Specular Reflection Effects Elimination in Terrestrial Laser Scanning Intensity Data Using Phong Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Explore the mechanism of the specular reflection effects in TLS intensity;
- Use the Phong model to eliminate the highlight phenomenon caused by specular reflections; and
- Propose a new method to estimate the parameters of the Phong model.
2. Methodology
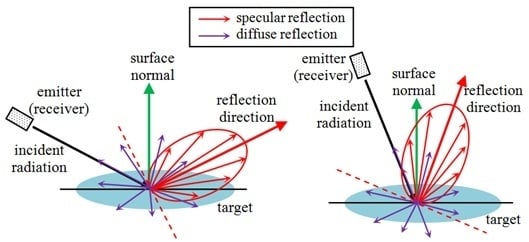
2.1. Specular Reflections and Highlight Phenomenon
2.2. Physical Background of TLS Intensity
2.3. Proposed Method
3. Experiments
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kashani, A.G.; Olsen, M.J.; Parrish, C.E.; Wilson, N. A review of LiDAR radiometric processing: From Ad Hoc intensity correction to rigorous radiometric calibration. Sensors 2015, 15, 28099–28128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X. Surface reflectance retrieval from the intensity data of a terrestrial laser scanner. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2016, 33, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, X. Modeling hemispherical reflectance for natural surfaces based on terrestrial laser scanning backscattered intensity data. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 22971–22988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, D.; Angelini, M.G. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the luminance of laser scanner radiation for the classification of materials. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-5/W2, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrea, D.; Abellan, A.; Humair, F.; Matasci, B.; Derron, M.H.; Jaboyedoff, M. Correction of terrestrial LiDAR intensity channel using Oren-Nayar reflectance model: An application to lithological differentiation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 113, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, T.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Skidmore, A.K.; Niemann, K.O. 3D leaf water content mapping using terrestrial laser scanner backscatter intensity with radiometric correction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 110, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, T.; Skidmore, A.K.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Niemann, K.O.; Liu, J. Canopy leaf water content estimated using terrestrial LiDAR. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; McElhinney, C.P.; Lewis, P.; McCarthy, T. Automated road markings extraction from mobile laser scanning data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 32, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, H.; Tan, J.; Li, Z.; Xie, H.; Chen, C. Scan line based road marking extraction from mobile LiDAR point clouds. Sensors 2016, 16, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X.; Ju, Q.; Wu, S. Correction of mobile TLS intensity data for water leakage spots detection in metro tunnels. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, R.; Danson, F.M.; Ramirez, F.A.; Gunawan, O. The potential of dual-wavelength laser scanning for estimating vegetation moisture content. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasalainen, S.; Niittymaki, H.; Krooks, A.; Koch, K.; Kaartinen, H.; Vain, A.; Hyyppä, H. Effect of target moisture on laser scanner intensity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, S.; Vastaranta, M.; Liang, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Kukko, A.; Kaasalainen, S.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, H.; Hyyppä, J. Measuring leaf water content with dual-wavelength intensity data from terrestrial laser scanners. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X.; Ju, Q. Combining mobile terrestrial laser scanning geometric and radiometric data to eliminate accessories in circular metro tunnels. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, M.; Teza, G.; Preto, N.; Pesci, A.; Galgaro, A.; Girardi, S. Discrimination between marls and limestones using intensity data from terrestrial laser scanner. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penasa, L.; Franceschi, M.; Preto, N.; Teza, G.; Polito, V. Integration of intensity textures and local geometry descriptors from terrestrial laser scanning to map chert in outcrops. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasalainen, S.; Jaakkola, A.; Kaasalainen, M.; Krooks, A.; Kukko, A. Analysis of incidence angle and distance effects on terrestrial laser scanner intensity: Search for correction methods. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasalainen, S.; Krooks, A.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H. Radiometric calibration of terrestrial laser scanner with external reference targets. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X. Correction of incidence angle and distance effects on TLS intensity data based on reference targets. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, D. Intensity correction of terrestrial laser scanning data by estimating laser transmission function. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Q. Intensity data correction for the distance effect in terrestrial laser scanners. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutzi, B.; Gross, H. Investigations on surface reflection models for intensity normalization in airborne laser scanning (ALS) data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukko, A.; Kaasalainen, S.; Litkey, P. Effect of incidence angle on laser scanner intensity and surface data. