate the carbon footprint (CF) of all research activities related to intangible assets (R&D projects, researchers’ knowledge and software libraries) with real-time data being provided. Selection of conversion factors to express all GHG emissions are described, in particular those related to air travel on account of its greatest contribution to CF. In addition, these data were used as a factor in assessing the environmental impact of the center, under ISO 14001. As a result, our center can manage its CF and make decisions about how to enhance sustainability awareness at all levels of the organization and gradually improve CF data, of which the main contributors were transportation and travel (66.4%) and electricity (33.1%) in 2018.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
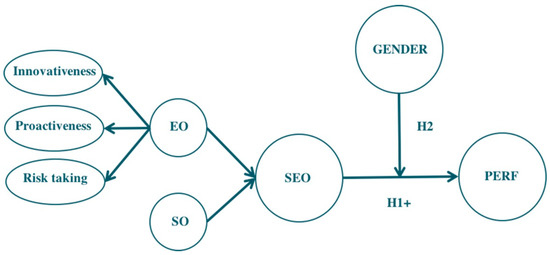
Women as Key Agents in Sustainable Entrepreneurship: A Gender Multigroup Analysis of the SEO-Performance Relationship
by
Ana Criado-Gomis, Maria-Angeles Iniesta-Bonillo, Amparo Cervera-Taulet and Domingo Ribeiro-Soriano
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 4091
Abstract
Literature points out that the effect of sustainable entrepreneurship on firm performance may be contingent on internal factors, such as top manager characteristics. This paper proposes that the gender of a firm’s chief executive officer (CEO) greatly influences the sustainable entrepreneurial orientation (SEO)-firm
[...] Read more.
Literature points out that the effect of sustainable entrepreneurship on firm performance may be contingent on internal factors, such as top manager characteristics. This paper proposes that the gender of a firm’s chief executive officer (CEO) greatly influences the sustainable entrepreneurial orientation (SEO)-firm performance relationship. An empirical study was conducted on a stratified random sampling, collecting 210 questionnaires from top managers of firms in Valencia (Spain). A multigroup moderation analysis method was used. The results confirm that women tend to increase the positive effect of SEO in firm performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
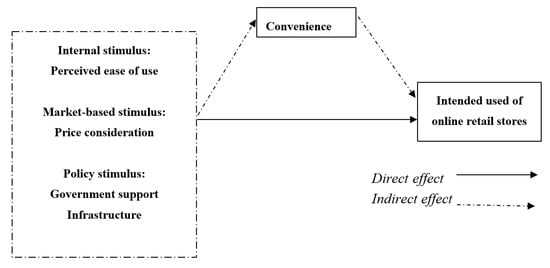
Towards Understanding the Initial Adoption of Online Retail Stores in a Low Internet Penetration Context: An Exploratory Work in Ghana
by
Abdul Bashiru Jibril, Michael Adu Kwarteng, Michal Pilik, Elsamari Botha and Christian Nedu Osakwe
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 4941
Abstract
Online shopping has become increasingly popular in the past two decades. Yet, despite its popularity, the use of online stores on the African continent pales in comparison to other parts of the world. Moreover, in many economic contexts in Africa and including Ghana,
[...] Read more.
Online shopping has become increasingly popular in the past two decades. Yet, despite its popularity, the use of online stores on the African continent pales in comparison to other parts of the world. Moreover, in many economic contexts in Africa and including Ghana, there has been very limited research on the subject of online adoption and in particular, the fundamental factors that can influence its initial adoption, especially among young and relatively educated consumers who constitute the largest demographic group there. We, therefore, make a determined effort to fill this growing knowledge gap by exploring some fundamental factors associated to shop online by young and educated consumers. This exploratory research draws on the stimulus-organism-response (SOR) framework and focuses on five variables of interest namely perceived ease of use, government support infrastructure, and economic considerations about pricing, perceived convenience and use intentions of online retail stores. Evidence collected from 294 research participants provides support for our research propositions Finally, our research contributions and future study directions are considered in the concluding part of the paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
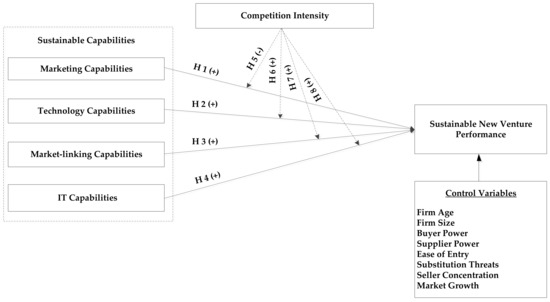
Does Competitive Intensity Moderate the Relationships between Sustainable Capabilities and Sustainable Organizational Performance in New Ventures?
by
Haili Zhang, Yufan Wang and Michael Song
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 2901
Abstract
Competitive intensity presents challenges to new ventures. Capabilities may lead to sustainable new venture performance. Yet, few studies have explored how competitive intensity moderates the effects of capabilities on sustainable new venture performance. Based on capability-based view, this study develops a research model
[...] Read more.
