Influence of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Factor X on species D Human Adenovirus Uptake and Transduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Adenovirus Library
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis of HSPG
2.4. Virus Transduction Detected by Luciferase Assay
2.5. Virus Cellular Entry Detected by Duplex qPCR
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. HSPG-Expression of the Used CHO Cell Lines
3.2. Sulfation of Heparan Chains Is Relevant for Adenovirus Transduction via HSPG
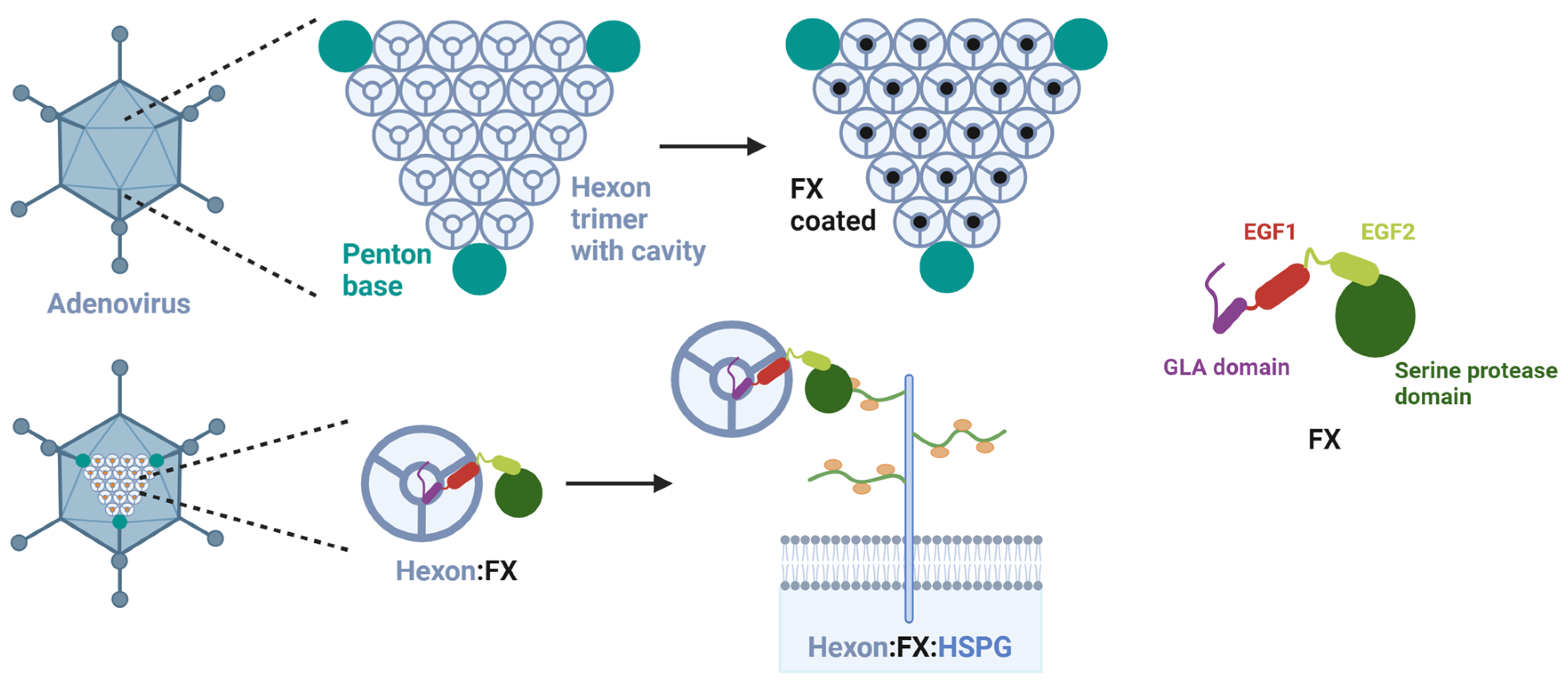
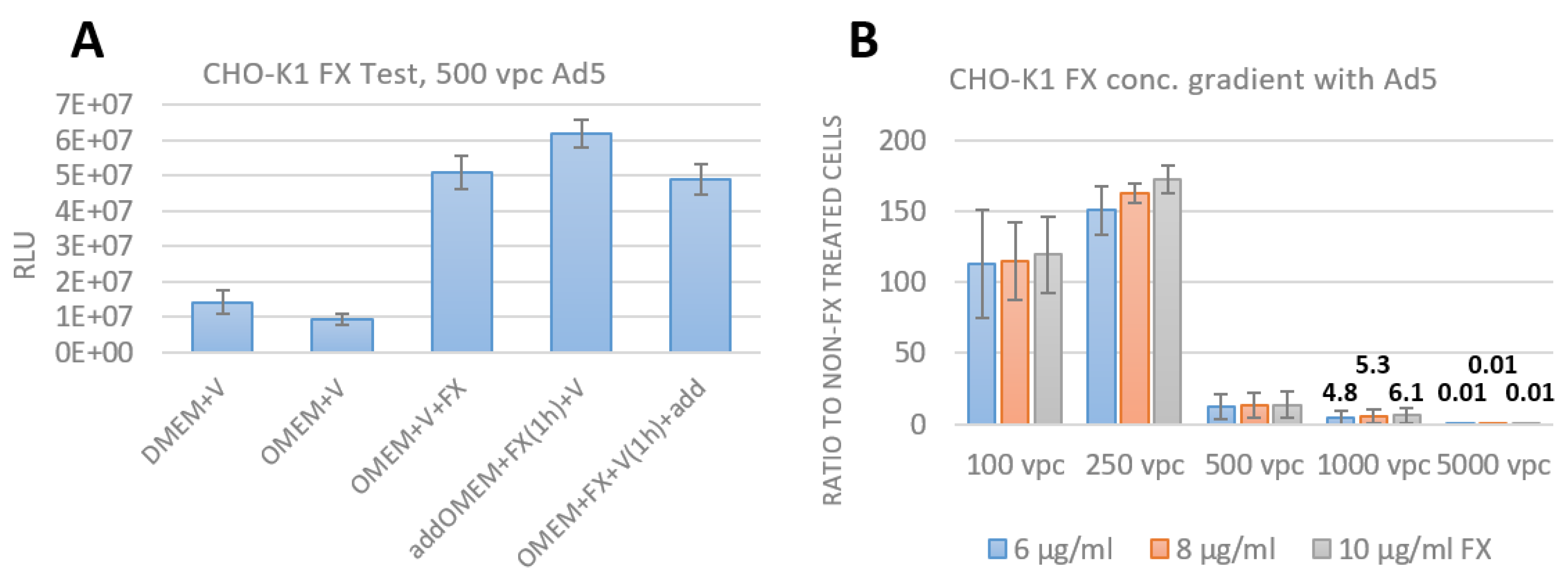
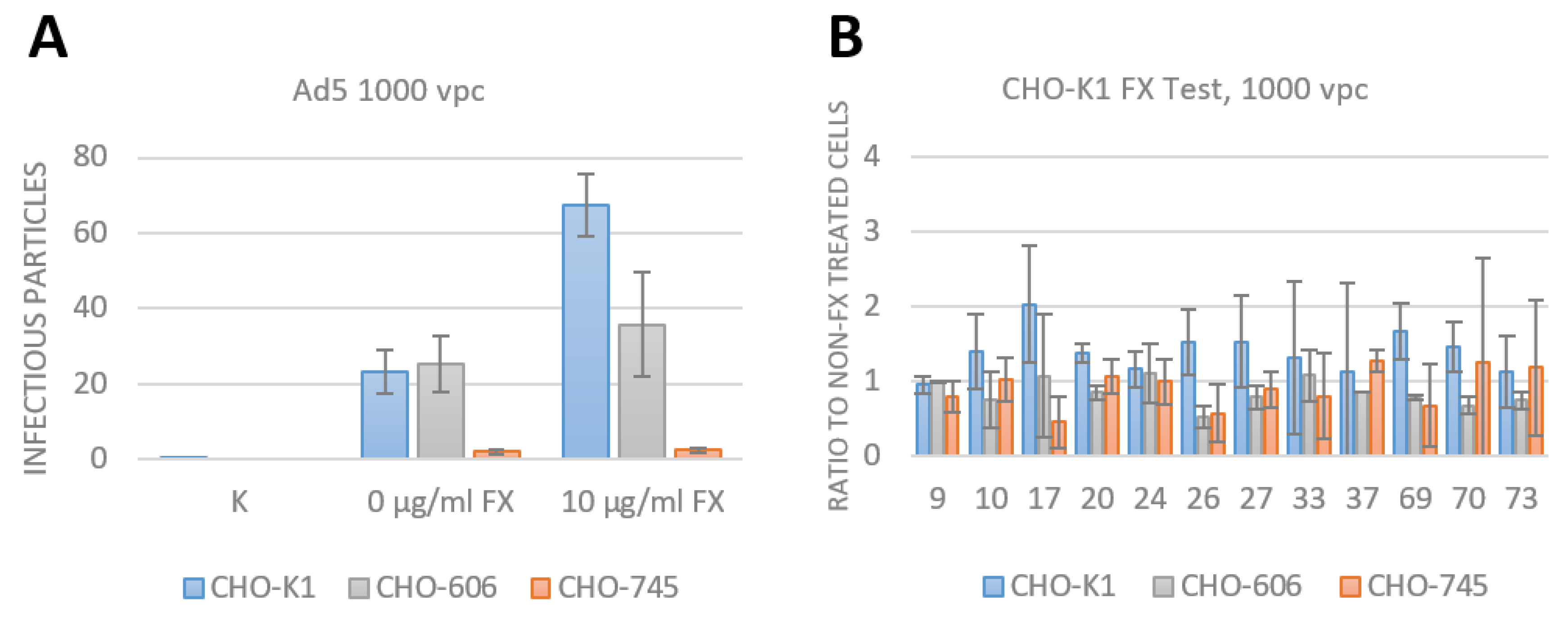
3.3. Assay Establishment of FX effect as an Adapter for Bridging the Adenovirus to HSPG
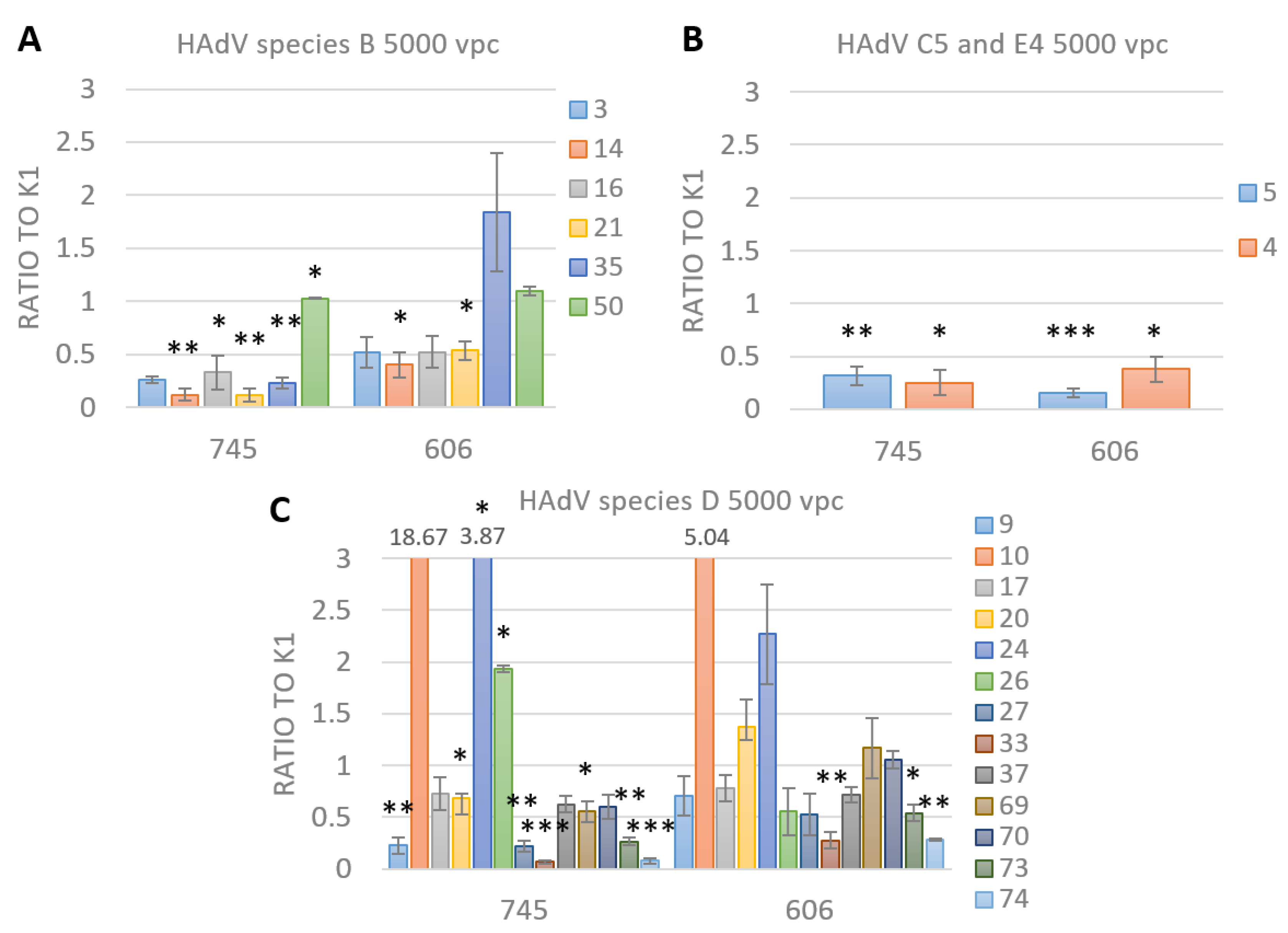
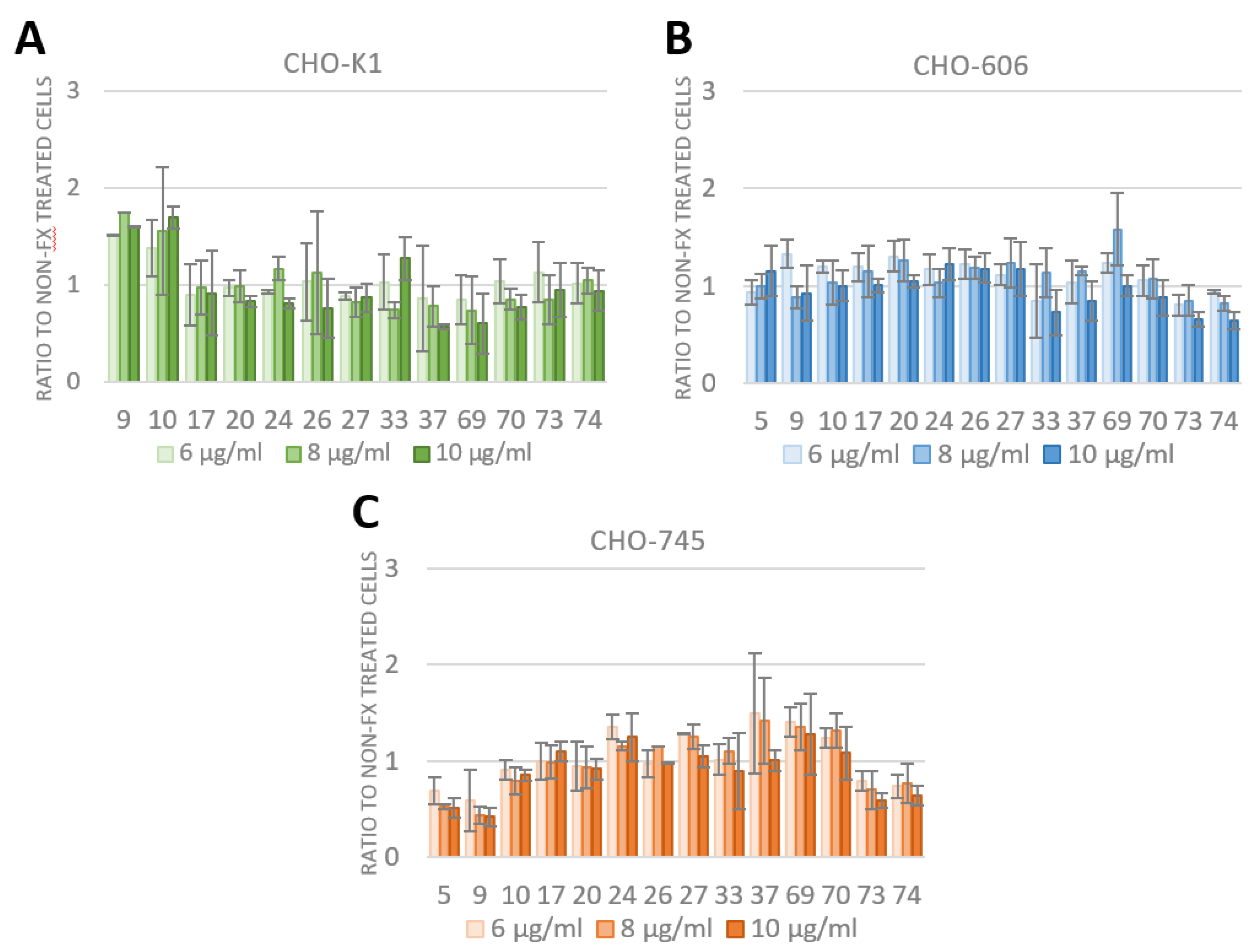
3.4. FX Has No Effect on Species D Adenovirus Transduction and Uptake
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corjon, S.; Gonzalez, G.; Henning, P.; Grichine, A.; Lindholm, L.; Boulanger, P.; Fender, P.; Hong, S.-S. Cell entry and trafficking of human adenovirus bound to blood factor X is determined by the fiber serotype and not hexon:heparan sulfate interaction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, J.; Pérez-Illana, M.; Martín-González, N.; Martín, C.S. Adenovirus Structure: What Is New? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaiya, J.; Saha, A.; Zhou, X.; Chodosh, J. Human Adenovirus Species D Interactions with Corneal Stromal Cells. Viruses 2021, 13, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemerow, G.R.; Stewart, P.L. Reddy, V.S. Structure of human adenovirus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Human Adenovirus Working Group Adenovirus Classification. Available online: http://hadvwg.gmu.edu/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Robinson, C.M.; Seto, D.; Jones, M.S.; Dyer, D.W.; Chodosh, J. Molecular evolution of human species D adenoviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, A.