Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by Peptide YD1 Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms through Suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF-κB Signaling Cascade
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
2.2. YD1 Production and Purification
2.3. Cell Viability Measurement
2.4. Measurement of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and PGE2
2.5. Intracellular ROS Generation Determination
2.6. NF-κB Reporter Assay
2.7. ARE Promoter Activity
2.8. Transfection of Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
2.9. Animals
2.10. RT-PCR, Protein Extraction, and Western Blotting Analysis
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
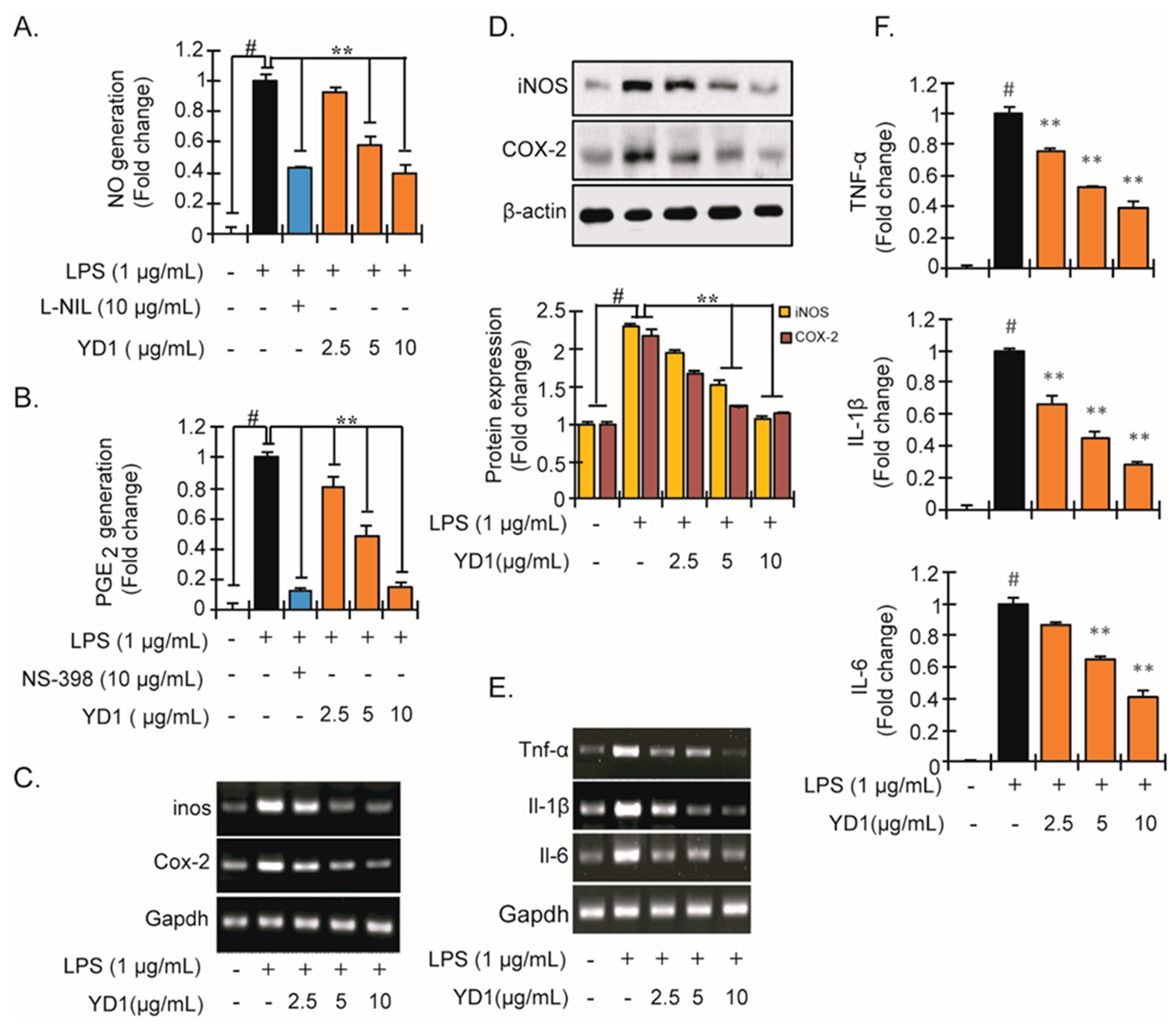
3.1. YD1 Inhibits Inflammatory Responses
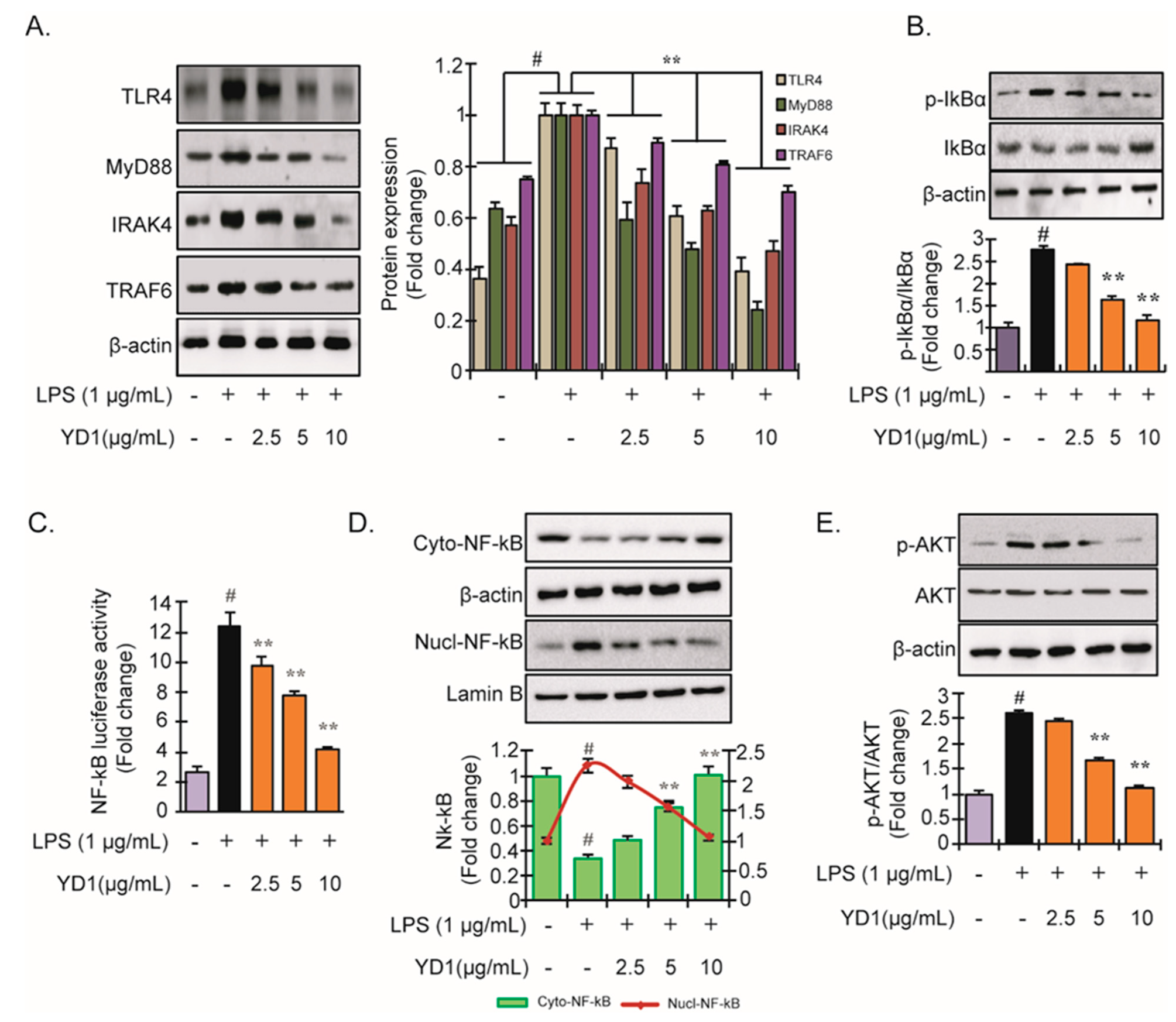
3.2. YD1 Inhibits LPS-Induced TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling
3.3. Nrf2-ARE Signaling and Its Downstream Phase II Antioxidant Enzymes
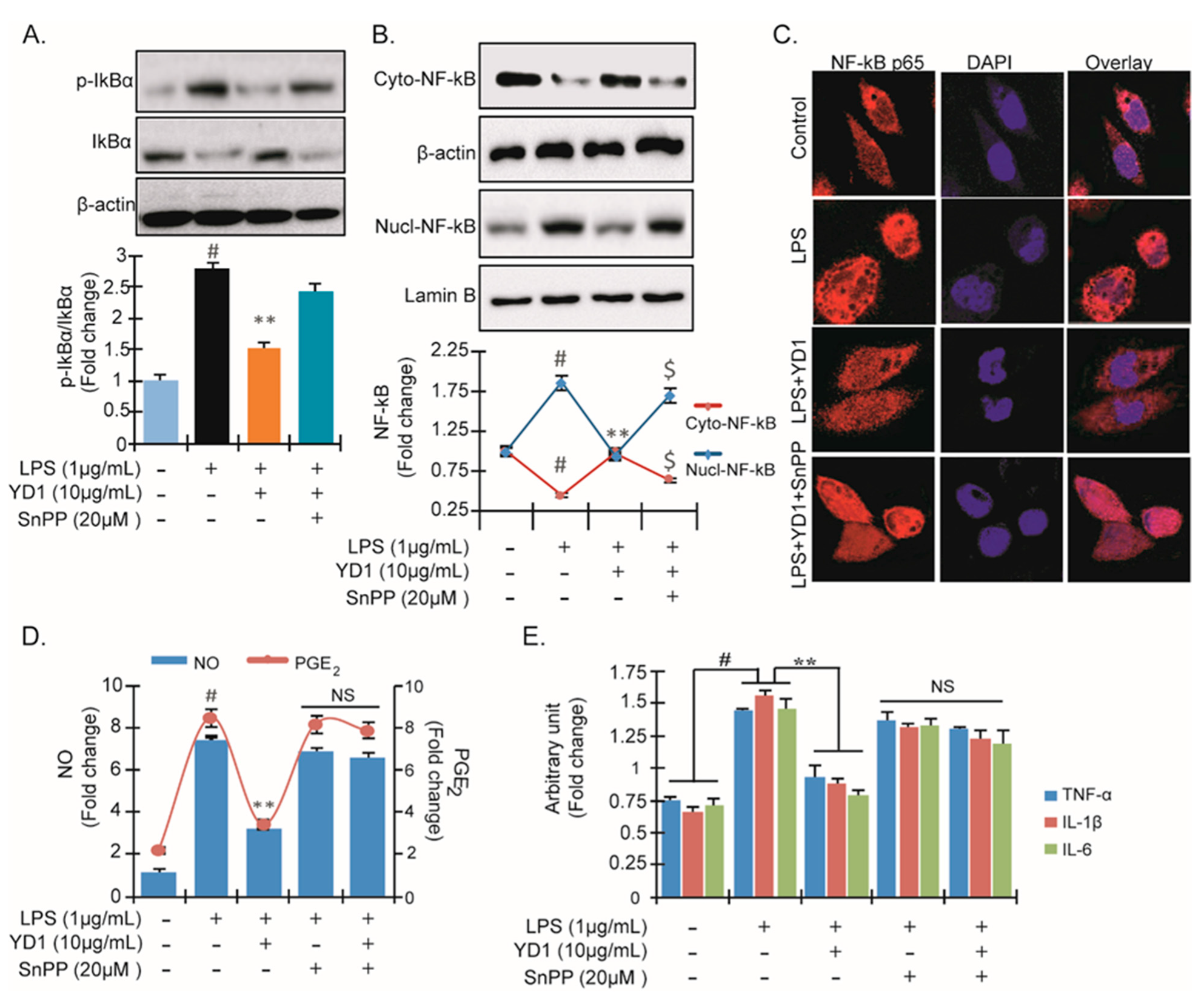
3.4. YD1 Suppresses NF-κB Activation via Nrf2/HO-1-Mediated Pathway
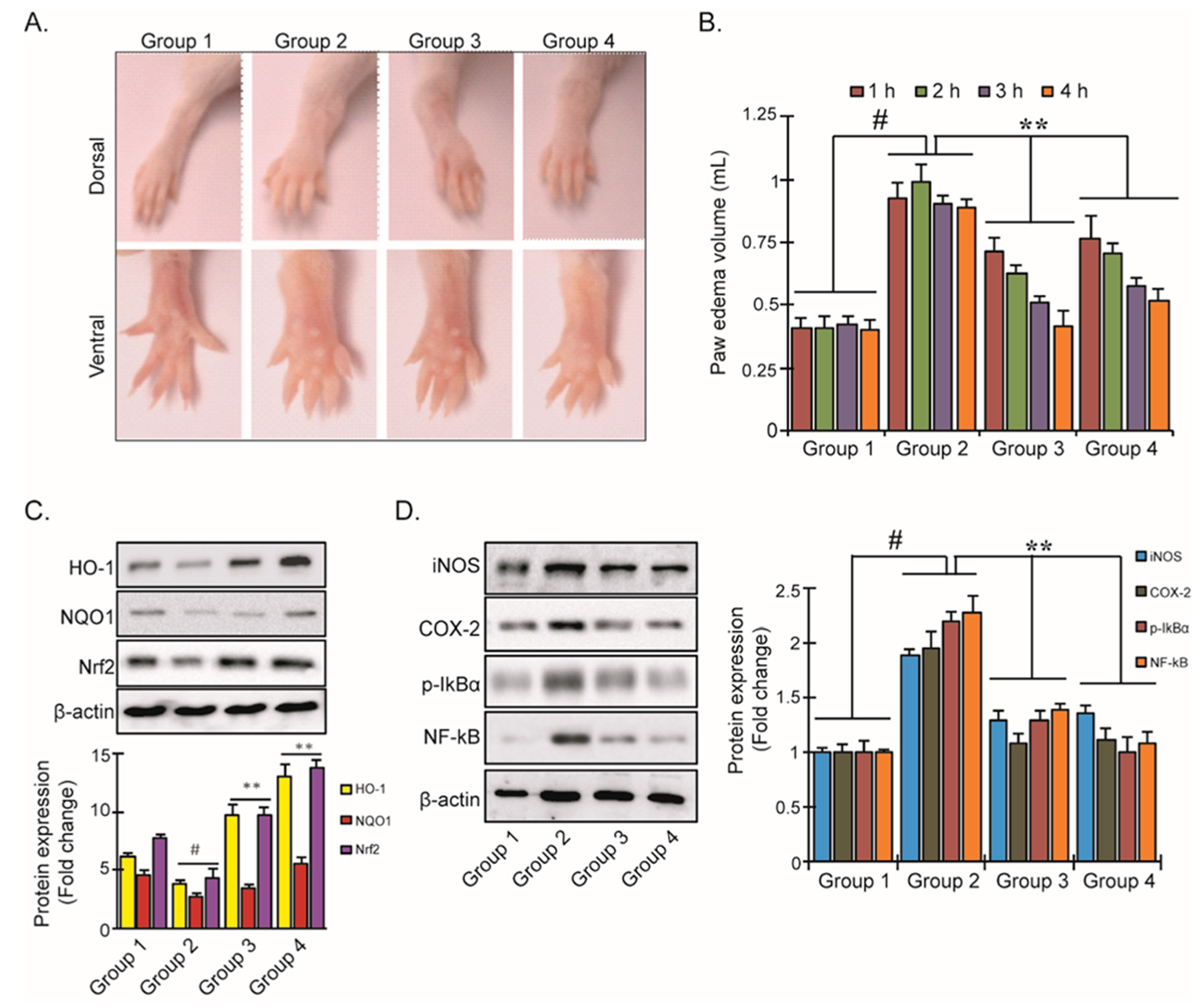
3.5. YD1 Effects on Mouse Paw Edema
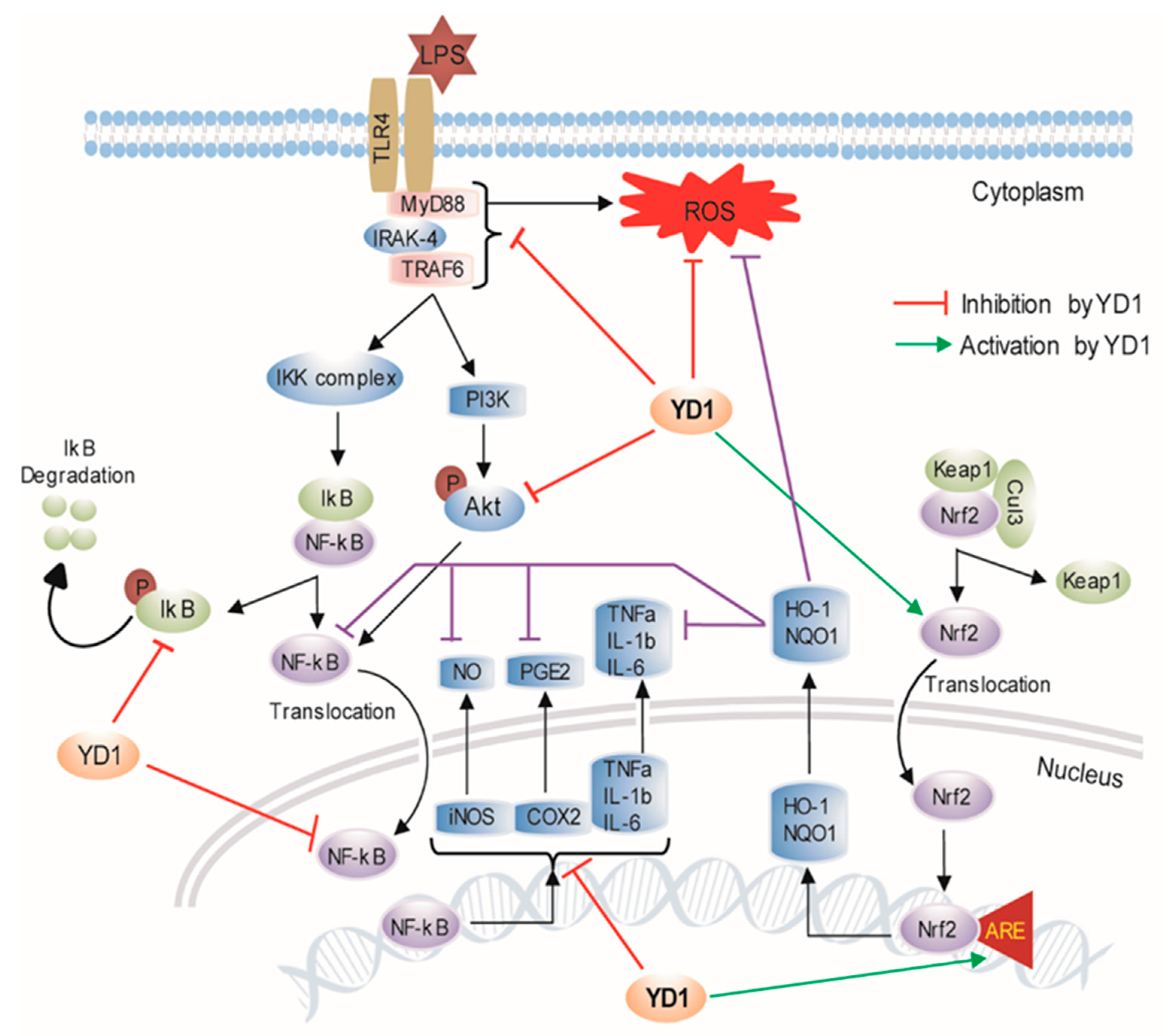
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, R.; Ju, X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, L.; Girgih, A.T.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant activities of rapeseed peptides produced by solid state fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoo, J.C. Glycin-rich antimicrobial peptide YD1 from B. amyloliquefaciens, induced morphological alteration in and showed affinity for plasmid DNA of E. coli. AMB Express 2017, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Alam, M.B.