Enhancing Osteogenic Potential: Controlled Release of Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist SKF38393 Compared to Free Administration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PLGA/SKF38393 Microspheres
2.2. Physicochemical Property Analyses of PLGA/SKF38393 Microspheres
2.3. SKF38393 Release Profile Testing Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.4. Cell Culture and Osteogenic Differentiation
2.5. Cell Proliferation
2.6. Cytocompatibility and Cell Adhesion
2.7. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Activity Assay, ALP, and Alizarin Red Staining
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (q-PCR)
2.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Animal Experiments
2.11. Micro-CT
2.12. Histologic Analysis
2.13. Osteogenic PCR Array
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PLGA/SKF38393 Microspheres
3.2. Cytocompatibility, Cell Adhesion, and Cell Proliferation
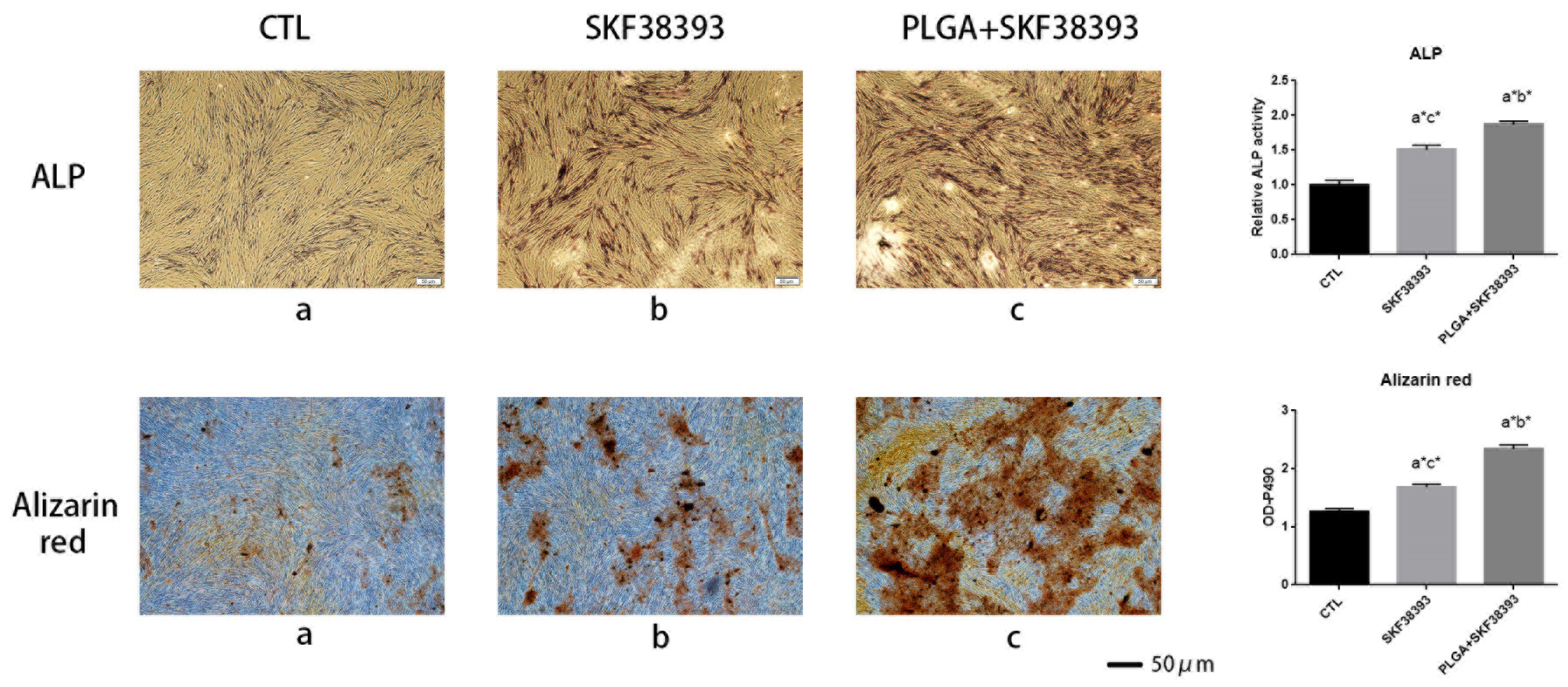
3.3. SKF38393 and PLGA/SKF38393 Regulate the Differentiation of hBMSCs
3.4. Animal Experiments
3.5. Different Effects of SKF38393 and PLGA/SKF38393 on Osteogenesis in the PCR Array
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Scientific Group on the Assessment of Osteoporosis at Primary Health Care Level; Summery Meeting Report; WHO: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cauley, J.A.; Thompson, D.E.; Ensrud, K.C.; Scott, J.C.; Black, D. Risk of mortality following clinical fractures. Osteoporos. Int. 2000, 11, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, D.M.; Rosen, C.J. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Shirota, T.; Tokugawa, Y.; Motohashi, M.; Ohno, K.; Michi, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Bone reactions to titanium screw implants in ovariectomized animals. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 1999, 87, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, S.; Hua, Y.; Hu, J. Effect of osteoporosis on fixation of osseointegrated implants in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseknecht, K.L.; Bouchard, C.; Black, C. Elucidating the mechanism(s) underlying antipsychotic- and antidepressant-mediated fractures. J. Ment. Health Clin. Psychol. 2017, 1, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenu, C.; Marenzana, M. Sympathetic nervous system and bone remodeling. Jt. Bone Spine 2005, 72, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, C.P.; Shim, S.S. Autonomic nerve supply of bone-experimental-study of intraosseous adrenergic nervi vasorum in rabbit. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1977, 59, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtori, S.; Inoue, G.; Koshi, T.; Ito, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yamashita, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Suzuki, M.; Doya, H.; Moriya, H.; et al. Sensory innervation of lumbar vertebral bodies in rats. Spine 2007, 32, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.-F. Osteoporosis risk and bone mineral density levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Bone 2013, 52, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliziotes, M.; McLoughlin, S.; Gunness, M.; Fumagalli, F.; Jones, S.; Caron, M. Bone histomorphometric and biomechanical abnormalities in mice homozygous for deletion of the dopamine transporter gene. Bone 2000, 26, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanami, K.; Nakano, K.; Saito, K.; Okada, Y.; Yamaoka, K.; Kubo, S.; Kondo, M.; Tanaka, Y. Dopamine D2-like receptor signaling suppresses human osteoclastogenesis. Bone 2013, 56, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wan, Q.; Pristupa, Z.B.; Yu, X.-M.; Wang, Y.T.; Niznik, H.B. Direct protein-protein coupling enables cross-talk between dopamine D5 and gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors. Nature 2000, 403, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.; Sneddon, W.B.; Yang, Y.; Wheeler, D.; Blair, H.C.; Friedman, P.A. Parathyroid hormone receptor directly interacts with dishevelled to regulate beta-Catenin signaling and osteoclastogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14756–14763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smajilovic, S.; Wellendorph, P.; Brauner-Osborne, H. Promiscuous seven transmembrane receptors sensing L-α-amino acids. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.-P.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; He, L. The modulatory role of dopamine receptors in brain neuroinflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, L.S.; Vekariya, R.H.; Free, R.B.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.-T.; Su, P.; Liu, F.; Namkung, Y.; Laporte, S.A.; Moritz, A.E.; et al. Structure-Activity Investigation of a G Protein-Biased Agonist Reveals Molecular Determinants for Biased Signaling of the D2 Dopamine Receptor. Front. Synaptic. Neurosci. 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilés-Rosas, V.H.; Rendón-Ochoa, E.A.; Hernández-Flores, T.; Flores-León, M.; Arias, C.; Galarraga, E.; Bargas, J. Role of M4-receptor cholinergic signaling in direct pathway striatal projection neurons during dopamine depletion. Synapse 2024, 78, e22287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-X.; Ge, X.-Y.; Wang, M.-Y.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y. Dopamine D1 receptor-mediated activation of the ERK signaling pathway is involved in the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, Y.; Gu, M.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Geng, D.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Z. The Dopamine D1 Receptor Attenuates Titanium Particle-Induced Inhibition of Osteogenesis by Activating the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 6331650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Tseng, H.C.; Wong, S.W.; Wang, Z.; Deng, M.; Ko, C.-C. Dopaminergic effects on in vitro osteogenesis. Bone Res. 2015, 3, 15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, D.; Shu, G.; Jin, F.; Du, Y. Recent advances in nanotherapeutics for the treatment and prevention of acute kidney injury. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filseth, O.M.; How, O.-J.; Kondratiev, T.; Gamst, T.M.; Sager, G.; Tveita, T. Changes in cardiovascular effects of dopamine in response to graded hypothermia in vivo*. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefayat, A.; Vaezifar, S. Biodegradable PLGA implants containing doxorubicin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles for treatment of breast tumor-bearing mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, S.; Kan, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Using Platelet-Rich Plasma Hydrogel to Deliver Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Three-Dimensional PLGA Scaffold for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 8607–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tian, M.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z. Berberine-Encapsulated Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)–Hydroxyapatite (PLGA/HA) Microspheres Synergistically Promote Bone Regeneration with DOPA-IGF-1 via the IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Shen, J. 3D printed scaffold for repairing bone defects in apical periodontitis. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wan, Z.; Wei, P.; Lu, X.; Mao, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Dual-Controlled Release of Icariin/Mg2+ from Biodegradable Microspheres and Their Synergistic Upregulation Effect on Bone Regeneration. Adv. Health Mater. 2020, 9, e2000211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann, P.; Rizzoli, R.; Bonjour, J.P.; Bourrin, S.; Meyer, J.M.; Vassalli, P.; Garcia, I. Transgenic mice expressing soluble tumor necrosis factor-receptor are protected against bone loss caused by estrogen deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Jin, H.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H. The mechanism of metformin combined with total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae on ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E.; Sawatari, Y.; Fortin, M.; Broumand, V. Bisphosphonate-induced exposed bone (osteonecrosis/osteopetrosis) of the jaws: Risk factors, recognition, prevention, and treatment. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iimura, K.; Watanabe, N.; Milliken, P.