Sustainability 2021, 13(19), 10849; https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910849 - 29 Sep 2021
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 3665
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to conceptualise a framework that reflects an intertwined relationship between the green board committee and firm performance. Agency and stakeholder theories hold a basic notion of supporting the relationship between the green board committee and firm performance.
[...] Read more.
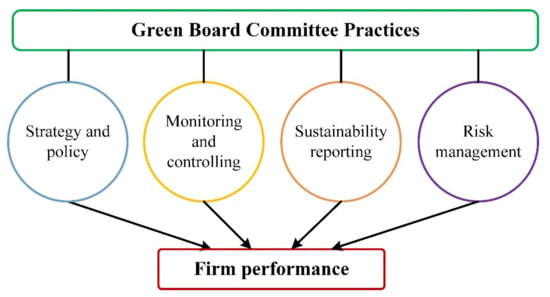
The purpose of this study was to conceptualise a framework that reflects an intertwined relationship between the green board committee and firm performance. Agency and stakeholder theories hold a basic notion of supporting the relationship between the green board committee and firm performance. The moderating role of intellectual capital (IC) was introduced in the intertwined relationship between green board committees and firm performance based on a resource-based view theory. This study proposes a new measurement index, namely, the “green board committee index”, to measure the green practices of organisations. This index is comprised of four dimensions: strategy and policymaking, monitoring and control, sustainability, and risk management. The current study hypothesised a significant and positive relationship between the green board committee and firm performance. It was believed that the moderation effect of IC strengthens the relationship between the green board committee and firm performance. The data for this study were proposed to be measured through a content analysis of the company’s annual and embedded reports and a Thomson Reuters DataStream terminal. It adds to the body of knowledge by alluding to an integrated notion of green board committees and IC concerning firm performance. The mentioned conceptual framework sends signals to legislators, regulators, policymakers, and practitioners on the critical insights and actions of green board committees in setting strategies and objectives, addressing sustainability issues, forging a relationship with stakeholders, and increasing the firm’s value from the business operations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Enterprise Resources Planning Systems: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Directions)
►
Show Figures