Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Acanthochiton rubrolineatus (Polyplacophora) Based on Mitochondrial and Nuclear Gene Markers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity Based on Mitochondrial Gene Markers
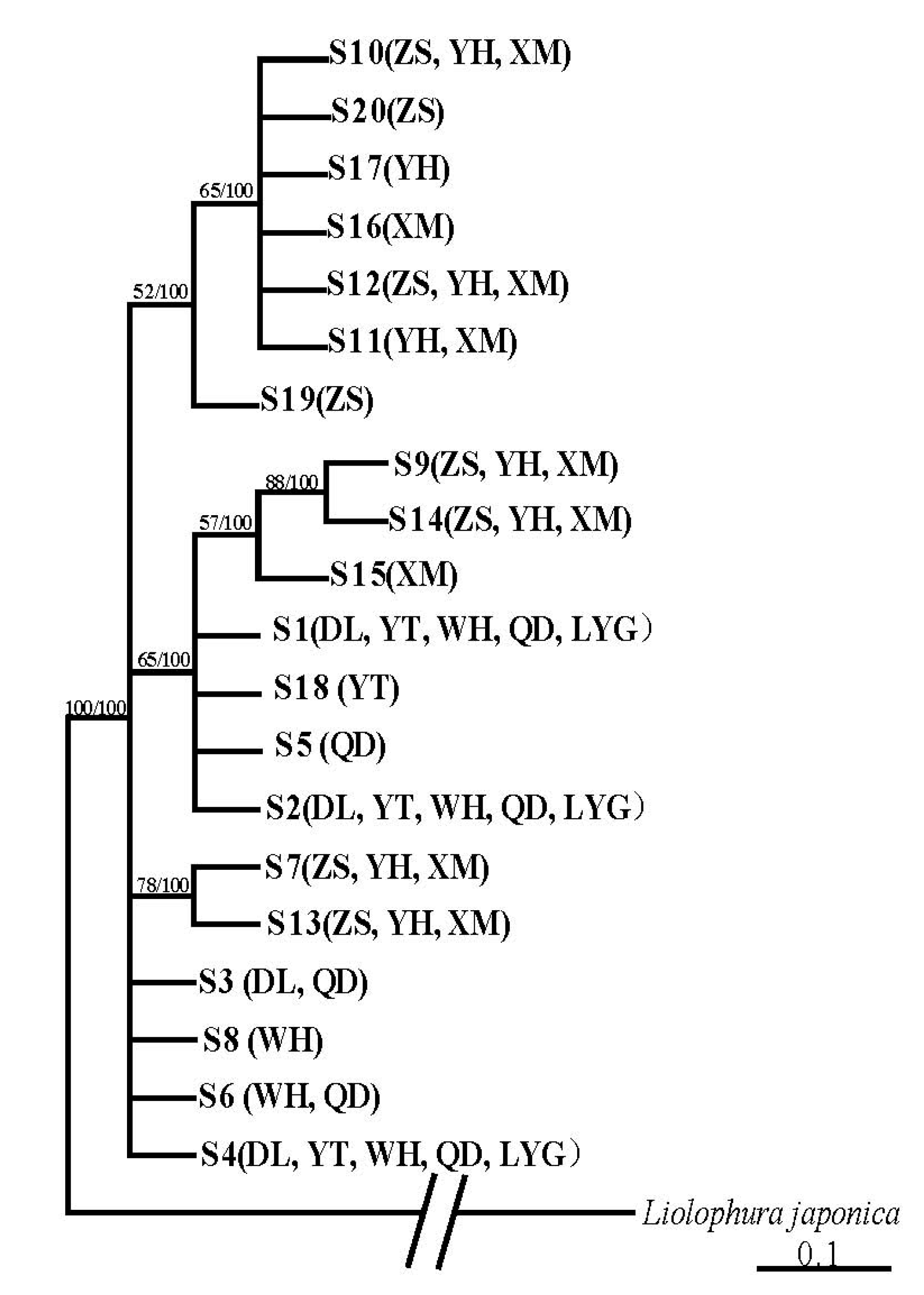
3.2. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity of A. rubrolineatus Inferred from 28S-rRNA Sequences
4. Discussion
4.1. Significant Genetic Divergence Between Northern and Southern Groups of A. rubrolineatus
4.2. Historic Demography of A. rubrolineatus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwabe, E. A catalogue of Recent and fossil chitons (Mollusca: Polyplacophora). Addenda. Novapex 2005, 6, 89–105. [Google Scholar]
- Puchalski, S.S.; Eernisse, D.J.; Johnson, C.C. The effect of sampling bias on the fossil record of chitons (Mollusca, Polyplacophora)*. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2008, 25, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S. Taxonomic study on some common species of Polyplacophora in the coast of China based on valves and rudular morphology. Mar. Sci. 2015, 39, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusu, A.; Schwabe, E.; Eernisse, D.J.; Giribet, G. Towards a phylogeny of chitons (Mollusca, Polyplacophora) based on combined analysis of five molecular loci. Org. Divers. Evol. 2003, 3, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denny, M.W.; Gaines, S.D. Encyclopedia of tidepools and rocky shores. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 154, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigwart, J.D. Morphological cladistic analysis as a model for character evaluation in primitive living chitons (Polyplacophora, Lepidopleurina)*. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2009, 27, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherholz, M.; Redl, E.; Wollesen, T.; Todt, C.; Wanninger, A. Aplacophoran mollusks evolved from ancestors with polyplacophoran-like features. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigwart, J.D.; Sutton, M.D. Deep molluscan phylogeny: Synthesis of palaeontological and neontological data. Proc. R. Soc. B 2007, 274, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, R.; Sun, X.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. The complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Acanthochitona rubrolineatus (Lischke, 1873). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 2622–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wray, C.G.; Jacobs, D.K.; Kostriken, R.; Vogler, A.P.; Baker, R.; Desalle, R. Homologues of the engrailed gene from five molluscan classes. FEBS Lett. 1995, 365, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winnepenninckx, B.; Backeljau, T.; Wachter, R.D. Complete small ribosomal subunit RNA sequence of the chiton Acanthopleura japonica (Lischke, 1873) (Mollusca, Polyplacophora). Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyle, P.R. Aspects of the ecology of a littoral chiton, Sypharochiton pellisekpentis (Mollusca: Polyplacophora). N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 4, 364–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clode, P.L. Charge contrast imaging of biomaterials in a variable pressure scanning electron microscope. