Interaction of the Transcription Factors BES1/BZR1 in Plant Growth and Stress Response
Abstract
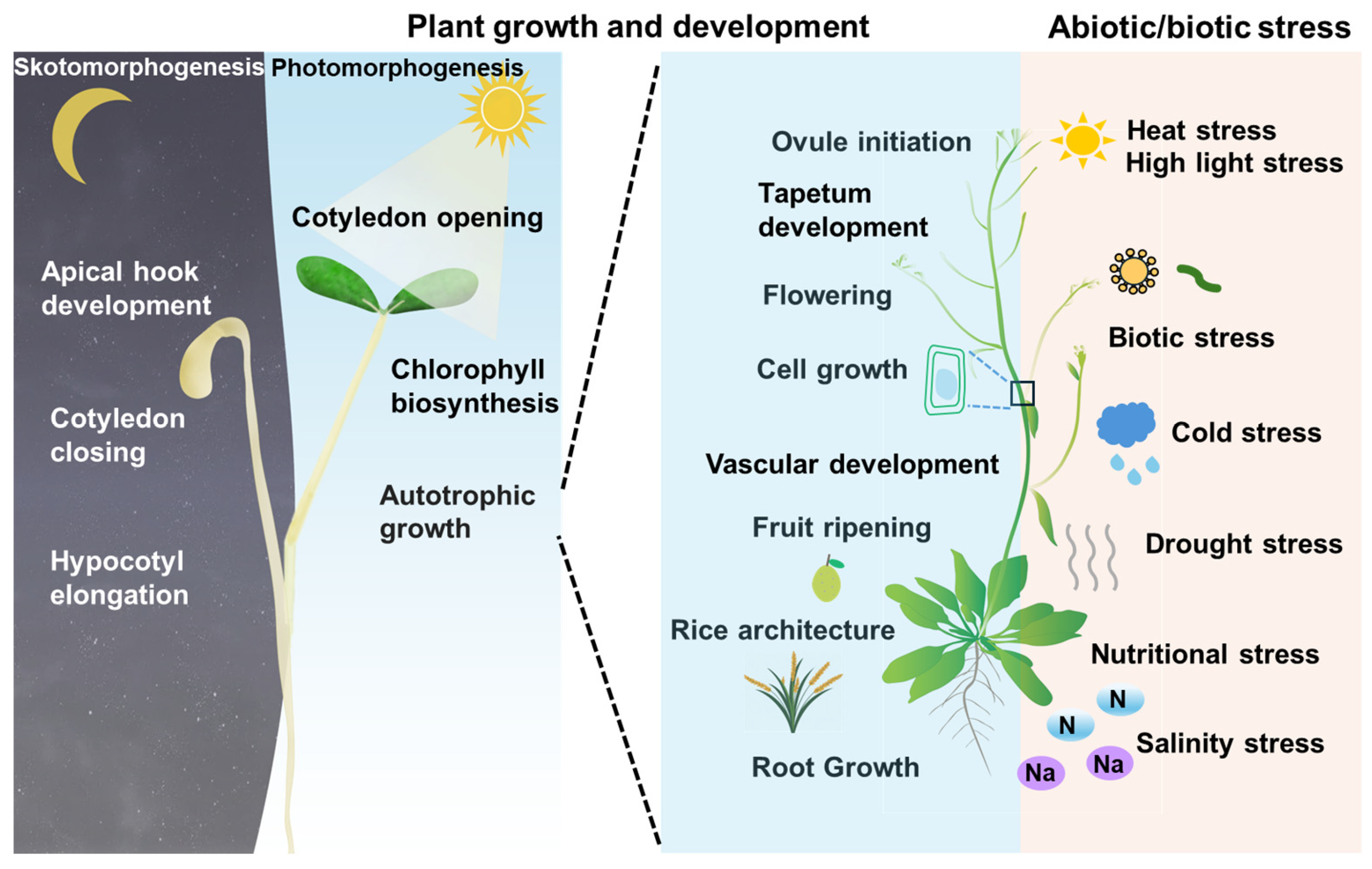
:1. Introduction
2. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Plant Growth and Development
2.1. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Skotomorphogenesis and Photomorphogenesis
2.2. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Root Growth
2.3. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Other Developmental Processes
3. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Stress Response
3.1. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Abiotic Stress Response
3.2. Interactors of BES1/BZR1 in Biotic Stress Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Chory, J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell 1997, 90, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Seto, H.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Chory, J. BRI1 is a critical component of a plasma-membrane receptor for plant steroids. Nature 2001, 410, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Cano-Delgado, A.; Seto, H.; Hiranuma, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Chory, J. Binding of brassinosteroids to the extracellular domain of plant receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 2005, 433, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Delgado, A.; Yin, Y.; Yu, C.; Vafeados, D.; Mora-Garcia, S.; Cheng, J.C.; Nam, K.H.; Li, J.; Chory, J. BRL1 and BRL3 are novel brassinosteroid receptors that function in vascular differentiation in Arabidopsis. Development 2004, 131, 5341–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Wang, H.; Walker, J.C.; Li, J. BRL1, a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase, is functionally redundant with BRI1 in regulating Arabidopsis brassinosteroid signaling. Plant J. 2004, 40, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.; Lease, K.A.; Doke, J.T.; Tax, F.E.; Walker, J.C. BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Li, J. BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hothorn, M.; Belkhadir, Y.; Dreux, M.; Dabi, T.; Noel, J.P.; Wilson, I.A.; Chory, J. Structural basis of steroid hormone perception by the receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 2011, 474, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Han, Z.; Kim, T.W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, W.; Chang, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Structural insight into brassinosteroid perception by BRI1. Nature 2011, 474, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.; Henzler, C.; Hothorn, M. Molecular mechanism for plant steroid receptor activation by somatic embryogenesis co-receptor kinases. Science 2013, 341, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Lu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.X.; Ma, H.; Wang, X. Dual role of BKI1 and 14-3-3s in brassinosteroid signaling to link receptor with transcription factors. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Nam, K.H. Regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase. Science 2002, 295, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Nakano, T.; Gendron, J.; He, J.; Chen, M.; Vafeados, D.; Yang, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; et al. Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Mora-Garcia, S.; Li, J.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 2002, 109, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Yuan, M.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Kim, T.W.; Zhou, H.W.; Deng, Z.; Gampala, S.S.; et al. PP2A activates brassinosteroid-responsive gene expression and plant growth by dephosphorylating BZR1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, X.Y.; Cao, D.M.; Tang, W.; He, K.; Zhu, J.Y.; He, J.X.; Bai, M.Y.; Zhu, S.; Oh, E.; et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, L.; Zola, J.; Aluru, M.; Ye, H.; Foudree, A.; Guo, H.; Anderson, S.; Aluru, S.; Liu, P.; et al. A brassinosteroid transcriptional network revealed by genome-wide identification of BES1 target genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2011, 65, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukasinovic, N.; Liu, D.; Russinova, E.