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaasalainen, S.; Vain, A.; Krooks, A.; Kukko, A. Topographic and distance effects in laser scanner intensity correction. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2009, 38, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, F.M.; Mills, J.P.; Miller, P.E. Echo amplitude normalization of full-waveform airborne laser scanning data based on robust incidence angle estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfle, B.; Pfeifer, N. Correction of laser scanning intensity data: Data and model-driven approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Chen, W.; King, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G. Combination of overlap-driven adjustment and Phong model for LiDAR intensity correction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 75, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, F.; Bréon, F.M.; Lacaze, R. Bidirectional reflectance of Earth targets: Evaluation of analytical models using a large set of spaceborne measurements with emphasis on the Hot Spot. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaze, R.; Chen, J.M.; Roujean, J.L.; Leblanc, S.G. Retrieval of vegetation clumping index using hot spot signatures measured by POLDER instrument. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffour, C.; Lagouarde, J.P.; Roujean, J.L. A two parameter model to simulate thermal infrared directional effects for remote sensing applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagol, J.R.; Sexton, J.O.; Kim, D.H.; Anand, A.; Morton, D.; Vermote, E.; Townshend, J.R. Bidirectional effects in Landsat reflectance estimates: Is there a problem to solve? ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Y.; Shaker, A. Radiometric correction and normalization of airborne LiDAR intensity data for improving land-cover classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7658–7673. [Google Scholar]
- Phong, B.T. Illumination for computer generated pictures. Commun. ACM 1975, 18, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, L.; Lachérade, S.; Jacquemoud, S.; Moya, I. Leaf BRDF measurements and model for specular and diffuse components differentiation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susaki, J.; Hara, K.; Kajiwara, K.; Honda, Y. Robust estimation of BRDF model parameters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X. Intensity data correction based on incidence angle and distance for terrestrial laser scanner. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 094094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerones, P.M.; Vélez, D.O.; Rojo, F.G.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Casanova, E.Z. Moisture detection in heritage buildings by 3D laser scanning. Stud. Conserv. 2016, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzetti, L.; Remondino, F.; Scaioni, M.; Lo Brutto, M.; Rizzi, A.; Brumana, R. Geometric and radiometric analysis of paintings. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, XXXVIII, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Soudarissanane, S.; Lindenbergh, R.; Menenti, M.; Teunissen, P. Scanning geometry: Influencing factor on the quality of terrestrial laser scanning points. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| 2.41 | 2.27 | −2.42 | 1 | |
| 3.71 × 109 | −7.23 × 108 | 2.90 × 108 | −5.20 × 107 | 4.92 × 106 |
| −2.66 × 105 | 8.33 × 103 | −140.91 | 1 |
| Scan 2 | Scan 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 1499 | 83.87 | 5.60/- | Original | 1558 | 85.50 | 5.49/- |
| 1560 | 89.03 | 5.71/−1.78 | 1616 | 90.56 | 5.60/−2.00 | ||
| Polynomial | 1572 | 84.07 | 5.35/4.46 | Polynomial | 1623 | 86.60 | 5.34/2.73 |
| Reference Targets | 1570 | 84.79 | 5.40/3.57 | Reference Targets | 1622 | 87.17 | 5.37/2.19 |
| Proposed | 1541 | 58.54 | 3.80/32.14 | Proposed | 1565 | 51.14 | 3.27/40.44 |
| Door | 484.86 | 0.44 | 16.55 |
| Curtain | 445.08 | 0.61 | 81.74 |
| Building facade | 446.32 | 0.42 | 22.44 |
| Plywood | 516.47 | 0.37 | 31.38 |
| Marble | 538.41 | 0.48 | 117.26 |
| Bookcase | 503.28 | 0.60 | 62.83 |
| Rubber board | 529.56 | 0.42 | 108.41 |
| Curtain | Building | Plywood | Marble | Bookcase | Rubber | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curtain | 4.88 | 2.85 | 3.66 | 4.78 | 4.27 | 4.57 |
| Building | 14.95 | 18.64 | 18.03 | 15.25 | 11.86 | 16.64 |
| Plywood | 10.62 | 10.23 | 11.00 | 10.04 | 9.85 | 9.46 |
| Marble | 60.89 | 41.94 | 53.23 | 61.29 | 51.21 | 60.08 |
| Bookcase | 69.63 | 32.23 | 40.14 | 64.48 | 69.98 | 57.90 |
| Rubber | 33.93 | 44.64 | 48.21 | 51.07 | 10.36 | 62.50 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, K.; Cheng, X. Specular Reflection Effects Elimination in Terrestrial Laser Scanning Intensity Data Using Phong Model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080853
Tan K, Cheng X. Specular Reflection Effects Elimination in Terrestrial Laser Scanning Intensity Data Using Phong Model. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080853
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Kai, and Xiaojun Cheng. 2017. "Specular Reflection Effects Elimination in Terrestrial Laser Scanning Intensity Data Using Phong Model" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080853
APA StyleTan, K., & Cheng, X. (2017). Specular Reflection Effects Elimination in Terrestrial Laser Scanning Intensity Data Using Phong Model. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080853