Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
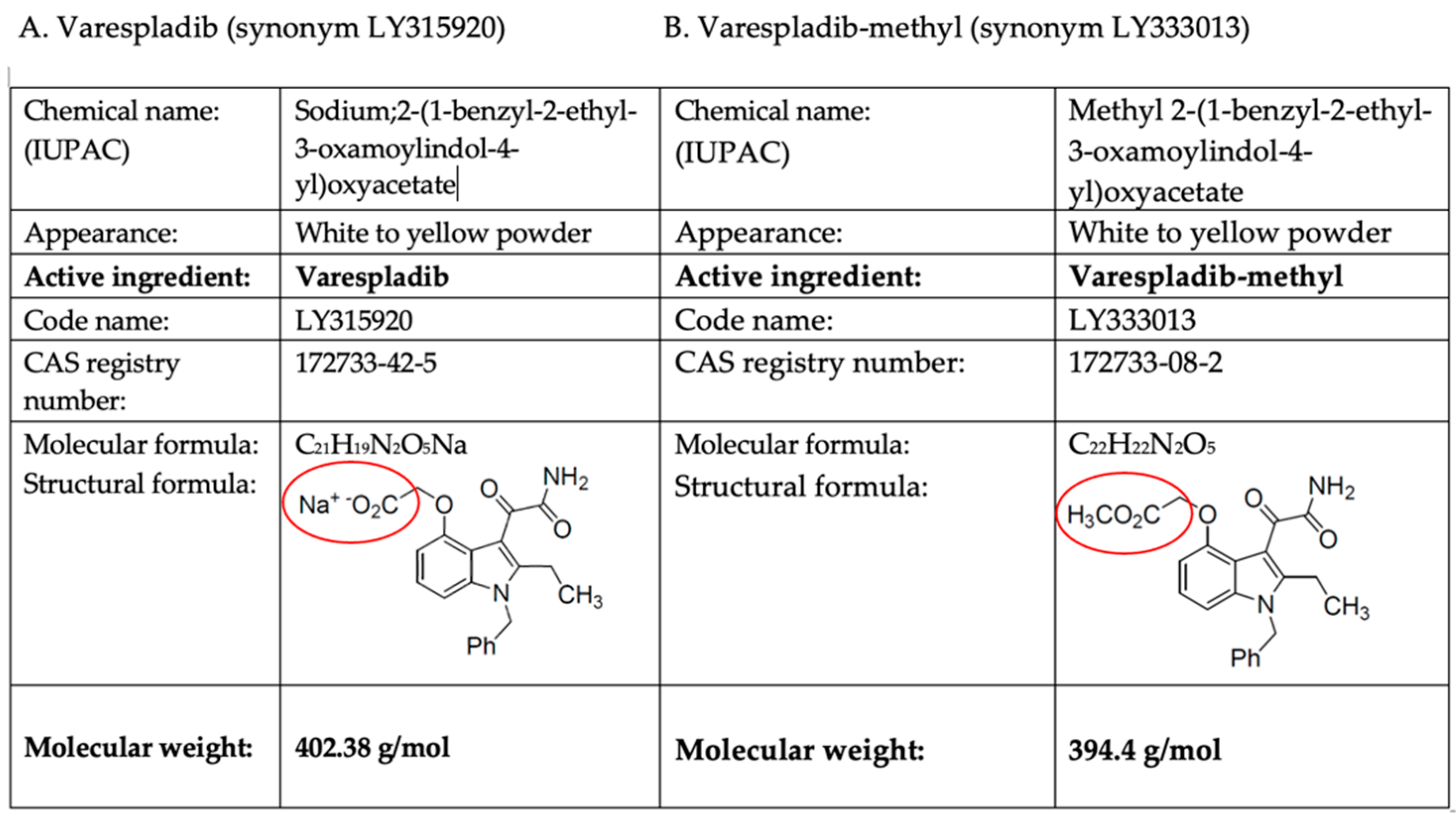
Varespladib (LY315920) and Varespladib-methyl (LY333013)
2. Key Laboratory Studies of Varespladib and Varespladib-methyl to Inhibit Venom sPLA2
3. Structural and Purified Toxin Studies
4. Varespladib and Neurotoxicity in Preclinical Studies
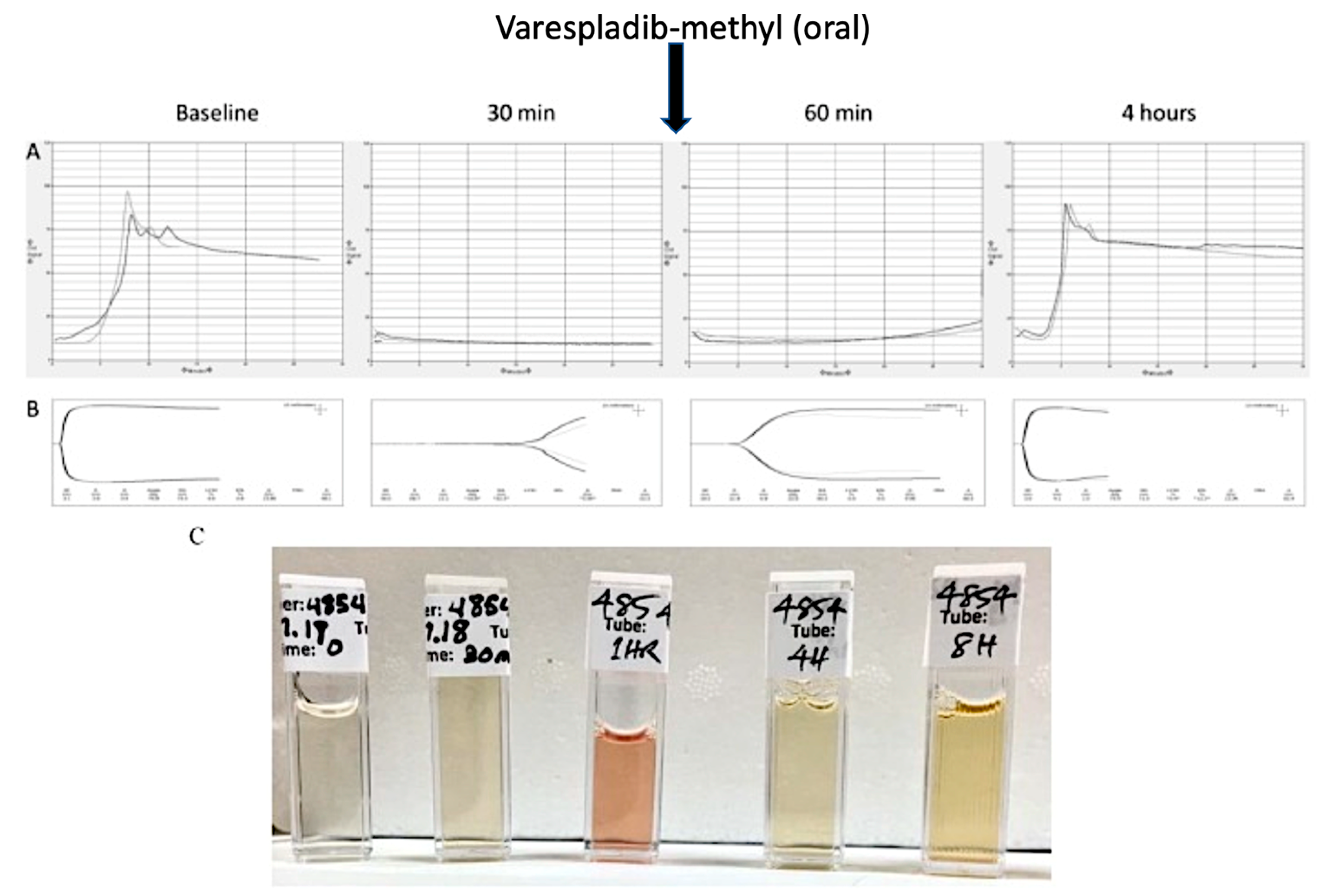
5. Drug Combinations and Preclinical Animal Models of Complex Non-Neurotoxic Envenoming Syndromes
- (1)
- inhibit the phospholipase activity of venom sPLA2s from a variety of snake species;
- (2)
- block sPLA2 activity in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo;
- (3)
- provide a therapeutic benefit throughout the time course of envenoming;
- (4)
- protect or reverses neurological damage caused by venom sPLA2s;
- (5)
- restore normal coagulation where anticoagulant sPLA2 are cause of incoagulability or sPLA2-driven consumption coagulopathy
- (6)
- have a synergistic effect with antivenom for many toxicities.
| Manuscript Title and Link to Abstract | Venoms/Toxins Tested a | Model/Drug & Dosage b | Author/Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation | Acanthophis antarcticus, Agkistrodon blomhoffii brevicaudus, A. contortrix, A. piscivorus, Bitis gabonica, Bothrops asper, B. jararaca, Bungarus caeruleus, B. fasciatus, Calloselasma rhodostoma, Crotalus adamanteus, C. atrox, C.d. terrificus, C. scutulatus scutulatus, Dendroaspis polylepis, Echis carinatus, Laticauda semifasciata, Micrurus fulvius, Naja atra, N. naja kaouthia, N. naja, Notechis scutatus scutatus, Ophiophagus hannah, Oxyuranus scutellatus, Pseudechis australis, Trimersurus elegans, Vipera berus, and Vipera russelli (Daboia) | In vitro (28 venoms) and in vivo toxicology and pharmacodynamics (mouse/rat) In vitro: 15-point dose–response curves In vivo: LY315920 4–8 mg/kg SC or IV † | Lewin et al., 2016 [54] |
| 2 | Exploration of the Inhibitory Potential of Varespladib for Snakebite Envenomation | D. acutus, A. halys, B multicinctus, and N. atra | In vitro, in vivo (mouse) LY315920 4 mg/kg SC † | Wang et al., 2018 [62] |
| 3 | Inactivation of Venom PLA2 Alleviates Myonecrosis and Facilitates Muscle Regeneration in Envenomed Mice: A Time Course Observation | D. acutus | In vitro, in vivo (mouse) LY315920 4 mg/kg SC † | Xiao et al., 2018 [47] |
| 4 | Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, lethal doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) | O. scutellatus | In vivo toxicology (mouse) LY333013 10 mg/kg PO | Lewin et al., 2018 [63] |
| 5 | Delayed LY333013 (Oral) and LY315920 (Intravenous) Reverse Severe Neurotoxicity and Rescue Juvenile Pigs from Lethal Doses of Micrurus fulvius (Eastern Coral Snake) Venom | M. fulvius | In vivo toxicology (porcine) LY315920 ‡ 5 mg/kg IV bolus, 2.5 mg/kg IV every 6 h and 1 mg/kg LY333013 PO after 24 h | Lewin et al., 2018 [64] |
| 6 | Coagulotoxic Cobras: Clinical Implications of Strong Anticoagulant Actions of African Spitting Naja Venoms That Are Not Neutralised by Antivenom but Are by LY315920 (Varespladib) | N. mossambica, N. nigricincta, N. nigricollis, and N. pallida | In vitro pharmacology (human plasma and fibrinogen) LY315920 6.25 µg/mL † | Bittenbinder et al., 2018 [65] |
| 7 | Neutralizing properties of LY315920 toward snake venom group I and II myotoxic phospholipases A2 | P. colletti and B. asper | In vitro and in vivo toxicology, cell culture LY315920 ‡ 400 µM | Bryan-Quirós et al., 2019 [21] |
| 8 | Structural basis for phospholipase A2-like toxin inhibition by the synthetic compound Varespladib (LY315920) | B. moojenic | Crystallography with cocrystallization of LY315920 † with purified MjTX-II in vitro studies LY315920 † up to 400 µM | Salvador et al., 2019 [23] |
