Overview of Atopic Dermatitis in Different Ethnic Groups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Features
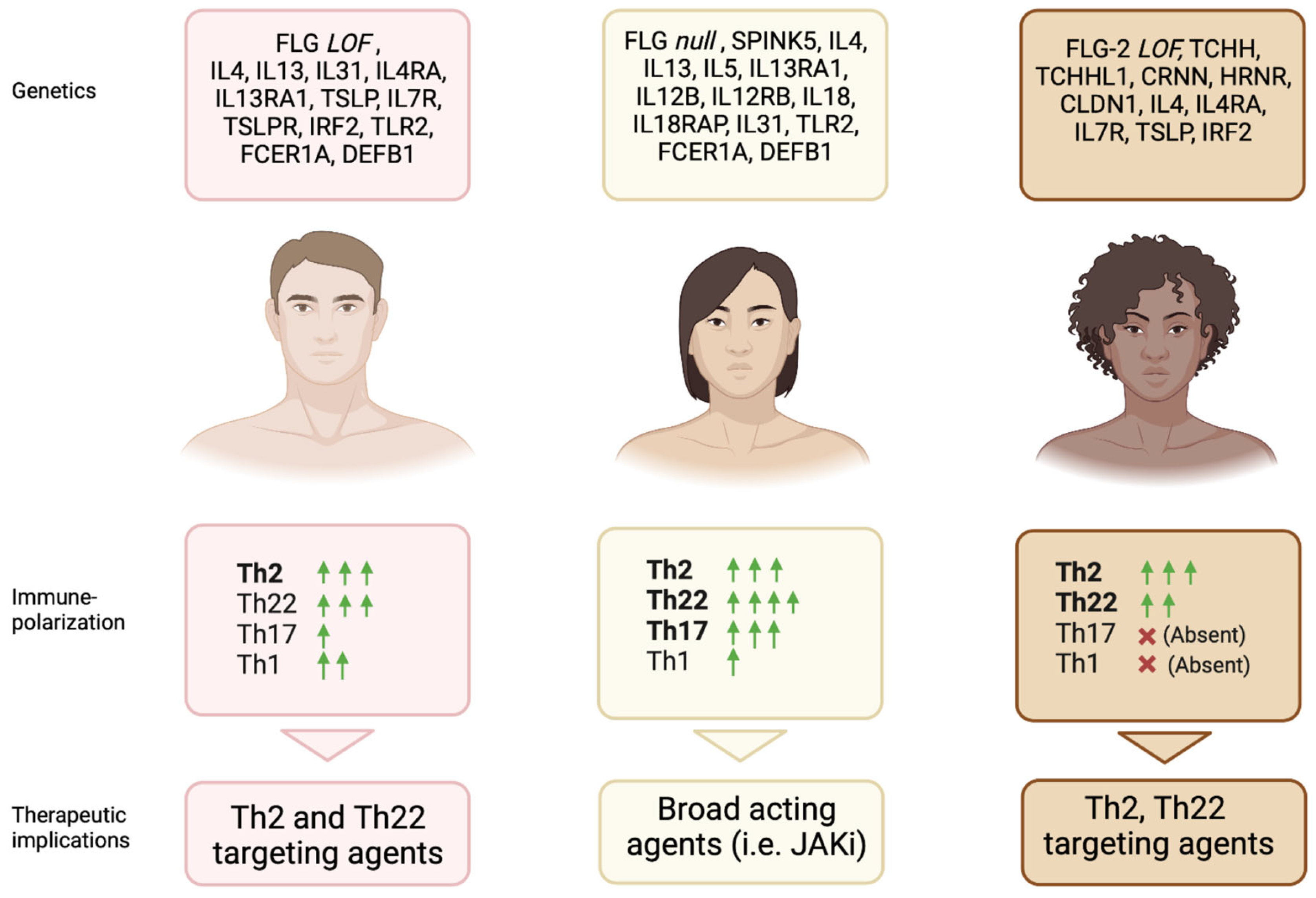
3. Genetic Variability across Ethnic Groups
4. Pathogenesis
Immune Mechanisms Involved in AD Pathogenesis
5. Therapeutic Implications in Different Ethnic Subgroups
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, H.A.; Tarmizi, A.I.; Khalid, K.A.; Gajdacs, M.; Aslam, A.; Jamshed, S. The Epidemiology and Global Burden of Atopic Dermatitis: A Narrative Review. Life 2021, 11, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Boothe, W.; Tarbox, J.A.; Tarbox, M.B. Atopic Dermatitis: Pathophysiology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1027, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, Y.; Hayano, S. Subtypes of atopic dermatitis: From phenotype to endotype. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnowicki, T.; He, H.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.M.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Racial differences in atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma. Immunol. 2019, 122, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girolomoni, G.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Aoki, V.; Kabashima, K.; Deleuran, M.; Puig, L.; Bansal, A.; Rossi, A.B. Nomenclature and clinical phenotypes of atopic dermatitis. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211002979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, M.; Joseph, M. Dermatology: How to manage atopic dermatitis in patients with skin of colour. Drugs Context 2022, 11, 2021-12-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y. Atopic dermatitis: Age and race do matter! J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1265–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noda, S.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Ungar, B.; Kim, S.J.; de Guzman Strong, C.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; Estrada, Y.D.; Nakajima, S.; Honda, T.; et al. The Asian atopic dermatitis phenotype combines features of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis with increased TH17 polarization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachiramon, V.; Tey, H.L.; Thompson, A.E.; Yosipovitch, G. Atopic dermatitis in African American children: Addressing unmet needs of a common disease. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnoruka, E.N. Current epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in south-eastern Nigeria. Int. J. Dermatol. 2004, 43, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynfield, Y.L. Prominent pruritic periumbilical papules. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2000, 17, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.B.; Jones, N.P.; Bowen, S.E. Lichenoid and other clinical presentations of atopic dermatitis in an inner city practice. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Thurston, M.; Omoto, M.; Cherill, R.; Tofte, S.J.; Graeber, M. The eczema area and severity index (EASI): Assessment of reliability in atopic dermatitis. EASI Evaluator Group. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: The SCORAD index. Consensus Report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology 1993, 186, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gashir, M.A.; Hay, R.J. Reliance on erythema scores may mask severe atopic dermatitis in black children compared with their white counterparts. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, A.F.; Sergay, A.B.; Taylor, S.C. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: A comparative practice survey. Cutis 2007, 80, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Nedoszytko, B.; Reszka, E.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Trzeciak, M.; Lange, M.; Jarczak, J.; Niedoszytko, M.; Jablonska, E.; Romantowski, J.; Strapagiel, D.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Aspects of Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.C. An update on the genetics of atopic dermatitis: Scratching the surface in 2009. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 16–29.