Competitive intensity presents challenges to new ventures. Capabilities may lead to sustainable new venture performance. Yet, few studies have explored how competitive intensity moderates the effects of capabilities on sustainable new venture performance. Based on capability-based view, this study develops a research model to investigate how new ventures translate capabilities (marketing, technology, market-linking, and information technology capabilities) to achieve sustainability of new venture growth and performance under the different levels of competitive intensity. Using data collected from 146 U.S. new ventures, this study uses ordinary least squares regression analysis to test the research model and employs “pick-a-point” approach to examine how capabilities affect sustainable new venture performance at different levels of competitive intensity. The empirical results suggest that increasing competitive intensity decreases,
not increases, the positive effects of marketing capabilities on performance. When competitive intensity is very high, the positive effects of marketing capabilities on performance become insignificant. In contrast, the positive effects of market-linking capabilities on performance increase,
not decrease, as competitive intensity increases. For technology and information technology capabilities, there are no moderating effects of competitive intensity. The theoretical and managerial implications are suggested for sustainable entrepreneurship and sustainable development of new enterprises.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
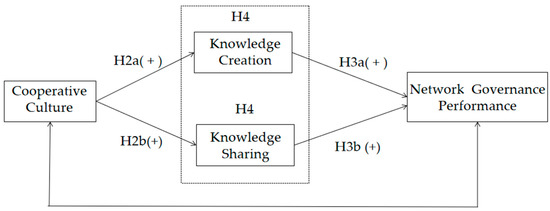
A Sustainable Development Perspective on Cooperative Culture, Knowledge Flow, and Innovation Network Governance Performance
by
Yaya Sun, Tao Wang and Xin Gu
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2962
Abstract
The contemporary sustainable development imperative sees enterprises seeking competitive advantages in innovation networks, the distinguishing features of which are continuous interaction and knowledge flow between participants. As an informal governance mechanism, cooperative culture influences the stability and durability of the members’ interactions. Knowledge
[...] Read more.
The contemporary sustainable development imperative sees enterprises seeking competitive advantages in innovation networks, the distinguishing features of which are continuous interaction and knowledge flow between participants. As an informal governance mechanism, cooperative culture influences the stability and durability of the members’ interactions. Knowledge flow is a core network activity that is highly dependent on the cultural environment. The purpose of this paper is to explore whether innovation governance performance is affected by cooperative culture and knowledge flow. How do they play an influential role? We use structural equation modeling (SEM) to analyze the linear relationships among the three variables: cooperative culture, knowledge flow, and governance performance. The results suggest that knowledge flow has a mediating effect on the relationship between cooperative culture and governance performance. We also use fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) to explore how cooperative culture and knowledge flow combined can influence governance performance. The results indicate that different combinations of cooperative culture and knowledge flow lead to different levels of governance performance, with two paths leading to high governance performance, which are fit creation-oriented and compatible sharing-oriented paths. These findings have significant implications for improving innovation governance performance and their sustainable development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
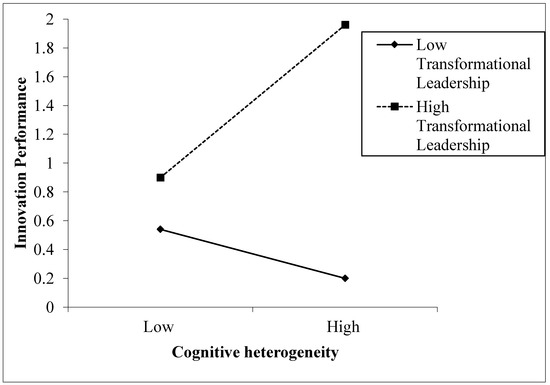
The Effect of Heterogeneity and Leadership on Innovation Performance: Evidence from University Research Teams in China
by
Shufang Huang, Jin Chen, Liang Mei and Weiqiao Mo
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3085
Abstract
Interdisciplinary cooperation is an important way to achieve scientific innovation breakthrough. Currently, great scientific innovation often occurs in interdisciplinary areas. However, they still face challenges in relation to theoretical support and strategic choices. This paper identifies the extent to which interdisciplinary cooperation-induced heterogeneity
[...] Read more.
