Molecules 2013, 18(12), 15329-15343; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181215329 - 11 Dec 2013
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 7439
Abstract
Multi-origin Chinese herbal medicines, with herbs originating from more than one species of plants, is a common phenomenon but an important issue in Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs). In the present study, a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)—based fatty acid profiling approach to rapidly discriminate
[...] Read more.
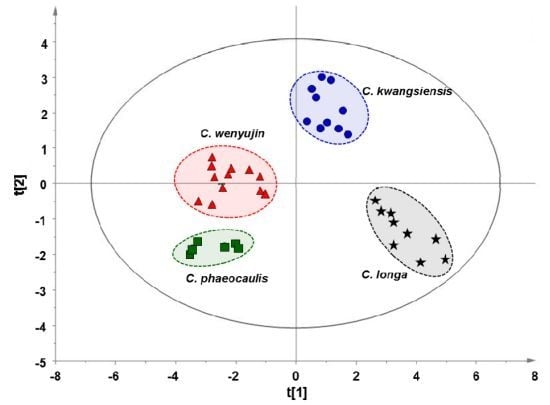
Multi-origin Chinese herbal medicines, with herbs originating from more than one species of plants, is a common phenomenon but an important issue in Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs). In the present study, a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)—based fatty acid profiling approach to rapidly discriminate multi-origin Chinese medicines in terms of species and medicinal parts was proposed and validated using tuberous roots (Curcumae Radix) and rhizomes (Curcumae Rhizoma and Curcumae Longae Rhizoma) derived from four Curcuma species (e.g., C. wenyujin, C. kwangsiensis, C. phaeocaulis and C. longa) as models. Both type and content of fatty acids varied among different species of either tuberous roots or rhizomes, indicating each species has its own fatty acid pattern. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) and hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA) based on dataset of global fatty acid profiling showed that either tuberous roots or rhizomes samples could be clearly classified into four clusters according to their species. Furthermore, those tested samples could also be discriminated in terms of their medicinal parts (e.g., tuberous root and rhizome). Our findings suggest that the proposed GC-MS-based fatty acid profiling followed by multivariate statistical analysis provides a reliable platform to discriminate multi-origin Chinese herbal medicines according to species and medicinal parts, which will be helpful for ensuring their quality, safety and efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fatty Acids)
►
Show Figures