MicroRNA In Lung Cancer: Novel Biomarkers and Potential Tools for Treatment
Abstract
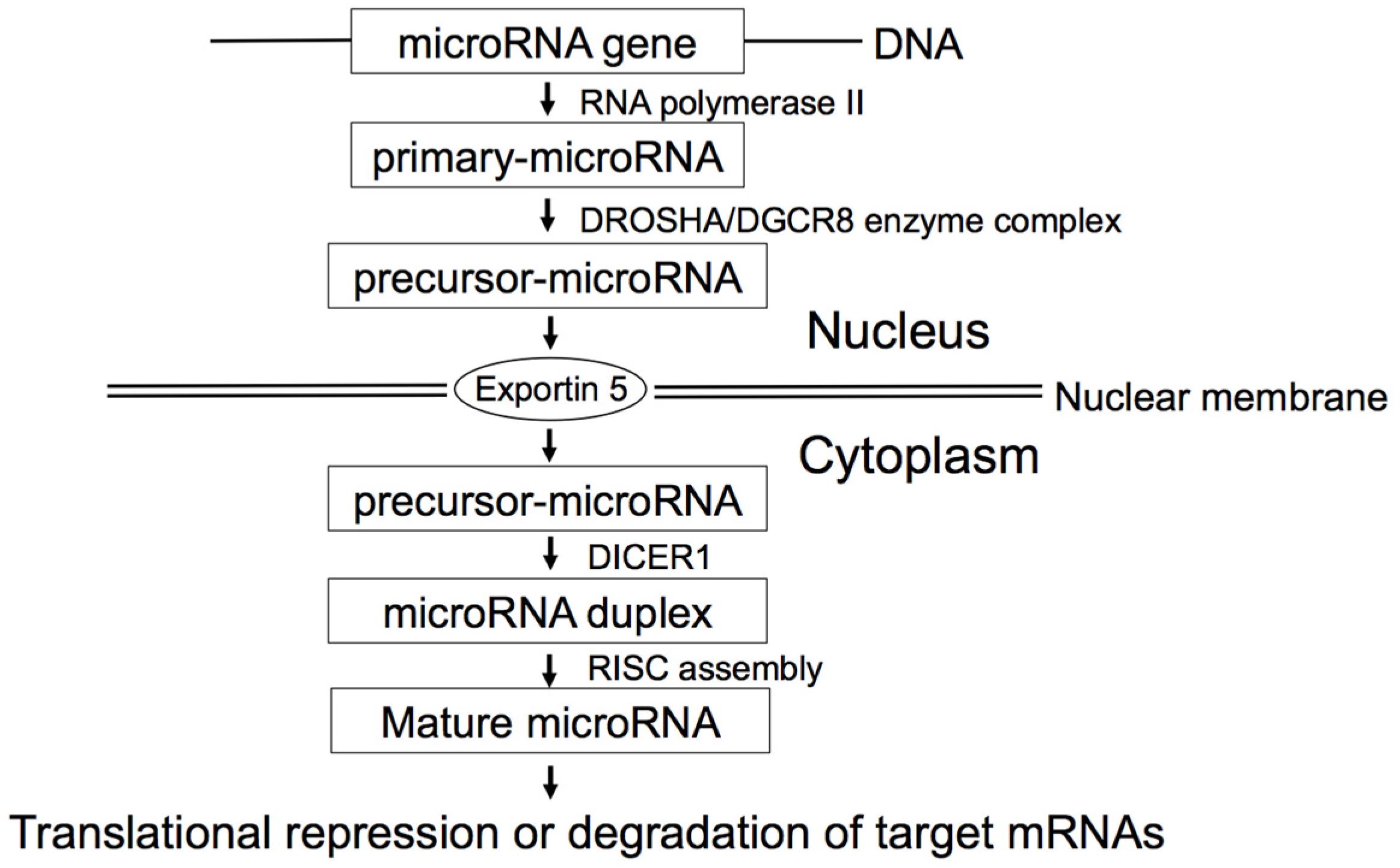
:1. Introduction
2. MicroRNA Biogenesis
3. MicroRNAs as Tumor Suppressor Genes and Oncogenes
3.1. Tumor Suppressor microRNAs
3.1.1. Let-7 Family
3.1.2. miR-34 Family
3.1.3. miR-200 Family
3.2. Oncogenic microRNAs
3.2.1. miR-21
3.2.2. miR-17-92 Cluster
3.2.3. miR-221/222
4. Diagnostic microRNAs
4.1. Diagnostic microRNAs in Tissues
4.2. Diagnostic microRNAs in Body Fluids
5. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Histological Classification
6. Prognostic microRNAs
6.1. Investigation for Prognostic microRNAs
6.2. Integrated Prognostic Classifier for Stage I Lung Cancer
6.3. Let-7, DICER1, and Survival of Lung Cancer
7. MicroRNA Associated with Driver Mutations and Therapeutic microRNAs
8. Prospects from Basic to Clinical Application of microRNAs
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.; Middleton, J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Garofalo, M. MicroRNAs in lung cancer. World J. Methodol. 2014, 4, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishikawa, T.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Takata, A.; Koike, K. Circulating RNAs as new biomarkers for detecting pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8527–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollis, M.; Nair, K.; Vyas, A.; Chaturvedi, L.S.; Gambhir, S.; Vyas, D. MicroRNAs potential utility in colon cancer: Early detection, prognosis, and chemosensitivity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8284–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, S.; Meiri, E.; Yogev, Y.; Benjamin, S.; Lebanony, D.; Yerushalmi, N.; Benjamin, H.; Kushnir, M.; Cholakh, H.; Melamed, N.; et al. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Challenges in circulating tumour cell research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, K.A.; Kim, J.; Gwak, H.; Jung, H.I. Isolation and enrichment of circulating biomarkers for cancer screening, detection, and diagnostics. Analyst 2016, 141, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.F.; Otoc, N.; Sethi, J.K.; Gupta, A.; Antes, T.J. Integrated systems for exosome investigation. Methods 2015, 87, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, M.G.; Sol, N.; Kooi, I.; Tannous, J.; Westerman, B.A.; Rustenburg, F.; Schellen, P.; Verschueren, H.; Post, E.; Koster, J.; et al. RNA-Seq of Tumor-Educated Platelets Enables Blood-Based Pan-Cancer, Multiclass, and Molecular Pathway Cancer Diagnostics. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, J.F.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P. MicroRNA as tools and therapeutics in lung cancer. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.; Martindale, M.Q.; Kuroda, M.I.; Maller, B.; Hayward, D.C.; Ball, E.E.; Degnan, B.; Muller, P.; et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000, 408, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.D.; Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Stefani, G.; Byrom, M.; Kelnar, K.; Ovcharenko, D.; Wilson, M.; Wang, X.; Shelton, J.; Shingara, J.; et al. The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7713–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumaru, S.; Suzuki, M.; Yamada, H.; Nagino, M.; Takahashi, T. let-7 regulates Dicer expression and constitutes a negative feedback loop. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2073–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; He, X.; Lim, L.P.; de Stanchina, E.; Xuan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Magnus, J.; Ridzon, D.; et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 2007, 447, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommer, G.T.; Gerin, I.; Feng, Y.; Kaczorowski, A.J.; Kuick, R.; Love, R.E.; Zhai, Y.; Giordano, T.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Moore, B.B.; et al. p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasinski, A.L.; Slack, F.J. MiRNA-34 prevents cancer initiation and progression in a therapeutically resistant K-ras and p53-induced mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5576–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Jeon, Y.J.; Nuovo, G.J.; Middleton, J.; Secchiero, P.; Joshi, P.; Alder, H.; Nazaryan, N.; di Leva, G.; Romano, G.; et al. miR-34a/c-Dependent PDGFR-alpha/beta Downregulation Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceppi, P.; Mudduluru, G.; Kumarswamy, R.; Rapa, I.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Papotti, M.; Allgayer, H. Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyama, Y.; Sato, M.; Horio, M.; Hase, T.; Yoshida, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Nakashima, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Sekido, Y.; Gazdar, A.F.; et al. Knockdown of ZEB1, a master epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) gene, suppresses anchorage-independent cell growth of lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 296, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.G.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, K.; Yang, G.H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, I.; Lee, A.; James, V.; Hall, R.I.; Lund, J.N.; Tufarelli, C.; Lobo, D.N.; Larvin, M. Knockdown of microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2011, 15, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Wu, F.; Nie, D.; Sheng, S.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Nishikawa, E.; Yanagisawa, K.; Hayashita, Y.; Ebi, H.; Yamada, H.; Suzuki, M.; Nagino, M.; Nimura, Y.; et al. Apoptosis induction by antisense oligonucleotides against miR-17–5p and miR-20a in lung cancers overexpressing miR-17-92. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6099–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, H.; Takahashi, T. let-7 and miR-17-92: Small-sized major players in lung cancer development. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Quintavalle, C.; di Leva, G.; Zanca, C.; Romano, G.; Taccioli, C.; Liu, C.G.; Croce, C.M.; Condorelli, G. MicroRNA signatures of TRAIL resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3845–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; di Leva, G.; Romano, G.; Nuovo, G.; Suh, S.S.; Ngankeu, A.; Taccioli, C.; Pichiorri, F.; Alder, H.; Secchiero, P.; et al. miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vosa, U.; Vooder, T.; Kolde, R.; Vilo, J.; Metspalu, A.; Annilo, T. Meta-analysis of microRNA expression in lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2884–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Todd, N.W.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, M.; Fang, H.; Peng, H.; Alattar, M.; Deepak, J.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Altered miRNA expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Todd, N.W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Lingxiao, X.; Mei, Y.; Guarnera, M.; Liao, J.; Chou, A.; Lu, C.L.; et al. Plasma microRNAs as potential biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, Z.; Todd, N.W.; Zhang, H.; Liao, J.; Yu, L.; Guarnera, M.A.; Li, R.; Cai, L.; Zhan, M.; et al. Diagnosis of lung cancer in individuals with solitary pulmonary nodules by plasma microRNA biomarkers. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Todd, N.W.; Xing, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Fang, H.; Zhang, J.; Katz, R.L.; Jiang, F. Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2870–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebanony, D.; Benjamin, H.; Gilad, S.; Ezagouri, M.; Dov, A.; Ashkenazi, K.; Gefen, N.; Izraeli, S.; Rechavi, G.; Pass, H.; et al. Diagnostic assay based on hsa-miR-205 expression distinguishes squamous from nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.A.; Benjamin, H.; Cholakh, H.; Chajut, A.; Clark, D.P.; Westra, W.H. Accurate classification of non-small cell lung carcinoma using a novel microRNA-based approach. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, J.; Soejima, K.; Yoda, S.; Naoki, K.; Nakayama, S.; Satomi, R.; Terai, H.; Ikemura, S.; Sato, T.; Yasuda, H.; et al. Identification of microRNAs differentially expressed between lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, E.; Osada, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Arima, C.; Tomida, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Taguchi, A.; Shimada, Y.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yatabe, Y.; et al. miR-375 is activated by ASH1 and inhibits YAP1 in a lineage-dependent manner in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6165–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamizawa, J.; Konishi, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Osada, H.; Endoh, H.; Harano, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Nagino, M.; Nimura, Y.; et al. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3753–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Nomura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Hiramatsu, M.; Satoh, Y.; Okumura, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Ishikawa, Y. let-7 microRNA expression is reduced in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, a non-invasive carcinoma, and is not correlated with prognosis. Lung Cancer 2007, 58, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Singh, S.; Cheng, C.L.; Yu, C.