New Treatment for the Cognitive and Emotional Deficits Linked with Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. PTX Treatment
2.3. Allodynia Tests
2.4. Cognitive Behavior Test
2.5. Emotional Behavior Tests
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Experimental Procedures
2.8. Drugs
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
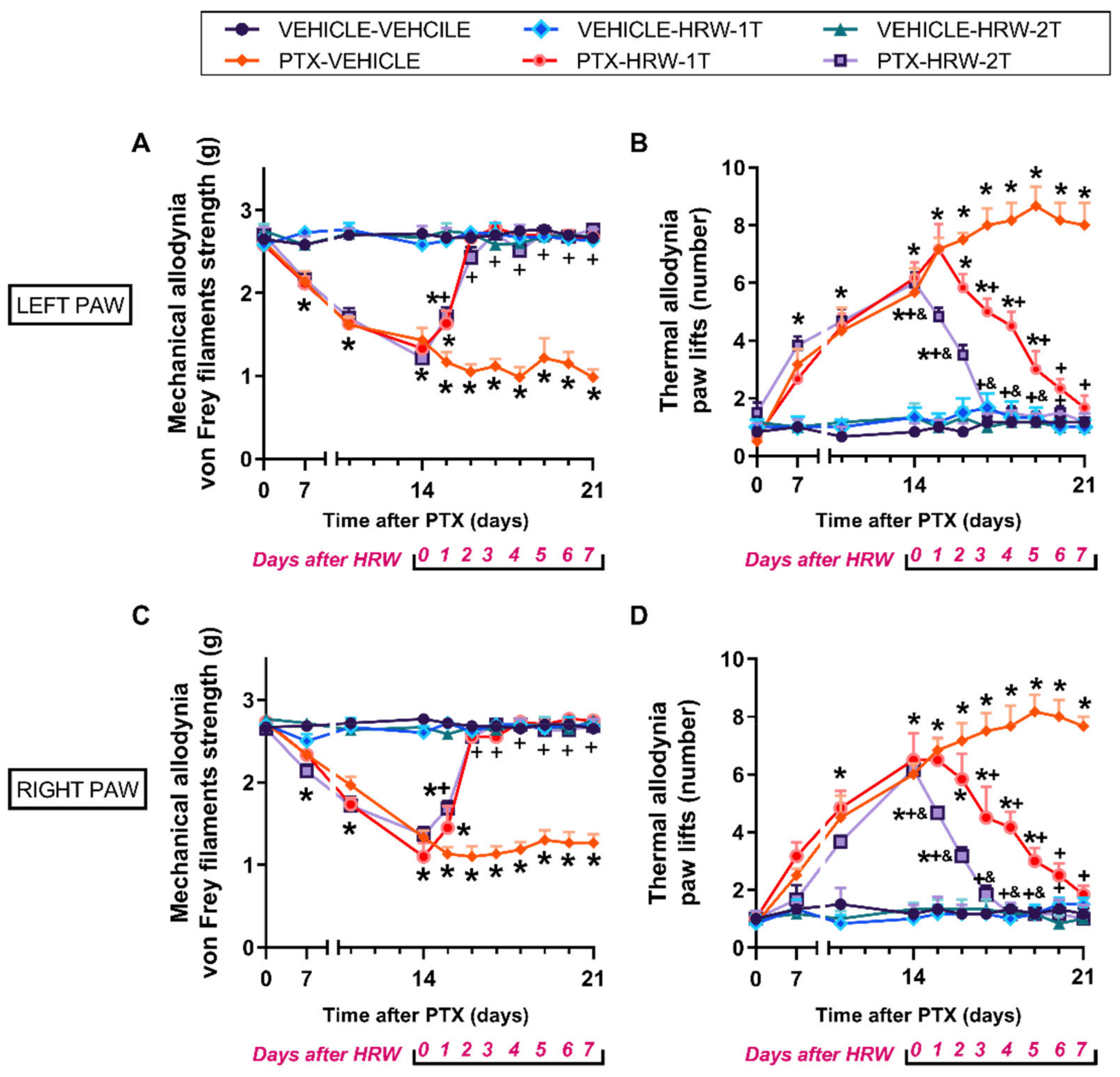
3.1. The Mechanical and Cold Allodynia Provoked by PTX Were Inhibited by the Repetitive Administration of HRW
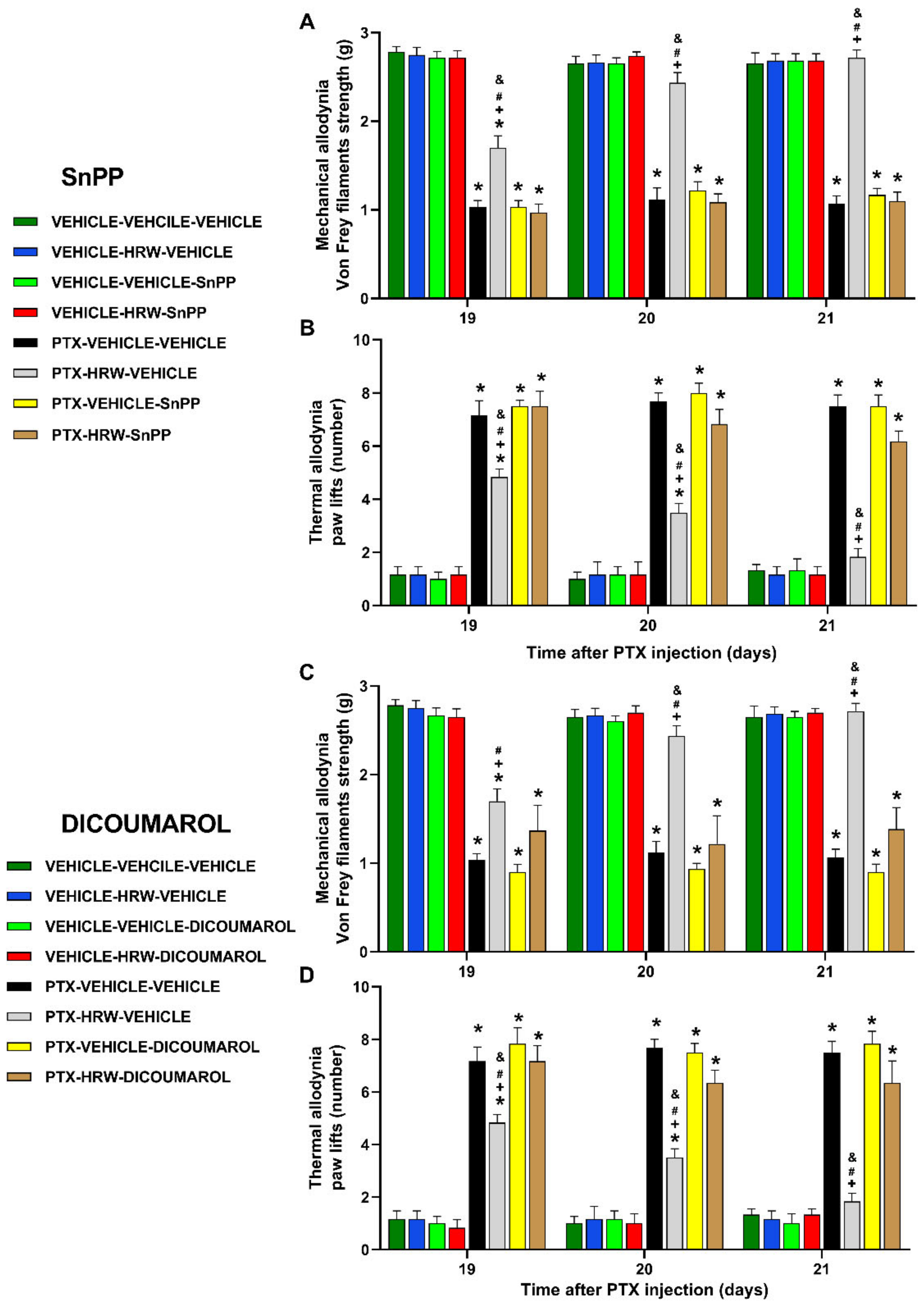
3.2. Reversion of the Antiallodynic Actions Induced by HRW Treatment with a Kv7 Potassium Channels Blocker and Specific Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 Inhibitors
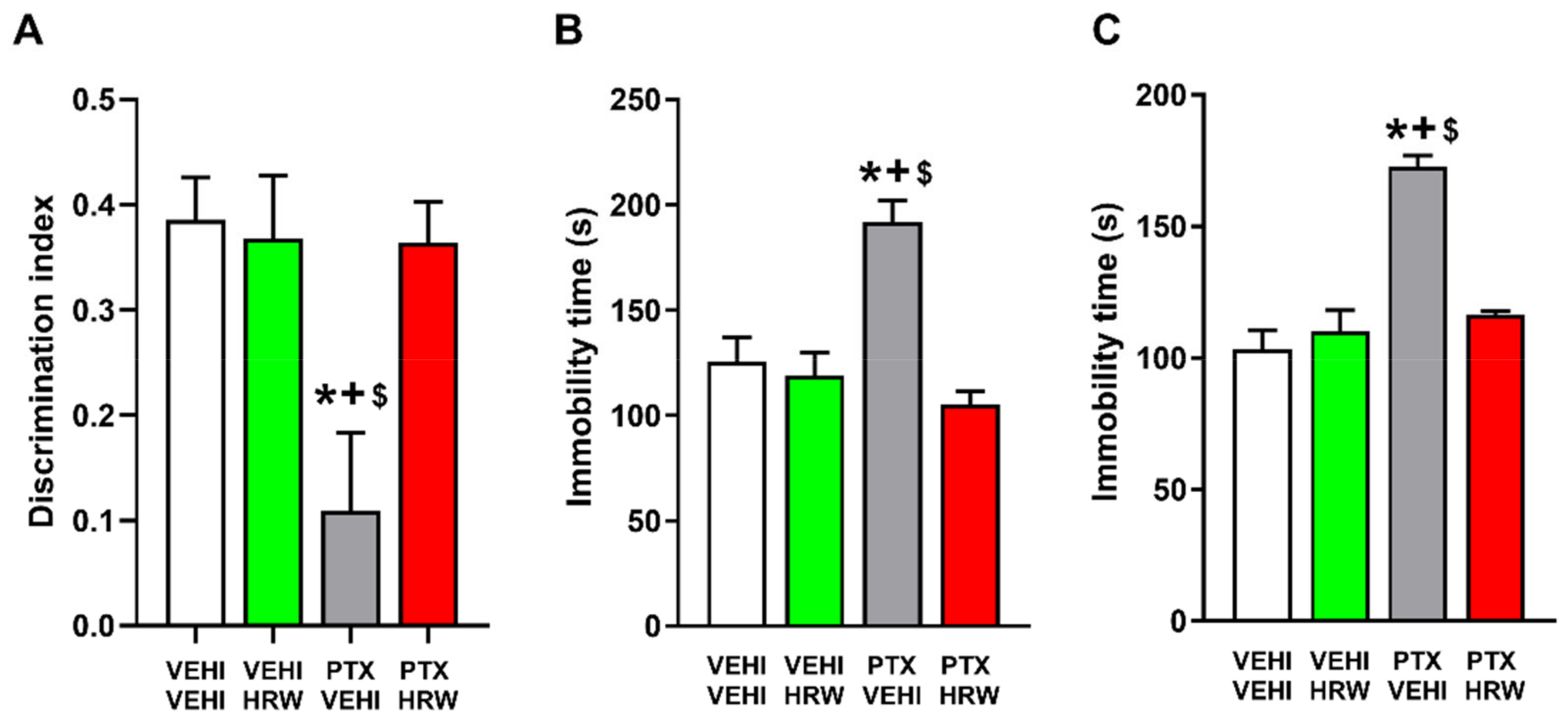
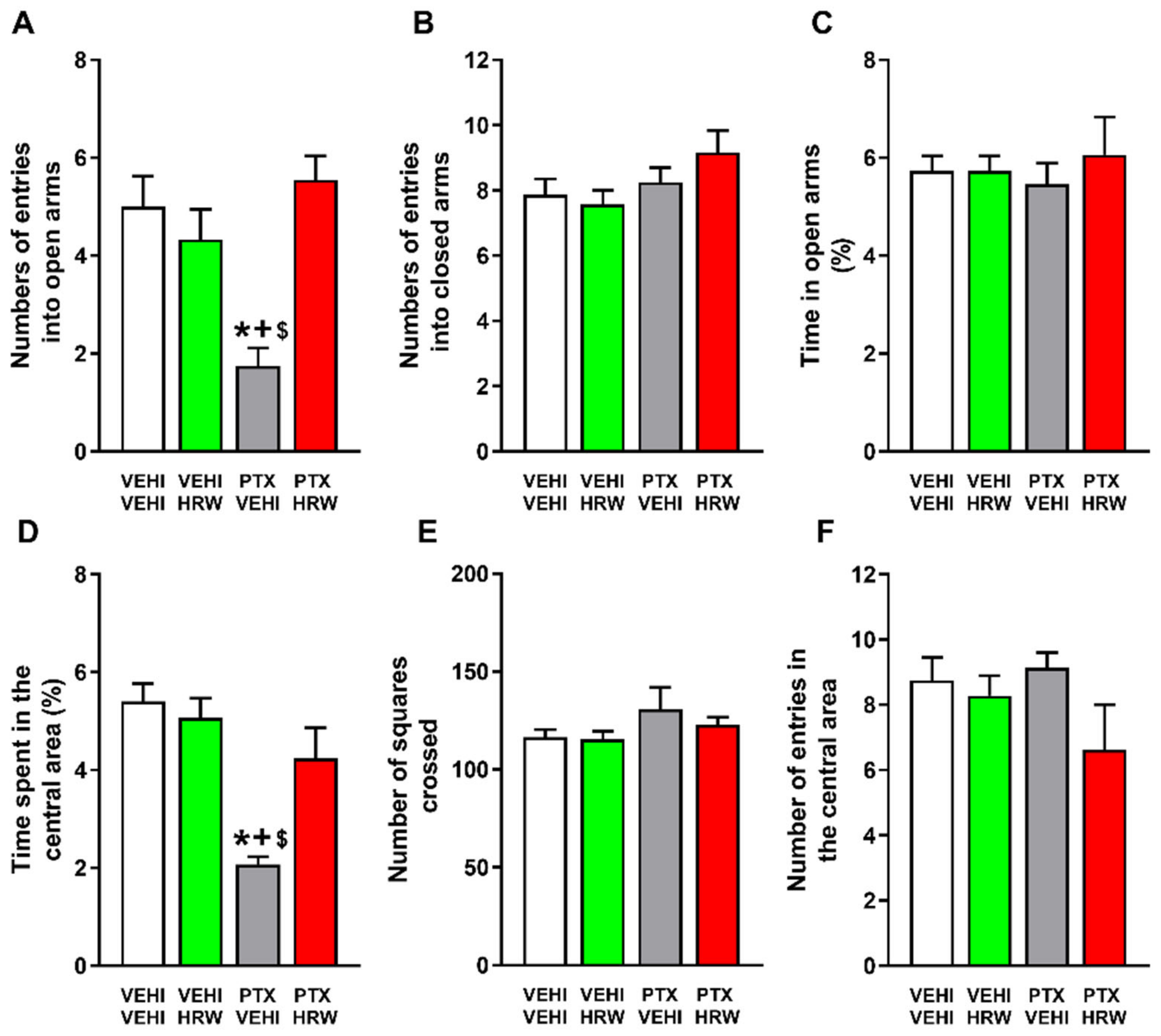
3.3. HRW Treatment Inhibited the Cognitive and Emotional Disorders Associated with PIPN
3.4. Effects of Treatment with HRW on the Expression of p-ERK ½, p-Akt, p-IKBα and BAX in the PFC of PTX-Injected Mice
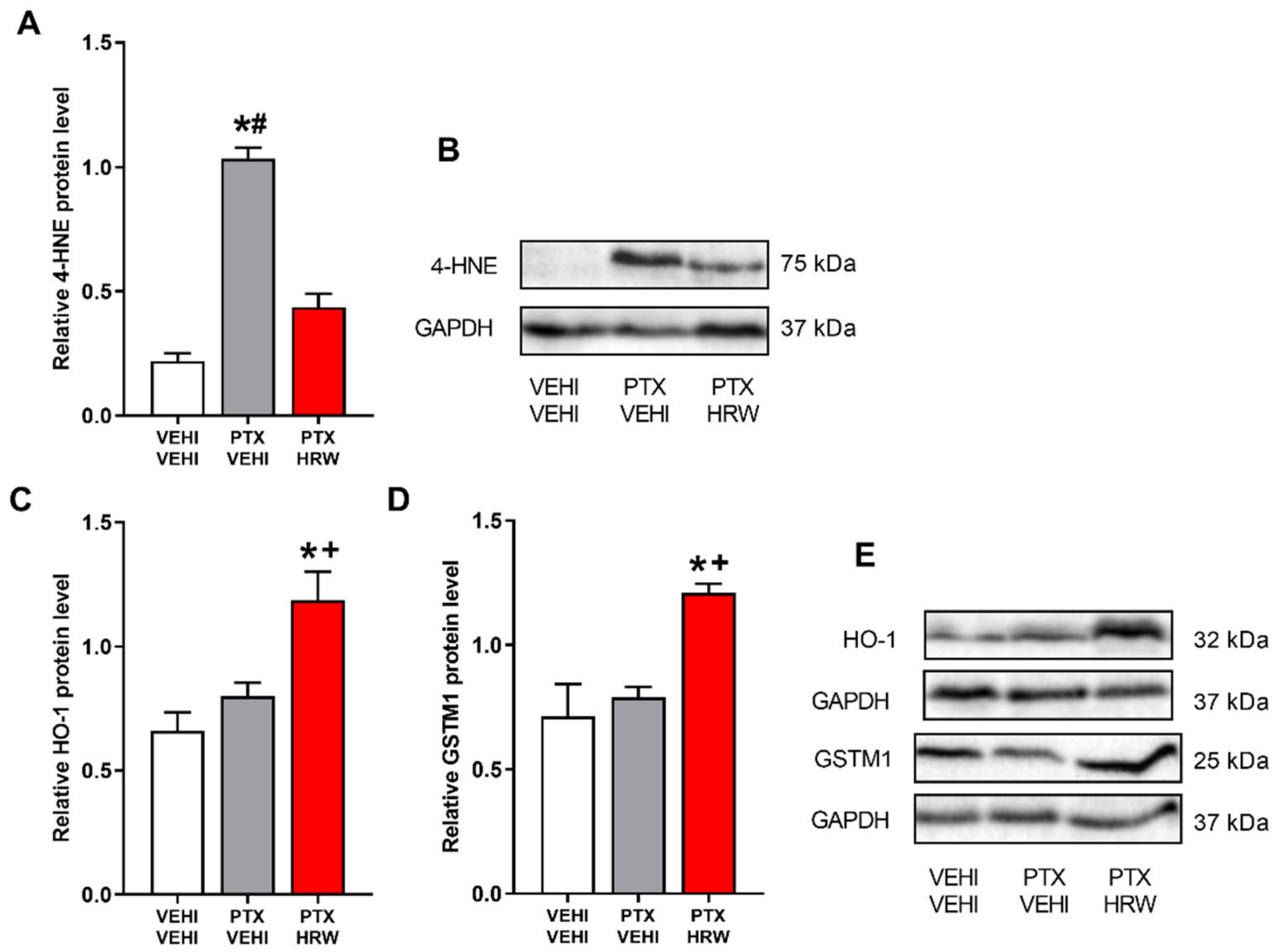
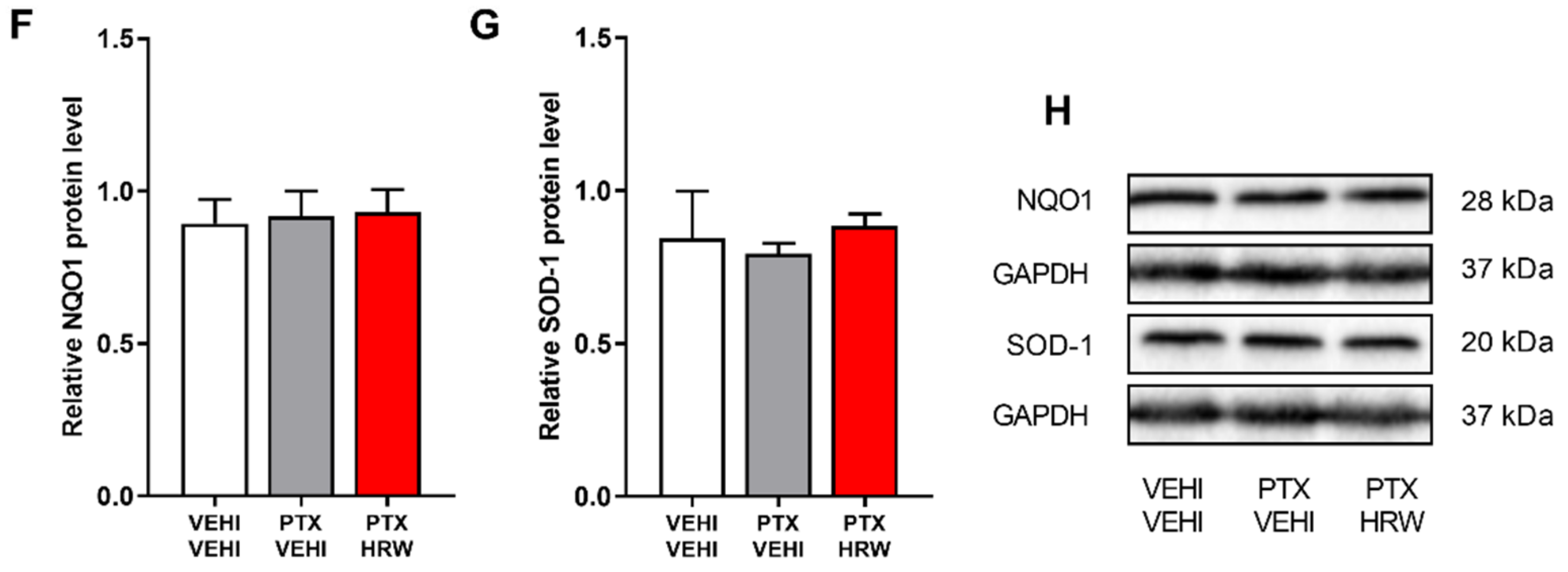
3.5. Effects of Treatment with HRW on the Expression of 4-HNE, HO-1, GSTM1, NQO1 and SOD-1 in the PFC of PTX-Injected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flatters, S.J.L.; Dougherty, P.M.; Colvin, L.A. Clinical and preclinical perspectives on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN): A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engvall, K.; Gréen, H.; Fredrikson, M.; Lagerlund, M.; Lewin, F.; Åvall-Lundqvist, E. Impact of persistent peripheral neuropathy on health-related quality of life among early-stage breast cancer survivors: A population-based cross-sectional study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 195, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massie, M.J. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2004, 32, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, T.; Turton, P. ‘Chemobrain’: Concentration and memory effects in people receiving chemotherapy—A descriptive phenomenological study. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2011, 20, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.J.; Schwartz, G.K. Chemotherapy in the management of advanced cutaneous malignant melanoma. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Ogden, A.; Aneja, R.; Zhou, J. Microtubule-Binding Proteins as Promising Biomarkers of Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Cancer Chemotherapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipton, R.B.; Apfel, S.C.; Dutcher, J.P.; Rosenberg, R.; Kaplan, J.; Berger, A.; Einzig, A.I.; Wiernik, P.; Schaumburg, H.H. Taxol produces a predominantly sensory neuropathy. Neurology 1989, 39, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, X. Mechanisms underlying paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain: Channels, inflammation and immune regulations. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 933, 175288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seretny, M.; Currie, G.L.; Sena, E.S.; Ramnarine, S.; Grant, R.; MacLeod, M.R.; Colvin, L.A.; Fallon, M. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dranitsaris, G.; Yu, B.; King, J.; Kaura, S.; Zhang, A. Nab-paclitaxel, docetaxel, or solvent-based paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer: A cost-utility analysis from a Chinese health care perspective. Clinicoecon. Outcomes Res. 2015, 7, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, W.; Kyte, S.L.; Bagdas, D.; Alkhlaif, Y.; Alsharari, S.D.; Lichtman, A.H.; Chen, Z.J.; Del Fabbro, E.; Bigbee, J.W.; Gewirtz, D.A.; et al. Effects of paclitaxel on the development of neuropathy and affective behaviors in the mouse. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, A.; Chung, N.C.; Lawther, A.J.; Ziegler, A.I.; Shackleford, D.M.; Sloan, E.K.; Walker, A.K. The Anti-Inflammatory Drug Aspirin Does Not Protect Against Chemotherapy-Induced Memory Impairment by Paclitaxel in Mice. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 564965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roch, G.; Batallé, G.; Bai, X.; Pouso-Vázquez, E.; Rodríguez, L.; Pol, O. The Beneficial Effects of Heme Oxygenase 1 and Hydrogen Sulfide Activation in the Management of Neuropathic Pain, Anxiety- and Depressive-like Effects of Paclitaxel in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.X.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, X.L. Paclitaxel induces cognitive impairment via necroptosis, decreased synaptic plasticity and M1 polarisation of microglia. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewandter, J.S.; Kleckner, A.S.; Marshall, J.H.; Brown, J.S.; Curtis, L.H.; Bautista, J.; Dworkin, R.H.; Kleckner, I.R.; Kolb, N.; Mohile, S.G.; et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and its treatment: An NIH Collaboratory study of claims data. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Ito, M.; Ichihara, M.; Ito, M. Molecular hydrogen as an emerging therapeutic medical gas for neurodegenerative and other diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant: Overview of the advantages of hydrogen for medical applications. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 555, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.T.; Qin, S.C. Neuroprotective Effects of Molecular Hydrogen: A Critical Review. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Shi, Q.Q.; Zhang, L.; Yue, C.P.; He, Z.J.; Li, X.X.; He, Q.J.; Liu, Q.; Du, X.B. Hydrogen-rich water ameliorates neuropathological impairments in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease through reducing neuroinflammation and modulating intestinal microbiota. Neural Regen Res. 2022, 17, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Choi, J.I. Hydrogen-Rich Water Improves Cognitive Ability and Induces Antioxidative, Antiapoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an Acute Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Mouse Model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9956938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, W.J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, T.Y.; Gong, H.; Shen, X.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Sun, X.J.; Jiang, C.L. Effects of hydrogen-rich water on depressive-like behavior in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuda, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Kanehisa, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Inoue, A.; Higuma, H.; Kawashima, C.; Nakanishi, M.; Okamoto, K.; Akiyoshi, J. Natural reduced water suppressed anxiety and protected the heightened oxidative stress in rats. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 2357–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.; Peng, L.; Xu, B.