J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10(4), 683; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040683 - 10 Feb 2021
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 9151
Abstract
Knowledge on heparin-induced thrombocytopenia keeps increasing. Recent progress on diagnosis and management as well as several discoveries concerning its pathogenesis have been made. However, many aspects of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia remain partly unknown, and exact application of these new insights still need to be
[...] Read more.
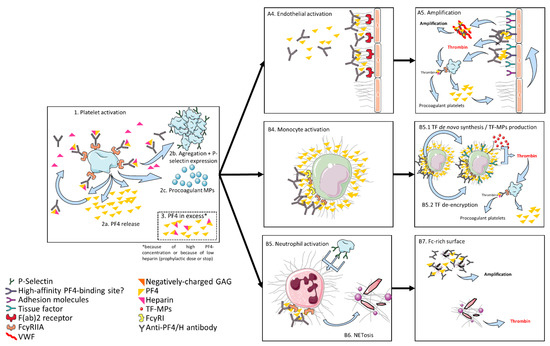
Knowledge on heparin-induced thrombocytopenia keeps increasing. Recent progress on diagnosis and management as well as several discoveries concerning its pathogenesis have been made. However, many aspects of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia remain partly unknown, and exact application of these new insights still need to be addressed. This article reviews the main new concepts in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Latest Clinical Advances in Thrombocytopenia)
►
Show Figures