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Nomura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Hiramatsu, M.; Okui, M.; Satoh, Y.; Okumura, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Tsuchiya, E.; et al. Up-regulation of PTEN at the transcriptional level is an adverse prognostic factor in female lung adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer 2007, 57, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, A.I.; Arai, E.; Mathe, E.A.; Okayama, H.; Schetter, A.J.; Brown, D.; Petersen, D.; Bowman, E.D.; Noro, R.; Welsh, J.A.; et al. An Integrated Prognostic Classifier for Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on mRNA, microRNA, and DNA Methylation Biomarkers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, T.; Jin, G.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.; et al. Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; Roth, J.A.; Hildebrandt, M.A.; Lippman, S.M.; Ye, Y.; Minna, J.D.; Wu, X. Pathway-based serum microRNA profiling and survival in patients with advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4801–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Osada, H.; Tomida, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yatabe, Y.; Takamizawa, J.; Miyoshi, S.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Reduced expression of Dicer associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, J.; Brennan, C.; Shih, J.Y.; Riely, G.; Viale, A.; Wang, L.; Chitale, D.; Motoi, N.; Szoke, J.; Broderick, S.; et al. MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20932–20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, K.; Soda, M.; Togashi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Sakata, S.; Hatano, S.; Asaka, R.; Hamanaka, W.; Ninomiya, H.; Uehara, H.; et al. RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Totoki, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Hiramoto, M.; Nammo, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Tsuta, K.; Furuta, K.; Shimada, Y.; et al. KIF5B-RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Capelletti, M.; Le, A.T.; Kako, S.; Butaney, M.; Ercan, D.; Mahale, S.; Davies, K.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Pilling, A.B.; et al. Oncogenic and drug-sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Plenker, D.; Osada, H.; Sun, R.; Menon, R.; Leenders, F.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Peifer, M.; Bos, M.; Dassler, J.; et al. CD74-NRG1 fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaoku, T.; Tsuta, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Enari, M.; Furuta, K.; Shimada, Y.; Ogiwara, H.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Druggable oncogene fusions in invasive mucinous lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3087–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, H.; Hiramatsu, M.; Inamura, K.; Nomura, K.; Okui, M.; Miyoshi, T.; Okumura, S.; Satoh, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Nishio, M.; et al. Correlation between morphology and EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinomas significance of the micropapillary pattern and the hobnail cell type. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Matsubara, O. Is the epidermal growth factor receptor status in lung cancers reflected in clinicopathologic features? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Togashi, Y.; Nomura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Okui, M.; Satoh, Y.; Okumura, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Soda, M.; et al. EML4-ALK fusion is linked to histological characteristics in a subset of lung cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Ninomiya, H.; Motoi, N.; Mun, M.Y.; Sakao, Y.; Okumura, S.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. EML4-ALK lung cancers are characterized by rare other mutations, a TTF-1 cell lineage, an acinar histology, and young onset. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Costa, D.B.; Heist, R.S.; Solomon, B.; Stubbs, H.; Admane, S.; McDermott, U.; et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4247–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Ye, T.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. ALK, ROS1 and RET fusions in 1139 lung adenocarcinomas: A comprehensive study of common and fusion pattern-specific clinicopathologic, histologic and cytologic features. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seike, M.; Goto, A.; Okano, T.; Bowman, E.D.; Schetter, A.J.; Horikawa, I.; Mathe, E.A.; Jen, J.; Yang, P.; Sugimura, H.; et al. miR-21 is an EGFR-regulated anti-apoptotic factor in lung cancer in never-smokers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12085–12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Garfield, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; Chen, M.; Kuang, P.; et al. miR-21 overexpression is associated with acquired resistance of EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacic, S.; Kelly, L.; Shuai, Y.; Nikiforova, M.N. miRNA expression profiling of lung adenocarcinomas: Correlation with mutational status. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjaanaes, M.M.; Halvorsen, A.R.; Solberg, S.; Jorgensen, L.; Dragani, T.A.; Galvan, A.; Colombo, F.; Anderlini, M.; Pastorino, U.; Kure, E.; et al. Unique microRNA-profiles in EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, G.J.; Bemis, L.T.; Nakajima, E.; Sugita, M.; Birks, D.K.; Robinson, W.A.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Haney, J.; Helfrich, B.A.; et al. EGFR regulation by microRNA in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response and survival to gefitinib and EGFR expression in cell lines. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Umelo, I.A.; Lv, S.; Teugels, E.; Fostier, K.; Kronenberger, P.; Dewaele, A.; Sadones, J.; Geers, C.; de Greve, J. miR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Romano, G.; Di Leva, G.; Nuovo, G.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ngankeu, A.; Sun, J.; Lovat, F.; Alder, H.; Condorelli, G.; et al. EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat. Med. 2011, 18, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Su, X.; Bai, H.; Zhao, J.; Duan, J.; An, T.; Zhuo, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Identification of plasma microRNA profiles for primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR activating mutation. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, M.G.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, W.J.; Shin, D.H.; Roh, M.S. Unique microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma groups according to major TKI sensitive EGFR mutation status. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Miao, L.; Chen, X.; Cai, H. Axl-altered microRNAs regulate tumorigenicity and gefitinib resistance in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciuti, B.; Mecca, C.; Cenci, M.; Leonardi, G.C.; Perrone, L.; Mencaroni, C.; Crino, L.; Grignani, F.; Baglivo, S.; Chiari, R.; et al. miRNAs and resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: Beyond “traditional mechanisms” of resistance. Ecancermedicalscience 2015, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.; Rahman, M.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P. MicroRNAs in respiratory disease. A clinician’s overview. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| microRNAs | Gene Targets | Biological Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor suppressor microRNAs with down-regulation in lung cancer | ||
| let-7 family | RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, MYC, DICER1 | (i) Cell proliferation (RAS, MYC, HMGA2) |
| (ii) Cell cycle regulation (CDK6) | ||
| (iii) microRNA maturation (DICER1) | ||
| miR-34 family | MET, BCL2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB | TRAIL-induced cell death and cell proliferation |
| miR-200 family | ZEB1, ZEB2, E-cadherin (CDH1), vimentin (VIM) | Promotion of EMT and metastasis |
| Oncogenic microRNAs with up-regulation in lung cancer | ||
| miR-21 | PTEN, PDCD4, TPM1 | Apoptosis, cell proliferation, and migration |
| miR-17-92 cluster | E2F1, PTEN, HIF1A | Cell proliferation and carcinogenesis |
| miR-221/222 | PTEN, TIMP3 | Apoptosis and cell migration |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inamura, K.; Ishikawa, Y. MicroRNA In Lung Cancer: Novel Biomarkers and Potential Tools for Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5030036
Inamura K, Ishikawa Y. MicroRNA In Lung Cancer: Novel Biomarkers and Potential Tools for Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2016; 5(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleInamura, Kentaro, and Yuichi Ishikawa. 2016. "MicroRNA In Lung Cancer: Novel Biomarkers and Potential Tools for Treatment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 5, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5030036
APA StyleInamura, K., & Ishikawa, Y. (2016). MicroRNA In Lung Cancer: Novel Biomarkers and Potential Tools for Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 5(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5030036