| 9 | Varespladib (LY315920) and Methyl Varespladib (LY333013) Abrogate or Delay Lethality Induced by Presynaptically Acting Neurotoxic Snake Venoms | B. fasciatus, C.d. terrificus, N. scutatus, and O. scutellatus | In vivo (mouse) acute toxicity/survival LY315920 ‡ and LY333013 10 mg/kg IV, PO | Gutierréz et al., 2020 [78] |
| 10 | PLA2 Inhibitor Varespladib as an Alternative to the Antivenom Treatment for Bites from Nikolsky’s Viper Vipera berus nikolskii | V. b. nikolskii | In vivo (mouse) acute toxicity/survival LY315920† 8 mg/kg SC† | Zinenko et al., 2020 [85] |
| 11 | Anticoagulant activity of black snake (Elapidae: Pseudechis) venoms: Mechanisms, potency, and antivenom efficacy | P. colletti | In vitro coagulation/hemotoxicity with comparison to antivenom LY315920 2.5 μg/mL † | Zdenek et al., 2020 [67] |
| 12 | Varespladib Inhibits the Phospholipase A2 and Coagulopathic Activities of Venom Components from Hemotoxic Snakes | B. asper, C. rhodostoma, D. acutus, D. russelii, E. carinatus, E. ocellatus, and O. scutellatus | In vitro coagulation studies (human plasma) LY315920 † 0.8, 4, 20 µM | Xie et al., 2020 [71] |
| 13 | Neutralizing Effects of Small Molecule Inhibitors and Metal Chelators on Coagulopathic Viperinae Snake Venom Toxins | E. carinatus, E. ocellatus, D. russelii, and B. arietans | In vitro pharmacology human plasma LY315920 † 4 to 20µM bath | Xie et al., 2020 [70] |
| 14 | Sodium oleate, arachidonate, and linoleate enhance fibrinogenolysis by Russell’s viper venom proteinases and inhibit FXIIIa; a role for phospholipase A2 in venom induced consumption coagulopathy | D. russelii | In vitro, in vitro, coagulation studies, hemotoxicity (human plasma) LY315920 4 × 10−3 mg/mL † | Alangode et al., 2020 [69] |
| 15 | Varespladib (LY315920) neutralises phospholipase A2 mediated prothrombinase-inhibition induced by Bitis snake venoms | Bitis cornuta, B. xeropaga, B. atropos, and B. caudalis | In vitro coagulation studies (human plasma) LY315920 ‡ 5.7 nM | Youngman et al., 2020 [89] |
| 16 | Varespladib (LY315920) inhibits neuromuscular blockade induced by Oxyuranus scutellatus venom in a nerve-muscle preparation | O. scutellatus | Ex vivo nerve preparation (mouse) LY315920 ‡ 10 µg/mL bath | Oliveira et al., 2020 [82] |
| 17 | A therapeutic combination of two small molecule toxin inhibitors provides pancontinental preclinical efficacy against viper snakebite | E. ocellatus, E. carinatus, B. asper, B. arietans, and D. russelii | In vitro and in vivo (mouse) LY315920 † 120 µg IV ~6 mg/kg | Albulescu et al., 2020 [88] |
| 18 | Anticoagulant Micrurus venoms: Targets and neutralization | M. fulvius, M. ibiboboca, M. laticollaris, M. obscurus, and M. tener | Ex vivo coagulation studies (human plasma) LY315920 † 10 mg/mL (1% w/v) | Dashevsky et al., 2021 [90] |
| 19 | Snake venom proteome of Protobothrops mucrosquamatus in Taiwan: Delaying venom-induced lethality in a rodent model by inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity with varespladib. | P. mucrosquamatus | In vivo toxicology (mouse); LY315920 † 0.1 mg/kg IP | Liu et al., 2021 [86] |
| 20 | Anticoagulant Activity of Naja nigricollis Venom Is Mediated by Phospholipase A2 Toxins and Inhibited by Varespladib | N. nigricollis | In vitro coagulation (human plasma); LY315920 150 to 450 µM † | Kazandjian et al., 2021 [73] |
| 21 | The synthetic varespladib molecule is a multi-functional inhibitor for PLA 2 and PLA 2-like ophidic toxins | B. moojenic | LY315920 † co-crystallized with purified MJTX-I computational and in vitro studies | Salvador et al., 2021. [22] |
| 22 | Action of Varespladib (LY-315920), a Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor, on the Enzymatic, Coagulant and Haemorrhagic Activities of Lachesis muta rhombeata (South American Bushmaster) Venom | L. m. rhombeata | In vitro and in vivo pharmacology (rat) LY315920 † 0.001 to 1 µM | Gutierres et al., 2022 [87] |