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 155, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrasco, M.J.; Wood, T.E.; Runnegar, B.N. Articulated Palaeozoic fossil with 17 plates greatly expands disparity of early chitons. Nature 2004, 429, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, S.; Wanninger, A.; Brückner, M.; Haszprunar, G. Neurogenesis in the mossy chiton, Mopalia muscosa (Gould) (Polyplacophora): Evidence against molluscan metamerism. J. Morphol. 2002, 253, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Tyurin, S.A.; Nezlin, L.P. Neuronal development in larval chiton Ischnochiton hakodadensis (Mollusca: Polyplacophora). J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 444, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, A.; Haszprunar, G. Chiton myogenesis: Perspectives for the development and evolution of larval and adult muscle systems in molluscs. J. Morphol. 2002, 251, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Jacobs, D.K. Expression of Distal-less in molluscan eggs, embryos, and larvae. Evol. Dev. 1999, 1, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Deng, M. Medicinal Fauna of China, 2rd ed.; Tianjin Science & Technology Press: Tianjin, China, 1983; p. 571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Li, X. Anticancer activity of 21 marine invertebrate species. Mar. Sci. 2003, 27, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Han, L. Antitumor and immune regulation activities of the extracts of some Chinese marine invertebrates. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2005, 23, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Niu, R. Immunomodulatory acitity determination of ethanol extracts from some marine invertebrates. Chin. J. Immunol. 2003, 19, 739–743. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Huang, C.; Miao, H.; Jiao, B.; Yuan, Q. Screening of bioactive products in twelve kinds of marine animals from Zhoushan archipelago in Zhejiang province. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2005, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Cui, L.; Liu, X. Morphology and mineral contents of the radula of chiton (Acanthochiton rubrolineatus lischke). Acta Zool. Sin. 2001, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X. Magnetite in the radula teeth of chiton. J. Sichuan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 55, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschvink, J.L.; Lowenstam, H.A. Mineralization and magnetization of chiton teeth: Paleomagnetic, sedimentologic, and biologic implications of organic magnetite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 44, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joester, D.; Brooker, L.R. Chapter 8. The Chiton Radula: A Model System for Versatile Use of Iron Oxides*. In Iron Oxides: From Nature to Applications; Faivre, D., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masato, O. Phylogenetic Relationships Among