Interdisciplinary cooperation is an important way to achieve scientific innovation breakthrough. Currently, great scientific innovation often occurs in interdisciplinary areas. However, they still face challenges in relation to theoretical support and strategic choices. This paper identifies the extent to which interdisciplinary cooperation-induced heterogeneity affects team innovation performance in Chinese universities. The questionnaire survey is employed in this study and the samples selection covers a wide range of multidisciplinary or interdisciplinary collaboration. This study used Poisson regression analysis to create a new method to evaluate innovation performance. Then, the relationship between team heterogeneity and innovation performance was examined and the moderating role of transformational leadership was also introduced. The empirical results show that three independent variables (disciplinary heterogeneity, cognitive heterogeneity, and organisational heterogeneity) all had a significant positive effect on the team innovation performance. Transformational leadership has a significant positive effect on cognitive heterogeneity and innovation performance, but moderating effects did not appear to be seen in the other two relationships. Our study contributes to a deeper understanding of the value of interdisciplinary research collaboration.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
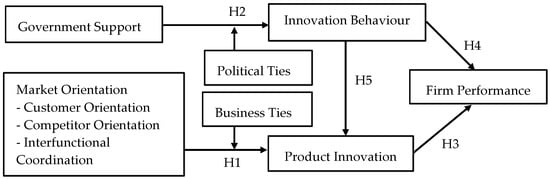
Interactions Among Factors Influencing Product Innovation and Innovation Behaviour: Market Orientation, Managerial Ties, and Government Support
by
Natenapang Thongsri and Alex Kung-Hsiung Chang
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 5705
Abstract
Ongoing globalization and changing customer needs make it increasingly difficult for firms to survive in the long term. Innovation is considered an important tool for firms in this environment. In particular, a firm’s ability to cultivate innovative behaviour and implement product innovation for
[...] Read more.
Ongoing globalization and changing customer needs make it increasingly difficult for firms to survive in the long term. Innovation is considered an important tool for firms in this environment. In particular, a firm’s ability to cultivate innovative behaviour and implement product innovation for sustainability is important. This study explores resources and capabilities to enhance firm innovation behaviour and implementation of sustainable product innovation. The results provide insights on how firms can manage strategies for future sustainable innovations. We used a sample of 645 small- and medium-sized enterprises and presented the conceptual framework according to a resource-based view and relational capital. We specified three independent factors that enhance sustainable innovation and superior performance: market orientation, managerial ties, and government support. We used a questionnaire survey and structural equation modelling to evaluate the conceptual model. We found that interactions between business ties, customers, and competitor orientation can enhance sustainable product innovation, whereas interactions between government support and political relations can enhance the sustainability of innovation behaviour. Moreover, product innovation and innovation behaviour are mediators that can lead to superior firm performance. The results suggest ways entrepreneurs and public policy makers can promote sustainable innovation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
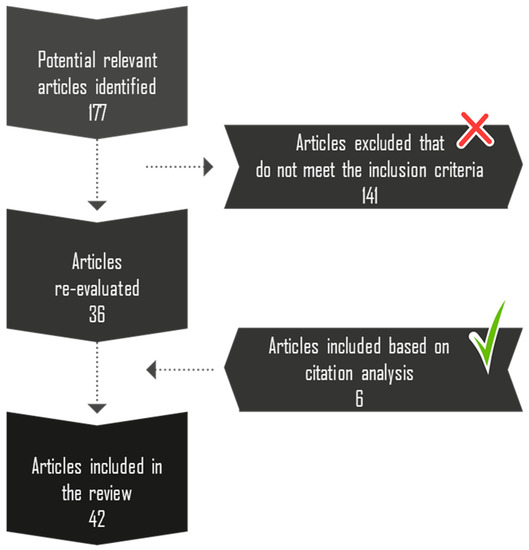
Circular Business Models for the Bio-Economy: A Review and New Directions for Future Research
by
Wiebke Reim, Vinit Parida and David R. Sjödin
Cited by 58 | Viewed by 7776
Abstract
Circular and bio-economy represents a political and industrial initiative to ensure that our society can rely on renewable biological sources while achieving economic growth. However, there is a need to critical review how realistic and feasible such initiatives are towards fulfilling the promised
[...] Read more.