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, J.C. A novel antioxidant peptide, purified from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, showed strong antioxidant potential via Nrf-2 mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.-M.; Shi, W.; Tian, J.-M.; Lei, M.; Kim, J.H.; Sun, Y.N.; Kim, Y.H.; Gao, J.-M. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitory and Anti-inflammatory Components from the Leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (Duzhong). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, O.A.; Lee, S.-C.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, T.-C. Macrophages in oxidative stress and models to evaluate the antioxidant function of dietary natural compounds. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, W.-W.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Li, W.-C.; Lin, B.-F. The production of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 in peritoneal macrophages is inhibited by Andrographis paniculata, Angelica sinensis and Morus alba ethyl acetate fractions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Glass, C.K. Anti-Inflammatory Therapy in Chronic Disease: Challenges and Opportunities. Science 2013, 339, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. Endogenous toll-like receptor ligands and their biological significance. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2592–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilton, P.M.; Embry, C.A.; Mitchell, T.C. Effects of Differences in Lipid A Structure on TLR4 Pro-Inflammatory Signaling and Inflammasome Activation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laird, M.H.; Rhee, S.H.; Perkins, D.J.; Medvedev, A.E.; Piao, W.; Fenton, M.J.; Vogel, S.N. TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions regulate TLR4 signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, L.H.; Ouyang, D.Y.; Liu, K.P.; Pan, H.; He, J.; He, X.H. Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages through differentially modulating the NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, G.-C.; Duh, P.-D.; Huang, D.-W.; Hsu, C.-L.; Fu, T.Y.-C. Protective effect of pine (Pinus morrisonicola Hay.) needle on LDL oxidation and its anti-inflammatory action by modulation of iNOS and COX-2 expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.-I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative Stress Sensor Keap1 Functions as an Adaptor for Cul3-Based E3 Ligase to Regulate Proteasomal Degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scapagnini, G.; Sonya, V.; Nader, A.G.; Calogero, C.; Zella, D.; Fabio, G. Modulation of Nrf2/ARE Pathway by Food Polyphenols: A Nutritional Neuroprotective Strategy for Cognitive and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, H.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Cheng, G.; Ci, X. Isovitexin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activities on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting MAPK and NF-kappaB and Activating HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sostres, C.; Gargallo, C.J.; Arroyo, M.T.; Lanas, A. Adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, aspirin and coxibs) on upper gastrointestinal tract. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscia, G.; Falciani, C.; Bracci, L.; Pini, A. The Development of Antimicrobial Peptides as New Antibacterial Drugs. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, A.; Falciani, C.; Mantengoli, E.; Bindi, S.; Brunetti, J.; Iozzi, S.; Rossolini, G.M.; Bracci, L. A novel tetrabranched antimicrobial peptide that neutralizes bacterial lipopolysaccharide and prevents septic shock in vivo. FASEB J. 2009, 24, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetti, J.; Roscia, G.; Lampronti, I.; Gambari, R.; Quercini, L.; Falciani, C.; Bracci, L.; Pini, A. Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Activity in Vitro and in Vivo of a Novel Antimicrobial Candidate. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25742–25748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, B.; Ju, M.-K.; Lee, S.-H. DNA Protecting Activities of Nymphaea nouchali (Burm. f) Flower Extract Attenuate t-BHP-Induced Oxidative Stress Cell Death through Nrf2-Mediated Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression by Activating MAP-Kinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Alam, M.B.; Quan, K.T.; Ju, M.K.; Majumder, R.; Shukla, S.; Huh, Y.S.; Na, M.K.; Lee, S.H.; Han, Y.K. Attenuation of inflammatory responses by (+)-syringaresinol via MAP-Kinase-mediated suppression of NF-kappaB signaling in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, C.; Graziano, S.; Zimmerman, B.F.; Weidlich, H.H. Antioxidant potential of aqueous plant extracts assessed by the cellular antioxidant activity assay. Am. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2014, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.-S.; Lim, J.; Gal, J.; Kang, J.C.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, B.Y.; Choi, H.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of xanthohumol involves heme oxygenase-1 induction via NRF2-ARE signaling in microglial BV2 cells. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorina, R.; Font-Nieves, M.; Márquez-Kisinousky, L.; SantaLucia, T.; Planas, A.M. Astrocyte TLR4 activation induces a proinflammatory environment through the interplay between MyD88-dependent NFκB signaling, MAPK, and Jak1/Stat1 pathways. Glia 2010, 59, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Ueno, L.; Vogt, P.K. Akt-mediated regulation of NFkappaB and the essentialness of NFkappaB for the oncogenicity of PI3K and Akt. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.Y.; Chen, Z.; Jasmer, K.J.; Chuang, D.Y.; Gu, Z.; Hannink, M.; Simonyi, A. Quercetin Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in BV-2 Microglial Cells: Role of MAPKs on the Nrf2 Pathway and Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, E.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jung, D.H.; Ku, S.K.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C. Hemistepsin A ameliorates acute inflammation in macrophages via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB and activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Shen, S.S.; Deng, X.; Shiu, H.T.; Siu, W.S.; Leung, P.C.; Ko, C.H.; Cheng, B.H. Dihydrofisetin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects associated with suppressing ERK/p38 MAPK and Heme Oxygenase-1 activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and carrageenan-induced mice paw edema. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiehui, Z.; Liuliu, M.; Haihong, X.; Yang, G.; Yingkai, J.; Lun, Z.; Li, D.X.A.; Dongsheng, Z.; Shaohui, Z. Immunomodulating effects of casein-derived peptides QEPVL and QEPV on lymphocytes in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.-L.; Xie, Q.-F. Purification and identification of anti-inflammatory peptides derived from simulated gastrointestinal digests of velvet antler protein (Cervus elaphus Linnaeus). J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, M.-L.; Wang, H.-C.; Hsu, K.-C. Anti-inflammatory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of tuna cooking juice. Food Agric. Immunol. 2015, 26, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Teng, H.; Fang, T.; Xiao, J. Agrimonolide from Agrimonia pilosa suppresses inflammatory responses through down-regulation of COX-2/iNOS and inactivation of NF-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yang, L.; Wan, C.