Oxidative Effects during Irreversible Electroporation of Melanoma Cells—In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
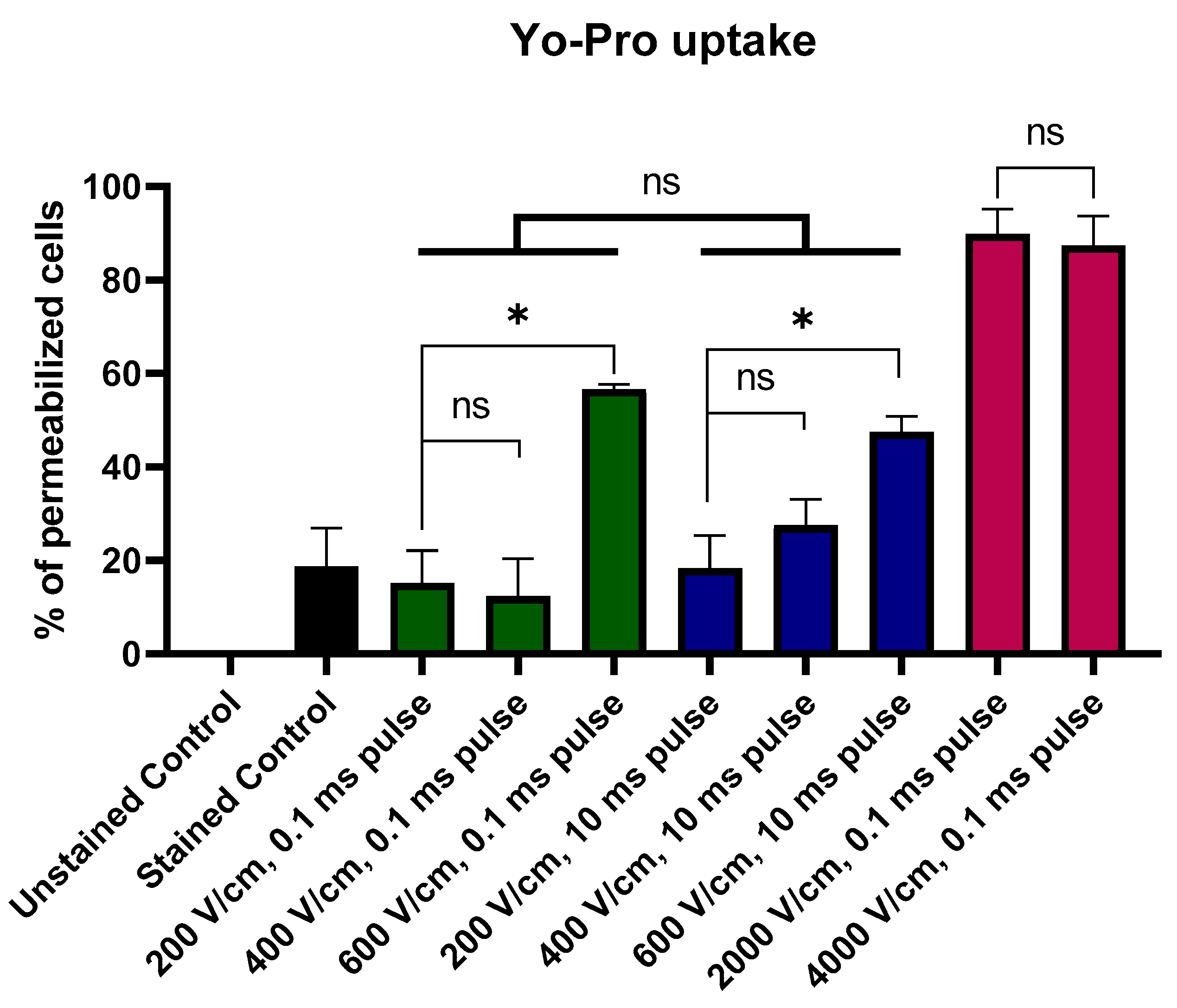
2.1. Yo-Pro Uptake Studies
2.2. Trypan Blue Staining of Permeabilized Cells
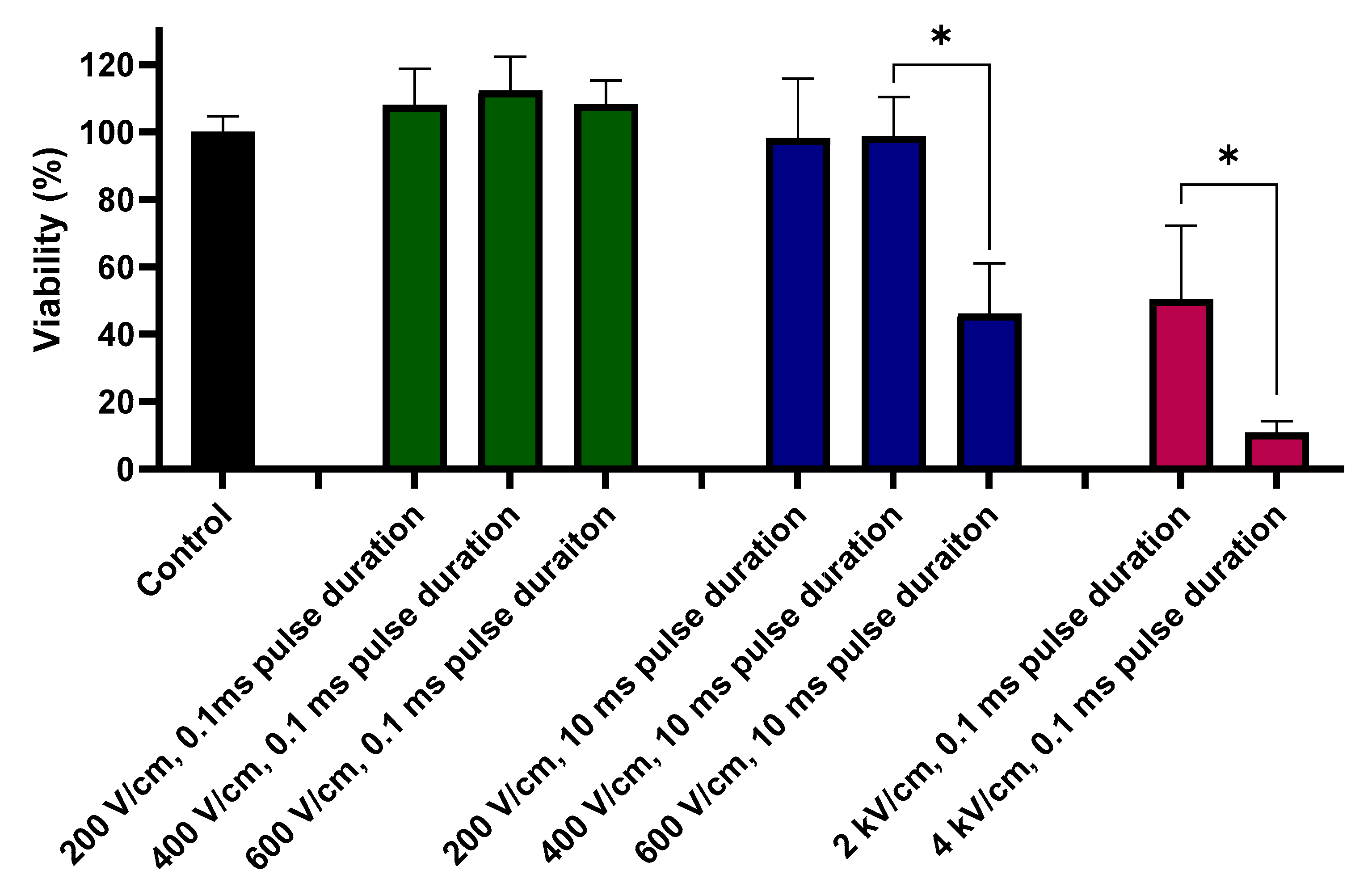
2.3. Viability Assay
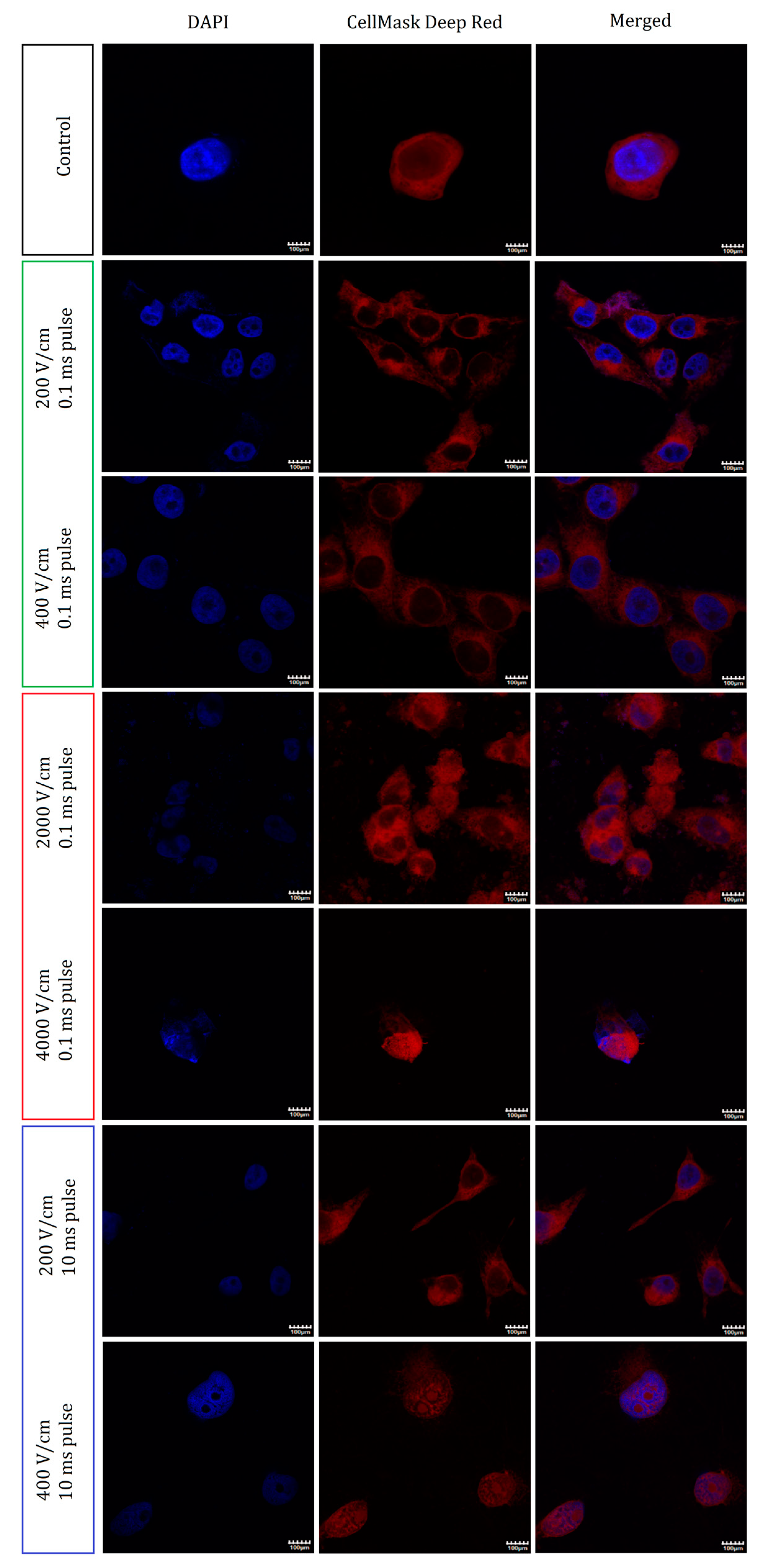
2.4. Nuclei and Membrane Staining
2.5. Holotomographic Microscopy Studies
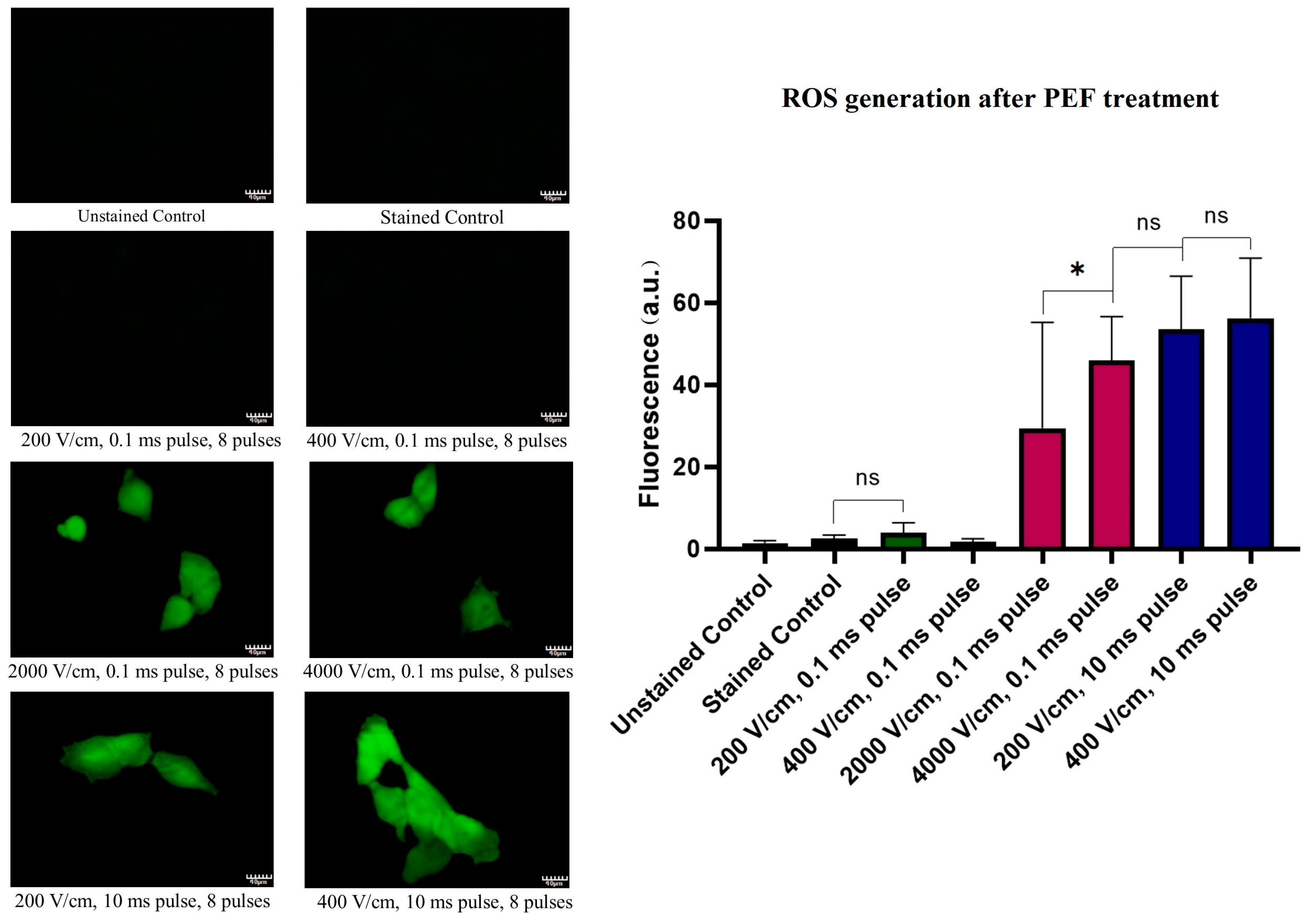
2.6. ROS Cellular Content Staining Studies after PEF Treatment
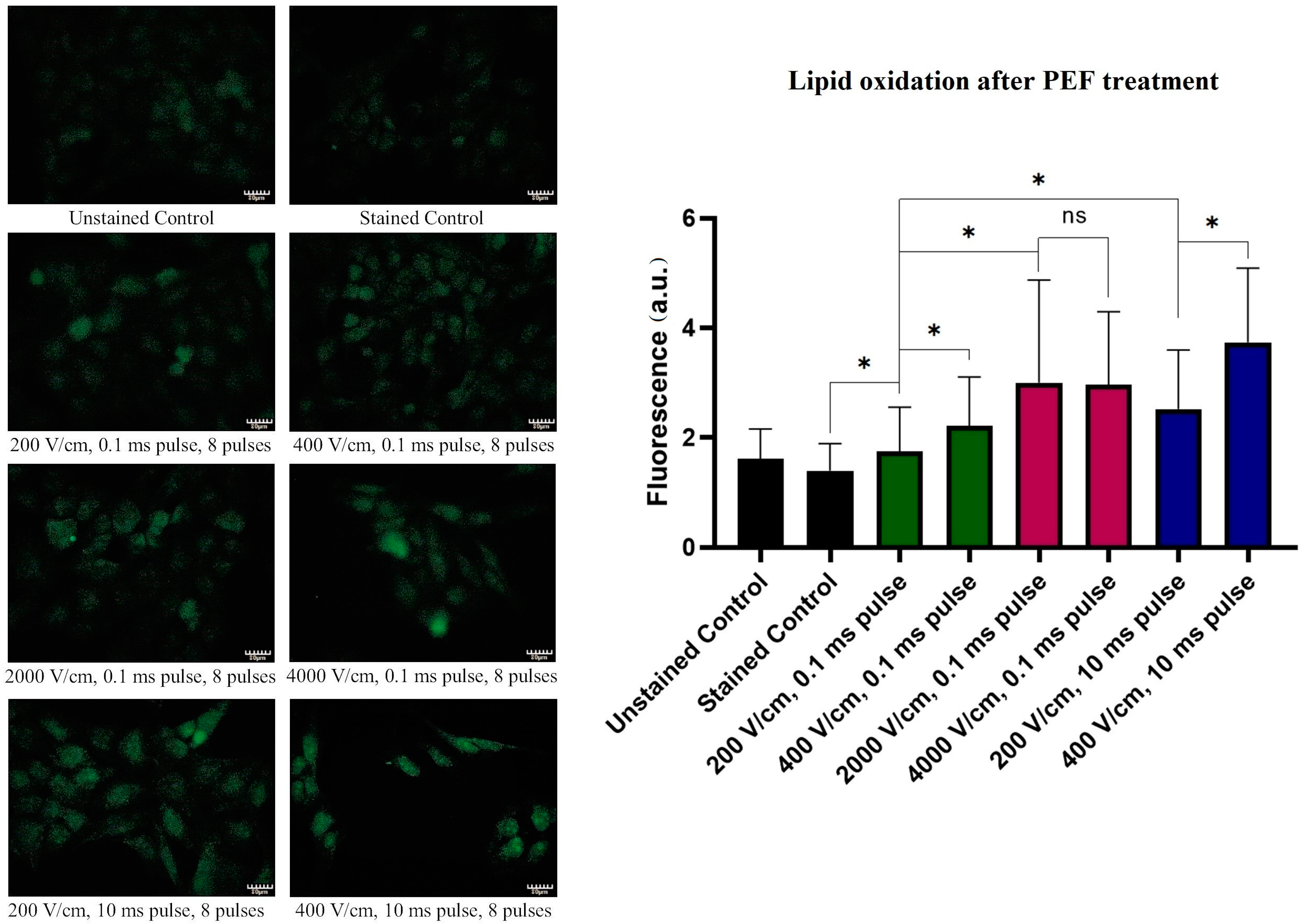
2.7. Lipid Oxidation
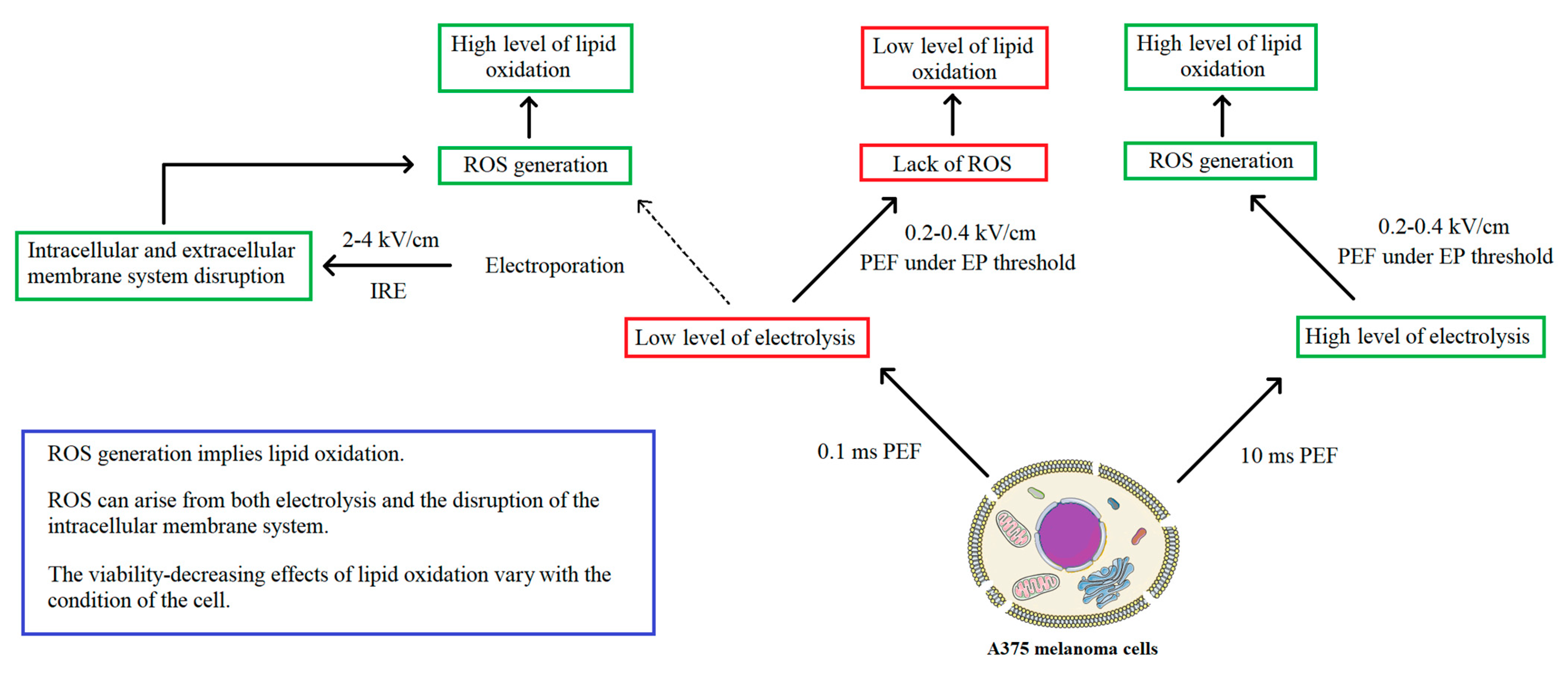
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Electric Field Treatment
4.3. Yo-Pro Uptake Studies
4.4. Trypan Blue Cells Staining
4.5. MTT Viability Assay
4.6. Confocal Microscopy Studies
4.7. Holotomographic Microscopy Studies
4.8. ROS Burst Fluorescent Microscopy Studies
4.9. Lipid Oxidation Fluorescent Microscopy Studies
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moya-Díaz, J.; Peña, O.A.; Sánchez, M.; Ureta, D.A.; Reynaert, N.G.; Anguita-Salinas, C.; Marín, G.; Allende, M.L. Electroablation: A method for neurectomy and localized tissue injury. BMC Dev. Biol. 2014, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raymond-Paquin, A.; Andrade, J.; Macle, L. Catheter ablation: An ongoing revolution. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S212–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, D.F.; Khiatani, V.L.; Carrillo, T.C.; Yap, F.Y.; Bui, J.T.; Knuttinen, M.G.; Owens, C.A.; Gaba, R.C. Current tumor ablation technologies: Basic science and device review. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 27, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brace, C. Thermal tumor ablation in clinical use. IEEE Pulse 2011, 2, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knavel, E.M.; Brace, C.L. Tumor ablation: Common modalities and general practices. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 16, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarts, B.M.; Klompenhouwer, E.G.; Rice, S.L.; Imani, F.; Baetens, T.; Bex, A.; Horenblas, S.; Kok, M.; Haanen, J.B.A.G.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; et al. Cryoablation and immunotherapy: An overview of evidence on its synergy. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghazi, K.; Bergman, J.J.; Pouw, R.E. Radiofrequency Ablation. In Barrett’s Esophagus: Emerging Evidence for Improved Clinical Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 151–169. ISBN 9780128026496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, C.S.; Yu, Y.; Si, Y.M. Thermal ablation in cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2293–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Signoretti, M.; Valente, R.; Repici, A.; Delle Fave, G.; Capurso, G.; Carrara, S. Endoscopy-guided ablation of pancreatic lesions: Technical possibilities and clinical outlook. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.; Landman, J.; Sundaram, C.; Clayman, R.V. Tissue Chemoablation. J. Endourol. 2003, 17, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, T.; Georgiades, C. Percutaneous Cryoablation for Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2015, 2, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Özdoğan, M.; Cevener, M.; Ozluk, A.; Kargi, A.; Kendiroglu, F.; Ogretmen, I.; Yildiz, A. Use of cryoablation beyond the prostate. Insights Imaging 2016, 7, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pusceddu, C.; Paliogiannis, P.; Nigri, G.; Fancellu, A. Cryoablation In The Management Of Breast Cancer: Evidence To Date. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 11, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, P.L. Catheter cryoablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2005, 20, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, S.; Rodriguez, A.P.; Reddy, S.M.L.; Badheka, A.; Deshmukh, A.; Paydak, H. Complications of atrial fibrillation ablation. In Atrial Fibrillation: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 10, pp. 197–217. ISBN 9781629489285. [Google Scholar]
- Abramovits, W.; Graham, G.F.; Har-Shai, Y.; Strumia, R. Dermatological cryosurgery and cryotherapy; Springer: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781447167655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotova, T.G.; Tsybusov, S.N.; Kochenov, V.I.; Tcyganov, M.I. Application of Cryogenic Methods in Skin Diseases of Different Etiology. In Dermatologic Surgery and Procedures; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Park, H.; Lee, H. Comparison of laser-induced damage with forward-firing and diffusing optical fiber during laser-assisted lipoplasty. Lasers Surg. Med. 2013, 45, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Youn, J.I.; Holcomb, J.D. Ablation efficiency and relative thermal confinement measurements using wavelengths 1064, 1320, and 1444 nm for laser-assisted lipolysis. Lasers Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farista, S.; Kalakonda, B.; Koppolu, P.; Baroudi, K.; Elkhatat, E.; Dhaifullah, E. Comparing Laser and Scalpel for Soft Tissue Crown Lengthening: A Clinical Study. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, M.; Matini, N.S. Laser surgery of soft tissue in orthodontics: Review of the clinical trials. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 8, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddama, M.M.R.; Everson, M.; Renshaw, S.; Taj, T.; Boulton, R.; Crosbie, J.; Cohen, C.R. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of haemorrhoidal disease: A minimally invasive and effective treatment modality. Tech. Coloproctol. 