Circular and bio-economy represents a political and industrial initiative to ensure that our society can rely on renewable biological sources while achieving economic growth. However, there is a need to critical review how realistic and feasible such initiatives are towards fulfilling the promised benefits of this economy. The literature on bio-economy often discusses the importance of innovative business models and their role in a successful shift to a bio-economy. Still, much of the discussion that is related to circular business models is fragmented and immature. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to conduct a systematic literature review of circular business model activities and the barriers to a bio-economy. Further, this review provides future research directions for a shift to a bio-economy. This study is based on a systematic review of 42 scientific journal articles and book chapters on a forest-based bio-economy. The business model canvas is used to provide a structured aggregation of the existing circular business models activities being used by the forestry sector. In addition, we develop a framework that describes the barriers to bio-economy-based circular business models and suggest new directions for future research. The study highlights the need for alignment among the elements of a business model as a key condition for its successful implementation in a bio-economy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
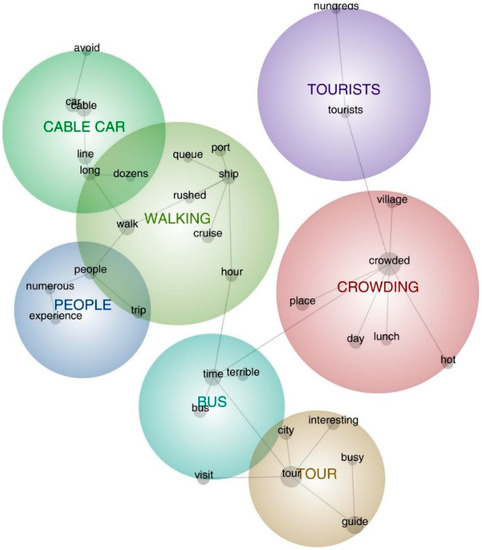
The Sustainability of Cruise Tourism Onshore: The Impact of Crowding on Visitors’ Satisfaction
by
Silvia Sanz-Blas, Daniela Buzova and Walesska Schlesinger
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 6918
Abstract
The sustainability of cruise tourism has been questioned in relation to its negative effects on ports of call, among which crowding has recently become more pronounced. However, an understanding of how crowdedness influences cruise tourists’ experience onshore is lacking. The study analyzed online
[...] Read more.
The sustainability of cruise tourism has been questioned in relation to its negative effects on ports of call, among which crowding has recently become more pronounced. However, an understanding of how crowdedness influences cruise tourists’ experience onshore is lacking. The study analyzed online reviews on onshore experiences in the main European ports of call through Leximancer, an automated text analytics software. The results revealed that the perceived destination crowding was not always negatively evaluated by tourists, but was also discussed as a factor adding up to the authenticity of the visit under certain circumstances. Nevertheless, the evidence indicates that only human crowding might be positively assessed, while the spatial crowdedness was always reported as detracting from the enjoyment of the visit. The analysis also showed that the crowding phenomenon was represented differently in the accounts of the low, average and high satisfaction cruise tourists’ groups. The role of the guide, as well as the attractiveness of the sightseeing were identified as factors that can ameliorate the negative effect of crowding on the destination visit. The findings yield relevant implications for all actors involved in the cruise tourism activity, which should manage destination crowdedness in a more sustainably innovative way.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Selection of Manufacturing Enterprise Innovation Design Project Based on Consumer’s Green Preferences
by
Jie Yang, Jiafu Su and Lijun Song
Cited by 46 | Viewed by 3567
Abstract
For enterprise, how to quickly realize the selection of green innovative design projects has become a key issue for improving innovation performance. Based on an analysis of enterprise product innovation and customer green preferences, an indicator set for innovation performance in enterprise was
[...] Read more.
For enterprise, how to quickly realize the selection of green innovative design projects has become a key issue for improving innovation performance. Based on an analysis of enterprise product innovation and customer green preferences, an indicator set for innovation performance in enterprise was established. Considering the fuzziness of the correlation between indicators for innovation performance in enterprise and consumer’s green preferences, a fuzzy clustering method was used to identify the internal relations among the indicators for innovation performance with green preferences of customers. Then a wavelet neural network was used to select the innovation design project for various green preferences of customers. Finally, a case study was proposed to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the method. This work can help the enterprise to develop green design, products, and serve uniformly, which can effectively shorten green product development cycles, reduce cost, and improve enterprise innovation performance greatly.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
How Does A Firm’s Previous Social Network Position Affect Innovation? Evidence from Chinese Listed Companies
by
Xuan Wei and Wei Chen
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4360
Abstract
The impact of social network position on innovation has been widely confirmed in past studies. However, research on the time-lag structure of the impact is still insufficient. Within the time window 2010 to 2017, this study constructs a two-mode social network between Chinese
[...] Read more.
The impact of social network position on innovation has been widely confirmed in past studies. However, research on the time-lag structure of the impact is still insufficient. Within the time window 2010 to 2017, this study constructs a two-mode social network between Chinese listed companies and other participants. To analyze the lag structure of the effect of social network position on innovation, this study uses a panel negative binomial regression model transformed by the Almon polynomial. The results show that a firm does need an advantageous past social network position for innovation. Previous local and global centrality in a social network has a different influence on innovation. For the local centrality indices, degree centrality has a positive impact in the short-term, but has a negative impact in the long-term; the impact of betweenness centrality is not significant in the short-term and is negative in the long run. For the global centrality indices, closeness centrality has a positive influence that decreases with the increase of the time-lag. At the same time, using the method of necessary condition analysis (NCA), this study calculates the bottleneck for a given innovation level. Finally, based on these research conclusions, the theoretical implications and management practice implications are summarized.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Green Marketing’s Roles in Sustainability and Ecopreneurship. Case Study: Green Packaging’s Impact on Romanian Young Consumers’ Environmental Responsibility
by
Mihaela Kardos, Manuela Rozalia Gabor and Nicoleta Cristache
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 8228
Abstract
In contemporary society, which is preoccupied with sustainability issues, green marketing highlights a new dimension of the economic, social, and environmental responsibilities of businesses. This article aims to provide an integrative vision on green marketing roles in informing, raising awareness, educating, and changing
[...] Read more.