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Li, J. Molecular mechanisms of brassinosteroid-mediated responses to changing environments in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.X.; Gendron, J.M.; Sun, Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Gendron, N.; Sun, C.Q.; Wang, Z.Y. BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 2005, 307, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Vafeados, D.; Tao, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell 2005, 120, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampala, S.S.; Kim, T.W.; He, J.X.; Tang, W.; Deng, Z.; Bai, M.Y.; Guan, S.; Lalonde, S.; Sun, Y.; Gendron, J.M.; et al. An essential role for 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Guan, S.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Z.; Tang, W.; Shang, J.X.; Sun, Y.; Burlingame, A.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Brassinosteroid signal transduction from cell-surface receptor kinases to nuclear transcription factors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.X.; Gendron, J.M.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.Y. The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates and destabilizes BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10185–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, C.; Cai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Nolan, T.; Yu, F.; Yin, Y.; Xie, Q.; Tang, G.; Wang, X. SINAT E3 ligases control the light-mediated stability of the brassinosteroid-activated transcription factor BES1 in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2017, 41, 47–58.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Jeong, Y.J.; Corvalan, C.; Fujioka, S.; Cho, S.; Park, T.; Choe, S. Darkness and gulliver2/phyB mutation decrease the abundance of phosphorylated BZR1 to activate brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2014, 77, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, W.; Jia, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Strigolactone/MAX2-induced degradation of brassinosteroid transcriptional effector BES1 regulates shoot branching. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.H.; Kim, S.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, T.W. Plant U-Box40 mediates degradation of the brassinosteroid-responsive transcription factor BZR1 in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.J.; Cui, L.H.; Oh, T.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, W.T. OsBZR1 turnover mediated by OsSK22-regulated U-box E3 ligase OsPUB24 in rice BR response. Plant J. 2019, 99, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Bai, Q.; Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, G.; Ren, H.; She, X.; Wu, G. EMS1 and BRI1 control separate biological processes via extracellular domain diversity and intracellular domain conservation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.A.; Cui, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Gou, X.; Li, J. BES1 is activated by EMS1-TPD1-SERK1/2-mediated signaling to control tapetum development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Chai, M.; Xi, X.; Aslam, M.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Su, H.; et al. Signaling by the EPFL-ERECTA family coordinates female germline specification through the BZR1 family in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, X.; Thompson, A.; Guo, M.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J.; Yin, Y. Arabidopsis MYB30 is a direct target of BES1 and cooperates with BES1 to regulate brassinosteroid-induced gene expression. Plant J. 2009, 58, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Li, L.; Guo, H.; Yin, Y. MYBL2 is a substrate of GSK3-like kinase BIN2 and acts as a corepressor of BES1 in brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20142–20147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ye, H.; Guo, H.; Johnson, A.; Zhang, M.; Lin, H.; Yin, Y. Transcription factor HAT1 is phosphorylated by BIN2 kinase and mediates brassinosteroid repressed gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2014, 77, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Zhu, J.Y.; Bai, M.Y.; Arenhart, R.A.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Cell elongation is regulated through a central circuit of interacting transcription factors in the Arabidopsis hypocotyl. Elife 2014, 3, e03031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, B.; Dong, H.; He, G.