| 23 | Varespladib (LY315920) prevents neuromuscular blockage and myotoxicity induced by crotoxin on mouse neuromuscular preparations | C. d. terrificusc | In vitro, ex vivo purified toxin, neurotoxicity, electromyography LY315920 † 0.25:1, 0.5:1, 1:1 w/w ratios relative to each purified toxin | Maciel et al., 2021 [83] |
| 24 | Role of Phospholipases A2 in Vascular Relaxation and Sympatholytic Effects of Five Australian Brown Snake, Pseudonaja spp., Venoms in Rat Isolated Tissues | P. affinis, P. aspidorhyncha, P. inframacula, P. nuchalis, and P. textilis | Ex vivo (rat) cardiovascular physiology LY315920 † 1 µM bath | Vuong et al., 2021 [45] |
| 25 | In vivo treatment with varespladib, a phospholipase A inhibitor, prevents the peripheral neurotoxicity and systemic disorders induced by Micrurus corallinus (coral snake) venom in rats | M. corallinus | In vivo toxicology (rat) survival, comparison to antivenom, multiorgan histology LY315920 † 0.5 mg/mL IP without and with antivenom IV | Silva-Carvalho et al., 2021 [79] |
| 26 | Quantum Biochemical Investigation of Lys49-PLA2 from Bothrops moojeni | B. moojeni | Computational | Barbosa et al., 2021 [74] |
| 27 | Varespladib (LY315920) rescued mice from fatal neurotoxicity 1 caused by venoms of five major Asiatic kraits (Bungarus spp.) in an experimental envenoming and rescue model | B. caeruleus, B. candidus, B. fasciatus, B. multicinctus, and B. sindanus | In vivo toxicology (mouse) LY315920† 10 to 20 mg/kg IP | Tan et al., 2022 [81] |
| 28 | Effect of the phospholipase A inhibitor Varespladib, and its synergism with crotalic antivenom on the neuromuscular blockade induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus venom (with and without crotamine) in mouse neuromuscular preparations | C. d. terrificus | Ex vivo neuromuscular preparation (mouse) LY315920 ‡ 10 to 30 µg/mL bath | de Souza et al., 2022 [84] |
| 29 | Repurposed drugs and their combinations prevent morbidity-inducing dermonecrosis caused by diverse cytotoxic snake venoms | B. arietans, B. asper, C. atrox, C. rhodostoma, E. carinatus, E. ocellatus, N. nigricollis, N. pallida, D. russelii, B. asper, C. atrox, C. rhodostoma, E. carinatus, E. ocellatus, and N. haje | In vitro (cell culture) and in vivo (mouse) | Hall et al., 2022 (in production) |
| 30 | Partial efficacy of a Brazilian coralsnake antivenom and varespladib in neutralizing distinct toxic effects induced by sublethal Micrurus dumerilii carinicauda envenoming in rats | M. d. carinicauda | In vivo (rat) LY315920 † 0.5 mg/kg IP | Silva-Carvalho et al., 2022 [80] |
| 31 | Erythrocyte haemotoxicity profiling of snake venom toxins after nanofractionation | C. rhodostoma, N. mossambica, N.nigricollis, N. pallida | In vitro (human RBCs) LY315920 † 0.4, 8, 20 µM | Xie et al., 2022 [72] |
6. Discussion
7. Future Studies
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longbottom, J.; Shearer, F.M.; Devine, M.; Alcoba, G.; Chappuis, F.; Weiss, D.J.; Ray, S.E.; Ray, N.; Warrell, D.A.; Ruiz de Castañeda, R.; et al. Vulnerability to Snakebite Envenoming: A Global Mapping of Hotspots. Lancet 2018, 392, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Ashokan, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Nattamaisundar, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Chandran, V.; Gajjeraman, P.; Baksh, M.F.; Gibbins, J.M.; et al. Snakebite and Its Socio-Economic Impact on the Rural Population of Tamil Nadu, India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, D.J.; Faiz, M.A.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ainsworth, S.; Bulfone, T.C.; Nickerson, A.D.; Habib, A.G.; Junghanss, T.; Fan, H.W.; Turner, M.; et al. Strategy for a Globally Coordinated Response to a Priority Neglected Tropical Disease: Snakebite Envenoming. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, R.; Gutiérrez, J. Priority Actions and Progress to Substantially and Sustainably Reduce the Mortality, Morbidity and Socioeconomic Burden of Tropical Snakebite. Toxins 2016, 8, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohapatra, B.; Warrell, D.A.; Suraweera, W.; Bhatia, P.; Dhingra, N.; Jotkar, R.M.; Rodriguez, P.S.; Mishra, K.; Whitaker, R.; Jha, P.; et al. Snakebite Mortality in India: A Nationally Representative Mortality Survey. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerardo, C.J.; Vissoci, J.R.N.; Evans, C.S.; Simel, D.L.; Lavonas, E.J. Does This Patient Have a Severe Snake Envenomation? JAMA Surg. 2019, 154, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozay, G.; Bosnak, M.; Ece, A.; Davutoglu, M.; Dikici, B.; Gurkan, F.; Bosnak, V.; Haspolat, K. Clinical Characteristics of Children with Snakebite Poisioning and Management of Complications in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Int. 2005, 47, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samprathi, M.; Gupta, V.; Jayashree, M.; Bansal, A.; Baranwal, A.; Nallasamy, K. Epidemiology and Outcomes of Early Morning Neuroparalytic Syndrome Following Snake Bite—A Retrospective Study. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2020, 66, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, I.K.; Satapathy, A.K. Neurotoxic Snake Envenomation: Neostigmine-Induced Paradoxical Weakness. Indian J. Pediatr. 2021, 88, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Geyt, J.; Pach, S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Habib, A.G.; Maduwage, K.P.; Hardcastle, T.C.; Hernández Diaz, R.; Avila-Aguero, M.L.; Ya, K.T.; Williams, D.; et al. Paediatric Snakebite Envenoming: Recognition and Management of Cases. Arch. Dis. Child 2021, 106, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryanarayana, G.; Rameshkumar, R.; Mahadevan, S. Retrospective Hospital-Based Cohort Study on Risk Factors of Poor Outcome in Pediatric Snake Envenomation. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Variawa, S.; Buitendag, J.; Marais, R.; Wood, D.; Oosthuizen, G. Prospective Review of Cytotoxic Snakebite Envenomation in a Paediatric Population. Toxicon 2021, 190, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pach, S.; le Geyt, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Williams, D.; Maduwage, K.P.; Habib, A.G.; Gustin, R.; Avila-Agüero, M.L.; Ya, K.T.; Halbert, J. Paediatric Snakebite Envenoming: The World’s Most Neglected “Neglected Tropical Disease”? Arch. Dis. Child 2020, 105, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Herrera, C.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Fox, J.W. Unresolved Issues in the Understanding of the Pathogenesis of Local Tissue Damage Induced by Snake Venoms. Toxicon 2018, 148, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Gutiørrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Cellular Pathology Induced by Snake Venom Phospholipase A 2 Myotoxins and Neurotoxins: Common Aspects of Their Mechanisms of Action. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Rangel, J. Snake Venom Lys49 Myotoxins: From Phospholipases A2 to Non-Enzymatic Membrane Disruptors. Toxicon 2012, 60, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A2: Unveiling the Secrets of a Functionally Versatile Group of Snake Venom Toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.; Mora, R.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Effects of Bothrops Asper Snake Venom on Lymphatic Vessels: Insights into a Hidden Aspect of Envenomation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan-Quirós, W.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lewin, M.R.; Lomonte, B. Neutralizing Properties of LY315920 toward Snake Venom Group I and II Myotoxic Phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2019, 157, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Borges, R.J.; Lomonte, B.; Lewin, M.R.; Fontes, M.R.M. The Synthetic Varespladib Molecule Is a Multi-Functional Inhibitor for PLA2 and PLA2-like Ophidic Toxins. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Gomes, A.A.S.; Bryan-Quirós, W.; Fernández, J.; Lewin, M.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Fontes, M.R.M. Structural Basis for Phospholipase A2-like Toxin Inhibition by the Synthetic Compound Varespladib (LY315920). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clare, R.H.; Hall, S.R.; Patel, R.N.; Casewell, N.R. Small Molecule Drug Discovery for Neglected Tropical Snakebite. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Engmark, M.; Milbo, C.; Johannesen, J.J.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Lohse, B.; Gutiérrez, J.; Lohse, B. From Fangs to Pharmacology: The Future of Snakebite Envenoming Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5270–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulfone, T.C.; Samuel, S.P.; Bickler, P.E.; Lewin, M.R. Developing Small Molecule Therapeutics for the Initial and Adjunctive Treatment of Snakebite. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, H.F.; Mellows, B.A.; Mitchell, R.; Sfyri, P.; Layfield, H.J.; Salamah, M.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Collins-Hooper, H.; Bicknell, A.B.; Matsakas, A.; et al. Mechanisms Underpinning the Permanent Muscle Damage Induced by Snake Venom Metalloprotease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, H.; Pan, H.; Liao, K.; Yang, M.; Huang, C. Snake Venom PLA2, a Promising Target for Broad-Spectrum Antivenom Drug Development. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6592820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasarnpun, S.; Walsh, J.; Awad, S.S.; Harris, J.B. Envenoming Bites by Kraits: The Biological Basis of Treatment-Resistant Neuromuscular Paralysis. Brain 2005, 128, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senji Laxme, R.R.; Khochare, S.; de Souza, H.F.; Ahuja, B.; Suranse, V.; Martin, G.; Whitaker, R.; Sunagar, K. Beyond the ‘Big Four’: Venom Profiling of the Medically Important yet Neglected Indian Snakes Reveals Disturbing Antivenom Deficiencies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Naum, C.; Bandi, V.; Gervich, D.; Lowry, S.F.; Wunderink, R.; Schein, R.M.; Macias, W.; Skerjanec, S.; Dmitrienko, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of LY315920Na/S-5920, a Selective Inhibitor of 14-KDa Group IIA Secretory Phospholipase A2, in Patients with Suspected Sepsis and Organ Failure. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Physical Structure, Biological Function, Disease Implication, Chemical Inhibition, and Therapeutic Intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bickler, P.E. Amplification of Snake Venom Toxicity by Endogenous Signaling Pathways. Toxins 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ranawaka, U.K.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. Neurotoxicity in Snakebite—The Limits of Our Knowledge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, M.L.; Quartino, P.Y.; Arce-Bejarano, R.; Fernández, J.; Camacho, L.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Kuemmel, D.; Fidelio, G.; Lomonte, B. Intravascular Hemolysis Induced by Phospholipases A 2 from the Venom of the Eastern Coral Snake, Micrurus Fulvius: Functional Profiles of Hemolytic and Non-Hemolytic Isoforms. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 286, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berling, I.; Isbister, G.K. Hematologic Effects and Complications of Snake Envenoming. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutsos, T.; Currie, B.J.; Isbister, G.K. Snakebite Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Protocol for the Systematic Review of Clinical Features, Outcomes, and Role of Interventions. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitprija, V. Animal Toxins and the Kidney. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2008, 4, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, N. Snake Envenoming─An Underreported Cause of Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfred, S.; Bates, D.; White, J.; Mahmood, M.A.; Warrell, D.A.; Thwin, K.T.; Thein, M.M.; Sint San, S.S.; Myint, Y.L.; Swe, H.K.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury Following Eastern Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Snakebite in Myanmar. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Gunasekaran, K.; Mahadevan, S.; Bobby, Z.; Kumar, A.P. Russell’s Viper Envenomation-Associated Acute Kidney Injury in Children in Southern India. Indian Pediatr. 2015, 52, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Arcot Thanjan, M.; Gopalakrishnan, N.; Jeyachandran, D.; Thanigachalam, D.; Ramanathan, S. Snake Envenomation-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Prognosis and Long-Term Renal Outcomes. Postgrad Med. J. 2022, 98, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshavardhan, L.; Lokesh, A.; Tejeshwari, H.; Halesha, B.; Metri, S.S. A Study on the Acute Kidney Injury in Snake Bite Victims in a Tertiary Care Centre. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, M.; Sampaio, T.L.; de Menezes, R.R.P.P.B.; Lima, D.B.; Jorge, A.R.C.; Alves, R.S.; Monteiro, H.S.A.; Gawarammana, I.; Maduwage, K.; Malleappah, R.; et al. Nephrotoxicity Induced by the Venom of Hypnale Hypnale from Sri Lanka: Studies on Isolated Perfused Rat Kidney and Renal Tubular Cell Lines. Toxicon 2019, 165, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, N.T.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Wright, C.E. Role of Phospholipases A2 in Vascular Relaxation and Sympatholytic Effects of Five Australian Brown Snake, Pseudonaja spp., Venoms in Rat Isolated Tissues. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Arroyo, O.; Chaves, F.; Lomonte, B.; Cerdas, L. Pathogenesis of Myonecrosis Induced by Coral Snake (Micrurus nigrocinctus) Venom in Mice. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1986, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Huang, C.; Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Inactivation of Venom PLA2 Alleviates Myonecrosis and Facilitates Muscle Regeneration in Envenomed Mice: A Time Course Observation. Molecules 2018, 23, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neale, V.; Smout, M.J.; Seymour, J.E. Spine-Bellied Sea Snake (Hydrophis curtus) Venom Shows Greater Skeletal Myotoxicity Compared with Cardiac Myotoxicity. Toxicon 2018, 143, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Roodt, A.R.; Lago, N.R.; Stock, R.P. Myotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity by Micrurus Venoms in Experimental Envenomation. Toxicon 2012, 59, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ownby, C.L. Skeletal Muscle Degeneration Induced by Venom Phospholipases A2: Insights into the Mechanisms of Local and Systemic Myotoxicity. Toxicon 2003, 42, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.I.; Brown, S.G.A.; O’Leary, M.A.; Currie, B.J.; Greenberg, R.; Taylor, M.; Barnes, C.; White, J.; Isbister, G.K. Mulga Snake (Pseudechis australis) Envenoming: A Spectrum of Myotoxicity, Anticoagulant Coagulopathy, Haemolysis and the Role of Early Antivenom Therapy—Australian Snakebite Project (ASP-19). Clin. Toxicol. (Phila) 2013, 51, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Burnouf, T.; Harrison, R.A.; Calvete, J.J.; Kuch, U.; Warrell, D.A.; Williams, D.J. A Multicomponent Strategy to Improve the Availability of Antivenom for Treating Snakebite Envenoming. Bull. World Health Organ. 2014, 92, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams; Layfield; Vallance; Patel; Bicknell; Trim; Vaiyapuri The Urgent Need to Develop Novel Strategies for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Snakebites. Toxins 2019, 11, 363. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adis R&D Profile Varespladib. Adis R&D Insight 2011, 11, 137–143.