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Singh, G.; Dyer, D.W.; Seto, D.; Chodosh, J.; Rajaiya, J. Adenoviromics: Mining the Human Adenovirus Species D Genome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persson, B.D.; John, L.; Rafie, K.; Strebl, M.; Frängsmyr, L.; Ballmann, M.Z.; Mindler, K.; Havenga, M.; Lemckert, A.; Stehle, T.; et al. Human species D adenovirus hexon capsid protein mediates cell entry through a direct interaction with CD46. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020732118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, A.C.; Parker, A.L.; Duffy, M.R.; Coughlan, L.; van Rooijen, N.; Kähäri, V.-M.; Nicklin, S.A.; Baker, A.H. Requirements for receptor engagement during infection by adenovirus complexed with blood coagulation factor X. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuve, S.; Wang, H.; Jacobs, J.D.; Yumul, R.C.; Smith, D.F.; Lieber, A. Role of cellular heparan sulfate proteoglycans in infection of human adenovirus serotype 3 and 35. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, A.; Palm, E.; Trulsson, F.; Mundigl, S.; Becker, M.; Persson, B.; Frängsmyr, L.; Lenman, A. Heparan Sulfate Is a Cellular Receptor for Enteric Human Adenoviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, S.; Lamanna, W.C.; Esko, J.D. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaiss, A.K.; Lawrence, R.; Elashoff, D.; Esko, J.D.; Herschman, H.R. Differential effects of murine and human factor X on adenovirus transduction via cell-surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24535–24543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Gordo, E.; Denby, L.; Nicklin, S.A.; Baker, A.H. The importance of coagulation factors binding to adenovirus: Historical perspectives and implications for gene delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1795–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagno, V.; Tseligka, E.D.; Jones, S.T.; Tapparel, C. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias? Viruses 2019, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, M.; Wang, H.; Bernfield, M.; Gallagher, J.; Turnbull, J. Cell surface syndecan-1 on distinct cell types differs in fine structure and ligand binding of its heparan sulfate chains. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 18881–18890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.; Doszpoly, A.; Turner, G.; Nicklin, S.; Baker, A. The relevance of coagulation factor X protection of adenoviruses in human sera. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greig, J.A.; Buckley, S.M.; Waddington, S.N.; Parker, A.L.; Bhella, D.; Pink, R.; Rahim, A.A.; Morita, T.; Nicklin, S.A.; McVey, J.H.; et al. Influence of coagulation factor x on in vitro and in vivo gene delivery by adenovirus (Ad) 5, Ad35, and chimeric Ad5/Ad35 vectors. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, S.N.; McVey, J.H.; Bhella, D.; Parker, A.L.; Barker, K.; Atoda, H.; Pink, R.; Buckley, S.M.K.; Greig, J.A.; Denby, L.; et al. Adenovirus serotype 5 hexon mediates liver gene transfer. Cell 2008, 132, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Findlay, J.S.; Cook, G.P.; Blair, G.E. Blood Coagulation Factor X Exerts Differential Effects on Adenovirus Entry into Human Lymphocytes. Viruses 