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J. BIC1 acts as a transcriptional coactivator to promote brassinosteroid signaling and plant growth. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e104615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Liu, P.; Zhang, T.; Dong, H.; Jing, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, M.; Liu, J.; et al. Plant-specific BLISTER interacts with kinase BIN2 and BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT1 during skotomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 1580–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.Y.; Shang, J.X.; Oh, E.; Fan, M.; Bai, Y.; Zentella, R.; Sun, T.P.; Wang, Z.Y. Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plitsi, P.K.; Samakovli, D.; Roka, L.; Rampou, A.; Panagiotopoulos, K.; Koudounas, K.; Isaioglou, I.; Haralampidis, K.; Rigas, S.; Hatzopoulos, P.; et al. GA-mediated disruption of RGA/BZR1 complex requires HSP90 to promote hypocotyl elongation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, M.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, C.; Fan, M.; Guo, H.; Bai, M.Y. Interaction between BZR1 and EIN3 mediates signalling crosstalk between brassinosteroids and ethylene. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 2308–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, N.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, F.; Xiang, M.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.W.; Wei, N. Brassinosteroids promote etiolated apical structures in darkness by amplifying the ethylene response via the EBF-EIN3/PIF3 circuit. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Lv, M.; He, L.; Bai, W.; Cheng, S.; Chu, J.; He, K.; et al. Jasmonates regulate apical hook development by repressing brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 1561–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tian, Y.; Shi, W.; Yu, P.; Hu, Y.; Lv, J.; Fu, C.; Fan, M.; Bai, M.Y. The miR396-GRFs module mediates the prevention of photo-oxidative damage by brassinosteroids during seedling de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2525–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Liu, J.; He, G.; Liu, P.; Sun, J. Photoexcited phytochrome B interacts with brassinazole resistant 1 to repress brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Li, L.; Lian, H.; Mao, Z.; Xu, P.; Guo, T.; Xu, F.; Du, S.; Cao, X.; et al. Photoexcited CRYPTOCHROME1 interacts with dephosphorylated BES1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1989–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Liu, J.; Dong, H.; Sun, J. The blue-light receptor CRY1 interacts with BZR1 and BIN2 to modulate the phosphorylation and nuclear function of BZR1 in repressing BR signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Mei, S.; Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Yin, Y.; et al. UVR8 interacts with BES1 and BIM1 to regulate transcription and photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2018, 44, 512–523.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, N.; Ramachandran, H.; Job, N.; Yadav, A.; Vaishak, K.P.; Datta, S. B-box protein BBX32 integrates light and brassinosteroid signals to inhibit cotyledon opening. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Niu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; et al. Brassinosteroid signaling restricts root lignification by antagonizing SHORT-ROOT function in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 1182–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Guo, J.; Han, C.; Zhou, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, S.; Tang, W.; et al. Integrated regulation of periclinal cell division by transcriptional module of BZR1-SHR in Arabidopsis roots. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilarrasa-Blasi, J.