Japanese Species of the Genus Ischnochiton (Polyplacophora: Ischnochitonidae), Including a New Species. Zool. Sci. 2018, 35, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Luo, X. Compendium of Materia Medica; Foreign Languages Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, L. Study on Invertebrate Communities in Rocky Intertidal Zones Influenced by Human Activities. J. Oceanogr. Huanghai Bohai Seas 2001, 19, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y. Structure and behavior of Chitons. Reserv. Fish. 2007, 27, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, A.C.; Chartosia, N.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Kleitou, P.; Jimenez, C.; Antoniou, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Kletou, D.; Sfenthourakis, S. Genetic Data Suggest Multiple Introductions of the Lionfish (Pterois miles) into the Mediterranean Sea. Diversity 2019, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, A.R. An Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2010, 83, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riesgo, A.; Pérez-Portela, R.; Pita, L.; Blasco, G.; Erwin, P.M.; Lόpez-Legentil, S. Population structure and connectivity in the Mediterranean sponge Ircinia fasciculata are affected by mass mortalities and hybridization. Heredity 2016, 117, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ammon, U.V.; Wood, S.A.; Laroche, O.; Zaiko, A.; Tait, L.; Lavery, S.; Inglis, G.J.; Pochon, X. Combining morpho-taxonomy and metabarcoding enhances the detection of non-indigenous marine pests in biofouling communities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, C.; Clark, M.R.; Rowden, A.A.; Kelly, M.; Gardner, J.P.A. The use of spatially explicit genetic variation data from four deep-sea sponges to inform the protection of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Zhao, R.; Deng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, J.; Huang, L.; Jing, M. Genetic diversity and population structure of penis fish (Urechis unicinctus) based on mitochondrial and nuclear gene markers. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Yoo, W.G.; Park, H.C.; Yoo, H.S.; Kang, D.W.; Jin, S.D.; Min, H.K.; Paek, W.K.; Lim, J. DNA barcoding of fish, insects, and shellfish in Korea. Genom. Inform. 2012, 10, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Du, W.; Hou, J.; Yao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J. Genetic Diversity of Acanthochiton rubrolineatus in the Bohai Rim. Sichuan J. Zool. 2019, 38, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, S. Observations on the Shell Plates of 9 Chiton Species (Polyplacophora). Period. Ocean Univ. China 2010, 40, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The ClustalX windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: An important software for molecular biology. Gerf. Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258565830 (accessed on 4 January 2019).
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genet. Soc. Am. 1989, 123, 585–595. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1203831/ (accessed on 13 August 2019).
