A Facile Approach towards Fluorescent Nanogels with AIE-Active Spacers
Abstract
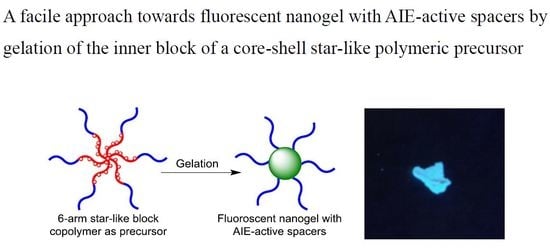
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regents and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of Hexafunctional Initiator
2.3. Synthesis of 4-Benzoylphenyl Methacrylate (BPMA)
2.4. Synthesis of 2-(4-Benzoylphenoxy) Ethyl Methacrylate (BPOEMA)
2.5. Protection of Hydroxyl Group of 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate (HEMA)
2.6. Synthesis of Star-Shaped Block Copolymers
2.7. Synthesis of Fluorescent Organic Nanogels by McMurry Coupling Reaction
2.8. Fabrication of Fluorescent Film by Mixing the Nanogel with PMMA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Precise Synthesis Star-Shaped Block Copolymers by ATRP with a Hexafunctional Initiator
3.2. Synthesis of Fluorescent Nanogels by Crosslinking the Inner Blocks through McMurry Reaction of the Pendent Benzophenone Groups
3.3. The Fluorescent Behaviors and Sizes of the Organic Nanogels
3.4. Fabrication of a Fluorescent Film by Mixing the P(BPMA-co-ProHEMA)gel-b-PMMA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, H.S.; Chiu, D.T. Soft fluorescent nanomaterials for biological and biomedical imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4699–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfbeis, O.S. An overview of nanoparticles commonly used in fluorescent bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4743–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chernov, K.G.; Redchuk, T.A.; Omelina, E.S.; Verkhushaa, V.V. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Proteins, Biosensors, and Optogenetic Tools Engineered from Phytochromes. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6423–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.; Bogdanov, A.M.; Grigorenko, B.L.; Bravaya, K.B.; Nemukhin, A.V.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Krylov, A.I. Photoinduced Chemistry in Fluorescent Proteins: Curse or Blessing? Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 758–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Shi, X.; Bai, S.; Zhang, J.; Hou, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.S.; Xue, P.; Kang, Y.; Xu, Z. Water-soluble fluorescent unimolecular micelles: Ultra-small size, tunable fluorescence emission from the visible to NIR region and enhanced biocompatibility for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging. Chem. Commun. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Mao, Z.; Gao, C.; Huang, F. Pillar [6] arene/Paraquat Molecular Recognition in Water: High Binding Strength, pH-Responsiveness, and Application in Controllable Self-Assembly, Controlled Release, and Treatment of Paraquat Poisoning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19489–19497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jin, S.; Li, S.; Xue, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.Q.; Zou, G.; Liang, X.J. Imaging intracellular anticancer drug delivery by self-assembly micelles with aggregation-induced emission (AIE micelles). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5212–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisch, A.; Klymchenko, A.S. Fluorescent Polymer Nanoparticles Based on Dyes: Seeking Brighter Tools for Bioimaging. Small 2016, 12, 1968–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, G. A novel nanogel-based fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection of intracellular pH values. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8787–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.S.; Stolwijk, J.A.; Sun, L.N.; Wegener, J.; Wolfbeis, O.S. A nanogel for ratiometric fluorescent sensing of intracellular pH values. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 4246–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, S.; Tsuji, T.; Kawamoto, K.; Okano, K.; Fukatsu, E.; Noro, T.; Ikado, K.; Yamada, S.; Shibata, Y.; Hayashi, T.; et al. A Cell-Targeted Non-Cytotoxic Fluorescent Nanogel Thermometer Created with an Imidazolium-Containing Cationic Radical Initiator. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 5413–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gota, C.; Okabe, K.; Funatsu, T.; Harada, Y.; Uchiyama, S. Hydrophilic fluorescent nanogel thermometer for intracellular thermometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2766–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, T.; Mao, C.; Lai, B.; Yan, L. Synthesis of disulfide-cross-linked polypeptide nanogel conjugated with a near-infrared fluorescence probe for direct imaging of reduction-induced drug release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5662–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Bae, B.C.; Na, K. Acetylated hyaluronic acid/photosensitizer conjugate for the preparation of nanogels with controllable phototoxicity: Synthesis, characterization, autophotoquenching properties, and in vitro phototoxicity against HeLa cells. Bioconj. Chem. 2010, 21, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.I.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lin, L.; Kim, D.P. Direct Synthesis of a Covalently Self-Assembled Peptide Nanogel from a Tyrosine-Rich Peptide Monomer and Its Biomineralized Hybrids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5630–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Wei, Y. Facile preparation of biocompatible and robust fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles via PEGylation and cross-linking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4241–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amamoto, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Arm-replaceable star-shaped nanogels: Arm detachment and arm exchange reactions by dynamic covalent exchanges of alkoxyamine units. Polym. J. 2010, 42, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amamoto, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Masunaga, H.; Sasaki, S.