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.P.; Frigola, D.; Fabregas, N.; Alexiou, K.G.; Lopez-Bigas, N.; Rivas, S.; Jauneau, A.; Lohmann, J.U.; Benfey, P.N.; et al. Regulation of plant stem cell quiescence by a brassinosteroid signaling module. Dev. Cell 2014, 30, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Caruana, J.C.; Yang, H.Q.; Lian, H. Arabidopsis G-Protein beta subunit AGB1 interacts with BES1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and cell elongation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jing, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, R. The chromatin-remodeling factor PICKLE integrates brassinosteroid and gibberellin signaling during skotomorphogenic growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2472–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, G.; Qi, G.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, H.; Bai, Z.; Bai, M.Y.; Hu, R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, G.; et al. The CCCH zinc finger protein C3H15 negatively regulates cell elongation by inhibiting brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Mao, Z.; Guo, S.; Yang, C.; Weng, Y.; et al. The cyclophilin CYP20-2 modulates the conformation of BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT1, which binds the promoter of FLOWERING LOCUS D to regulate flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2504–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Qu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, J.; Chu, J.; Xu, M.; Su, X.; Yuan, H.; Wang, A. The mechanism for brassinosteroids suppressing climacteric fruit ripening. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1875–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Tong, H.; Fang, J.; Bu, Q. Transcription factor OsWRKY53 positively regulates brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; He, M.; Mei, E.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, W.; et al. WRKY53 integrates classic brassinosteroid signaling and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to regulate rice architecture and seed size. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2753–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, S.; Mei, E.; He, M.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Oryza sativa mediator subunit OsMED25 interacts with OsBZR1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendreau, E.; Traas, J.; Desnos, T.; Grandjean, O.; Caboche, M.; Hofte, H. Cellular basis of hypocotyl growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1997, 114, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiwanon, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.Y.; Oh, E.; Wang, Z.Y. Information integration and communication in plant growth regulation. Cell 2016, 164, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Xiang, W.; Liang, Q.; Wen, L.; Shi, Y.; Song, B.; Liu, Y.; Xian, Z.; Li, Z. Tomato SlBES1.8 influences leaf morphogenesis by mediating gibberellin metabolism and signaling. Plant Cell Physiol. 2022, 63, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, D.M.; Bai, M.Y.; Luo, X.M.; Yang, H.J.; Wei, C.Q.; Zhu, S.W.; Sun, Y.; Chong, K.; et al. BZS1, a B-box protein, promotes photomorphogenesis downstream of both brassinosteroid and light signaling pathways. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtan, H.E.; Bandong, S.; Marion, C.M.; Adam, L.; Tiwari, S.; Shen, Y.; Maloof, J.N.; Maszle, D.R.; Ohto, M.; Preuss, S.; et al. BBX32, an Arabidopsis B-box protein, functions in light signaling by suppressing HY5-regulated gene expression and interacting with STH2/BBX21. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, C.; Delker, C.; Martinez, C.; Burstenbinder, K.; Janitza, P.; Lippmann, R.; Ludwig, W.; Sun, H.; James, G.V.; Klecker, M.; et al. Brassinosteroids dominate hormonal regulation of plant thermomorphogenesis via BZR1. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 303–310.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiwanon, J.; Wang, Z.Y. Spatiotemporal brassinosteroid signaling and antagonism with auxin pattern stem cell dynamics in Arabidopsis roots. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzani, R.; Cui, H.; Moreno-Risueno, M.A.; Busch, W.; Van Norman, J.M.; Vernoux, T.; Brady, S.M.; Dewitte, W.; Murray, J.A.; Benfey, P.N. Spatiotemporal regulation of cell-cycle genes by SHORTROOT links patterning and growth. Nature 2010, 466, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, S.H.; Jiang, Y.T.; Chang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xue, H.W.; Lin, W.H. Interaction of brassinosteroid and cytokinin promotes ovule initiation and increases seed number per silique in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Nolan, T.M.; Ye, H.; Zhang, M.; Tong, H.; Xin, P.; Chu, J.; Chu, C.