In contemporary society, which is preoccupied with sustainability issues, green marketing highlights a new dimension of the economic, social, and environmental responsibilities of businesses. This article aims to provide an integrative vision on green marketing roles in informing, raising awareness, educating, and changing consumer behaviour towards sustainability and ecopreneurship and to highlight the results of research regarding PlantBottle
® green packaging’s impact on the environmental responsibility of young consumers. The research was conducted based on a survey, and data were processed with statistical methods. The research results validate a set of hypotheses regarding: Romanian consumers’ lack of information leading to environmental responsibility; the impact of environmental information and awareness on green responsible behaviour; and the need to intensify efforts towards environmental responsibility. By the novelty of the research, which was conducted in a country that has rather recently become preoccupied with sustainability issues, the paper fills in a gap in a relatively limited research area: countries where green culture is developing and can become a landmark with implications for managers, educators, and the scientific community.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Why Do Sustainable Mergers Fail to Manage Entrepreneurship?
by
María Sarabia, Fernando Crecente and Rafael Castaño
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 4900
Abstract
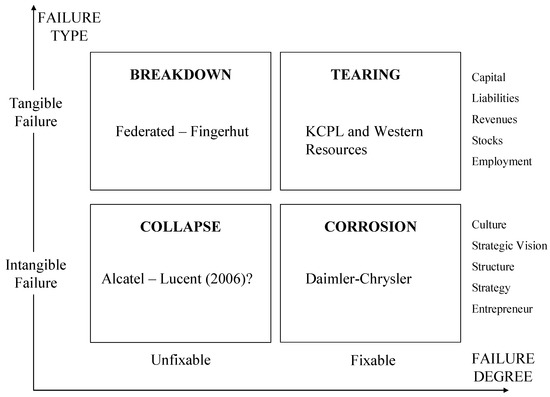
This paper proposes a conceptual model using four failed mergers (Federated -Fingerhut, KCPL and Western Resources, Daimler–Chrysler and Alcatel–Lucent) and distinguishes two types of dimensions: type of failure (tangible and intangible) and degree of failure (fixable and unfixable). Using case studies as a
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a conceptual model using four failed mergers (Federated -Fingerhut, KCPL and Western Resources, Daimler–Chrysler and Alcatel–Lucent) and distinguishes two types of dimensions: type of failure (tangible and intangible) and degree of failure (fixable and unfixable). Using case studies as a research strategy and focusing on the Alcatel–Lucent merger, as an example of an idiosyncratic type of “merger of equals”, the model identifies the entrepreneurial conflict variable as a missed step for obtaining a sustainable merger process over time.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Partnership-Based Supply Chain Collaboration: Impact on Commitment, Innovation, and Firm Performance
by
Nina Shin, Sun Hyun Park and Sangwook Park
Cited by 67 | Viewed by 9048
Abstract
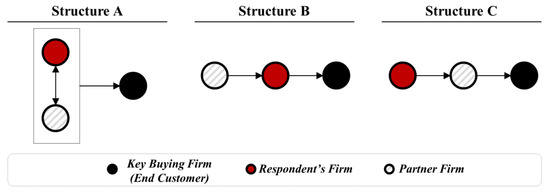
With increasing numbers of nodes and links in supply network relationships, understanding partnership management and the required level of collaboration is important for sustainable supply network alignment. This study explores the impact of partnership orientation on partnership commitment and firm performance using a
[...] Read more.