-X.; Xia, Y.-Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, Z.-D.; Li, Z.-R.; Li, X.-M.; Geng, Y.-D.; et al. Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides in LPS-activated BV2 microglia by MAPK, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-P.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Ye, Y.-J.; Shang, X.-M.; Cai, Y.-L.; Xiong, C.-M.; Wu, Y.-X.; Xu, H.-X. Topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of kirenol isolated from Siegesbeckia orientalis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, L.; Zavatti, M.; Geminiani, E.; Zanoli, P.; Baraldi, M. Anti-inflammatory activity of the non-peptidyl low molecular weight radical scavenger IAC in carrageenan-induced oedema in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.-Y.; Ju, J.M.; Mo, L.H.; Ma, L.; Hu, W.H.; You, R.R.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qiu, S.Q. Anti-inflammation action of xanthones from Swertia chirayita by regulating COX-2/NF-κB/MAPKs/Akt signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Sanjo, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takeda, Y.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: Evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 3749–3752. [Google Scholar]
- Son, D.H.; Yang, D.J.; Sun, J.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, N.; Kang, J.Y.; Choi, Y.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Moh, S.H.; Shin, D.M.; et al. A Novel Peptide, Nicotinyl–Isoleucine–Valine–Histidine (NA–IVH), Promotes Antioxidant Gene Expression and Wound Healing in HaCaT Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, C.H.; Chen, T.P.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.M.; Lin, P.J. HO-1 activation can attenuate cardiomyocytic apoptosis via inhibition of NF-kappaB and AP-1 translocation following cardiac global ischemia and reperfusion. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 155, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-S.; Chau, L.-Y. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 in mice. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.S.; Alam, M.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Madina, M.H.; Fliss, I.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, J.C. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by Peptide YD1 Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms through Suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF-κB Signaling Cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105161
Rahman MS, Alam MB, Kim YK, Madina MH, Fliss I, Lee SH, Yoo JC. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by Peptide YD1 Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms through Suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF-κB Signaling Cascade. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105161
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Saifur, Md Badrul Alam, Young Kyun Kim, Mst Hur Madina, Ismail Fliss, Sang Han Lee, and Jin Cheol Yoo. 2021. "Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by Peptide YD1 Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms through Suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF-κB Signaling Cascade" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105161
APA StyleRahman, M. S., Alam, M. B., Kim, Y. K., Madina, M. H., Fliss, I., Lee, S. H., & Yoo, J. C. (2021). Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by Peptide YD1 Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms through Suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF-κB Signaling Cascade. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105161