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Y. Protective Effects of Hydrogen-Rich Water Against Cartilage Damage in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Matrix Catabolism, and Apoptosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e92021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Satoh, Y.; Otsubo, Y.; Kazama, T. Molecular hydrogen attenuates neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Huo, X.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, K.; Yu, Y.; Shi, K. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Activated Autophagy via HIF-1 α Pathways in Neuropathic Pain Model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4670834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Wu, F.; Sun, X.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, L.; Huang, S.; Lu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yu, W.F. Intrathecal infusion of hydrogen-rich normal saline attenuates neuropathic pain via inhibition of activation of spinal astrocytes and microglia in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Serrat, M.; Martínez-Martel, I.; Coral-Pérez, S.; Bai, X.; Batallé, G.; Pol, O. Hydrogen-Rich Water as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for the Affective Disorders Linked with Chronic Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Fang, D.; Liu, M.; Cai, J.; Wan, Y.; Han, J.S.; Xing, G.G. Suppression of KCNQ/M (Kv7) potassium channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons contributes to the development of bone cancer pain in a rat model. Pain 2013, 154, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busserolles, J.; Tsantoulas, C.; Eschalier López García, J.A. Potassium channels in neuropathic pain: Advances, challenges, and emerging ideas. Pain 2016, 157 (Suppl. 1), S7–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodera, H.; Spieker, A.; Sung, M.; Rutkove, S. Neuroprotective effects of Kv7 channel agonist, retigabine, for cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 505, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Lucarini, E.; Micheli, L.; Mosca, I.; Ambrosino, P.