Land Use Optimization for Coastal Urban Agglomerations Based on Economic and Ecological Gravitational Linkages and Accessibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Objectives
- (a)
- Modified GDP
- (b)
- Modified ESV
- (c)
- Compactness
2.2.2. Constraints
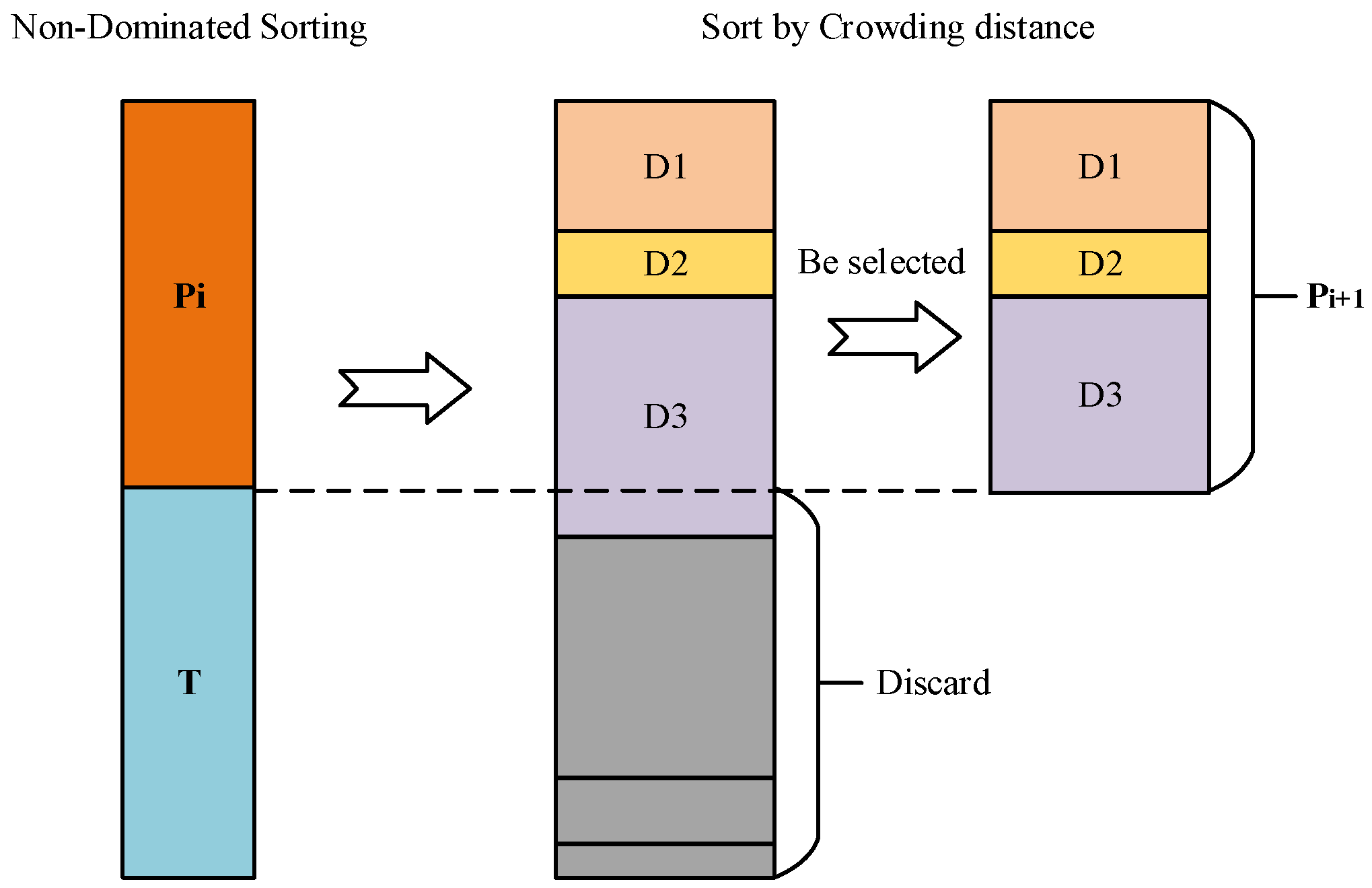
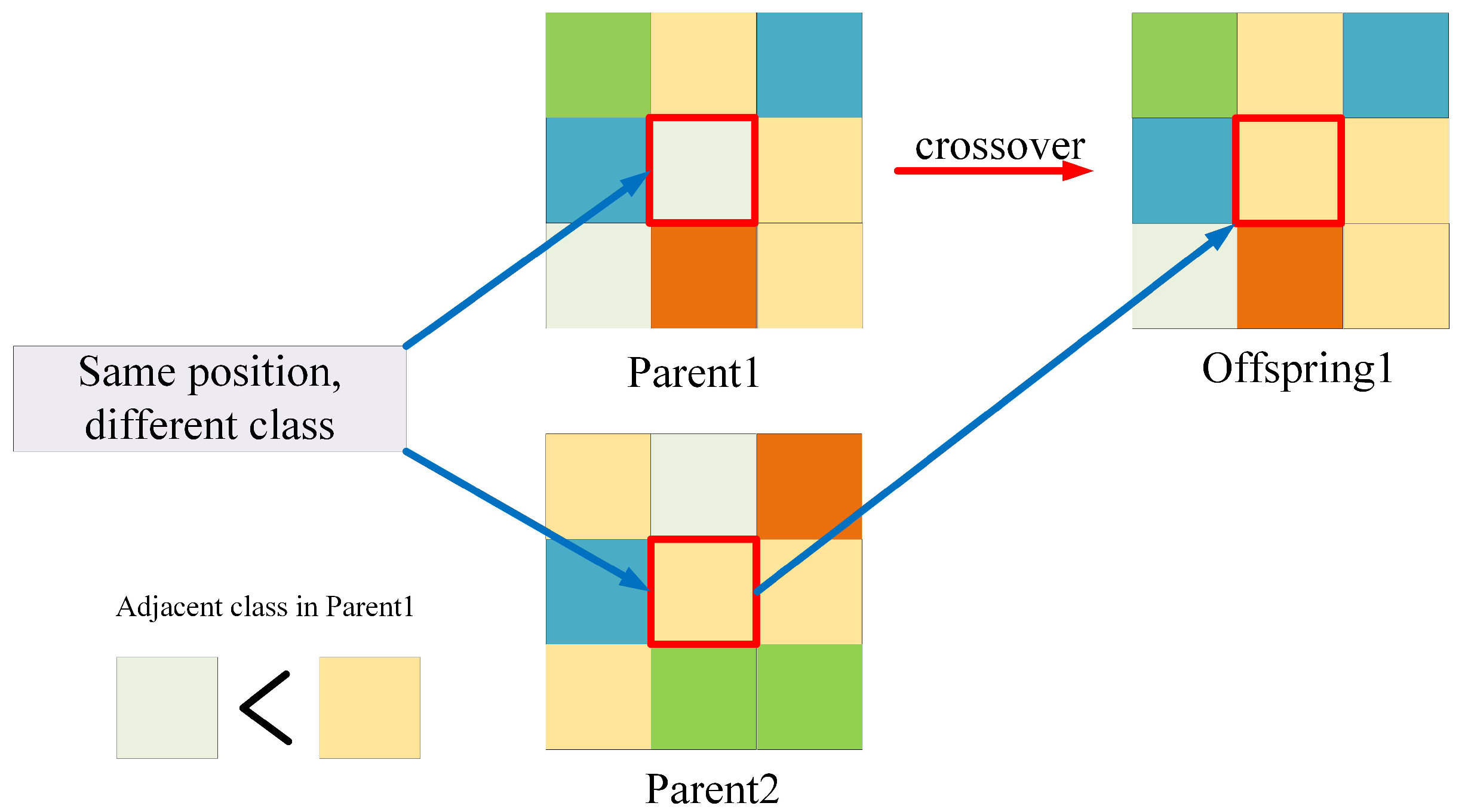
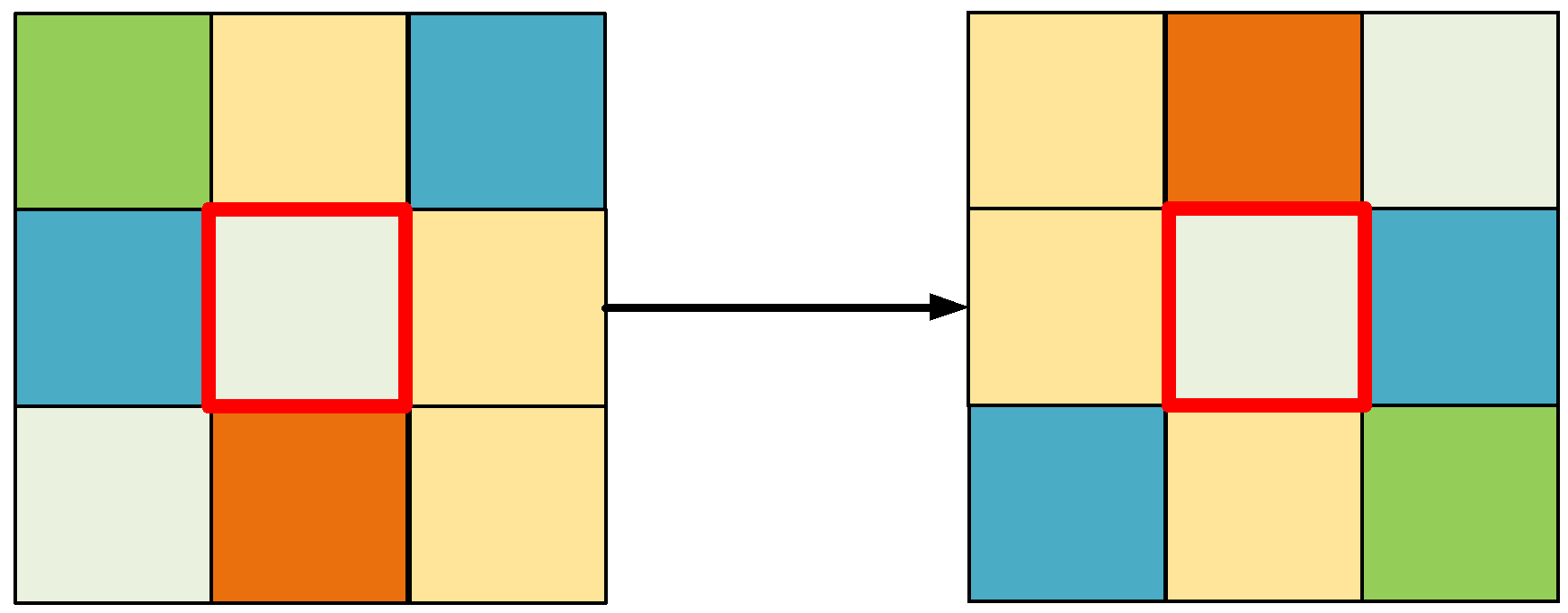
2.2.3. Parallel NSGA-II
3. Results
3.1. Objective Quantification and Constraints
3.2. Implementation and Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, M. Assessment and analysis of regional economic collaborative development within an urban agglomeration: Yangtze River Delta as a case study. Habitat Int. 2019, 83, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Sen, J. Livability assessment within a metropolis based on the impact of integrated urban geographic factors (IUGFs) on clustering urban centers of Kolkata. Cities 2018, 74, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Peng, X.; Yin, C. Simulating urban cooperative expansion in a single-core metropolitan region based on improved CA model integrated information flow: Case study of Wuhan urban agglomeration in China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 05018002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.C.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Lang, W. Deciphering the spatial structure of China’s megacity region: A new bay area—The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in the making. Cities 2018, 105, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kii, M. Projecting future populations of urban agglomerations around the world and through the 21st century. npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Yang, X. Examining the relationship between urban land expansion and economic linkage using coupling analysis: A case study of the Yangtze river economic belt, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, M.; Su, F.; Cui, Y. Changes in Ecosystems and Ecosystem Services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area