Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21(12), 4283; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124283 - 16 Jun 2020
Cited by 171 | Viewed by 13348
Abstract
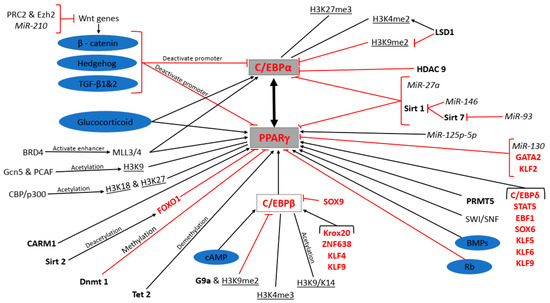
The formation of adipocytes during embryogenesis has been largely understudied. However, preadipocytes appear to originate from multipotent mesenchymal stromal/stem cells which migrate from the mesoderm to their anatomical localization. Most studies on adipocyte formation (adipogenesis) have used preadipocytes derived from adult stem/stromal cells.
[...] Read more.
The formation of adipocytes during embryogenesis has been largely understudied. However, preadipocytes appear to originate from multipotent mesenchymal stromal/stem cells which migrate from the mesoderm to their anatomical localization. Most studies on adipocyte formation (adipogenesis) have used preadipocytes derived from adult stem/stromal cells. Adipogenesis consists of two phases, namely commitment and terminal differentiation. This review discusses the role of signalling pathways, epigenetic modifiers, and transcription factors in preadipocyte commitment and differentiation into mature adipocytes, as well as limitations in our understanding of these processes. To date, a limited number of transcription factors, genes and signalling pathways have been described to regulate preadipocyte commitment. One reason could be that most studies on adipogenesis have used preadipocytes already committed to the adipogenic lineage, which are therefore not suitable for studying preadipocyte commitment. Conversely, over a dozen molecular players including transcription factors, genes, signalling pathways, epigenetic regulators, and microRNAs have been described to be involved in the differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes; however, only peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma has proven to be clinically relevant. A detailed understanding of how the molecular players underpinning adipogenesis relate to adipose tissue function could provide new therapeutic approaches for addressing obesity without compromising adipose tissue function.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Adipogenesis and Adipose Tissue Metabolism 2.0)
►
Show Figures