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Martelli, A.; Testai, L.; Taglialatela, M.; Calderone, V.; et al. Effects of natural and synthetic isothiocyanate-based H2S-releasers against chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain: Role of Kv7 potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 2017, 121, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L. Nociceptive behavior induced by chemotherapeutic paclitaxel and beneficial role of antioxidative pathways. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Batallé, G.; Pol, O. The anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of diallyl disulfide and GYY4137 in animals with chronic neuropathic pain. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kosturakis, A.K.; Cassidy, R.M.; Zhang, H.; Kennamer-Chapman, R.M.; Jawad, A.B.; Colomand, C.M.; Harrison, D.S.; Dougherty, P.M. MAPK signaling downstream to TLR4 contributes to paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Chen, D.; Yan, F.; Wu, S.; Kang, S.; Xing, W.; Zeng, W.; Xie, J. JTC-801 alleviates mechanical allodynia in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, P.; Heles, M.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Pontearso, M.; Slepicka, J.; Palecek, J. Dual PI3Kδ/γ Inhibitor Duvelisib Prevents Development of Neuropathic Pain in Model of Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 1864–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wei, J.; Tian, L.; Padma Nagendra Borra, V.; Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Huo, F.Q. Paclitaxel induces sex-biased behavioral deficits and changes in gene expression in mouse prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 2020, 426, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.L.; Byun, N.E.; Tantawy, M.N.; Mackey, C.A.; Wilson, G.H.; Stark, A.J.; Flom, M.P.; Gee, L.C.; Quarles, C.C. In vivo neuroimaging and behavioral correlates in a rat model of chemotherapy-induced cognitive dysfunction. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, S.H.; Abdi, S. Pentoxifylline Ameliorates Mechanical Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Pain Physician 2016, 19, E589–E600. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Qian, Y.; Suo, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, J. Duloxetine Attenuates Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Nerve Injury by Inhibiting p53-Related Pathways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 373, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federman, N.; de la Fuente, V.; Zalcman, G.; Corbi, N.; Onori, A.; Passananti, C.; Romano, A. Nuclear factor κB-dependent histone acetylation is specifically involved in persistent forms of memory. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7603–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steru, L.; Chermat, R.; Thierry, B.; Simon, P. The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Le Pichon, M.; Jalfre, M. Depression: A new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 1977, 266, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Open Field Test for Measuring Locomotor Activity and Anxiety-Like Behavior. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Venkannagari, S.; Oh, K.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Rohde, J.M.; Liu, L.; Nimmagadda, S.; Sudini, K.; Brimacombe, K.R.; Gajghate, S.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitor of NRF2 Selectively Intervenes Therapeutic Resistance in KEAP1-Deficient NSCLC Tumors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.K.; Lin, C.K.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, W.C.; Young, K.C.; Lee, J.C. Human heme oxygenase 1 is a potential host cell factor against dengue virus replication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.T.; Hu, J.L.; Ren, J.H.; Yu, H.B.; Zhong, S.; Wai Wong, V.K.; Kwan Law, B.Y.; Chen, W.X.; Xu, H.M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Dicoumarol, an NQO1 inhibitor, blocks cccDNA transcription by promoting degradation of HBx. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shu, R.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, G. Hydrogen-rich saline prevents remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia and inhibits MnSOD nitration via regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptor in rats. Neuroscience 2014, 280, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, N.; Shen, M.; Zhang, K.; Pan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Y. Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Water Alleviates Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain Through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Xie, K.