2019, 23, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navaneethan, U.; Thosani, N.; Goodman, A.; Manfredi, M.; Pannala, R.; Parsi, M.A.; Smith, Z.L.; Sullivan, S.A.; Banerjee, S.; Maple, J.T. Radiofrequency ablation devices. VideoGIE 2017, 2, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, F.; Li, G.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, R.; Li, W.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of pulmonary tumors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109791–109798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geavlete, B.; Niţă, G.; Jecu, M.; Stănescu, F.; Geavlete, P. Electrovaporization of Prostate Adenoma. In Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment in Prostate Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, R.; Fernández Aparicio, T.; Barceló Bayonas, I.; Pardo Martínez, A.; Muñoz Guillermo, V.; Jiménez Peralta, D.; Carrillo George, C.; Pietricica, B.N.; Izquierdo Morejón, E.; Rosino Sánchez, A.; et al. Outpatient Holmium laser fulguration: A safe procedure for treatment of recurrence of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. Actas Urol. Esp. 2018, 42, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, B.B.; Lowrance, W.T. Office-based Bladder Tumor Fulguration and Surveillance. Indications and Techniques. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 40, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, B.; Lopes, J.; Soares, P.; Populo, H. Melanoma treatment in review. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2018, 7, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudno-rudzinska, J.; Kielan, W.; Guziński, M.; Płochocki, M.; Kulbacka, J. The First Study of Irreversible Electroporation with Calcium Ions and Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, T.; Rems, L.; Tarek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Membrane Electroporation and Electropermeabilization: Mechanisms and Models. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembiałkowska, N.; Dubińska-Magiera, M.; Sikora, A.; Szlasa, W.; Szewczyk, A.; Czapor-Irzabek, H.; Daczewska, M.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Doxorubicin assisted by microsecond electroporation promotes irreparable morphological alternations in sensitive and resistant human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heller, R.; Heller, L.C. Gene Electrotransfer Clinical Trials. Adv. Genet. 2015, 89, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, R.V.; Otten, D.M.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. Electrical Impedance Tomography for Imaging Tissue Electroporation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, S.; Stockert, J.C.; Moreno, V.; Gámez, A.; Pacheco, M.; Juarranz, A.; Cañete, M.; Villanueva, A. Morphological criteria to distinguish cell death induced by apoptotic and necrotic treatments. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffey, B.G.; Anderson, J.K. Current and future technology for minimally invasive ablation of renal cell carcinoma. Indian J. Urol. 2010, 26, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełbik, A.; Szlasa, W.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Electroporation-Based Treatments in Urology. Cancers 2020, 12, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, N.; Gupta, P.; Gorsi, U.; Bhujade, H. Irreversible Electroporation for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Initial Experience. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsky, L.; Guenther, E.; Mikus, P.; Stehling, M.; Rubinsky, B. Electrolytic Effects During Tissue Ablation by Electroporation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, NP95–NP103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pakhomova, O.N.; Khorokhorina, V.A.; Bowman, A.M.; Rodaite, R. Oxidative effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure in cells and cell-free media. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benov, L.C.; Antonov, P.A.; Ribarov, S.R. Oxidative Damage of the Membrane Lipids after Electroporation. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1994, 13, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, B.; Teissié, J. Generation of reactive-oxygen species induced by electropermeabilization of Chinese hamster ovary cells and their consequence on cell viability. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 223, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, B.; Teissié, J. Mammalian cell electropermeabilization as revealed by millisecond imaging of fluorescence changes of ethidium bromide in interaction with the membrane. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1998, 47, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Bladergroen, M.R.; Rosato, N.; Agro, A.F. Role of lipid Peroxidation in Electroporation-induced Cell Permeability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 209, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Rosato, N.; Agrò, A.F. Electroporation enhances cell membrane peroxidation and luminescence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 206, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rems, L.; Viano, M.; Kasimova, M.A.; Miklavčič, D.; Tarek, M. The contribution of lipid peroxidation to membrane permeability in electropermeabilization: A molecular dynamics study. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 125, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Leor, J.; Rubinsky, B. Cancer Cells Ablation with Irreversible Electroporation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 4, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. Effects of irreversible electroporation on cervical cancer cell lines in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, K. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Defenses, and Damage Removal, Repair, and Replacement Systems. IUBMB Life 2001, 50, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, L.F.; Kanaseki, T.; Sabirov, R.; Morishima, S. Apoptotic and necrotic blebs in epithelial cells display similar neck diameters but different kinase dependency. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breton, M.; Mir, L.M. Bioelectrochemistry Investigation of the chemical mechanisms involved in the electropulsation of membranes at the molecular level. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 119, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.; Pakhomova, O.N.; Kolb, J.; Schoenbach, K.S.; Stuck, B.E.; Murphy, M.R.; Pakhomov, A.G. Oxygen Enhances Lethal Effect of High-Intensity, Ultrashort Electrical Pulses. Bioelectromagnetics 2006, 27, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, P.T.; Levine, Z.A.; Wu, Y.-H.; Joubert, V.; Ziegler, M.J.; Mir, L.M.; Tieleman, D.P. Electroporating Fields Target Oxidatively Damaged Areas in the Cell Membrane. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusupov, M.; Van Der Paal, J.; Neyts, E.C.; Bogaerts, A. Synergistic effect of electric field and lipid oxidation on the permeability. BBA Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, N.; Mercadal, B.; Stehling, M.; Ivorra, A. In vitro study on the mechanisms of action of electrolytic electroporation (E2) Bioelectrochemistry In vitro study on the mechanisms of action of electrolytic electroporation. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 133, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Permeability of the Membrane during PEF Treatment | Permeability of the Membrane after PEF Treatment | Long-Term Reduced Viability | ROS Burst | Lipid Oxidation | Change in the Plasma Membrane Integrity | Changes in the Membranes of the Internal Organelles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRE protocols (2–4 kV/cm, 0.1 ms, 8 pulses). | YES | HIGH | YES | YES, voltage-dependent | HIGH, voltage-independent | YES | YES |
| (200–400 V/cm, 0.1 ms, 8 pulses). | NO (same as control) | NO | NO | NO | LOW | NO | NO |
| (200–400 V/cm, 10 ms, 8 pulses). | NO (same as control) | LOW | NO | YES, voltage-independent | HIGH, voltage-dependent | NO | YES, 400 V/cm PEF exclusively |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szlasa, W.; Kiełbik, A.; Szewczyk, A.; Rembiałkowska, N.; Novickij, V.; Tarek, M.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Oxidative Effects during Irreversible Electroporation of Melanoma Cells—In Vitro Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010154
Szlasa W, Kiełbik A, Szewczyk A, Rembiałkowska N, Novickij V, Tarek M, Saczko J, Kulbacka J. Oxidative Effects during Irreversible Electroporation of Melanoma Cells—In Vitro Study. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010154
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzlasa, Wojciech, Aleksander Kiełbik, Anna Szewczyk, Nina Rembiałkowska, Vitalij Novickij, Mounir Tarek, Jolanta Saczko, and Julita Kulbacka. 2021. "Oxidative Effects during Irreversible Electroporation of Melanoma Cells—In Vitro Study" Molecules 26, no. 1: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010154
APA StyleSzlasa, W., Kiełbik, A., Szewczyk, A., Rembiałkowska, N., Novickij, V., Tarek, M., Saczko, J., & Kulbacka, J. (2021). Oxidative Effects during Irreversible Electroporation of Melanoma Cells—In Vitro Study. Molecules, 26(1), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010154