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R.A.; Barnes, K.C. Genetics of allergic diseases. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paternoster, L.; Standl, M.; Waage, J.; Baurecht, H.; Hotze, M.; Strachan, D.P.; Curtin, J.A.; Bonnelykke, K.; Tian, C.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association study of 21,000 cases and 95,000 controls identifies new risk loci for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Baurecht, H.; Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Rodriguez, E.; Matanovic, A.; Marenholz, I.; Hubner, N.; Schaarschmidt, H.; Novak, N.; Michel, S.; et al. High-density genotyping study identifies four new susceptibility loci for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. The Genetics and Epigenetics of Atopic Dermatitis-Filaggrin and Other Polymorphisms. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 51, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, T.; Takahashi, A.; Kubo, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Tomita, K.; Sakashita, M.; Yamada, T.; Fujieda, S.; Tanaka, S.; Doi, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight new susceptibility loci for atopic dermatitis in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.D.; Xiao, F.L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.M.; Tang, H.Y.; Tang, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Schaarschmidt, H.; Zuo, X.B.; Foelster-Holst, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies two new susceptibility loci for atopic dermatitis in the Chinese Han population. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Baurecht, H.; Herberich, E.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Brown, S.J.; Cordell, H.J.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Meta-analysis of filaggrin polymorphisms in eczema and asthma: Robust risk factors in atopic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1361–1370.e1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrelo, A. Atopic dermatitis in different skin types. What is to know? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28 (Suppl. 3), 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Jekarl, D.W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.M. Novel FLG null mutations in Korean patients with atopic dermatitis and comparison of the mutational spectra in Asian populations. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.J.; McLean, W.H. One remarkable molecule: Filaggrin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drislane, C.; Irvine, A.D. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.H.; Leung, D.Y. Filaggrin mutations associated with skin and allergic diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margolis, D.J.; Apter, A.J.; Gupta, J.; Hoffstad, O.; Papadopoulos, M.; Campbell, L.E.; Sandilands, A.; McLean, W.H.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Mitra, N. The persistence of atopic dermatitis and filaggrin (FLG) mutations in a US longitudinal cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, F.J.; Irvine, A.D.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Evans, A.T.; Goudie, D.R.; Lewis-Jones, S.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding filaggrin cause ichthyosis vulgaris. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawer-Esmail, F.; Jakasa, I.; Todd, G.; Wen, Y.; Brown, S.J.; Kroboth, K.; Campbell, L.E.; O’Regan, G.M.; McLean, W.H.; Irvine, A.D.; et al. South African amaXhosa patients with atopic dermatitis have decreased levels of filaggrin breakdown products but no loss-of-function mutations in filaggrin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 280–282.e281-282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margolis, D.J.; Gupta, J.; Apter, A.J.; Hoffstad, O.; Papadopoulos, M.