With increasing numbers of nodes and links in supply network relationships, understanding partnership management and the required level of collaboration is important for sustainable supply network alignment. This study explores the impact of partnership orientation on partnership commitment and firm performance using a model based on social capital theory and resource dependence theory. It aims to understand the appropriate partnership orientation for the desired level of commitment and firm performance, including innovation, operational, and financial performance. Using a survey of 423 respondents representing three different partnership structure types (supplier, buyer, and parallel-aligned firms’ perspectives), the relationship between partnership orientation and commitment in enhancing firm performance is investigated using structural equation modeling. Additional analysis identifies the moderating role of commitment and investment exchange on performance. The findings show that positive relationships between both investment and contractual-based partnership orientation positively contribute to partnership commitment, but the direct association between partnership commitment and firm performance type varies by partnership structure. Furthermore, (i) investment exchange level moderates the relationship between commitment and innovation and operational performance regardless of partnership structure type, (ii) negative investment exchange signals higher firm performance from the buyer firm’s perspective, and (iii) positive investment exchange is absolutely necessary for financial performance from the supplier firm’s perspective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Empirical Study on Green Innovation Strategy and Sustainable Competitive Advantages: Path and Boundary
by
Baoshan Ge, Yibing Yang, Dake Jiang, Yang Gao, Xiaomin Du and Tingting Zhou
Cited by 85 | Viewed by 8093
Abstract
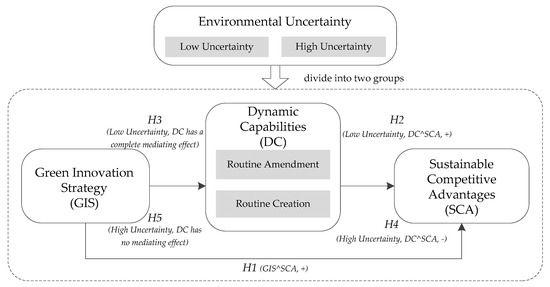
Although green innovation strategy (GIS) is the driving force for the sustainable development of enterprises, while the strategy is implemented, an increased cost and a change in organizational routines will cause an organization to become fragile, and even affect the sustainable competitive advantages.
[...] Read more.
Although green innovation strategy (GIS) is the driving force for the sustainable development of enterprises, while the strategy is implemented, an increased cost and a change in organizational routines will cause an organization to become fragile, and even affect the sustainable competitive advantages. So, the purpose of this paper is to explore the impact path of GIS on sustainable competitive advantages and the implementation boundary of GIS. To explain the impact path, we consider the concept of dynamic capabilities to be the mediator variable. To explain the implementation boundary of GIS, we systematically explore the relationships among GIS, dynamic capabilities and sustainable competitive advantages under different levels of environmental uncertainty. Based on 241 new Chinese green firms, the empirical results find that GIS helps enterprises to gain sustainable competitive advantages. However, in the process of strategy implementation, enterprises should choose appropriate methods according to different degrees of environmental uncertainty. In a low environmental uncertainty, dynamic capabilities play a full intermediary role between GIS and sustainable competitive advantages. However, in a high environmental uncertainty, dynamic capabilities have no mediating effect between GIS and sustainable competitive advantages. This study not only integrates green management theory and strategic management theory but also makes up for the deficiencies in research on these theories and has important reference value for enterprises that seek to carry out green innovation activities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Fit between Organizational Culture and Innovation Strategy: Implications for Innovation Performance
by
Zhi Chen, Shenglan Huang, Chong Liu, Min Min and Liying Zhou
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 10326
Abstract
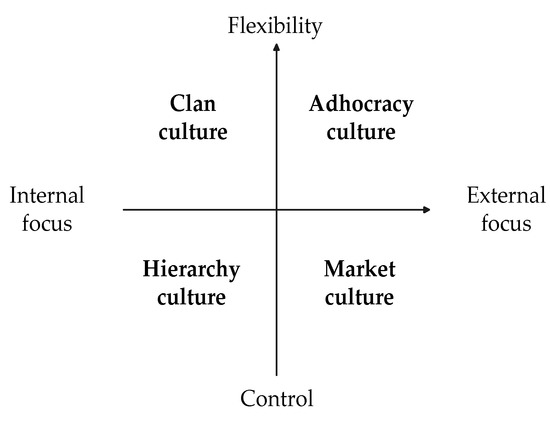
Although prior studies have indicated the interrelationships between specific types of innovation strategy and specific elements of organizational culture, few studies simultaneously evaluate the relationship between the two multi-dimensional constructs in holistic perspective. Based on configuration theory, we conceptualize fit as ‘profile deviation’,
[...] Read more.
Although prior studies have indicated the interrelationships between specific types of innovation strategy and specific elements of organizational culture, few studies simultaneously evaluate the relationship between the two multi-dimensional constructs in holistic perspective. Based on configuration theory, we conceptualize fit as ‘profile deviation’, and investigate the fit between an organization’s culture and its innovation strategy. Data were collected from 183 Chinese organizations. We examine the hypothesis that greater fit between organizational culture and innovation strategy encourages superior innovation speed and innovation quality. Our results provide evidence that in the group of organizations exhibiting either exploratory or exploitative innovation strategy, the more similar the organizational culture configurations are to those of the top performers, the higher their innovation speed and innovation quality are. In the group of organizations exhibiting ambidextrous innovation strategy, the fit between organizational culture and innovation strategy is insignificantly associated with innovation speed and innovation quality. Implications for applying the culture–strategy fit in innovation management are discussed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Analysis of the Factors behind the Citizen’s Attitude of Rejection towards Tourism in a Context of Overtourism and Economic Dependence on This Activity
by
José María Martín Martín, Jose Manuel Guaita Martínez and José Antonio Salinas Fernández
Cited by 183 | Viewed by 20387
Abstract
New tourism trends, such as vacation rentals websites and low-cost tourism, have generated a new environment of interactions between tourism and the citizens. To this, we must add the fortuitous increase in demand in some touristic destinations. This has derived in situations of
[...] Read more.