since the Reform and Opening Up in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Xue, B.; Geng, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fujita, T.; Hao, H. Inter-city passenger transport in larger urban agglomeration area: Emissions and health impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lu, X.; Jin, G.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, M. Optimization of urban land-use structure in China’s rapidly developing regions with eco-environmental constraints. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 110, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wen, Z. Optimization of land use structure to balance economic benefits and ecosystem services under uncertainties: A case study in Wuhan, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, Z.; Wen, M.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Zhuang, C. Identifying the spatial disparities and determinants of ecosystem service balance and their implications on land use optimization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T. Spatio-temporal land use multi-objective optimization: A case study in Central China. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, X.; Peng, L.; Shao, J.; Chi, T. An improved artificial bee colony algorithm for optimal land-use allocation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 29, 1470–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gong, Y.; Cai, L.; Sun, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P. Sustainable Land-Use Allocation: A Multiobjective Particle Swarm Optimization Model and Application in Changzhou, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 04018010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaim, A.; Cord, A.F.; Volk, M. A review of multi-criteria optimization techniques for agricultural land use allocation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 105, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatio-temporal investigation of the interactive relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: Case study of the Jingjinji urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi, B.; Mansourianfar, M.H.; Haghshenas, H.; Kim, I. Multimodal accessibility-based equity assessment of urban public facilities distribution. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.A.; Schwarz-von Raumer, H.-G.; Esswein, H.; Müller, M.; Schmidt-Lüttmann, M. Time series of landscape fragmentation caused by transportation infrastructure and urban development: A case study from Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Cao, K.; He, S.; Shan, L. Ecological conservation–and economic development–based multiobjective land-use optimization: Case study of a rapidly developing city in central China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2019, 145, 05018023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Su, F.; Lyne, V.; Cheng, F.; Xiao, H. Practical Efficient Regional Land-Use Planning Using Constrained Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm Optimization. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yue, W.; Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, D. Re-evaluating polycentric urban structure: A functional linkage perspective. Cities 2020, 101, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, M. A Study on Economic Spatial Structure of Urban Agglomerations in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2018, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, D.; Fang, X.; Wu, Q.; Cao, Y. Exploring Spatiotemporal Integration Evolution of the Urban Agglomeration through City Networks. Land 2022, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, J.; Li, T.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D. Morphological and functional polycentric structure assessment of megacity: An integrated approach with spatial distribution and interaction. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Guo, Z.; Li, J. The dynamic linkage among urbanisation, industrialisation and carbon emissions in China: Insights from spatiotemporal effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Z. How regional economic integration influence on urban land use efficiency? A case study of Wuhan metropolitan area, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Derudder, B.; Huang, J. Examining the transition processes in the Pearl River Delta polycentric mega-city region through the lens of corporate networks. Cities 2017, 60, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Z. Research on the Spatial Features of the E-RetailingEconomic Linkages at County Level: A Case Study for Zhejiang Province, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, P.; Wang, H.; Cushman, S.A.; Cheng, C.; Song, C.; Ye, S. Sustainable land-use optimization using NSGA-II: Theoretical and experimental comparisons of improved algorithms. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Su, M. Influence of rapid transit on accessibility pattern and economic linkage at urban agglomeration scale in China. Open Geosci. 2019, 11, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paritosh, P.; Kalita, B.; Sharma, D. A game theory based land layout optimization of cities using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2019, 14, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaab, J.; Deb, K.; Goodman, E.; Lautenbach, S.; van Strien, M.J.; Grêt-Regamey, A. Improving the performance of genetic algorithms for land-use allocation problems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 907–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, X. The Application of Genetic Algorithm in Land Use Optimization Research: A Review. Land 2021, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santé, I.; Rivera, F.F.; Crecente, R.; Boullón, M.; Suárez, M.; Porta, J.; Parapar, J.; Doallo, R. A simulated annealing algorithm for zoning in planning using parallel computing. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 59, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X. An improved simulated annealing algorithm for interactive multi-objective land resource spatial allocation. Ecol. Complex. 