- Wery, J.P.; Schevitz, R.W.; Clawson, D.K.; Bobbitt, J.L.; Dow, E.R.; Gamboa, G.; Goodson, T.; Hermann, R.B.; Kramer, R.M.; McClure, D.B.; et al. Structure of Recombinant Human Rheumatoid Arthritic Synovial Fluid Phospholipase A2 at 2.2 A Resolution. Nature 1991, 352, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Hislop, C.; Elliott, M.; Stasiv, Y.; Goulder, M.; Waters, D. Effects of Varespladib Methyl on Biomarkers and Major Cardiovascular Events in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Cavender, M.A.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Schwartz, G.; Waters, D.D.; Rosenson, R.S.; Bash, D.; Hislop, C. Inhibition of Secretory Phospholipase A2 in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Rationale and Design of the Vascular Inflammation Suppression to Treat Acute Coronary Syndrome for 16 Weeks (VISTA-16) Trial. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2012, 26, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, A.; Heriansyah, T.; Rohman, M.S. Phospholipase A2 Is an Inflammatory Predictor in Cardiovascular Diseases: Is There Any Spacious Room to Prove the Causation? Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 16, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue, M.L. Acute Coronary Syndromes: Targeting Inflammation-What Has the VISTA-16 Trial Taught Us? Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Schwartz, G.G.; Bash, D.; Rosenson, R.S.; Cavender, M.A.; Brennan, D.M.; Koenig, W.; Jukema, J.W.; Nambi, V.; et al. Varespladib and Cardiovascular Events in Patients with an Acute Coronary Syndrome. JAMA 2014, 311, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, H.; Xiong, S.; Huang, C. Exploration of the Inhibitory Potential of Varespladib for Snakebite Envenomation. Molecules 2018, 23, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewin, M.R.M.R.M.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Samuel, S.P.S.P.S.P.; Herrera, M.; Bryan-Quirós, W.; Lomonte, B.; Bickler, P.E.P.E.P.E.; Bulfone, T.C.T.C.; Williams, D.J.D.J.D.J.; María Gutiérrez, J.; et al. Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus Scutellatus) Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, M.R.M.R.; Gilliam, L.L.L.; Gilliam, J.; Samuel, S.P.S.P.; Bulfone, T.C.T.C.; Bickler, P.E.P.E.; Gutiérrez, J.M.J.M. Delayed LY333013 (Oral) and LY315920 (Intravenous) Reverse Severe Neurotoxicity and Rescue Juvenile Pigs from Lethal Doses of Micrurus Fulvius (Eastern Coral Snake) Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittenbinder, M.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; op den Brouw, B.; Youngman, N.J.; Dobson, J.S.; Naude, A.; Vonk, F.J.; Fry, B.G. Coagulotoxic Cobras: Clinical Implications of Strong Anticoagulant Actions of African Spitting Naja Venoms That Are Not Neutralised by Antivenom but Are by LY315920 (Varespladib). Toxins 2018, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdenek, C.N.; den Brouw, B.O.; Dashevsky, D.; Gloria, A.; Youngman, N.; Watson, E.; Green, P.; Hay, C.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; et al. Clinical Implications of Convergent Procoagulant Toxicity and Differential Antivenom Efficacy in Australian Elapid Snake Venoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Youngman, N.J.; Hay, C.; Dobson, J.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Milanovic, L.; Fry, B.G. Anticoagulant Activity of Black Snake (Elapidae: Pseudechis) Venoms: Mechanisms, Potency, and Antivenom Efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 330, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alangode, A.; Reick, M.; Reick, M. Sodium Oleate, Arachidonate, and Linoleate Enhance Fibrinogenolysis by Russell’s Viper Venom Proteinases and Inhibit FXIIIa; a Role for Phospholipase A2 in Venom Induced Consumption Coagulopathy. Toxicon 2020, 186, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alangode, A.; Rajan, K.; Nair, B.G. Snake Antivenom: Challenges and Alternate Approaches. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Albulescu, L.-O.O.; Bittenbinder, M.A.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. Neutralizing Effects of Small Molecule Inhibitors and Metal Chelators on Coagulopathic Viperinae Snake Venom Toxins. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Albulescu, L.-O.O.; Still, K.B.M.M.; Slagboom, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. Varespladib Inhibits the Phospholipase A2 and Coagulopathic Activities of Venom Components from Hemotoxic Snakes. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Bittenbinder, M.A.; Slagboom, J.; Arrahman, A.; Bruijns, S.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; García-Vallejo, J.J.; Kool, J. Erythrocyte Haemotoxicity Profiling of Snake Venom Toxins after Nanofractionation. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1176, 122586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazandjian, T.D.; Arrahman, A.; Still, K.B.M.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Wilkinson, M.C.; Kool, J. Anticoagulant Activity of Naja nigricollis Venom Is Mediated by Phospholipase A2 Toxins and Inhibited by Varespladib. Toxins 2021, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, E.D.; Lima Neto, J.X.; Bezerra, K.S.; Oliveira, J.I.N.; Machado, L.D.; Fulco, U.L. Quantum Biochemical Investigation of Lys49-PLA2 from Bothrops moojeni. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 12972–12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ownby, C.L.; Selistre de Araujo, H.S.; White, S.P.; Fletcher, J.E. Lysine 49 Phospholipase A2 Proteins. Toxicon 1999, 37, 411–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, H.S.; White, S.P.; Ownby, C.L. Sequence Analysis of Lys49 Phospholipase A2 Myotoxins: A Highly Conserved Class of Proteins. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacur, M.; Milligan, E.D.; Sloan, E.M.; Wieseler-Frank, J.; Barrientos, R.M.; Martin, D.; Poole, S.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Maier, S.F.; et al. Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s (Asp49 and Lys49) Induce Mechanical Allodynia upon Peri-Sciatic Administration: Involvement of Spinal Cord Glia, Proinflammatory Cytokines and Nitric Oxide. Pain 2004, 108, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lewin, M.R.; Williams, D.J.; Lomonte, B. Varespladib (LY315920) and Methyl Varespladib (LY333013) Abrogate or Delay Lethality Induced by Presynaptically Acting Neurotoxic Snake Venoms. Toxins 2020, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva-Carvalho, R.; Gaspar, M.Z.; Quadros, L.H.B.; Lobo, L.G.G.; Rogério, L.M.; Santos, N.T.S.; Zerbinatti, M.C.; Santarém, C.L.; Silva, E.O.; Gerez, J.R.; et al. In Vivo Treatment with Varespladib, a Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor, Prevents the Peripheral Neurotoxicity and Systemic Disorders Induced by Micrurus Corallinus (Coral Snake) Venom in Rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 356, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Carvalho, R.; Gaspar, M.Z.; Quadros, L.H.B.; Lobo, L.G.G.; Giuffrida, R.; Santarém, C.L.; Silva, E.O.; Gerez, J.R.; Silva, N.J.; Hyslop, S.; et al. Partial Efficacy of a Brazilian Coralsnake Antivenom and Varespladib in Neutralizing Distinct Toxic Effects Induced by Sublethal Micrurus Dumerilii Carinicauda Envenoming in Rats. Toxicon 2022, 213, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Lingam, T.M.C.; Tan, K.Y. Varespladib (LY315920) Rescued Mice from Fatal Neurotoxicity Caused by Venoms of Five Major Asiatic Kraits (Bungarus Spp.) in an Experimental Envenoming and Rescue Model. Acta Trop. 2022, 227, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana Oliveira, I.C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lewin, M.R.; Oshima-Franco, Y. Varespladib (LY315920) Inhibits Neuromuscular Blockade Induced by Oxyuranus Scutellatus Venom in a Nerve-Muscle Preparation. Toxicon 2020, 187, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, F.V.; Ramos Pinto, Ê.K.; Valério Souza, N.M.; Gonçalves de Abreu, T.A.; Ortolani, P.L.; Fortes-Dias, C.L.; Garrido Cavalcante, W.L. Varespladib (LY315920) Prevents Neuromuscular Blockage and Myotoxicity Induced by Crotoxin on Mouse Neuromuscular Preparations. Toxicon 2021, 202, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.; Oliveira, I.C.F.; Yoshida, E.H.; Cantuaria, N.M.; Cogo, J.C.; Torres-Bonilla, K.A.; Hyslop, S.; Silva Junior, N.J.; Floriano, R.S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Effect of the Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor Varespladib, and Its Synergism with Crotalic Antivenom, on the Neuromuscular Blockade Induced by Crotalus Durissus Terrificus Venom (with and without Crotamine) in Mouse Neuromuscular Preparations. Toxicon 2022, 214, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinenko, O.; Tovstukha, I.; Korniyenko, Y. PLA2 Inhibitor Varespladib as an Alternative to the Antivenom Treatment for Bites from Nikolsky’s Viper Vipera Berus Nikolskii. Toxins 2020, 12, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Wu, C.-J.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Liu, K.-L.; Huang, G.-J.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Chen, C.-K.; Liaw, G.-W. Snake Venom Proteome of Protobothrops Mucrosquamatus in Taiwan: Delaying Venom-Induced Lethality in a Rodent Model by Inhibition of Phospholipase A2 Activity with Varespladib. J Proteomics 2021, 234, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierres, P.G.; Pereira, D.R.; Vieira, N.L.; Arantes, L.F.; Silva, N.J.; Torres-Bonilla, K.A.; Hyslop, S.; Morais-Zani, K.; Nogueira, R.M.B.; Rowan, E.G.; et al. Action of Varespladib (LY-315920), a Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor, on the Enzymatic, Coagulant and Haemorrhagic Activities of Lachesis Muta Rhombeata (South-American Bushmaster) Venom. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, L.-O.; Xie, C.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Softley, R.; Bartlett, K.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. A Therapeutic Combination of Two Small Molecule Toxin Inhibitors Provides Broad Preclinical Efficacy against Viper Snakebite. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Walker, A.; Naude, A.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; Fry, B.G. Varespladib (LY315920) Neutralises Phospholipase A2 Mediated Prothrombinase-Inhibition Induced by Bitis Snake Venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 236, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashevsky, D.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Neri-Castro, E.; Youngman, N.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Alagón, A.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Frank, N.; Fry, B.G. Anticoagulant Micrurus Venoms: Targets and Neutralization. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 337, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce-Bejarano, R.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Intravascular Hemolysis Induced by the Venom of the Eastern Coral Snake, Micrurus Fulvius, in a Mouse Model: Identification of Directly Hemolytic Phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2014, 90, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrahman, A.; Kazandjian, T.D.; Still, K.B.M.; Slagboom, J.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. A Combined Bioassay and Nanofractionation Approach to Investigate the Anticoagulant Toxins of Mamba and Cobra Venoms and Their Inhibition by Varespladib. Toxins 2022, 14, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.W.; Matteo, I.A.; Samuel, S.P.; Rao, S.; Fry, B.G.; Bickler, P.E. Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins 2022, 14, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110783
Lewin MR, Carter RW, Matteo IA, Samuel SP, Rao S, Fry BG, Bickler PE. Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins. 2022; 14(11):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewin, Matthew R., Rebecca W. Carter, Isabel A. Matteo, Stephen P. Samuel, Sunita Rao, Bryan G. Fry, and Philip E. Bickler. 2022. "Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes" Toxins 14, no. 11: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110783
APA StyleLewin, M. R., Carter, R. W., Matteo, I. A., Samuel, S. P., Rao, S., Fry, B. G., & Bickler, P. E. (2022). Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins, 14(11), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110783