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Lewis, S.J.; Sridhar, A.; Hotta, H. Chronic Electrical Stimulation of the Superior Laryngeal Nerve in the Rat: A Potential Therapeutic Approach for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienkowski, D.; Doers, T.M.; Geng, Z.; Camacho, N.P.; Boskey, A.L.; Malluche, H.H.; Monier-Faugere, M.-C. Calcitonin alters bone quality in beagle dogs. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.D.; Udemba, S.C.; Saleh, S.; Hill, H.; Song, G.; Fass, R. Raloxifene increases the risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus, and esophageal stricture in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, I.-C.; Mo, G.-H.; Chen, M.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liao, D.-L.; Bai, Y.-M.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, T.-T.; Liou, Y.-J. Analysis of genetic variations in the dopamine D1 receptor (DRD1) gene and antipsychotics-induced tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenia. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Feng, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, M.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Yin, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Activation of dopamine receptor D1 promotes osteogenic differentiation and reduces glucocorticoid-induced bone loss by upregulating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danagody, B.; Bose, N.; Rajappan, K.; Iqbal, A.; Ramanujam, G.M.; Anilkumar, A.K. Electrospun PAN/PEG Nanofibrous Membrane Embedded with a MgO/gC3N4 Nanocomposite for Effective Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L. Zoledronate combined metal-organic frameworks for bone-targeting and drugs deliveries. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Swarup, J.; Priya, S.; Jain, R.; Singhvi, G. Exploring the potential of polysaccharide-based hybrid hydrogel systems for their biomedical and therapeutic applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y. Controlled release of dopamine coatings on titanium bidirectionally regulate osteoclastic and osteogenic response behaviors. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 129, 112376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Yang, P.; Peng, S.; Cao, Y.; Yao, X.; Guo, S.; Yang, W. A phosphorylcholine-based zwitterionic copolymer coated ZIF-8 nanodrug with a long circulation time and charged conversion for enhanced chemotherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6128–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, L.L.; Thapa, R.K.; Sullivan, M.O.; Kiick, K.L. Hybrid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 24, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Gao, X.; Ullah, M.W.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, G. Electroconductive natural polymer-based hydrogels. Biomaterials 2016, 111, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Downing, G.; Olsen, K.F.; Sawyer, T.K.; Cone, R.D.; Schwendeman, S.P. Aqueous remote loading of setmelanotide in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for long-term obesity treatment. J. Control. Release 2023, 364, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Y.; Wang, C.; Ge, X.; Lin, Y. Enhancing Osteogenic Potential: Controlled Release of Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist SKF38393 Compared to Free Administration. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051046
Hua Y, Wang C, Ge X, Lin Y. Enhancing Osteogenic Potential: Controlled Release of Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist SKF38393 Compared to Free Administration. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051046
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Yunwei, Chenxi Wang, Xiyuan Ge, and Ye Lin. 2024. "Enhancing Osteogenic Potential: Controlled Release of Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist SKF38393 Compared to Free Administration" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051046
APA StyleHua, Y., Wang, C., Ge, X., & Lin, Y. (2024). Enhancing Osteogenic Potential: Controlled Release of Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist SKF38393 Compared to Free Administration. Biomedicines, 12(5), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051046