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y. Arabidopsis WRKY46, WRKY54, and WRKY70 Transcription factors are involved in brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and drought responses. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Liu, S.; Tang, B.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z.; Nolan, T.M.; Jiang, H.; Guo, H.; Lin, H.Y.; Li, L.; et al. RD26 mediates crosstalk between drought and brassinosteroid signalling pathways. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Nolan, T.; Jiang, H.; Tang, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y. The AP2/ERF transcription factor TINY modulates brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and drought responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1788–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.S.; Nakashima, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Simpson, S.D.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Fujita, M.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Isolation and functional analysis of Arabidopsis stress-inducible NAC transcription factors that bind to a drought-responsive cis-element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 promoter. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertos, P.; Dundar, G.; Schenk, P.; Carrera, S.; Cavelius, P.; Sieberer, T.; Poppenberger, B. Transcription factor BES1 interacts with HSFA1 to promote heat stress resistance of plants. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e108664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, G.; Tohge, T.; Matsuda, F.; Saito, K.; Scheible, W.R. Members of the LBD family of transcription factors repress anthocyanin synthesis and affect additional nitrogen responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3567–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.; Chen, J.; Yue, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; de Dios, V.R.; Yao, Y.; Tan, W. Interaction of BES1 and LBD37 transcription factors modulates brassinosteroid-regulated root forging response under low nitrogen in arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 998961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loque, D.; von Wiren, N. Regulatory levels for the transport of ammonium in plant roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, A.; Moriya, K.; Sonoda, Y.; Ikeda, A.; Von Wiren, N.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Yamaya, T. Constitutive expression of a novel-type ammonium transporter OsAMT2 in rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.H.; Priatama, R.A.; Huang, J.; Je, B.I.; Liu, J.M.; Park, S.J.; Piao, H.L.; Son, D.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Park, S.H.; et al. Indeterminate domain 10 regulates ammonium-mediated gene expression in rice roots. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xuan, Y.H. BZR1 regulates brassinosteroid-mediated activation of AMT1;2 in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 665883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, S.; Li, D.; Priatama, R.A.; Kumar, V.; Xuan, Y.H. Mutation of phytochrome B promotes resistance to sheath blight and saline-alkaline stress via increasing ammonium uptake in rice. Plant J. 2023, 113, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.; Peng, Y.J.; Yuan, L.B.; Dai, Y.S.; Chen, Q.F.; Yu, L.J.; Bai, M.Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Xie, L.J.; Xiao, S. Brassinosteroids antagonize jasmonate-activated plant defense responses through BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR1 (BES1). Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Zheng, H.; Tang, X.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Bai, M.Y.; et al. The BZR1-EDS1 module regulates plant growth-defense coordination. Mol Plant 2021, 14, 2072–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Yang, S.; Feng, L.; Chu, J.; Dong, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Yamamoto, N.; Zheng, A.; et al. Red-light receptor phytochrome B inhibits BZR1-NAC028-CAD8B signaling to negatively regulate rice resistance to sheath blight. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Si, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Berne, S.; Yuan, D.; Lindsey, K.; et al. Orchestration of plant development and defense by indirect crosstalk of salicylic acid and brassinosteorid signaling via transcription factor GhTINY2. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 4721–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divi, U.K.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid: A biotechnological target for enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance. New Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Locus | Effect on Plant Growth through Interaction with BES1/BZR1 | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARF6 | AT1G30330 | Promoting cell elongation and hypocotyl growth | [36] |
| PIF4 | AT2G43010 | Promoting cell elongation and hypocotyl growth | [36] |
| BIC1 | AT3G52740 | Promoting cell and hypocotyl elongation | [37] |
| BLI | AT3G23980 | Promoting hypocotyl elongation in darkness | [38] |
| RGA | AT2G01570 | Inhibiting cell elongation and BR-regulated plant growth | [39] |
| HSP90 | AT5G52640 | Promoting hypocotyl elongation | [40] |
| EIN3 | AT3G20770 | Promoting apical hook development | [41] |
| SAUR17 | AT4G09530 | Promoting apical hook and closed cotyledon | [42] |
| WAG2 | AT3G14370 | Inhibiting apical hook development | [43] |
| GRF7 | AT5G53660 | Repressing chlorophyll biosynthesis promoting cell elongation | [44] |
| phyB | AT2G18790 | Repressing BR signaling | [45] |
| CRY1 | AT4G08920 | Inhibiting hypocotyl elongation under blue light | [46,47] |
| UVR8 | AT5G63860 | Repressing BR-regulated photomorphogenesis | [48] |
| BBX32 | AT3G21150 | Inhibiting cotyledon opening | [49] |
| SHR | AT4G37650 | Suppressing root lignification promoting periclinal division | [50,51] |
| BRAVO | AT5G17800 | Suppressing root quiescent center division | [52] |
| AGB1 | AT4G34460 | Promoting cell elongation | [53] |
| PKL | AT2G25170 | Promoting cell elongation | [54] |
| C3H15 | AT1G68200 | Inhibiting cell elongation | [55] |
| CYP20-2 | AT5G13120 | Promoting flowering | [56] |
| ACO1 | AT2G19590 | Promoting fruit ripening | [57] |
| OsWRKY53 | Os05g0343400 | Regulating rice architecture and increasing seed size | [58,59] |
| OsMED25 | Os09g0306700 | Regulating rice architecture | [60] |
| Gene Name | Locus | Effect on Stress Tolerance through Interaction with BES1/BZR1 | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| WRKY46 | AT2G46400 | Suppressing drought response | [70] |
| WRKY54 | AT2G40750 | Suppressing drought response | |
| WRKY70 | AT3G56400 | Suppressing drought response | |
| RD26 | AT4G27410 | Inhibiting BR-regulated growth under drought condition | [71] |
| TINY | AT5G25810 | Inhibiting BR-regulated growth under drought condition | [72] |
| HSFA1a | AT4G17750 | Improving heat stress | [74] |
| LBD37 | AT5G67420 | Promoting nitrogen response | [76] |
| OsIDD10 | Os04g47860 | Improving nitrogen uptake | [81] |
| phyB | AT2G18790 | Inhibiting nitrogen uptake and sheath blight resistance | [81,84] |
| MYB34 | AT5G60890 | Suppressing insect defense | [82] |
| MYB122 | AT1G74080 | Suppressing insect defense | [82] |
| MYB51 | AT1G18570 | Suppressing insect defense | [82] |
| EDS1 | AT3G48090 | Increasing pathogen resistance | [83] |
| GhTINY2 | GhD06G0642 | Increased immune response | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Wei, Y.; Shen, B.; Liu, L.; Mao, J. Interaction of the Transcription Factors BES1/BZR1 in Plant Growth and Stress Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136836
Cao X, Wei Y, Shen B, Liu L, Mao J. Interaction of the Transcription Factors BES1/BZR1 in Plant Growth and Stress Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):6836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136836
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xuehua, Yanni Wei, Biaodi Shen, Linchuan Liu, and Juan Mao. 2024. "Interaction of the Transcription Factors BES1/BZR1 in Plant Growth and Stress Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 6836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136836
APA StyleCao, X., Wei, Y., Shen, B., Liu, L., & Mao, J. (2024). Interaction of the Transcription Factors BES1/BZR1 in Plant Growth and Stress Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 6836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136836