2018, 36, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. A multi-type ant colony optimization (MACO) method for optimal land use allocation in large areas. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2012, 26, 1325–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, N.; Chandramouli, M. A GIS supported Ant algorithm for the linear feature covering problem with distance constraints. Decis. Support Syst. 2006, 42, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Batty, M.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, J. Spatial multi-objective land use optimization: Extensions to the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 1949–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Agrawal, S.; Pratap, A.; Meyarivan, T. A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 849–858. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Chen, D. An improved knowledge-informed NSGA-II for multi-objective land allocation (MOLA). Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 21, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Pant, M.; Snasel, V. A comprehensive review on NSGA-II for multi-objective combinatorial optimization problems. Ieee Access 2021, 9, 57757–57791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanian, R.; Hajipour, M. Integrated framework of system dynamics and meta-heuristic for multi-objective land use planning problem. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 16, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaygan, M.; Alimohammadi, A.; Mansourian, A.; Govara, Z.S.; Kalami, S.M. Spatial multi-objective optimization approach for land use allocation using NSGA-II. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, J.; Masoumi, Z.; Hakimpour, F.; Coello Coello, C.A. Many-objective land use planning using a hypercube-based NSGA-III algorithm. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 609–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artina, S.; Bragalli, C.; Erbacci, G.; Marchi, A.; Rivi, M. Contribution of parallel NSGA-II in optimal design of water distribution networks. J. Hydroinformatics 2012, 14, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, C.-J.; Huang, M.-X. Multi-objective optimal power flow considering transient stability based on parallel NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 30, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, W. A land-use spatial optimum allocation model coupling a multi-agent system with the shuffled frog leaping algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 77, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G. Integrating agricultural land, water yield and soil conservation trade-offs into spatial land use planning. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparros-Midwood, D.; Barr, S.; Dawson, R. Spatial optimization of future urban development with regards to climate risk and sustainability objectives. Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 2164–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fangmei, P. Economic Spatial Connection and Spatial Structure of Guangdong-Hong KongMacao Greater Bay and the Surrounding Area Cities—An Empirical Analysis Based on Improved Gravity Model and Social Network Analysis. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Parrott, L. An improved Genetic Algorithm for spatial optimization of multi-objective and multi-site land use allocation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 59, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Q.; Huang, B. Spatial multi-objective land use optimization toward livability based on boundary-based genetic algorithm: A case study in Singapore. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holzkämper, A.; Seppelt, R. A generic tool for optimising land-use patterns and landscape structures. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, Z.; Coello, C.A.C.; Mansourian, A. Dynamic urban land-use change management using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 4165–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.-X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C. Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Szabó, G. A Geospatial Approach to Measure Social Benefits in Urban Land Use Optimization Problem. Land 2021, 10, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Szabó, G. Multi-objective urban land use optimization using spatial data: A systematic review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xi, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, M.; Pan, X.; Ren, C. Land Use Optimization and Simulation of Low-Carbon-Oriented—A Case Study of Jinhua, China. Land 2021, 10, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Yang, Y.; Zou, L. How to reconcile land use conflicts in mega urban agglomeration? A scenario-based study in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





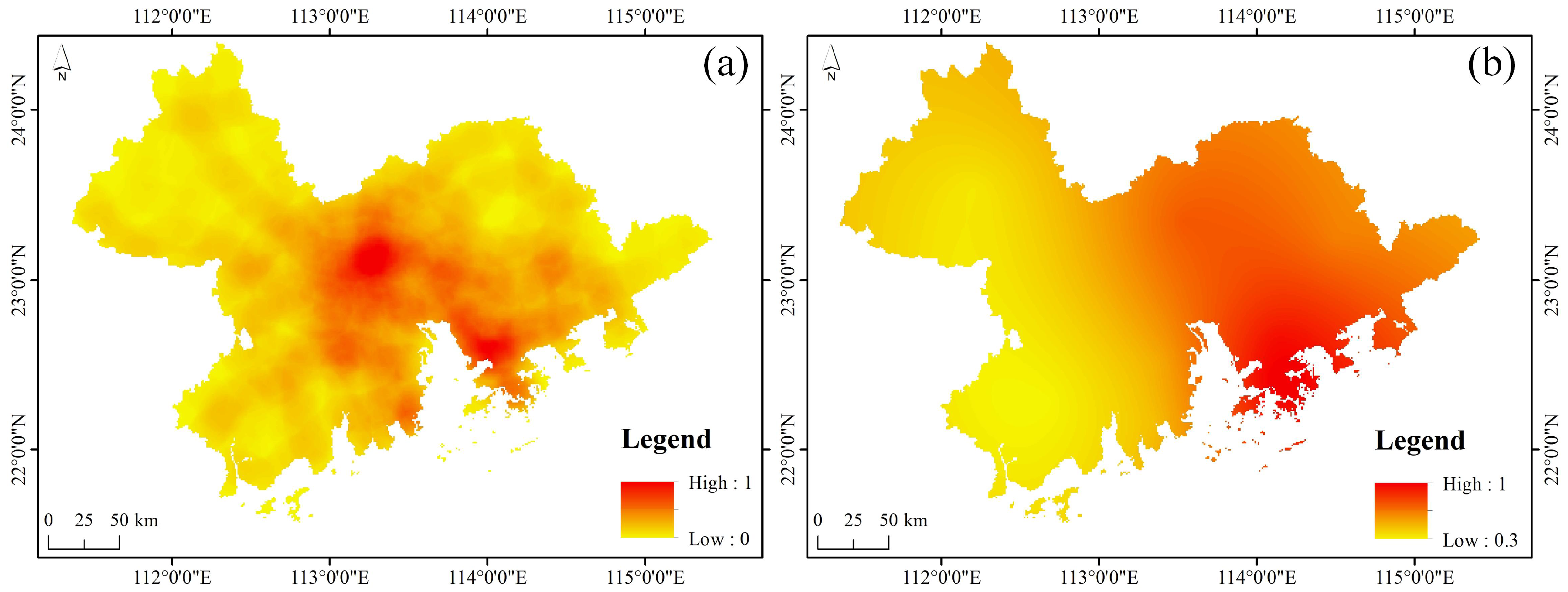


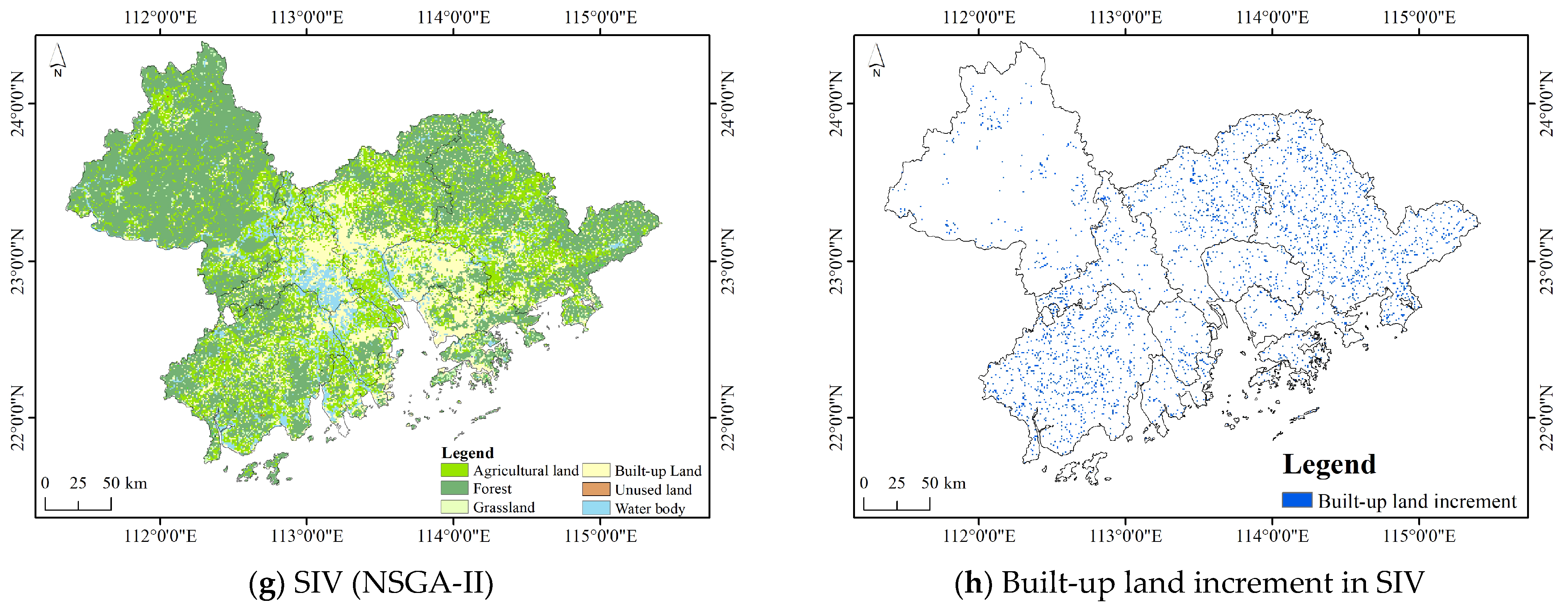
| City\Industry (100 Million CNY) | Primary Industry | Secondary Industry | Tertiary Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| SZ | 7.21 | 7678.10 | 10,328.76 |
| ZH | 48.30 | 1037.97 | 980.08 |
| GZ | 206.52 | 5873.54 | 12,233.74 |
| ZQ | 288.22 | 647.20 | 342.28 |
| FS | 127.29 | 4975.83 | 3030.55 |
| HZ | 146.13 | 1768.08 | 1264.48 |
| DG | 19.92 | 3007.87 | 3346.51 |
| ZS | 59.56 | 1680.96 | 1312.27 |
| JM | 170.46 | 1110.76 | 982.97 |
| HK | 1.13 | 129.23 | 1547.69 |
| Marco | 0.00 | 207.53 | 2888.67 |
| GDP Group by Sector | Corresponding Land Use | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary industry | Farming | - | Agricultural land |
| Forestry | - | Forest | |
| Animal husbandry | Cattle, sheep, chickens, pigs | Grassland, Agricultural land | |
| Fishery | - | Water | |
| Secondary industry | - | - | Built-up land |
| Tertiary industry | Service on farming | - | Agricultural land |
| Service on forestry | - | Forest | |
| Service on animal husbandry | - | Agricultural land | |
| Service on Fishery | - | Water | |
| Other | - | Built-up land |
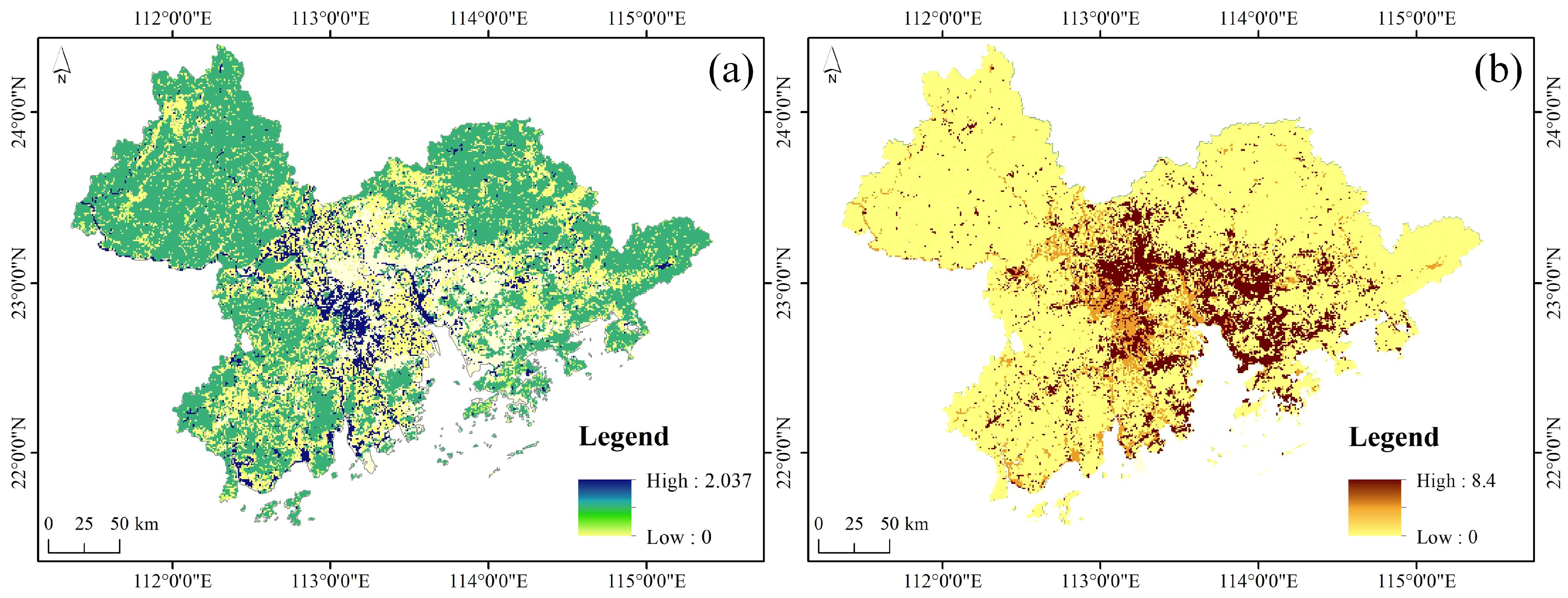
| Land Use | ESV (Million CNY × km−2 × a−1) | GDP (100 Million CNY × km−2) |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.355 | 0.104 |
| Forest | 0.524 | 0.004 |
| Grassland | 1.263 | 0.012 |
| Water | 2.037 | 0.137 |
| Built-up land | 0 | 8.4 |
| Scenario\Objective Value | Modified GDP Change | Modified ESV Change | Compactness Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| SI (GDP) | 19.22% | −11.48% | −8.67% |
| SII (ESV) | 9.28% | −8.03% | −4.75% |
| SIII (Compactness) | 9.17% | −9.18% | −4.69% |
| SIV (NSGA-II) | 11.81% | −10.94% | −8.67% |
| Scenario\Area Change (%) | Cropland | Forest | Grassland | Built-Up Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Pattern | 14929 | 35004 | 1472 | 8806 |
| SI (GDP) | 1.36% | −8.84% | 0.34% | 32.88% |
| SII (ESV) | 0.07% | −6.38% | −8.63% | 26.89% |
| SIII (Compactness) | −0.13% | −7.52% | −7.88% | 31.56% |
| SIV (NSGA-II) | −4.88% | −9.00% | 54.48% | 33.08% |
| Scenario\Change of Vegetation (%) | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| SI | 3.81% | 24.25% | 71.94% |
| SIV | 2.43% | 17.71% | 79.86% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, T.; Yan, F.; Su, F.; Lyne, V.; Zhou, C. Land Use Optimization for Coastal Urban Agglomerations Based on Economic and Ecological Gravitational Linkages and Accessibility. Land 2022, 11, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071003
Pan T, Yan F, Su F, Lyne V, Zhou C. Land Use Optimization for Coastal Urban Agglomerations Based on Economic and Ecological Gravitational Linkages and Accessibility. Land. 2022; 11(7):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071003
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Tingting, Fengqin Yan, Fenzhen Su, Vincent Lyne, and Chaodong Zhou. 2022. "Land Use Optimization for Coastal Urban Agglomerations Based on Economic and Ecological Gravitational Linkages and Accessibility" Land 11, no. 7: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071003
APA StylePan, T., Yan, F., Su, F., Lyne, V., & Zhou, C. (2022). Land Use Optimization for Coastal Urban Agglomerations Based on Economic and Ecological Gravitational Linkages and Accessibility. Land, 11(7), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071003









