Nutrients 2019, 11(9), 2161; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092161 - 9 Sep 2019
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 8945
Abstract
The number of patients with mental illnesses is rapidly increasing, and daily lifestyle is closely associated with the development of symptoms. It is suggested that inflammatory molecules derived from microglia play crucial roles for the pathophysiology of depression. In the present study, we
[...] Read more.
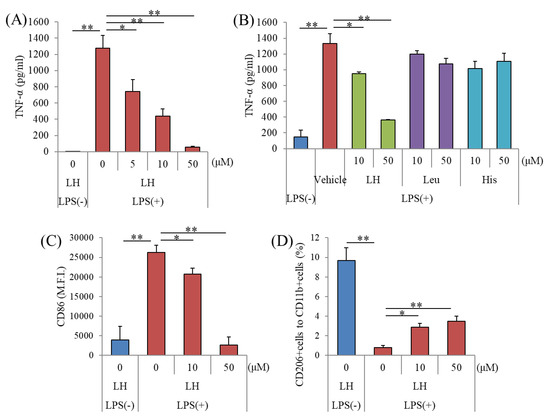
The number of patients with mental illnesses is rapidly increasing, and daily lifestyle is closely associated with the development of symptoms. It is suggested that inflammatory molecules derived from microglia play crucial roles for the pathophysiology of depression. In the present study, we discovered that leucine–histidine (LH) dipeptide suppressed activation of primary microglia. The effects of LH dipeptide orally administered were measured using tail suspension test (TST) in mice injected with lipopolysaccharide and social interaction test in mice received social defeat stress. LH dipeptide reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines upon stimulation in microglia. Orally administered LH dipeptide was delivered to the brain and suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the brain and concomitant depression-like behavior in the TST. Moreover, oral administration of LH dipeptide suppressed the induction of depression- and anxiety-like behaviors induced by repeated social defeat stress. These results indicate that LH dipeptide suppressed the activation of microglia and ameliorated depression-associated emotional disturbances. Further, we found that LH dipeptide was abundant in various fermented products. Together with previous epidemiological reports that daily intake of these fermented foods is negatively associated with the incidence of psychiatric diseases, our findings suggest that food rich in LH dipeptide may improve mental health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effect of Bioactive Peptides on Human Health)
►
Show Figures