Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis
Abstract
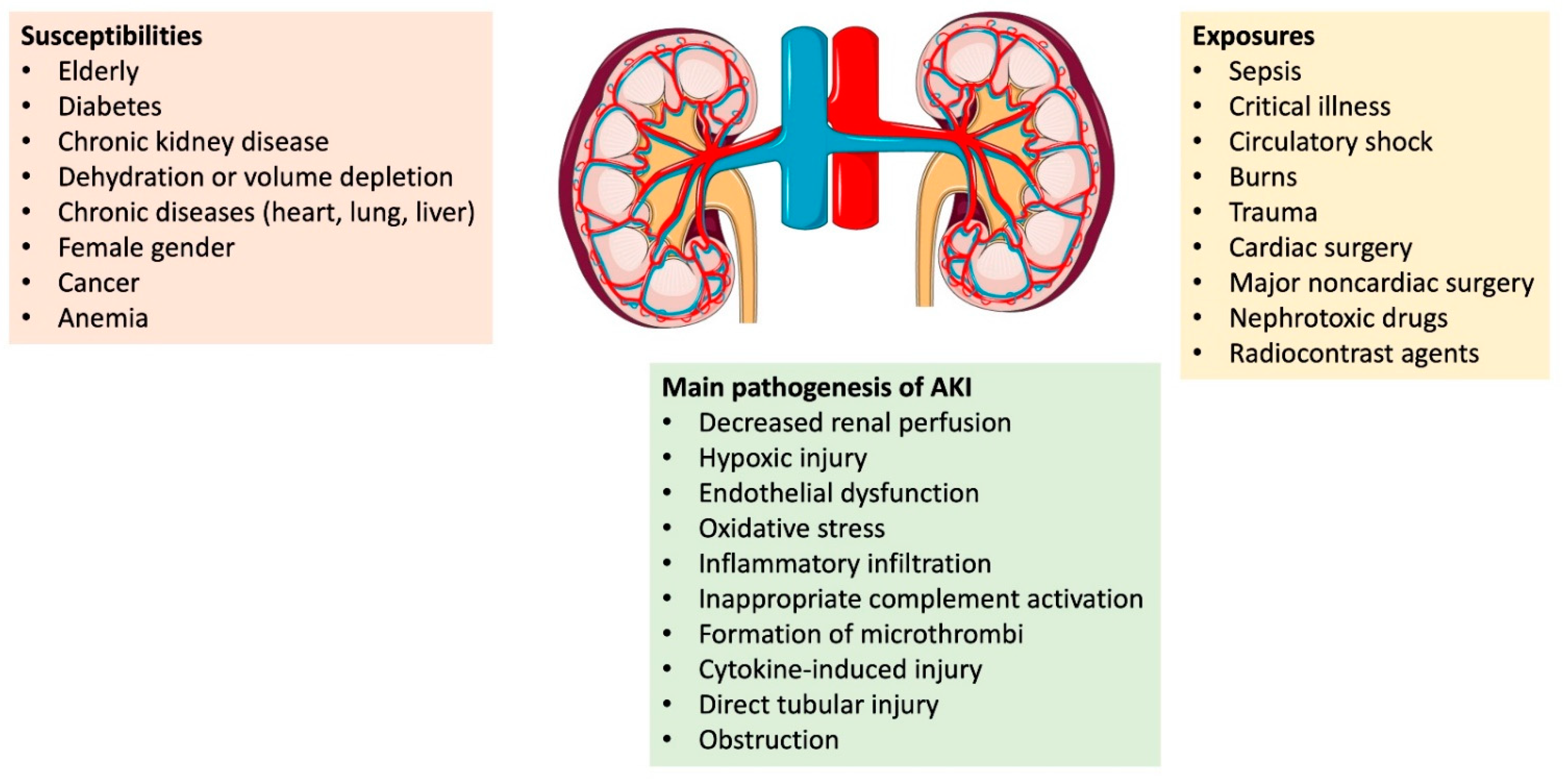
:1. Introduction
1.1. Subclinical AKI
1.2. AKI
2. Specific Causes for Pre-Renal AKI
2.1. Cardio-Renal Syndrome Type 1
2.2. Hepatorenal Syndrome
3. Intrarenal Causes of AKI
3.1. Acute Tubular Necrosis
3.2. Sepsis-Associated AKI
3.3. Rhabdomyolysis
3.4. Tumor Lysis Syndrome
4. Contrast-Induced AKI
4.1. Myeloma-Cast Nephropathy
4.1.1. Acute Interstitial Nephritis
4.1.2. Renal Parenchymal Disease
4.1.3. Vascular Disease
5. Specific Etiologies of AKI Affecting Multiple Renal Structures
5.1. Medications
5.2. Infections
5.3. COVID-19-Associated AKI
5.4. Post-Renal Causes of AKI
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohaney, R.; Yin, H.; Shahiniassn, V.; Saran, R.; Burrows, N.R.; Pavkov, M.E.; Banerjee, T.; Hsu, C.Y.; Powe, N.; Steffick, D.; et al. In-Hospital and 1-Year Mortality Trends in a National Cohort of US Veterans with Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jaghbeer, M.; Dealmeida, D.; Bilderback, A.; Ambrosino, R.; Kellum, J.A. Clinical Decision Support for In-Hospital AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; Clermont, G.; Kersten, A.; Venkataraman, R.; Angus, D.C.; De Bacquer, D.; Kellum, J.A. RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: A cohort analysis. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mesropian, P.D.; Othersen, J.; Mason, D.; Wang, J.; Asif, A.; Mathew, R.O. Community-acquired acute kidney injury: A challenge and opportunity for primary care in kidney health. Nephrology 2016, 21, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonnacott, A.; Meran, S.; Amphlett, B.; Talabani, B.; Phillips, A. Epidemiology and outcomes in community-acquired versus hospital-acquired AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siew, E.D.; Davenport, A. The growth of acute kidney injury: A rising tide or just closer attention to detail? Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- KDIGO AKIWG: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Inter. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. Available online: https//kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/KDIGO-2012-AKI-Guidelines.KI_SuppCover_2.1.indd(kdigo.org)/ (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Haase, M. Subclinical AKI is still AKI. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C. Subclinical AKI--an emerging syndrome with important consequences. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanmassenhove, J.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R.; Lameire, N. Subclinical AKI: Ready for primetime in clinical practice? J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, M.; Devarajan, P.; Haase-Fielitz, A.; Bellomo, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Wagener, G.; Krawczeski, C.D.; Koyner, J.L.; Murray, P.; Zappitelli, M.; et al. The outcome of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-positive subclinical acute kidney injury: A multicenter pooled analysis of prospective studies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yong, K.; Dogra, G.; Boudville, N.; Pinder, M.; Lim, W. Acute kidney injury: Controversies revisited. Int. J. Nephrol. 2011, 2011, 762634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhosale, S.J.; Kulkarni, A.P. Biomarkers in Acute Kidney Injury. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24 (Suppl. 3), S90–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, L.; Johnsen, A.H.; Sengeløv, H.; Borregaard, N. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10425–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.J. A long journey for acute kidney injury biomarkers. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaño, F.; Pascual, J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: A prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.H.; Bushinsky, D.A.; Wish, J.B.; Cohen, J.J.; Harrington, J.T. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency: A prospective study. Am. J. Med. 1983, 74, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Blair, J.E.A.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Lerma, E.V.; Mezue, K.; Molitch, M.; Mullens, W.; et al. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Classification, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, V.; Ginès, P.; Gerbes, A.L.; Dudley, F.J.; Gentilini, P.; Laffi, G.; Reynolds, T.B.; Ring-Larsen, H.; Schölmerich, J. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International Ascites Club. Hepatology 1996, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena Polanco, N.A.; Martin, P.; Carrion, A.F. Advances in the Management of Renal Dysfunction in Patients With Cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 17, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Iwakiri, Y. The molecules: Mechanisms of arterial vasodilatation observed in the splanchnic and systemic circulation in portal hypertension. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41 (Suppl. S3), S288–S294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrier, R.W.; Wang, W. Acute renal failure and sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.Z.; Badr, K.F. Endotoxin and renal function: Perspectives to the understanding of septic acute renal failure and toxic shock. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1999, 14, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G.S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for microRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boada-Romero, E.; Martinez, J.; Heckmann, B.L.; Green, D.R. The clearance of dead cells by efferocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, X.; Poch, E.; Grau, J.M. Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.H. Rhabdomyolosis and its pathogenesis. World J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 3, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, F.P.; Berns, J.S. Tumor lysis syndrome: New challenges and recent advances. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014, 21, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeliger, E.; Sendeski, M.; Rihal, C.S.; Persson, P.B. Contrast-induced kidney injury: Mechanisms, risk factors, and prevention. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batuman, V. The pathogenesis of acute kidney impairment in patients with multiple myeloma. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012, 19, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, F.; Stea, E.D.; Rossini, M.; Fiorentino, M.; Piancone, F.; Infante, B.; Stallone, G.; Castellano, G.; Gesualdo, L. Glomerulonephritis in AKI: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Intervention. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 582272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, J.W.; Renner, B.; Thurman, J.M. The role of the complement system in acute kidney injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, G.D.; Willis, N.S.; Cooper, T.E.; Craig, J.C. Interventions for renal vasculitis in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD003232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N.; Nester, C.M. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thadhani, R.I.; Camargo, C.A.; Xavier, R.J.; Fang, L.S.; Bazari, H. Atheroembolic renal failure after invasive procedures. Natural history based on 52 histologically proven cases. Medicine 1995, 74, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Song, H.; Tong, R.; Dong, M.; Ge, W.; Yang, H.; et al. Drug-Induced Hospital-Acquired Acute Kidney Injury in China: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Survey. Kidney Dis. 2021, 7, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A.; Rosner, M.H. Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, S.N.; Rosenberger, C.; Rosen, S. Regional alterations in renal haemodynamics and oxygenation: A role in contrast medium-induced nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20 (Suppl. S1), i6–i11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persson, P.B.; Hansell, P.; Liss, P. Pathophysiology of contrast medium-induced nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, N.; Patel, M.R. Infection-Induced Kidney Diseases. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robbins-Juarez, S.Y.; Qian, L.; King, K.L.; Stevens, J.S.; Husain, S.A.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Mohan, S. Outcomes for Patients With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Uppal, N.N.; Wanchoo, R.; Shah, H.H.; Yang, Y.; Parikh, R.; Khanin, Y.; Madireddy, V.; Larsen, C.P.; Jhaveri, K.D.; et al. COVID-19-Associated Kidney Injury: A Case Series of Kidney Biopsy Findings. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghian, T.; Kharazmi, A.B.; Ansari, A.; Omidi, F.; Kazemi, S.N.; Hajikhani, B.; Vaziri-Harami, R.