2018, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, M.I.; Lenman, A.E.; Frängsmyr, L.; Nyberg, C.; Abdullahi, M.; Arnberg, N. Coagulation factors IX and X enhance binding and infection of adenovirus types 5 and 31 in human epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3816–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, R.; Bradshaw, A.C.; Mestre-Francés, N.; Verdier, J.-M.; Henaff, D.; Baker, A.H. Coagulation factor X mediates adenovirus type 5 liver gene transfer in non-human primates (Microcebus murinus). Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, A.L.; Waddington, S.N.; Nicol, C.G.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Buckley, S.M.; Denby, L.; Kemball-Cook, G.; Ni, S.; Lieber, A.; McVey, J.H.; et al. Multiple vitamin K-dependent coagulation zymogens promote adenovirus-mediated gene delivery to hepatocytes. Blood 2006, 108, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemetson, K.J. Blood glycoproteins. New Compr. Biochem. 1997, 29, 173–201. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Tian, J.; Smith, J.S.; Conenello, G.M.; Morita, T.; Byrnes, A.P. Coagulation factor X shields adenovirus type 5 from attack by natural antibodies and complement. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TTsoukas, R.L.; Volkwein, W.; Gao, J.; Schiwon, M.; Bahlmann, N.; Dittmar, T.; Hagedorn, C.; Ehrke-Schulz, E.; Zhang, W.; Baiker, A.; et al. A Human In Vitro Model to Study Adenoviral Receptors and Virus Cell Interactions. Cells 2022, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnberg, N.; Kidd, A.H.; Edlund, K.; Olfat, F.; Wadell, G. Initial interactions of subgenus D adenoviruses with A549 cellular receptors: Sialic acid versus alpha(v) integrins. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7691–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnberg, N.; Edlund, K.; Kidd, A.H.; Wadell, G. Adenovirus type 37 uses sialic acid as a cellular receptor. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, A.T.; Mundy, R.M.; Davies, J.A.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Parker, A.L. Human adenovirus type 26 uses sialic acid-bearing glycans as a primary cell entry receptor. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Boehme, P.; Zhang, W.; Fu, J.; Yumul, R.; Mese, K.; Tsoukas, R.; Solanki, M.; Kaufmann, M.; Lu, R.; et al. Human adenovirus type 17 from species D transduces endothelial cells and human CD46 is involved in cell entry. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roelvink, P.W.; Lizonova, A.; Lee, J.G.M.; Li, Y.; Bergelson, J.M.; Finberg, R.W.; Brough, D.E.; Kovesdi, I.; Wickham, T.J. The coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor protein can function as a cellular attachment protein for adenovirus serotypes from subgroups A, C, D, E, and F. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7909–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, F.T.; Puck, T.T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells, VII. Induction and isolation of nutritional mutants in Chinese hamster cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 60, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bame, K.J.; Esko, J.D. Undersulfated heparan sulfate in a Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant defective in heparan sulfate N-sulfotransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 8059–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esko, J.D.; Stewart, T.E.; Taylor, W.H. Animal cell mutants defective in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Schiwon, M.; Janz, S.; Schaffarczyk, L.; von der Goltz, L.; Ehrke-Schulz, E.; Dörner, J.; et al. An Engineered Virus Library as a Resource for the Spectrum-wide Exploration of Virus and Vector Diversity. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnberg, N. Adenovirus receptors: Implications for targeting of viral vectors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensen, L.C.; Hoeben, R.C.; Bots, S.T. Adenovirus Receptor Expression in Cancer and Its Multifaceted Role in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, W.; Ehrhardt, A. Expanding the Spectrum of Adenoviral Vectors for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, P.A.; Juliano, R.L. Isolation and characterization of Chinese hamster ovary cell variants defective in adhesion to fibronectin-coated collagen. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 87, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, K.; Takada, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Takada, Y.; Zhao, M. Expression of integrins to control migration direction of electrotaxis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 9131–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Palankar, R.; Wesche, J.; Handtke, S.; Wolff, M.; Aurich, K.; Lalk, M.; Methling, K.; Völker, U.; et al. Insights in ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Blood 2021, 138, 2256–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.T.; Boyd, R.J.; Sarkar, D.; Teijeira-Crespo, A.; Chan, C.K.; Bates, E.; Waraich, K.; Vant, J.; Wilson, E.; Truong, C.D.; et al. ChAdOx1 interacts with CAR and PF4 with implications for thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabl8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primers and Probes | Sequence 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| Neo fwd | TGCTCCTGCCGAGAAAGTAT |
| Neo rev | GCTCTTCGTCCAGATCATC |
| Neo-probe-FAM | TACTCGGATGGAAGCCGGTCTTGTC |
| CHO GAPDH fwd | AAGGCCATCACCATCTTCCA |
| CHO GAPDH rev | GCGGAGATGATGACCCTCTT |
| CHO GAPDH probe-HEX | CTGGCGCCGAGTATGTTGTGGAATC |
| Adenovirus Species | Type | Receptor | Adapter |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 3, 14, 16, 21, 35, 50 | CD46 1, DSG2 2, CD80 1, CD86 1 | FX |
| C | 5 | CAR, HSPG, VCAM-1 3, MHC1-a2 4, SR 5 | FIX 7, FX, Lf 8, DPPC 9 |
| D | 9, 10, 17, 20, 24, 26, 27, 33, 37, 69, 70, 73, 74 | CAR, CD46, SA 6 | FX |
| E | 4 | CAR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schröer, K.; Alshawabkeh, M.; Schellhorn, S.; Bronder, K.; Zhang, W.; Ehrhardt, A. Influence of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Factor X on species D Human Adenovirus Uptake and Transduction. Viruses 2023, 15, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010055
Schröer K, Alshawabkeh M, Schellhorn S, Bronder K, Zhang W, Ehrhardt A. Influence of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Factor X on species D Human Adenovirus Uptake and Transduction. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchröer, Katrin, Montaha Alshawabkeh, Sebastian Schellhorn, Katrin Bronder, Wenli Zhang, and Anja Ehrhardt. 2023. "Influence of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Factor X on species D Human Adenovirus Uptake and Transduction" Viruses 15, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010055
APA StyleSchröer, K., Alshawabkeh, M., Schellhorn, S., Bronder, K., Zhang, W., & Ehrhardt, A. (2023). Influence of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Factor X on species D Human Adenovirus Uptake and Transduction. Viruses, 15(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010055