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Mitra, N. Exome sequencing of filaggrin and related genes in African-American children with atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2272–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, K.; Asad, S.; Taylan, F.; Wahlgren, C.F.; Bilcha, K.D.; Nordenskjold, M.; Winge, M.C.G.; Bradley, M. Intragenic Copy Number Variation in the Filaggrin Gene in Ethiopian Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2017, 34, e140–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcari, I.; Becker, L.; Stein, S.L.; Smith, M.S.; Paller, A.S. Filaggrin gene mutations in African Americans with both ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylan, F.; Nilsson, D.; Asad, S.; Lieden, A.; Wahlgren, C.F.; Winge, M.C.; Bilcha, K.D.; Nordenskjold, M.; Bradley, M. Whole-exome sequencing of Ethiopian patients with ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 507–509.e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.; Toulza, E.; Hsu, C.Y.; Pellerin, L.; Balica, S.; Mazereeuw-Hautier, J.; Paul, C.; Serre, G.; Jonca, N.; Simon, M. Update on the epidermal differentiation complex. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Hansmann, B.; Meyer-Hoffert, U.; Glaser, R.; Schroder, J.M. Molecular identification and expression analysis of filaggrin-2, a member of the S100 fused-type protein family. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Margolis, D.J.; Gupta, J.; Apter, A.J.; Ganguly, T.; Hoffstad, O.; Papadopoulos, M.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Mitra, N. Filaggrin-2 variation is associated with more persistent atopic dermatitis in African American subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pellerin, L.; Henry, J.; Hsu, C.Y.; Balica, S.; Jean-Decoster, C.; Mechin, M.C.; Hansmann, B.; Rodriguez, E.; Weindinger, S.; Schmitt, A.M.; et al. Defects of filaggrin-like proteins in both lesional and nonlesional atopic skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenholz, I.; Rivera, V.A.; Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Bauerfeind, A.; Lee-Kirsch, M.A.; Ciechanowicz, A.; Kurek, M.; Piskackova, T.; Macek, M.; Lee, Y.A. Association screening in the Epidermal Differentiation Complex (EDC) identifies an SPRR3 repeat number variant as a risk factor for eczema. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asad, S.; Winge, M.C.; Wahlgren, C.F.; Bilcha, K.D.; Nordenskjold, M.; Taylan, F.; Bradley, M. The tight junction gene Claudin-1 is associated with atopic dermatitis among Ethiopians. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1939–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Fukai, K.; Oiso, N.; Hosomi, N.; Murakami, T.; Ishii, M. Association of SPINK5 gene polymorphisms with atopic dermatitis in the Japanese population. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 148, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, Y.; Noguchi, E.; Shibasaki, M.; Kamioka, M.; Ichikawa, E.; Ichikawa, K.; Umebayashi, Y.; Otsuka, F.; Arinami, T. Association between polymorphisms in the SPINK5 gene and atopic dermatitis in the Japanese. Genes Immun. 2003, 4, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, C.C.; Tu, H.P.; Wu, C.S.; Ko, Y.C.; Yu, H.S.; Lu, Y.W.; Li, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, G.S. Distinct SPINK5 and IL-31 polymorphisms are associated with atopic eczema and non-atopic hand dermatitis in Taiwanese nursing population. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.P.; Di, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Lv, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wei, H.; Chen, H.D.; Gao, X.H. Association of SPINK5 gene polymorphisms with atopic dermatitis in Northeast China. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D. Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2 cytokines through STAT-6. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolowska-Wojdylo, M.; Glen, J.; Zablotna, M.; Rebala, K.; Sikorska, M.; Florek, A.; Trzeciak, M.; Baranska-Rybak, W.; Malek, M.; Nedoszytko, B. Association of distinct IL-31 polymorphisms with pruritus and severity of atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Cao, X.L.; Wan, Y.J.; Meng, J.; Guo, L.H. IL-4 Gene Polymorphism May Contribute to an Increased Risk of Atopic Dermatitis in Children. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 1021942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oiso, N.; Fukai, K.; Ishii, M. Interleukin 4 receptor alpha chain polymorphism Gln551Arg is associated with adult atopic dermatitis in Japan. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Y.M.; Shalaby, S.M.; Nassar, A.; Alzahrani, S.S.; Alharbi, A.S.; Nouh, M. Association between genes encoding components of the IL-4/IL-4 receptor pathway and dermatitis in children. Gene 2014, 545, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunemi, Y.; Saeki, H.; Nakamura, K.; Sekiya, T.; Hirai, K.; Kakinuma, T.; Fujita, H.; Asano, N.; Tanida, Y.; Wakugawa, M.; et al. Interleukin-13 gene polymorphism G4257A is associated with atopic dermatitis in Japanese patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 30, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Noguchi, E.; Arinami, T.; Yamakawa-Kobayashi, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Otsuka, F.; Hamaguchi, H. Linkage and association of an interleukin 4 gene polymorphism with atopic dermatitis in Japanese families. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 35, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Yu, C.X.; Fang, L.; Zheng, X.D.; Yin, X.Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Tang, X.F.; Zhou, F.S.; Zhang, X.J.; et al. Association analyses identify two susceptibility loci 5q31 and 5q22.1 for atopic dermatitis in Chinese Han population. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 35, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggana, M.; Walker, K.; Reilly, A.A.; Conroy, J.M.; Duva, S.; Walsh, A.C. Population-based studies reveal differences in the allelic frequencies of two functionally significant human interleukin-4 receptor polymorphisms in several ethnic groups. Genet. Med. 1999, 1, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Wilkie, H.; Das, M.; Timilshina, M.; Bainter, W.; Woods, B.; Daya, M.; Boorgula, M.P.; Mathias, R.A.; Lai, P.; et al. The IL-4Ralpha Q576R polymorphism is associated with increased severity of atopic dermatitis and exaggerates allergic skin inflammation in mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.S.; Rafaels, N.M.; Mu, D.; Hand, T.; Murray, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; Hata, T.; Schneider, L.; Hanifin, J.M.; Gallo, R.L.; et al. Genetic variants in thymic stromal lymphopoietin are associated with atopic dermatitis and eczema herpeticum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1403–1407.e1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esaki, H.; Ewald, D.A.; Ungar, B.; Rozenblit, M.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Estrada, Y.D.; Peng, X.; Mitsui, H.; Litman, T.; et al. Identification of novel immune and barrier genes in atopic dermatitis by means of laser capture microdissection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.L.; Yen, J.J.; Hsu, L.C.; Kuo, N.W.; Su, M.W.; Yang, M.F.; Hsiao, Y.P.; Wang, I.J.; Liu, F.T. Association of STAT6 genetic variants with childhood atopic dermatitis in Taiwanese population. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.S.; Leung, D.Y.; Rafaels, N.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Hand, T.; Gao, L.; Hata, T.R.; Schneider, L.C.; Hanifin, J.M.; Beaty, T.H.; et al. Genetic variants in interferon regulatory factor 2 (IRF2) are associated with atopic dermatitis and eczema herpeticum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Margolis, D.J.; Kim, B.; Apter, A.J.; Gupta, J.; Hoffstad, O.; Papadopoulos, M.; Mitra, N. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin variation, filaggrin loss of function, and the persistence of atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potaczek, D.P.; Nastalek, M.; Okumura, K.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Undas, A.; Nishiyama, C. An association of TLR2-16934A >T polymorphism and severity/phenotype of atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, Y.; Potaczek, D.P.; Kanada, S.; Takagi, A.; Shimokawa, N.; Ito, T.; Mitsuishi, K.; Okubo, Y.; Tajima, M.; Hobo, A.; et al. FcepsilonRIalpha gene (FCER1A) promoter polymorphisms and total serum IgE levels in Japanese atopic dermatitis patients. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2010, 37, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Montes de Oca, E.; Garcia-Vargas, A.; Lozano-Inocencio, R.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P.; Sandoval-Ramirez, L.; Davalos-Rodriguez, N.O.; Figuera, L.E. Association of beta-defensin 1 single nucleotide polymorphisms with atopic dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 142, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, J.E.; Namkung, J.H.; Kim, P.S.; Kim, S.; Shin, E.S.; Cho, E.Y.; Yang, J.M. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the haplotype in the DEFB1 gene are associated with atopic dermatitis in a Korean population. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 54, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segat, L.; Guimaraes, R.L.; Brandao, L.A.; Rocha, C.R.; Zanin, V.; Trevisiol, C.; de Lima Filho, J.L.; Crovella, S. Beta defensin-1 gene (DEFB1) polymorphisms are not associated with atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents from northeast Brazil (Recife, Pernambuco). Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, E.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Shin, E.S.; Cho, E.Y.; Yang, J.M. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the IL-12 (IL-12A and B) and IL-12 receptor (IL-12Rbeta1 and beta2) genes and gene-gene interactions with atopic dermatitis in Koreans. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 57, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Kong, H.H.; Seed, P.; Naik, S.; Scharschmidt, T.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Luger, T.; Irvine, A.D. The microbiome in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyden, J.J.; Marples, R.R.; Kligman, A.M. Staphylococcus aureus in the lesions of atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1974, 90, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, M.; Balica, S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Jean-Decoster, C.; Lauze, C.; Redoules, D.; Viode, C.; Schmitt, A.M.; Serre, G.; Simon, M.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus density on lesional and nonlesional skin is strongly associated with disease severity in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1272–1274.e1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, H.H.; Oh, J.; Deming, C.; Conlan, S.; Grice, E.A.; Beatson, M.A.; Nomicos, E.; Polley, E.C.; Komarow, H.D.; Program, N.C.S.; et al. Temporal shifts in the skin microbiome associated with disease flares and treatment in children with atopic dermatitis. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meylan, P.; Lang, C.; Mermoud, S.; Johannsen, A.; Norrenberg, S.; Hohl, D.; Vial, Y.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G.; Kypriotou, M.; et al. Skin Colonization by Staphylococcus aureus Precedes the Clinical Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis in Infancy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merriman, J.A.; Mueller, E.A.; Cahill, M.P.; Beck, L.A.; Paller, A.S.; Hanifin, J.M.; Ong, P.Y.; Schneider, L.; Babineau, D.C.; David, G.; et al. Temporal and Racial Differences Associated with Atopic Dermatitis Staphylococcusaureus and Encoded Virulence Factors. mSphere 2016, 1, e00295-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Chana, S.M.; Hawes, E.; Hendricks, P.S.; Cropsey, K.L.; Gaggar, A.; Scarinci, I.C. Examining Racial/Ethnic and Income Disparities on Tobacco Product Use Among US Adults Within Wave 5 of the PATH Study. J. Addict. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, J.; Scragg, R. Factors associated with self-reported sun exposure in a multi-ethnic community sample from New Zealand. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 221, 106131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerson, T.A.; Li, Q.; Sreeskandarajan, S.; Budunova, I.V.; He, Z.; Kang, J.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Patrick, M.T.; Tsoi, L.C. Roles Played by Stress-Induced Pathways in Driving Ethnic Heterogeneity for Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 845655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, M.E.; Wagner, J.; Tang, H.; Baker, D.C.; Chin, M.H. Self-reported racial discrimination in health care and diabetes outcomes. Med. Care 2011, 49, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verzeaux, L.; Vyumvuhore, R.; Boudier, D.; Le Guillou, M.; Bordes, S.; Essendoubi, M.; Manfait, M.; Closs, B. Atopic skin: In vivo Raman identification of global molecular signature, a comparative study with healthy skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulcano, M.; Albanesi, C.