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Omidi, S.; Haddadi, S.; et al. COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 705908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Bell, S.; Forni, L.; Joannidis, M.; Koyner, J.L.; Liu, K.; Cantaluppi, V. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, J.C.Q.; Caza, T.; Larsen, C.P. COVAN is the new HIVAN: The re-emergence of collapsing glomerulopathy with COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akposso, K.; Hertig, A.; Couprie, R.; Flahaut, A.; Alberti, C.; Karras, G.A.; Haymann, J.P.; Costa De Beauregard, M.A.; Lahlou, A.; Rondeau, E.; et al. Acute renal failure in patients over 80 years old: 25-years’ experience. Intensive Care Med. 2000, 26, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Canton, A.; Corradi, A.; Stanziale, R.; Maruccio, G.; Migone, L. Glomerular hemodynamics before and after release of 24-h bilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int. 1980, 17, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahr, S.; Harris, K.; Purkerson, M.L. Effects of obstruction on renal functions. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1988, 2, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Abnormality | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Prerenal | True volume depletion | Hemorrhage |
| Poor oral intake | ||
| Gastrointestinal losses (vomiting, diarrhea) | ||
| Third space losses (pancreatitis, peritonitis, burns) | ||
| Renal losses (over diuresis) | ||
| Skin or respiratory losses | ||
| Impaired cardiopulmonary functions | Congestive heart failure | |
| Pericardial tamponade | ||
| Pulmonary thromboembolism | ||
| Decreased vascular resistance | Systemic vasodilation | |
| Sepsis | ||
| Neurogenic shock | ||
| Anaphylaxis | ||
| Hepatorenal syndrome | ||
| Intrarenal hemodynamic changes | Medications (NSAID, RAS blockers, CNIs) | |
| Hypercalcemia | ||
| Intrinsic | Tubular damage | Renal ischemia |
| Nephrotoxins | ||
| Endogenous | ||
| Myoglobin, hemoglobin | ||
| Tumor lysis syndrome | ||
| Exogenous | ||
| Medications (e.g., contrast agents) | ||
| Glomerular damage | Acute glomerulonephritis | |
| Vasculitis | ||
| Malign hypertension | ||
| Thrombotic microangiopathies | ||
| Interstitial damage | Infections (Bacterial or viral) | |
| Medications (Antibiotics, NSAIDs) | ||
| Vascular damage | Renal artery/vein thrombosis | |
| Vasculitis (Polyarteritis nodosa) | ||
| Atheroembolism | ||
| Postrenal | Intrarenal obstruction | Nephrolithiasis |
| Extrarenal obstruction | Benign prostate hypertrophy | |
| Ureterolithiasis | ||
| Prostate, bladder, rectal or cervical cancer | ||
| Acute neurogenic bladder | ||
| Urethral stenosis or clotting | ||
| Retroperitoneal fibrosis | ||
| Renal papillary necrosis |
| Antibiotics | Aminoglycosides (Tobramycin, gentamycin) |
| Vancomycin | |
| β-Lactam antibiotics | |
| Fluoroquinolones | |
| Rifampin | |
| Antiviral agents | Tenofovir |
| Cidofovir | |
| Foscarnet | |
| Acyclovir | |
| Indinavir | |
| Antifungals | Amphotericin B |
| Analgesics | NSAIDs (Naproxen, ibuprofen) |
| Chemotherapeutic agents | Cisplatin |
| Ifosfamide | |
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | |
| PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors | |
| CTLA-4 inhibitors | |
| Other agents | Lithium |
| Phenytoin | |
| Proton pump inhibitors | |
| Furosemide | |
| Zoledronic acid | |
| Intravenous immunoglobulin | |
| Iodinated contrast media |
| Systemic disease | Diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis |
| ANCA-associated vasculitis | |
| Goodpasture’s syndrome | |
| Thrombotic microangiopathies (HUS/TTP) | |
| Polyarteritis nodosa | |
| Cryoglobulinemia | |
| Renal disease | Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease |
| Post-infectious glomerulonephritis | |
| Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis | |
| IgA nephropathy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turgut, F.; Awad, A.S.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010375
Turgut F, Awad AS, Abdel-Rahman EM. Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010375
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurgut, Faruk, Alaa S. Awad, and Emaad M. Abdel-Rahman. 2023. "Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010375
APA StyleTurgut, F., Awad, A. S., & Abdel-Rahman, E. M. (2023). Acute Kidney Injury: Medical Causes and Pathogenesis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010375