New tourism trends, such as vacation rentals websites and low-cost tourism, have generated a new environment of interactions between tourism and the citizens. To this, we must add the fortuitous increase in demand in some touristic destinations. This has derived in situations of rejection in traditionally tourism-dependent environments. In this study, which is focused on the city of Barcelona, we use work-field data to analyze the elements that lie behind the popular aversion to tourism. Assuming a non-forced analysis that takes the Social Exchange Theory as a framework, we have determined that the negative economic effects derived from the increase in the number of accommodations destined for vacation rentals and in the demand lie behind this rejection. The main impacts that are perceived directly from these factors are: the increase in residential rentals prices and a shift from a traditional market to one oriented to the tourist with higher prices. It has also been determined that the most vulnerable population groups are those who manifest a stronger rejection, tenants of apartments in city centers, and citizens with a low/medium income, who perceive rises in the prices and a change in the market focus to a larger extent.
Full article
Open AccessReview
A Definition and Theoretical Review of the Circular Economy, Value Creation, and Sustainable Business Models: Where Are We Now and Where Should Research Move in the Future?
by
Tom Lahti, Joakim Wincent and Vinit Parida
Cited by 181 | Viewed by 22561
Abstract
This paper contains a theory review of value creation and the implementation of next-generation sustainable business models to profit in the circular economy. While previous research has pointed to the influence of society and regulatory policy on companies’ ability to address larger sustainability
[...] Read more.
This paper contains a theory review of value creation and the implementation of next-generation sustainable business models to profit in the circular economy. While previous research has pointed to the influence of society and regulatory policy on companies’ ability to address larger sustainability concerns and to change their ways of working, the field suffers from little theoretical guidance outlining how undertake circular business mode transformation in practice. By reviewing the field’s main theories, we illustrate significant implications for how future research can study profitability and competitiveness in the circular economy. This paper introduces the central components of circular business models and discusses links to contingency theory, transaction cost theory, resource-based theory, theory on networks and industrial economics, and agency theory. Understanding the circular economy and the ways companies can compete in the circular economy based on these theories is important for establishing important new research directions for scholars of sustainable business and circular business models.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
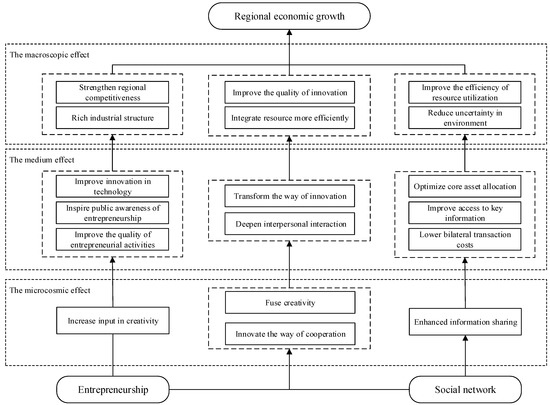
The Influence of Entrepreneurship and Social Networks on Economic Growth—From a Sustainable Innovation Perspective
by
Feng-Wen Chen, Long-Wang Fu, Kai Wang, Sang-Bing Tsai and Ching-Hsia Su
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 6869
Abstract
A large body of evidence demonstrates the key role played by entrepreneurship in promoting economic growth. However, the potential connections between entrepreneurship, social networking, and economic development still require in-depth exploration and discussion. This paper first establishes a theoretical framework combining entrepreneurship capital
[...] Read more.