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Bagnati, R.; D’Amico, G.; Struyf, S.; Transidico, P.; Bonecchi, R.; Del Prete, A.; Allavena, P.; et al. Dendritic cells as a major source of macrophage-derived chemokine/CCL22 in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoue, A.; Kabashima, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Mori, T.; Tokura, Y. Induction of eosinophil- and Th2-attracting epidermal chemokines and cutaneous late-phase reaction in tape-stripped skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 18, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumelis, V.; Reche, P.A.; Kanzler, H.; Yuan, W.; Edward, G.; Homey, B.; Gilliet, M.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Lauerma, A.; et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Duramad, O.; Hori, T.; Delespesse, G.J.; Watanabe, N.; Qin, F.X.; Yao, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.J. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salimi, M.; Barlow, J.L.; Saunders, S.P.; Xue, L.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.C.; Johnson, D.; Scanlon, S.T.; McKenzie, A.N.; et al. A role for IL-25 and IL-33-driven type-2 innate lymphoid cells in atopic dermatitis. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-Yen Yong, A.; Tay, Y.K. Atopic Dermatitis: Racial and Ethnic Differences. Dermatol. Clin. 2017, 35, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Coelho, S.G.; Ebsen, D.; Smuda, C.; Mahns, A.; Miller, S.A.; Beer, J.Z.; Kolbe, L.; Hearing, V.J. Epidermal gene expression and ethnic pigmentation variations among individuals of Asian, European and African ancestry. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, K. Atopic dermatitis endotypes: Knowledge for personalized medicine. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 22, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.C.; Sanyal, R.D.; Pavel, A.B.; Glickman, J.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Cho, Y.T.; Tsai, T.F.; Wen, H.C.; Peng, X.; et al. Atopic dermatitis in Chinese patients shows T(H)2/T(H)17 skewing with psoriasiform features. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.C.; Czarnowicki, T.; Noda, S.; Malik, K.; Pavel, A.B.; Nakajima, S.; Honda, T.; Shin, J.U.; Lee, H.; Chou, M.; et al. Serum from Asian patients with atopic dermatitis is characterized by T(H)2/T(H)22 activation, which is highly correlated with nonlesional skin measures. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 324–328.e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanyal, R.D.; Pavel, A.B.; Glickman, J.; Chan, T.C.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, N.; Cueto, I.; Peng, X.; Estrada, Y.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; et al. Atopic dermatitis in African American patients is T(H)2/T(H)22-skewed with T(H)1/T(H)17 attenuation. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 99–110.e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Ahluwalia, J.; Waldman, A.; Borok, J.; Udkoff, J.; Boguniewicz, M. Current guidelines for the evaluation and management of atopic dermatitis: A comparison of the Joint Task Force Practice Parameter and American Academy of Dermatology guidelines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S49–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollenberg, A.; Kinberger, M.; Arents, B.; Aszodi, N.; Avila Valle, G.; Barbarot, S.; Bieber, T.; Brough, H.A.; Calzavara Pinton, P.; Christen-Zach, S.; et al. European guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on atopic eczema-part II: Non-systemic treatments and treatment recommendations for special AE patient populations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1904–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Kinberger, M.; Arents, B.; Aszodi, N.; Avila Valle, G.; Barbarot, S.; Bieber, T.; Brough, H.A.; Calzavara Pinton, P.; Christen-Zach, S.; et al. European guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on atopic eczema: Part I-systemic therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1409–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Gelfand, J.M.; Margolis, D.J.; Boguniewicz, M.; Fonacier, L.; Grayson, M.H.; Simpson, E.L.; Ong, P.Y.; Chiesa Fuxench, Z.C. Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: A population-based cross-sectional study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Lucky, A.W.; Langley, R.G.; Lynde, C.; Kaufmann, R.; Todd, G.; Lindsley, L.; Barbier, N.; Felser, J.M. Use of pimecrolimus cream 1% (Elidel) in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants and children: The effects of ethnic origin and baseline disease severity on treatment outcome. Int. J. Dermatol. 2005, 44, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kono, T. Overview of efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment in patients with atopic dermatitis in Asia and other areas. Int. J. Dermatol. 2011, 50, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, Z.R.; Koh, M.J.; Chong, W.S. Is phototherapy useful in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in asian children? A 5-year report from singapore. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Z.U.; Hamzavi, I.H. Role of phototherapy in patients with skin of color. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg 2011, 30, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Z.U.; Hamzavi, I.H. Photomedicine and phototherapy considerations for patients with skin of color. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobe, H.T.; Cayce, R.; Nguyen, J. UVA1 phototherapy is effective in darker skin: A review of 101 patients of Fitzpatrick skin types I-V. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, B.M.A. Atopic Dermatitis in Patients with Skin of Color. Dermatologist. 2019. Available online: https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/thederm/nea-approved-features/atopic-dermatitis-patients-skin-color (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Seegraber, M.; Srour, J.; Walter, A.; Knop, M.; Wollenberg, A. Dupilumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaci, D.; Hamilton, J.D.; Graham, N.M.; Bieber, T.; Rocklin, R.; Ming, J.E.; Ren, H.; Kao, R.; Simpson, E.; et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simpson, E.L.; Bieber, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Beck, L.A.; Blauvelt, A.; Cork, M.J.; Silverberg, J.I.; Deleuran, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Lacour, J.P.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Dupilumab versus Placebo in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Gooderham, M.; Cather, J.C.; Weisman, J.; Pariser, D.; Simpson, E.L.; Papp, K.A.; Hong, H.C.; Rubel, D.; et al. Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids (LIBERTY AD CHRONOS): A 1-year, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2287–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, A.F.; Rendon, M.; Silverberg, J.I.; Pariser, D.M.; Lockshin, B.; Griffiths, C.E.; Weisman, J.; Wollenberg, A.; Chen, Z.; Davis, J.D.; et al. Efficacy of Dupilumab in Different Racial Subgroups of Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis in Three Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trials. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, 804–813. [Google Scholar]
- EMA Approval of Tralokinumab (Adtralza) for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Published June 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/adtralza-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- EMA Approval of Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Published May 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop/chmp-post-authorisation-summary-opinion-rinvoq-x-12-g_en.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- EMA Approval of Abrocitinib (Cibinqo) for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Published December 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/cibinqo-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Wollenberg, A.; Blauvelt, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Worm, M.; Lynde, C.; Lacour, J.P.; Spelman, L.; Katoh, N.; Saeki, H.; Poulin, Y.; et al. Tralokinumab for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from two 52-week, randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase III trials (ECZTRA 1 and ECZTRA 2). Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Toth, D.; Bieber, T.; Alexis, A.F.; Elewski, B.E.; Pink, A.E.; Hijnen, D.; Jensen, T.N.; Bang, B.; Olsen, C.K.; et al. Tralokinumab plus topical corticosteroids for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from the double-blind, randomized, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase III ECZTRA 3 trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Gooderham, M.; Bhatia, N.; Langley, R.G.; Schneider, S.; Zoidis, J.; Kurbasic, A.; Armstrong, A.; Silverberg, J.I. Tralokinumab Efficacy and Safety, with or without Topical Corticosteroids, in North American Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Subanalysis of Phase 3 Trials ECZTRA 1, 2, and 3. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 2499–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.H. Breaking the (un)sound barrier: Filaggrin is a major gene for atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thyssen, J.P.; Thuesen, B.; Huth, C.; Standl, M.; Carson, C.G.; Heinrich, J.; Kramer, U.; Kratzsch, J.; Berg, N.D.; Menne, T.; et al. Skin barrier abnormality caused by filaggrin (FLG) mutations is associated with increased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1204–1207.e1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, J.; Gupta, J.; Zhu, Y.; Berna, R.; Chiesa Fuxench, Z.C.; Margolis, D.J. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march: Considering racial and ethnic diversity in atopic disease progression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1590–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, J.M.; Kroner, J.W.; Baatyrbek Kyzy, A.; Gonzales, A.; He, H.; Stevens, M.; Grashel, B.; Spagna, D.; Paul, S.; Patel, R.; et al. Longitudinal atopic dermatitis endotypes: An atopic march paradigm that includes Black children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1702–1710.e1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, B.; Pavel, A.B.; Li, R.; Kimmel, G.; Nia, J.; Hashim, P.; Kim, H.J.; Chima, M.; Vekaria, A.S.; Estrada, Y.; et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.D.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Dhingra, N.; Cardinale, I.; Li, X.; Kostic, A.; Ming, J.E.; Radin, A.R.; Krueger, J.G.; Graham, N.; et al. Dupilumab improves the molecular signature in skin of patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howell, M.D.; Fitzsimons, C.; Smith, P.A. JAK/STAT inhibitors and other small molecule cytokine antagonists for the treatment of allergic disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrow, A.; Xia, F.D.; Joyce, C.; Mostaghimi, A. Diversity in Dermatology Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, T.; Silverberg, J.I. Efficacy of systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis in racial and ethnic minorities in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 1232–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirano, S.A.; Murray, S.B.; Harvey, V.M. Reporting, representation, and subgroup analysis of race and ethnicity in published clinical trials of atopic dermatitis in the United States between 2000 and 2009. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiricozzi, A.; Maurelli, M.; Calabrese, L.; Peris, K.; Girolomoni, G. Overview of Atopic Dermatitis in Different Ethnic Groups. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072701
Chiricozzi A, Maurelli M, Calabrese L, Peris K, Girolomoni G. Overview of Atopic Dermatitis in Different Ethnic Groups. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072701
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiricozzi, Andrea, Martina Maurelli, Laura Calabrese, Ketty Peris, and Giampiero Girolomoni. 2023. "Overview of Atopic Dermatitis in Different Ethnic Groups" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072701
APA StyleChiricozzi, A., Maurelli, M., Calabrese, L., Peris, K., & Girolomoni, G. (2023). Overview of Atopic Dermatitis in Different Ethnic Groups. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072701