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G. H2 Treatment Attenuated Pain Behavior and Cytokine Release Through the HO-1/CO Pathway in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Nakashima-Kamimura, N.; Mikami, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Consumption of molecular hydrogen prevents the stress-induced impairments in hippocampus-dependent learning tasks during chronic physical restraint in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batallé, G.; Bai, X.; Pouso-Vázquez, E.; Roch, G.; Rodríguez, L.; Pol, O. The Recovery of Cognitive and Affective Deficiencies Linked with Chronic Osteoarthritis Pain and Implicated Pathways by Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Treatment. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltian, J.J.; Dos Reis, A.S.; Martins, A.W.S.; Blödorn, E.B.; Dellagostin, E.N.; Soares, L.K.; Schumacher, R.F.; Campos, V.F.; Alves, D.; Luchese, C.; et al. 7-Chloro-4-(Phenylselanyl) Quinoline Is a Novel Multitarget Therapy to Combat Peripheral Neuropathy and Comorbidities Induced by Paclitaxel in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 6567–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starobova, H.; Vetter, I. Pathophysiology of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabedra Sousa, F.S.; Birmann, P.T.; Bampi, S.R.; Fronza, M.G.; Balaguez, R.; Alves, D.; Leite, M.R.; Nogueira, C.W.; Brüning, C.A.; Savegnago, L. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like, anxiogenic-like and hyperalgesic behavior is attenuated by acute administration of α-(phenylselanyl) acetophenone in mice. Neuropharmacology 2019, 146, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Jin, Z.; Li, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Role of GABAB receptors and p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway in paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, E.Y.; Ehrlich, B.E. Prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A review of recent findings. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 145, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.H.; Greenwald, M.K.; Schwartz, A.G. Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Avenues. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 2384–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.; Ko, S.G.; Kim, W. Analgesic Effect of SH003 and Trichosanthes kirilowii Maximowicz in Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Testai, L.; Angeli, A.; Carrino, D.; Pacini, A.; Margiotta, F.; Flori, L.; Supuran, C.T.; Calderone, V.; Ghelardini, C.; et al. Inhibitors of Mitochondrial Human Carbonic Anhydrases VA and VB as a Therapeutic Strategy against Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qabazard, B.; Masocha, W.; Khajah, M.; Phillips, O.A. H2S donor GYY4137 ameliorates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, C.; Avagliano, C.; Cuozzo, M.; Liguori, F.M.; Calignano, A.; Russo, R. The Beneficial Effects of Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide in the Management of Neuropathic Pain and Associated Mood Disorders Induced by Paclitaxel in Mice. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, C.; Cuozzo, M.; Coretti, L.; Liguori, F.M.; Cimmino, F.; Turco, L.; Avagliano, C.; Aviello, G.; Mollica, M.P.; Lembo, F.; et al. Oral sodium butyrate supplementation ameliorates paclitaxel-induced behavioral and intestinal dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Martel, I.; Bai, X.; Batallé, G.; Pol, O. New Treatment for the Cognitive and Emotional Deficits Linked with Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122387
Martínez-Martel I, Bai X, Batallé G, Pol O. New Treatment for the Cognitive and Emotional Deficits Linked with Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(12):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122387
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Martel, Ignacio, Xue Bai, Gerard Batallé, and Olga Pol. 2022. "New Treatment for the Cognitive and Emotional Deficits Linked with Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice" Antioxidants 11, no. 12: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122387
APA StyleMartínez-Martel, I., Bai, X., Batallé, G., & Pol, O. (2022). New Treatment for the Cognitive and Emotional Deficits Linked with Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Antioxidants, 11(12), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122387