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Intelligent Build-Up of Complementarily Reactive Diblock Copolymers via Dynamic Covalent Exchange toward Symmetrical and Miktoarm Star-shaped Nanogels. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, L.; Tu, C.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tong, R.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, J.; Cheng, J. Redox-Responsive, Core Cross-Linked Polyester Micelles. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, A.M.; Dyab, A.K.F.; Allohedan, H.A. A novel route to prepare highly surface active nanogel particles based on nonaqueous emulsion polymerization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ziener, U. Synthesis of nanostructured materials in inverse miniemulsions and their applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10093–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.Y.; Du, J.Z.; Song, W.J.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.Z.; Xiong, M.H.; Wang, J. Biocompatible and functionalizable polyphosphate nanogel with a branched structure. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9322–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Zhao, L.; Han, W.; Xin, X.; Lin, Z. A general and robust strategy for the synthesis of nearly monodisperse colloidal nanocrystals. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; He, Y.; Jung, J.; Lin, Z. 1D nanocrystals with precisely controlled dimensions, compositions, and architectures. Science 2016, 353, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Rzayev, J. Charge and size selective molecular transport by amphiphilic organic nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16726–16729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Pang, X.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Lin, Z. Robust Route to Unimolecular Core–Shell and Hollow Polymer Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6058–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Rzayev, J. Well-defined organic nanotubes from multicomponent bottlebrush copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6880–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.K.; Siegwart, D.J.; Matyjaszewski, K. Synthesis and biodegradation of nanogels as delivery carriers for carbohydrate drugs. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3326–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beija, M.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Martinho, J.M.G. Synthesis and applications of Rhodamine derivatives as fluorescent probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2410–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavis, L.D. Teaching Old Dyes New Tricks: Biological Probes Built from Fluoresceins and Rhodamines. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, R.M.; Veale, E.B.; Pfeffer, F.M.; Kruger, P.E.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Colorimetric and fluorescent anion sensors: An overview of recent developments in the use of 1,8-naphthalimide-based chemosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3936–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabchev, I.; Staneva, D.; Betcheva, R. Fluorescent Dendrimers As Sensors for Biologically Important Metal Cations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4976–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klymchenko, A.S. Solvatochromic and Fluorogenic Dyes as Environment-Sensitive Probes: Design and Biological Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Park, S.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Recent progress in the development of near-infrared fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Phenomenon, mechanism and applications. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4332–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.K.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.; Kwok, R.T.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Together We Shine, United We Soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, R.; Pan, Y.; Manghnani, P.N.; Liu, B. AIE Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Biological Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yu, J. AIEgens-Functionalized Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Materials: Fabrications and Applications. Small 2016, 12, 6478–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yao, C.; Tang, T.; Liu, X.; et al. A New Strategy To Access Polymers with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 5586–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Ravinathan, S.P.; Xue, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cao, C.; Zhu, X. Dual-responsive aggregation-induced emission-active supramolecular nanoparticles for gene delivery and bioimaging. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7950–7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liow, S.S.; Zhou, H.; Sugiarto, S.; Guo, S.; Chalasani, M.L.; Verma, N.K.; Xu, J.; Loh, X.J. Highly Efficient Supramolecular Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Pseudorotaxane Luminogen for Functional Bioimaging. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Qian, J.; Zhao, X.; Qin, W.; Hu, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Xu, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; He, S. Stable and Size-Tunable Aggregation-Induced Emission Nanoparticles Encapsulated with Nanographene Oxide and Applications in Three-Photon Fluorescence Bioimaging. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Bioprobes Based on AIE Fluorogens. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Huang, Y.; Tian, H. Progress and Trends in AIE-Based Bioprobes: A Brief Overview. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12217–12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, T.; Liang, X.J. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Lighting up Cells, Revealing Life! Small 2016, 12, 6451–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Enzyme-Responsive Bioprobes Based on the Mechanism of Aggregation-Induced Emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12278–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission probes for cancer theranostics. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. AlEgens for biological process monitoring and disease theranostics. Biomaterials 2017, 146, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; You, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. Bio-/Chemosensors and Imaging with Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 2142–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. A novel “turn-on” fluorescent chemosensor for the selective detection of Al3+ based on aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Qin, J.; Li, Z. A graphene oxide-based AIE biosensor with high selectivity toward bovine serum albumin. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12385–12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Tang, B.Z. Fluorescent Sensors Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission: Recent Advances and Perspectives. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Sun, N.; Chen, P.; Tang, R.; Li, Q.; Ma, D.; Li, Z. Largely blue-shifted emission through minor structural modifications: Molecular design, synthesis, aggregation-induced emission and deep-blue OLED application. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2136–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.J.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.; Fang, R.; Zhang, H.R.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Gao, J.; Wong, M.S. AIE-Active Fluorene Derivatives for Solution-Processable Nondoped Blue Organic Light-Emitting Devices (OLEDs). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28156–28165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Zhang, D.; Peng, R.; Yang, R.; Hong, L.; Song, W.; Wei, Q.; Duan, L.; Ge, Z. Non-Doped Sky-Blue OLEDs Based on Simple Structured AIE Emitters with High Efficiencies at Low Driven Voltages. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, R.; Nishimoto, T.; Park, I.S.; Lee, J.; Yasuda, T. Aggregation-Induced Delayed Fluorescence Based on Donor/Acceptor-Tethered Janus Carborane Triads: Unique Photophysical Properties of Nondoped OLEDs. Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 7171–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Fan, J.; Yu, H.; Ke, Z.; Nie, C.; Kuang, D.; Shao, G.; Su, C. Nonplanar Organic Sensitizers Featuring a Tetraphenylethene Structure and Double Electron-Withdrawing Anchoring Groups. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 9034–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.H.; Liu, B. Applications of Fluorogens with Rotor Structures in Solar Cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ablekim, T.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.J. Rational design of tetraphenylethylene-based luminescent down-shifting molecules: Photophysical studies and photovoltaic applications in a CdTe solar cell from small to large units. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 26193–26202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wei, Y. Zwitterionic red fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles for cell imaging. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Bilalis, P.; Zhang, H.; Gnanou, Y.; Hadjichristidis, N. Core Cross-Linked Multiarm Star Polymers with Aggregation-Induced Emission and Temperature Responsive Fluorescence Characteristics. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 4217–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Hu, R.; Sun, J.Z.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z. Click Synthesis, Aggregation-Induced Emission, E/Z Isomerization, Self-Organization, and Multiple Chromisms of Pure Stereoisomers of a Tetraphenylethene-Cored Luminogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9956–9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Star-shaped Blcok Copolymer | Star-shaped PA | Star-shaped PA-b-PB | PAgel-b-PB | QYsol. f (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mwa (kg/mol) | Đb | dn/dcc (mL/g) | Mwa (kg/mol) | Đb | dn/dcc (mL/g) | Dhd (nm)/PDI | λex, max e (nm) | λem e (nm) | ||
| P(BPMA125-co-ProHEMA125)-b-PMMA1059 | 63.60 | 1.17 | 0.153 | 169.50 | 1.28 | 0.112 | 21.4/0.43 | 368 | 484, 510 | 47.2 |
| P(BPMA113-co-MMA150)-b-P(ProHEMA)511 | 45.33 | 1.16 | 0.148 | 169.90 | 1.37 | 0.128 | 26.7/0.47 | 375 | 472, 513 | - g |
| P(BPOEMA275-co-ProHEMA559)-b-PMMA496 | 221.9 | 1.22 | 0.121 | 271.50 | 1.23 | 0.110 | 26.8/0.28 | 381 | 478, 513 | - g |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, M.; Fang, L.; Guan, F.; Huang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H. A Facile Approach towards Fluorescent Nanogels with AIE-Active Spacers. Polymers 2018, 10, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070722
Feng M, Fang L, Guan F, Huang S, Cheng Y, Liang Y, Zhang H. A Facile Approach towards Fluorescent Nanogels with AIE-Active Spacers. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070722
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Meiran, Laiping Fang, Fujun Guan, Siying Huang, Yinwei Cheng, Yancui Liang, and Hefeng Zhang. 2018. "A Facile Approach towards Fluorescent Nanogels with AIE-Active Spacers" Polymers 10, no. 7: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070722
APA StyleFeng, M., Fang, L., Guan, F., Huang, S., Cheng, Y., Liang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2018). A Facile Approach towards Fluorescent Nanogels with AIE-Active Spacers. Polymers, 10(7), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070722