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posada, D. Chapter 6. Unit 6.5. Using MODELTEST and PAUP* to select a model of nucleotide substitution. In Current Protocols in Bioinformatics; Bateman, A., Draghici, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P. ModelTest Server: A web-based tool for the statistical selection of models of nucleotide substitution online. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöger, I.; Sigwart, J.D.; Kano, Y.; Knebelsberger, T.; Marshall, B.A.; Schwabe, E.; Schrödl, M. The continuing debate on deep molluscan phylogeny: Evidence for Serialia (Mollusca, Monoplacophora + Polyplacophora). Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 407072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.P.; Paulay, G.G. Fine Scale Endemism on Coral Reefs: Archipelagic Differentiation in Turbinid Gastropods. Evolution 2005, 59, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, T.J.; Lemer, S.; Bouchet, P.; Kano, Y.; Giribet, G. Putting keyhole limpets on the map: Phylogeny and biogeography of the globally distributed marine family Fissurellidae (Vetigastropoda, Mollusca). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 135, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A. Phylogeny and Genetic Diversity of Palolo Worms (Palola, Eunicidae) from the Tropical North Pacific and the Caribbean. Biol. Bull. 2006, 210, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, A.; Liu, G.; Shao, K.; Wang, L. Genetic diversity and differentiation of seven geographical populations of hard clam (Meretrix, meretrix) assessed by COI and microsatellite markers. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y. Genetic polymorphisms of Liolophura japonica among the southern of Zhejiang Province based on DNA barcoding. Mar. Fish. 2018, 40, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupalo, K.; Teixeira, M.A.L.; Rewicz, T.; Sezgin, M.; Iannilli, V.; Karaman, G.S.; Grabowski, M.; Costa, F.O. Persistence of phylogeographic footprints helps to understand cryptic diversity detected in two marine amphipods widespread in the Mediterranean basin. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 132, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumisha, C.; Mdegela, R.H.; Gwakisa, P.S.; Kochzius, M. Genetic diversity and gene flow among the giant mud crabs (Scylla serrata) in anthropogenic-polluted mangroves of mainland Tanzania: Implications for conservation. Fish. Res. 2018, 205, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Evolution and the genetics of populations. Vol. 1. Genetic and biométrie foundations. Biometrics 1968, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. A Second Installment. (Book Reviews: Evolution and the Genetics of Populations. Vol. 2, The Theory of Gene Frequencies). J. Biosoc. Sci. 1970, 168, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Evolution and the genetics of populations. Volume 3. Experimental results and evolutionary deductions. Syst. Bot. 1977, 59, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, C.; Okusu, A.; Schander, C.; Schwabe, E. Chapter 4. Solenogastres, Caudofoveata, and Polyplacophroa. In Phylogeny and Evolution of the Mollusca; Ponder, W.F., Lindberg, D.R., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 71–96. [Google Scholar]
- Buckland-Nicks, J.; Gibson, G. Chapter 13. Phylum Mollusca: Polyplacophora, Aplacophora, and Scaphopoda. In Atlas of Marine Invertebrate Larvae; Yong, C.M., Sewell, M.A., Rice, M.E., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Eernisse, D.; Reynolds, P. Chapter 3. Polyplacophora. In Microscopic Anatomy of Invertebrates; Harrison, F.W., Kohn, A.J., Eds.; Wiley-Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 56–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pearse, J. Polyplacophora. In Reproduction in Marine Invertebrates; Giese, A.C., Pearse, J.S., Eds.; Pelecypods and Lesser Classes; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 27–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P. The ice-age China sea—Status and problems. Quat. Sci. 1990, 2, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- ECCBR. China Bay Records; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X. A preliminary study of the demarcation of marine molluscan faunal regions of China and its adjacent waters. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1963, 5, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, M.I. Warming strengthens an herbivore–plant interaction. Ecology 2009, 90, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniash, E.; Ivanina, A.; Lieb, N.S.; Kurochkin, I.; Sokolova, I.M. Elevated level of carbon dioxide affects metabolism and shell formation in oysters Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin). Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2010, 419, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C.; Neigel, J.E.; Arnold, J. Demographic influences on mitochondrial DNA lineage survivorship in animal population. J. Mol. Evol. 1984, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Leng, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Molecular analysis and genetic diversity of Aedes albopictus (Diptera, Culicidae) from China. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2017, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Liu, H. On the glacial and interglacial stages in quaternary of China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 1999, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, Q. Genetic evidence for the existence of cryptic species in an endangered clam Coelomactra antiquata. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chan, T.Y.; Tsang, L.M.; Chu, K.H. Phylogeography of the mitten crab Eriocheir sensu stricto in East Asia: Pleistocene isolation, population expansion and secondary contact. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 52, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Ge, S.; Wang, Q.; Yu, D.; Guan, S. Population structuring and historical demography of a common clam worm Perinereris aibuhitensis near the coasts of Shandong Peninsula. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 44, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G. Phylogeography of four marine bivalves along China’ coastline with views into the evolutionary processes and mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, M. Risk zoning of economic loss caused by storm surge in coastal provinces and cities of China. J. Nat. Disasters 2011, 20, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Locality | Abbreviation | Numbers | Longitude and Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dalian | DL | 30 | 38°86′N, 121°56′E |
| Yantai | YT | 30 | 37°53′N, 121°43′E |
| Weihai | WH | 30 | 36°88′N, 122°44′E |
| Qingdao | QD | 30 | 36°06′N, 120°32′E |
| Lianyungang | LYG | 30 | 34°70′N, 119°49′E |
| Zhoushan | ZS | 30 | 29°92′N, 122°41′E |
| Yuhuan | YH | 30 | 28°07′N, 121°29′E |
| Xiamen | XM | 28 | 24°43′N, 118°16′E |
| Locality | h | S | Hd | π | Tajima’ D | Fu’s Fs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern group | DL | 20 | 43 | 0.959 | 0.00987 | 0.00822 | −3.477 |
| YT | 21 | 37 | 0.943 | 0.00743 | −0.59889 | −6.558 | |
| WH | 17 | 44 | 0.922 | 0.00742 | −0.96299 | −2.432 | |
| QD | 19 | 136 | 0.908 | 0.01059 | −2.61845 *** | −2.368 ** | |
| LYG | 13 | 37 | 0.648 | 0.00389 | −2.08043 * | −2.388 * | |
| Southern group | ZS | 18 | 19 | 0.890 | 0.00152 | −2.24605 ** | −18.181 ** |
| YH | 17 | 16 | 0.841 | 0.00171 | −2.01532 * | −14.609 | |
| XM | 13 | 130 | 0.720 | 0.00980 | −2.76645 *** | 0.813 ** | |
| Northern group | 58 | 177 | 0.858 | 0.00871 | −2.34182 ** | −28.505 ** | |
| Southern group | 34 | 140 | 0.639 | 0.00379 | −2.93430 *** | −21.671 ** | |
| All | 92 | 249 | 0.889 | 0.03310 | −1.01579 | −8.042 ** | |
| Locality | DL | YT | WH | QD | LYG | ZS | YH | XM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL | 0.01096 | 0.01162 | 0.01182 | 0.01489 | 0.01223 | 0.06142 | 0.06106 | 0.06339 |
| YT | 0.06241 | 0.00733 | 0.00749 | 0.00885 | 0.00604 | 0.06463 | 0.06423 | 0.06651 |
| WH | 0.07094 | −0.02071 | 0.00804 | 0.00918 | 0.00637 | 0.06440 | 0.06401 | 0.06631 |
| QD | 0.13911 | 0.01659 | 0.04893 | 0.00988 | 0.00692 | 0.06838 | 0.06797 | 0.07025 |
| LYG | 0.11915 | 0.00016 | 0.01029 | 0.03733 | 0.00414 | 0.06572 | 0.06531 | 0.06761 |
| ZS | 0.67827 | 0.71471 | 0.73669 | 0.69332 | 0.72798 | 0.00101 | 0.00105 | 0.00577 |
| YH | 0.68957 | 0.72569 | 0.74835 | 0.70249 | 0.73939 | −0.02332 | 0.00107 | 0.00579 |
| XM | 0.59467 | 0.63200 | 0.64987 | 0.61816 | 0.64653 | −0.01641 | −0.00791 | 0.01050 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jing, M.; Huang, L. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Acanthochiton rubrolineatus (Polyplacophora) Based on Mitochondrial and Nuclear Gene Markers. Diversity 2020, 12, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12040159
Xu H, Chu Z, Zhang J, Jing M, Huang L. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Acanthochiton rubrolineatus (Polyplacophora) Based on Mitochondrial and Nuclear Gene Markers. Diversity. 2020; 12(4):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12040159
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Haowen, Zhailin Chu, Jing Zhang, Meidong Jing, and Ling Huang. 2020. "Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Acanthochiton rubrolineatus (Polyplacophora) Based on Mitochondrial and Nuclear Gene Markers" Diversity 12, no. 4: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12040159