A large body of evidence demonstrates the key role played by entrepreneurship in promoting economic growth. However, the potential connections between entrepreneurship, social networking, and economic development still require in-depth exploration and discussion. This paper first establishes a theoretical framework combining entrepreneurship capital theory, resource dependence theory and transaction cost theory, then examines the possible associations between entrepreneurship, social networks, and economic growth based on the dynamic panel data model. To achieve the research objectives, the investigators collected data spanning the period between 2007 and 2016 from 31 provinces and cities in China. The authors adopted the enterprise employment rate as a measure of entrepreneurship and used the information sharing rate to assess social networks, which were then both introduced into the economic growth model. Additionally, by using the system of generalized method of moments (GMM) estimation, this article measures the influence of entrepreneurship and social networks on the economic growth of a local area. The empirical results reveal that both entrepreneurship and social networking significantly promote regional economic growth in China. Further, the effect of entrepreneurship is significantly enhanced after introducing the joint effects of entrepreneurship and social network. The findings also expound that entrepreneurship of the eastern zone and social networking of the central section exhibit the strongest potential for economic development of the respective areas. Conversely, entrepreneurship may actually hinder the economic advancement of the central areas of China. Corresponding to the findings, the researchers suggest that it is necessary to devise flexible policies for heterogeneous entrepreneurial environments and to appropriately utilize interpersonal networks to maximize the efficiency of the outputs of economic activity, which are likely to strengthen the role of entrepreneurship and social networks in contemporary economic and business milieu.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
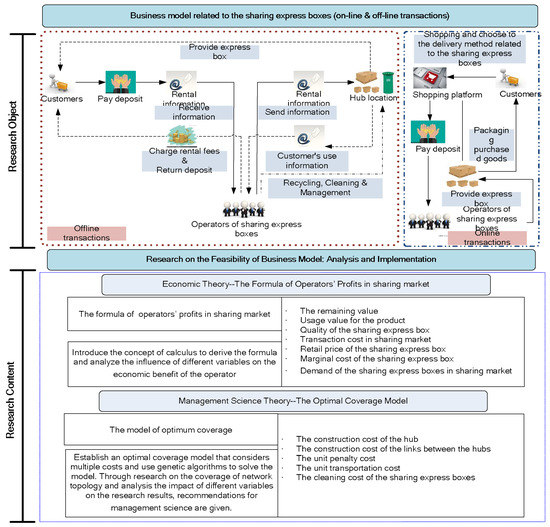
An Empirical Study on the Innovation Sharing Express Box: Collaborative Consumption and the Overlay Network Design
by
Aijun Liu, Xiaohui Ji, Sang-Bing Tsai, Hui Lu, Gang Du, Feng Li, Guodong Li and Jiangtao Wang
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3595
Abstract
Sharing express boxes is an effective disposal method for obsolete express packages. Its appearance also represents an unstoppable trend in the development of green logistics. This paper takes the sharing express box as research object and conducts two-stage research. In the first stage,
[...] Read more.
Sharing express boxes is an effective disposal method for obsolete express packages. Its appearance also represents an unstoppable trend in the development of green logistics. This paper takes the sharing express box as research object and conducts two-stage research. In the first stage, the collaborative consumption theory and calculus are used to analyze the economic benefits that sharing express boxes bring to operators, that is, to demonstrate the feasibility of this business model from an economic perspective. In the second stage, the design of the overlay network is studied from the management science perspective. Firstly, an optimal coverage model is established considering the characteristics of the sharing express box, and cleaning costs, relocation costs, etc. are all integrated into the model. Secondly, the genetic algorithm is used to solve the model. A numerical example is described to illustrate the feasibility of the proposed method. In addition, sensitivity analysis investigates the effect of hub coverage change on the results. Finally, the theoretical guidance gained from this paper can be beneficial to the sustainable development of sharing express boxes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
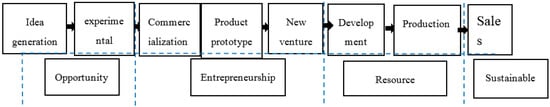
An Empirical Study on Sustainable Innovation Academic Entrepreneurship Process Model
by
Xiao-Duo Qian, Jing Xia, Wei Liu and Sang-Bing Tsai
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 5274
Abstract
As academic entrepreneurs, university faculty members and researchers with rich knowledge resources play an important role in the technology commercialization process, and in the creation and development of university spinoff enterprises. In this paper, we used a case study method to construct a
[...] Read more.
As academic entrepreneurs, university faculty members and researchers with rich knowledge resources play an important role in the technology commercialization process, and in the creation and development of university spinoff enterprises. In this paper, we used a case study method to construct a sustainable innovative academic entrepreneurship process model from the perspective of entrepreneurial behavior. Then, we used this model to provide a deeper understanding of the activities and roles of academic entrepreneurs. This paper also expounded the process of value creation that is a result of sustainable innovative academic entrepreneurship, and compared and analyzed three types of university technology commercialization models. Our results showed that in the sustainable innovative academic entrepreneurship process model, the motivation of academic entrepreneurs leads them to play multiple roles as academic researchers, enterprise founders, and enterprise managers. In creating enterprises as the founders, and establishing and developing their enterprises, academic entrepreneurs realize the commercial value of the technology, while also incrementing their personal value. The sustainable innovative academic entrepreneurship process model provides a new path for effective transfer of technological innovations from academic research to the commercial market, creates social as well as economic value, and promotes regional economic development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures