Prevalence of Salmonella by Serological and Direct Detection Methods in Piglets from Inconspicuous, Conspicuous, and Vaccinated Sow Herds
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
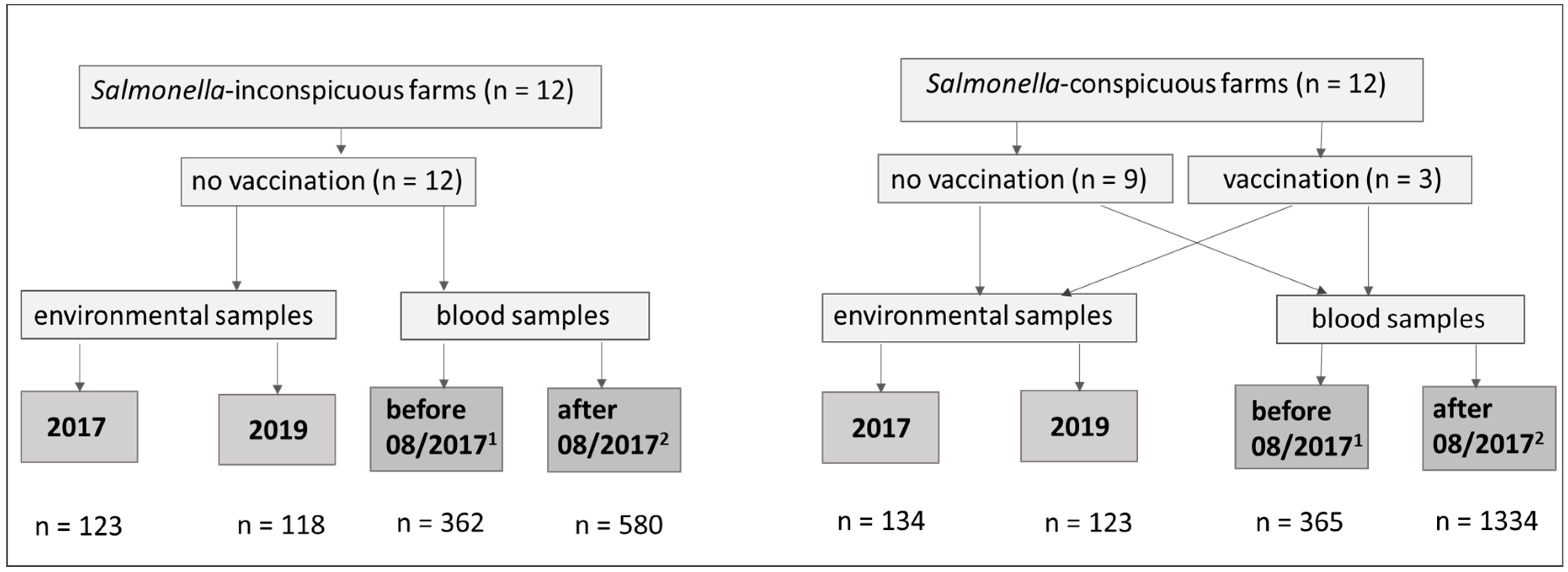
2.1. Design of the Study
2.2. Animals
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Tests for Salmonella
2.5. Biosecurity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Salmonella Prevalence in the Environment
3.2. Optical Densities (OD%) of the Examined Blood Samples
3.3. Biosecurity Check
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert Koch-Institut. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch Meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2018. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/Jahrbuch/Jahrbuch_2018.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends an sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 22–67. [Google Scholar]
- RKI. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch Meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2017. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/Jahrbuch/Jahrbuch_2017.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Smith, R.P.; Andres, V.; Cheney, T.; Martelli, F.; Gosling, R.; Marier, E.; Rabie, A.; Gilson, D.; Davies, R.H. How do pig farms maintain low Salmonella prevalence: A case-control study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andres, V.M.; Davies, R.H. Biosecurity measures to control Salmonella and other infectious agents in pig farms: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.L.; Alban, L.; Nielsen, B.; Dahl, J. The correlation between Salmonella serology and isolation of Salmonella in Danish pigs at slaughter. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 101, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Verodnung zur Verminderung der Salmonellenverbreitung durch Schlachtschweine (Schweine-Salmonellen-Verordnung) vom 13. März 2007. Bundesgesetzblatt Jahrgang 2007 Teil 1 2007, 10, 322–325. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzer, K.; Switt, A.I.M.; Wiedmann, M. Animal contact as a source of human non-typhoidal salmonellosis. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visscher, C.; Winter, P.; Verspohl, J.; Stratmann-Selke, J.; Upmann, M.; Beyerbach, M.; Kamphues, J. Effects of feed particle size at dietary presence of added organic acids on caecal parameters and the prevalence of Salmonella in fattening pigs on farm and at slaughter. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 93, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, C.F. Investigations (Field Study) on Salmonella Prevalence of Fattening Pigs with Regard to the Influcene of a Low Grinding Intensity and Feed Additives (Organic Acids and Potassium Diformate Respectively) (Dissertation); Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover Press: Hannover, Germany, 2006; pp. 198–200. [Google Scholar]
- zu Sundern, A.S.; Holling, C.; Rohn, K.; Schulte-Wülwer, J.; Deermann, A.; Visscher, C. Relationships between colostrum supply of suckling piglets and Salmonella prevalence in piglet rearing. Porc. Health Manag. 2018, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kump, F.W.S.; Löhren, U. Salmonellen Bekämpfung in der Primärproduktion–ein kritischer Vergleich der Strategie und der Erfolge. Veterinär Spiegel 2015, 25, 132–138. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaugh, M.P. Advances in swine immunology help move vaccine technology forward. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 159, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wales, A.; Davies, R. Salmonella vaccination in pigs: A review. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- zu Sundern, A.S.; Visscher, C. Untersuchungen zu Effekten der Reproduktionsleistung und der Kolostrumversorgung auf die Salmonellenseroprävalenz in der Ferkelaufzucht. Dissertation; Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover: Hannover, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- zu Sundern, A.S.; Rohn, K.; Holling, C.; Deermann, A.; Schulte-Wülwer, J.; Visscher, C. Einfluss einer gesteigerten Fruchtbarkeitsleistung auf die Salmonellenseroprävalenz von Aufzuchtferkeln. Prakt. Tierarzt 2017, 98, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Ghent University. Biocheck.Ugent. Available online: www.biocheck.ugent.be (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- European Parliament. Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and the Counsil of 17 November 2003 on the Control of Salmonella and Other Specified Zoonotic Agents. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32003R2160 (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Martelli, F.; Andres, V.M.; Davies, R.; Smith, R.P. Observations on the introduction and dissemination of Salmonella in three previously low prevalence status pig farms in the United Kingdom. Food Microbiol. 2018, 71, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of salmonella in holdings with breeding pigs in the EU, 2008: Part a: Salmonella prevalence estimates. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Gotter, V.; Klein, G.; Koesters, S.; Kreienbrock, L.; Blaha, T.; Campe, A. Main risk factors for Salmonella-infections in pigs in north-western Germany. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 106, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDT Biologica. SALMOPORC Product Description. Available online: www.idt-tiergesundheit.de/producte/salmoporc (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Hornstein, O. Impfung gegen Salmonella Typhimurium Infektionen des Schweines. Beratungsempfehlungen Schweinegesundheitsdienste 2014, 4, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.; Lee, J.H. Immunization of pregnant sows with a novel virulence gene deleted live Salmonella vaccine and protection of their suckling piglets against salmonellosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, U.; Heller, P.; Waldmann, K.H.; Truyen, U.; Hensel, A. Immunization of sows in an integrated pig-breeding herd using a homologous inactivated Salmonella vaccine decreases the prevalence of Salmonella typhimurium infection in the offspring. J. Vet. Med. B 2006, 53, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, A.; Cook, A.; Davies, R. Producing Salmonella-free pigs: A review focusing on interventions at weaning. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merialdi, G.; Barigazzi, G.; Bonilauri, P.; Tittarelli, C.; Bonci, M.; D’incau, M.; Dottori, M. Longitudinal study of Salmonella infection in Italian farrow-to-finish swine herds. Zoonoses Public Health 2008, 55, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloeil, P.A.; Chauvin, C.; Proux, K.; Rose, N.; Queguiner, S.; Eveno, E.; Houdayer, C.; Rose, V.; Fravalo, P.; Madec, F. Longitudinal serological responses to Salmonella enterica of growing pigs in a subclinically infected herd. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 60, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Parys, A.; Boyen, F.; Leyman, B.; Verbrugghe, E.; Maes, D.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Induction of seroconversion and persistence of Salmonella Typhimurium in pigs are strain dependent. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 36, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berends, B.; Urlings, H.; Snijders, J.; Van Knapen, F. Identification and quantification of risk factors in animal management and transport regarding Salmonella spp. in pigs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 30, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 2017 | 2019 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI | SC | SI | SC | |
| Samples (n) | 123 | 134 | 118 | 123 |
| Salmonella-positive (n) | 6 | 27 | 4 | 18 |
| Salmonella-positive (%) | 4.88 | 20.1 | 3.39 | 14.6 |
| Area 1 | Number of Positive Samples/Percentage of Positve Samples | |||
| 1 | 1/8.33 | 4/20.0 | 0/0.00 | 1/16.7 |
| 2 | 2/6.06 | 1/3.70 | 1/2.85 | 2/5.55 |
| 3 | 0/0.00 | 1/3.33 | 0/0.00 | 2/7.69 |
| 4 | 2/4.44 | 20/40.8 | 3/6.52 | 13/26.0 |
| 5 | 0/0.00 | 1/16.7 | 0/0.00 | 0/0.00 |
| 6 | 1/33.3 | 0/0.00 | 0/0.00 | 0/0.00 |
| Chi-square a | 0.0003 | 0.0024 | ||
| Farm 1 | 2017 | 2019 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| npos/nall | % | npos/nall | % | |
| 1 | 4/12 | 33.0 | 1/10 | 10.0 |
| 2 | 0/15 | 0.00 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 1/11 | 9.10 b | 5/10 | 50.0 a |
| 4 | 6/12 | 50.0 | 4/11 | 36.4 |
| 5 | 3/11 | 27.3 | 0/11 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 1/10 | 10.0 | 1/10 | 10.0 |
| 7 | 3/11 | 27.3 | 5/10 | 50.0 |
| 8 | 1/9 | 11.1 | 0/9 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 1/10 | 10.0 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 10 | 2/11 | 18.2 | 2/10 | 20.0 |
| 11 | 2/12 | 16.7 | 0/12 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 3/10 | 30.0 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 13 | 0/11 | 0.00 | 1/10 | 10.0 |
| 14 | 0/10 | 0.00 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 0/10 | 0.00 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 16 | 1/10 | 10.0 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 17 | 0/10 | 0.00 | 2/10 | 20.0 |
| 18 | 0/11 | 0.00 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 19 | 2/12 | 16.7 | 1/10 | 10.0 |
| 20 | 1/11 | 9.10 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 21 | 0/10 | 0.00 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 22 | 0/10 | 0.00 | 0/10 | 0.00 |
| 23 | 0/8 | 0.00 | 0/9 | 0.00 |
| 24 | 2/10 | 20.0 | 0/9 | 0.00 |
| Time | SI (n = 12 Farms) | SC (n = 9 Farms) | SC/Vaccination 1 (n = 3 Farms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Samples with ≥10% OD/Percentage of Samples ≥10% OD | |||
| Samples before 08.2017 2 | 50/13.81 c, A | 107/35.67 b, A | 28/43.08 a, B |
| Samples after 08.2017 3 | 33/5.69 c, B | 108/27.00 b, B | 563/60.28 a, A |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buch, J.-M.; Visscher, C.; Schulte zu Sundern, A.; Schulte-Wülwer, J.; Deermann, A.; Holling, C. Prevalence of Salmonella by Serological and Direct Detection Methods in Piglets from Inconspicuous, Conspicuous, and Vaccinated Sow Herds. Animals 2020, 10, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010029
Buch J-M, Visscher C, Schulte zu Sundern A, Schulte-Wülwer J, Deermann A, Holling C. Prevalence of Salmonella by Serological and Direct Detection Methods in Piglets from Inconspicuous, Conspicuous, and Vaccinated Sow Herds. Animals. 2020; 10(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuch, Juhle-Marijke, Christian Visscher, Anton Schulte zu Sundern, Josef Schulte-Wülwer, Ansgar Deermann, and Carolin Holling. 2020. "Prevalence of Salmonella by Serological and Direct Detection Methods in Piglets from Inconspicuous, Conspicuous, and Vaccinated Sow Herds" Animals 10, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010029
APA StyleBuch, J. -M., Visscher, C., Schulte zu Sundern, A., Schulte-Wülwer, J., Deermann, A., & Holling, C. (2020). Prevalence of Salmonella by Serological and Direct Detection Methods in Piglets from Inconspicuous, Conspicuous, and Vaccinated Sow Herds. Animals, 10(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010029





