Role of PatAB Transporter in Efflux of Levofloxacin in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Isolate 1852 Exhibits a Fluoroquinolone Efflux Phenotype
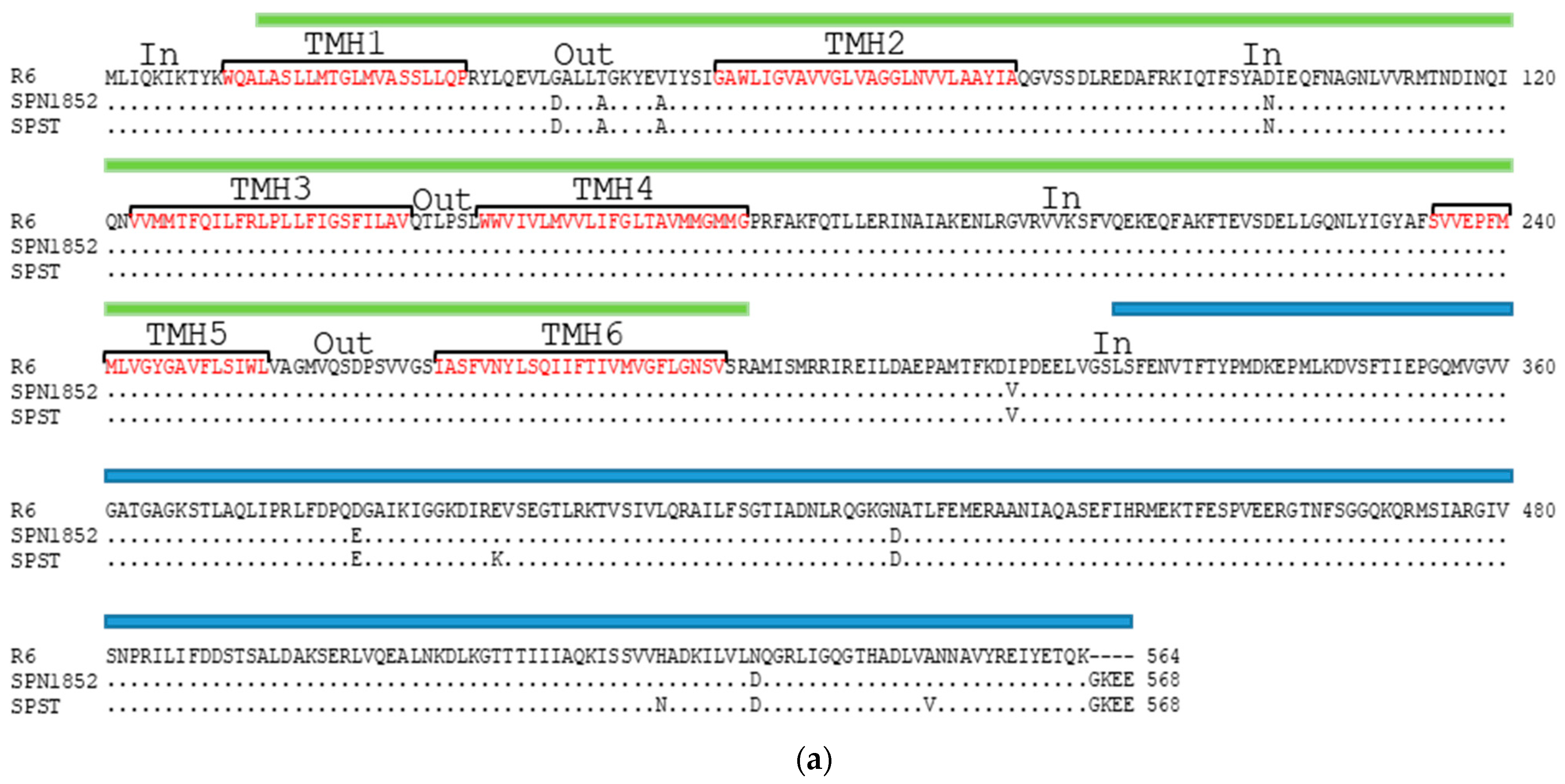
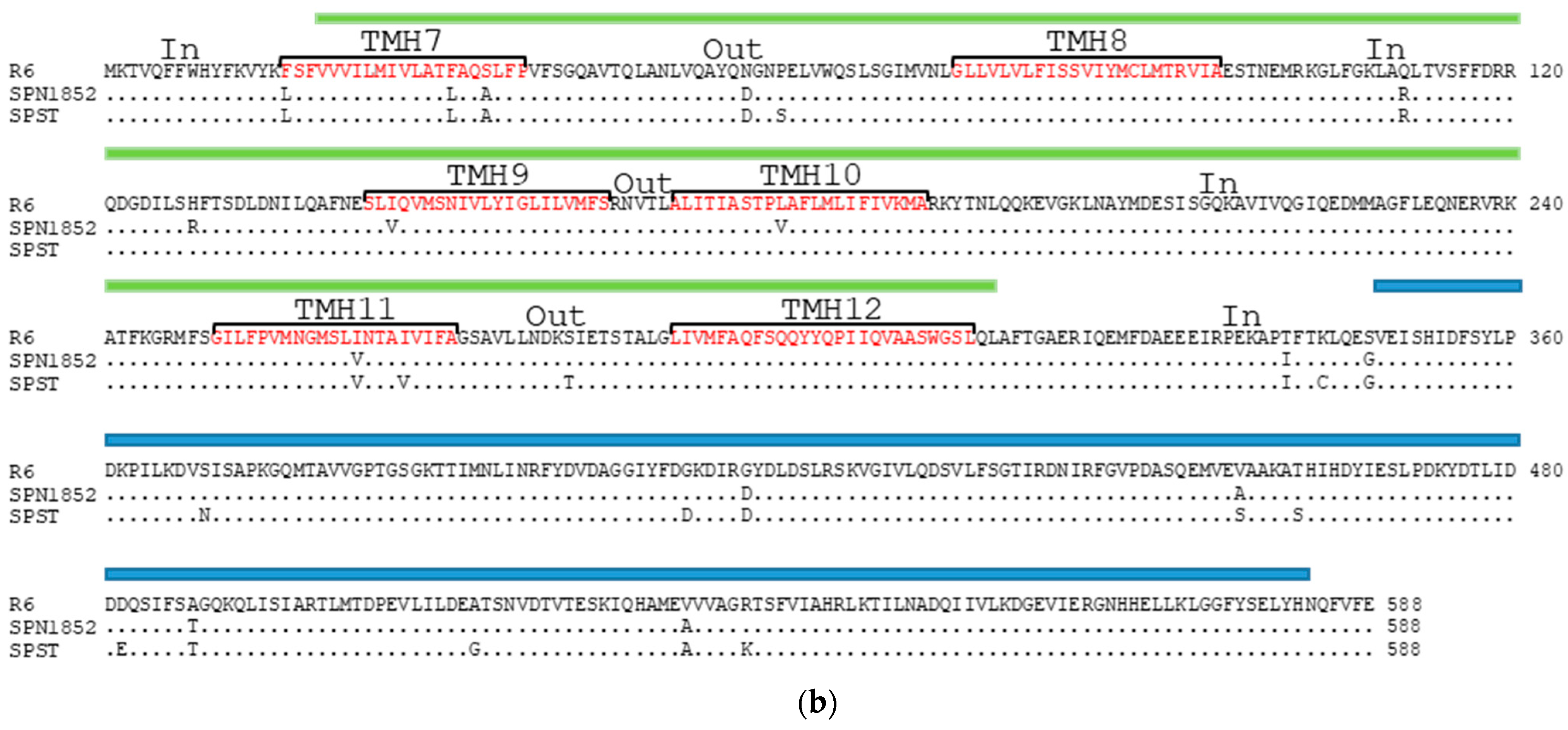
2.2. PatAB Operon Is Responsible for FQ-Efflux in SPN1852
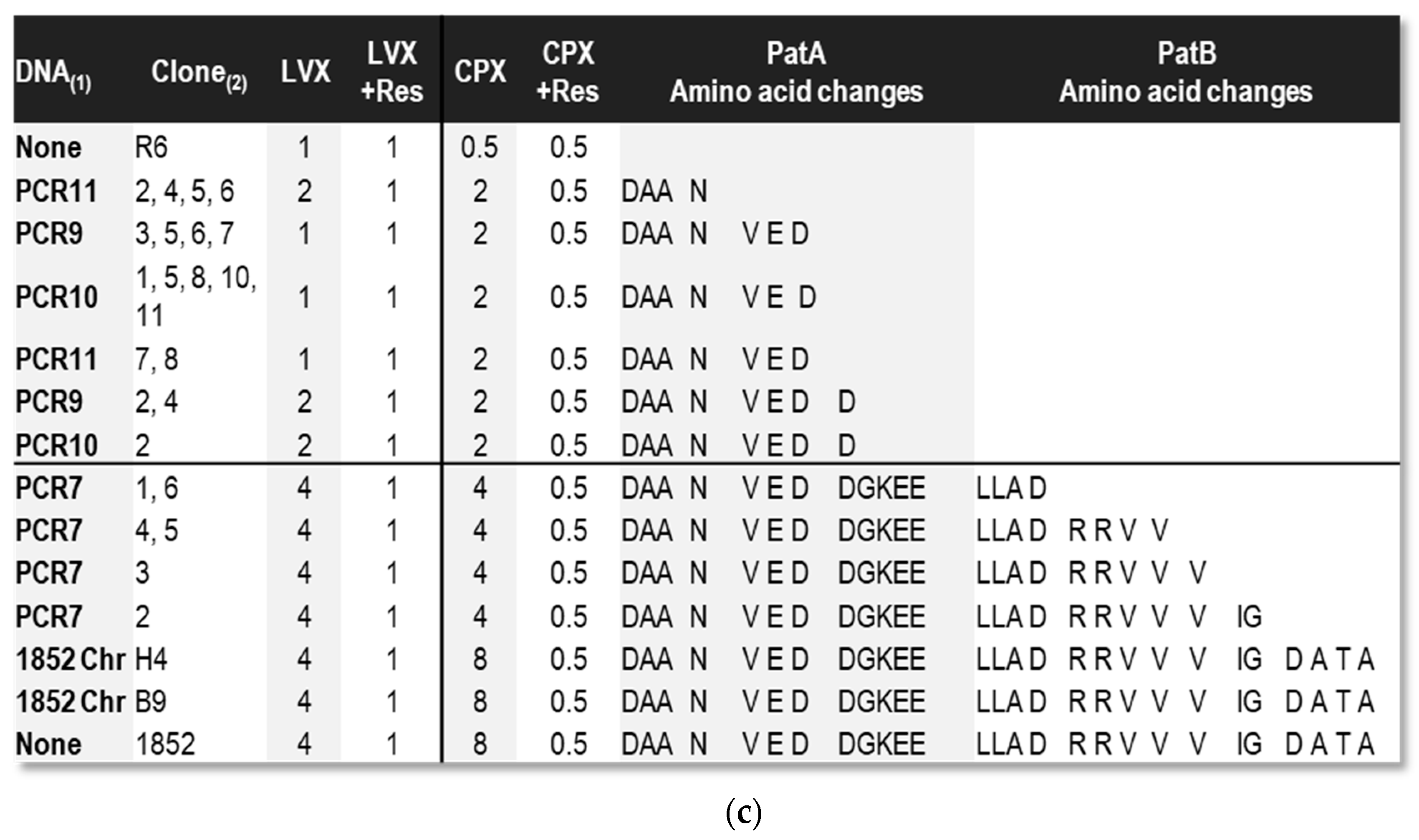
2.3. Some Changes in PatA and PatB Are Dispensable for CPX- but Not for LVX- Efflux
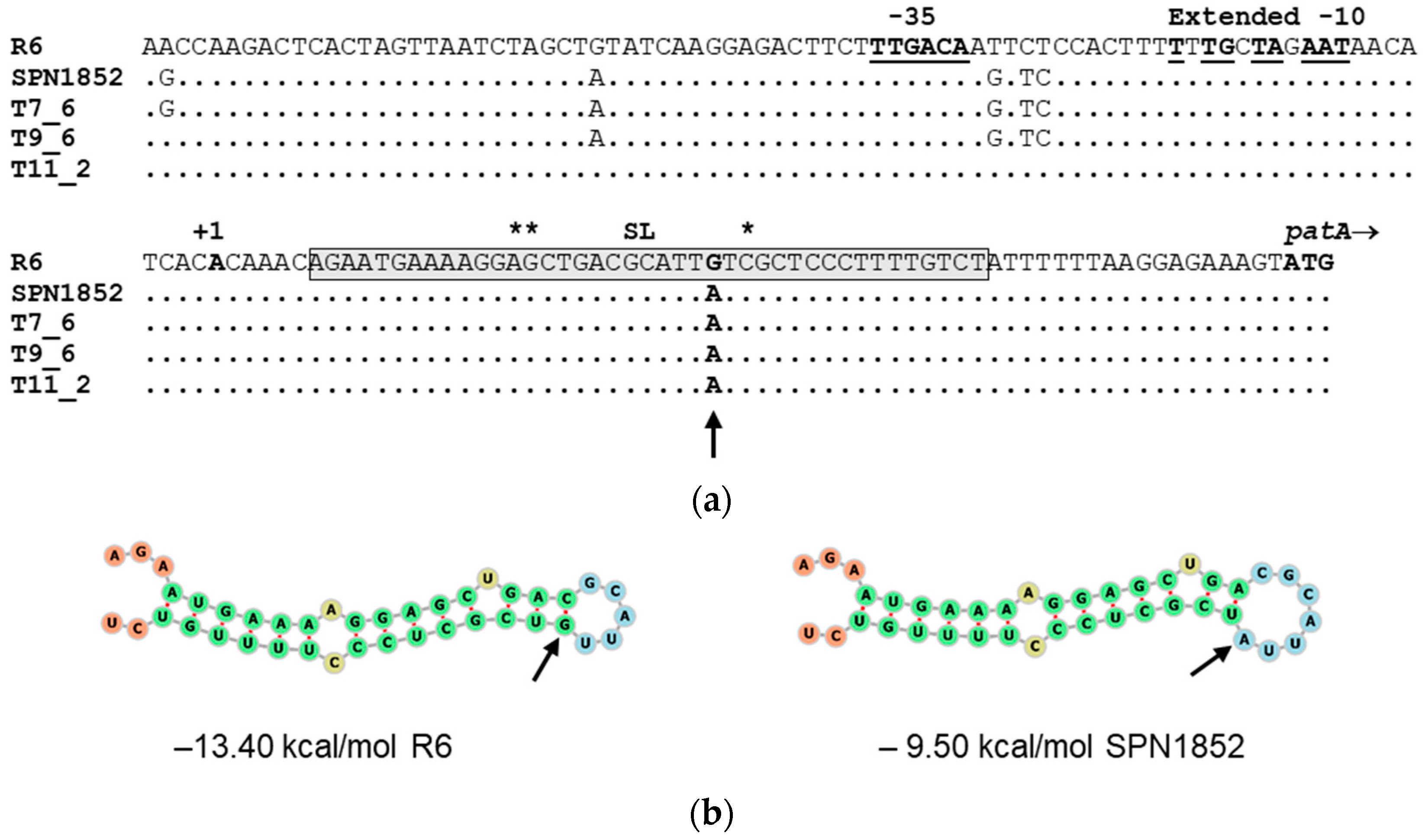
2.4. A Single Mutation in the Stem-Loop Structure Upstream PatA Increased PatAB Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Growth Condition and Transformation
4.2. MLST, Multilocus Sequence Analysis (MLSA)
4.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
4.4. Gene and Protein Analysis
4.5. PCR for Bacterial Transformation
4.6. MIC Determination
4.7. Intracellular Fluoroquinolone Accumulation Measurement
4.8. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, K.L.; Wolfson, L.J.; Watt, J.P.; Henkle, E.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; McCall, N.; Lee, E.; Mulholland, K.; Levine, O.S.; Cherian, T. Burden of Disease Caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in Children Younger than 5 Years: Global Estimates. Lancet 2009, 374, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.R.; Felmingham, D.; Appelbaum, P.C.; Grüneberg, R.N. Alexander Project Group The Alexander Project 1998–2000: Susceptibility of Pathogens Isolated from Community-Acquired Respiratory Tract Infection to Commonly Used Antimicrobial Agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahm, D.F.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Kelly, L.J.; Critchley, I.A.; Jones, M.E.; Thornsberry, C.; Mauriz, Y.; Kahn, J. Need for Annual Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States: 2-Year Longitudinal Analysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, S.G.; Brown, S.D.; Farrell, D.J. Trends in Antibacterial Resistance among Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolated in the USA: Update from PROTEKT US Years 1–4. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2008, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woodford, N.; Livermore, D.M. Infections Caused by Gram-Positive Bacteria: A Review of the Global Challenge. J. Infect. 2009, 59, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bambeke, F.; Michot, J.-M.; Van Eldere, J.; Tulkens, P.M. Quinolones in 2005: An Update. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segreti, J.; House, H.R.; Siegel, R.E. Principles of Antibiotic Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in the Outpatient Setting. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján, M.; Gallego, M.; Rello, J. Optimal Therapy for Severe Pneumococcal Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J.D.; Low, D.E. A Review of Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection Treatment Failures Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Champoux, J.J. DNA Topoisomerases: Structure, Function, and Mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 369–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre, L.; Ferrándiz, M.J.; Liñares, J.; Tubau, F.; de la Campa, A.G. Viridans Group Streptococci Are Donors in Horizontal Transfer of Topoisomerase IV Genes to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrándiz, M.J.; Fenoll, A.; Liñares, J.; de la Campa, A.G. Horizontal Transfer of parC and gyrA in Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baranova, N.N.; Neyfakh, A.A. Apparent Involvement of a Multidrug Transporter in the Fluoroquinolone Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenwald, N.P.; Gill, M.J.; Wise, R. Prevalence of a Putative Efflux Mechanism among Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 2032–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeller, V.; Janoir, C.; Kitzis, M.D.; Gutmann, L.; Moreau, N.J. Active Efflux as a Mechanism of Resistance to Ciprofloxacin in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jumbe, N.L.; Louie, A.; Miller, M.H.; Liu, W.; Deziel, M.R.; Tam, V.H.; Bachhawat, R.; Drusano, G.L. Quinolone Efflux Pumps Play a Central Role in Emergence of Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, M.J.; Brenwald, N.P.; Wise, R. Identification of an Efflux Pump Gene, pmrA, Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tocci, N.; Iannelli, F.; Bidossi, A.; Ciusa, M.L.; Decorosi, F.; Viti, C.; Pozzi, G.; Ricci, S.; Oggioni, M.R. Functional Analysis of Pneumococcal Drug Efflux Pumps Associates the MATE DinF Transporter with Quinolone Susceptibility. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrer, E.; Schad, K.; Satoh, A.T.; Page, M.G.P.; Johnson, M.M.; Piddock, L.J.V. Involvement of the Putative ATP-Dependent Efflux Proteins PatA and PatB in Fluoroquinolone Resistance of a Multidrug-Resistant Mutant of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, G.T.; Doyle, T.B.; Lynch, A.S. Use of an Efflux-Deficient Streptococcus pneumoniae Strain Panel to Identify ABC-Class Multidrug Transporters Involved in Intrinsic Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4781–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F. ABC Transporters: From Microorganisms to Man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1992, 8, 67–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Ambudkar, S.V. Overview: ABC Transporters and Human Disease. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2001, 33, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boncoeur, E.; Durmort, C.; Bernay, B.; Ebel, C.; Di Guilmi, A.M.; Croizé, J.; Vernet, T.; Jault, J.-M. PatA and PatB Form a Functional Heterodimeric ABC Multidrug Efflux Transporter Responsible for the Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae to Fluoroquinolones. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 7755–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, M.I.; Baylay, A.J.; Wong, R.L.; Piddock, L.J.V. Overexpression of patA and patB, Which Encode ABC Transporters, Is Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escudero, J.A.; San Millan, A.; Gutierrez, B.; Hidalgo, L.; La Ragione, R.M.; AbuOun, M.; Galimand, M.; Ferrándiz, M.J.; Domínguez, L.; de la Campa, A.G.; et al. Fluoroquinolone Efflux in Streptococcus suis Is Mediated by SatAB and Not by SmrA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5850–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croucher, N.J.; Mitchell, A.M.; Gould, K.A.; Inverarity, D.; Barquist, L.; Feltwell, T.; Fookes, M.C.; Harris, S.R.; Dordel, J.; Salter, S.J.; et al. Dominant Role of Nucleotide Substitution in the Diversification of Serotype 3 Pneumococci over Decades and during a Single Infection. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baylay, A.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Clinically Relevant Fluoroquinolone Resistance due to Constitutive Overexpression of the PatAB ABC Transporter in Streptococcus pneumoniae Is Conferred by Disruption of a Transcriptional Attenuator. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Garch, F.; Lismond, A.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Courvalin, P.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. Fluoroquinolones Induce the Expression of patA and patB, Which Encode ABC Efflux Pumps in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Peng, W.; Wang, N.; Dou, B.; Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Yuan, F.; Bei, W. Role of the Two-Component System CiaRH in the Regulation of Efflux Pump SatAB and Its Correlation with Fluoroquinolone Susceptibility. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Campa, A.G.; Ardanuy, C.; Balsalobre, L.; Pérez-Trallero, E.; Marimón, J.M.; Fenoll, A.; Liñares, J. Changes in Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae after 7-Valent Conjugate Vaccination, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrándiz, M.J.; Oteo, J.; Aracil, B.; Gómez-Garcés, J.L.; de La Campa, A.G. Drug Efflux and parC Mutations Are Involved in Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Viridans Group Streptococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2520–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarado, M.; Martín-Galiano, A.J.; Ferrándiz, M.J.; Zaballos, Á.; de la Campa, A.G. Upregulation of the PatAB Transporter Confers Fluoroquinolone Resistance to Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, M.I.; Piddock, L.J.V. The Efflux Pump Inhibitor Reserpine Selects Multidrug-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Strains That Overexpress the ABC Transporters PatA and PatB. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billal, D.S.; Feng, J.; Leprohon, P.; Légaré, D.; Ouellette, M. Whole Genome Analysis of Linezolid Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae Reveals Resistance and Compensatory Mutations. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Opijnen, T.; Camilli, A. A Fine Scale Phenotype–genotype Virulence Map of a Bacterial Pathogen. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrandiz, M.-J.; Martin-Galiano, A.J.; Schvartzman, J.B.; de la Campa, A.G. The Genome of Streptococcus pneumoniae Is Organized in Topology-Reacting Gene Clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 3570–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrándiz, M.-J.; Martín-Galiano, A.J.; Arnanz, C.; Camacho-Soguero, I.; Tirado-Vélez, J.-M.; de la Campa, A.G. An Increase in Negative Supercoiling in Bacteria Reveals Topology-Reacting Gene Clusters and a Homeostatic Response Mediated by the DNA Topoisomerase I Gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, gkw602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loo, T.W.; Clarke, D.M. The Transmembrane Domains of the Human Multidrug Resistance P-Glycoprotein Are Sufficient to Mediate Drug Binding and Trafficking to the Cell Surface. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24759–24765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venter, H.; Shilling, R.A.; Velamakanni, S.; Balakrishnan, L.; van Veen, H.W. An ABC Transporter with a Secondary-Active Multidrug Translocator Domain. Nature 2003, 426, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Velamakanni, S.; Deery, M.J.; Howard, J.; Wei, S.L.; van Veen, H.W. ATP-Dependent Substrate Transport by the ABC Transporter MsbA Is Proton-Coupled. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guffick, C.; Hsieh, P.; Ali, A.; Shi, W.; Howard, J.; Chinthapalli, D.K.; Kong, A.C.; Salaa, I.; Crouch, L.I.; Ansbro, M.R.; et al. Drug-dependent Inhibition of Nucleotide Hydrolysis in the Heterodimeric ABC Multidrug Transporter PatAB from Streptococcus pneumoniae. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 3770–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, J.R.; Spolar, R.S.; Record, M.T. Contribution to the Thermodynamics of Protein Folding from the Reduction in Water-Accessible Nonpolar Surface Area. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 4237–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V.K.; Palgunachari, M.N.; Krishna, N.R.; Glushka, J.; Segrest, J.P.; Anantharamaiah, G.M. Effect of Leucine to Phenylalanine Substitution on the Nonpolar Face of a Class A Amphipathic Helical Peptide on Its Interaction with Lipid. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34393–34402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, R.J.P.; Locher, K.P. Structure of a Bacterial Multidrug ABC Transporter. Nature 2006, 443, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, S.J.; Kane, S.E.; Willingham, M.C.; Cardarelli, C.O.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Identification of Residues in the First Cytoplasmic Loop of P-Glycoprotein Involved in the Function of Chimeric Human MDR1-MDR2 Transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 25153–25159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Spratt, B.G. A Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Streptococcus pneumoniae: Identification of Clones Associated with Serious Invasive Disease. Microbiol. Read. Engl. 1998, 144 Pt 11, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, K. Preparation of Genomic DNA from Bacteria. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; Ausbel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., Struhl, K., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Acebo, P.; Martin-Galiano, A.J.; Navarro, S.; Zaballos, A.; Amblar, M. Identification of 88 Regulatory Small RNAs in the TIGR4 Strain of the Human Pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. RNA 2012, 18, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; 18th Informational supplement; CLSI Document M100-S18; Clinical-and-Laboratory-Standards-Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, L.; Wilton, J.; Ferrándiz, M.J.; Gómez-Sanz, A.; de la Campa, A.G.; Amblar, M. Absence of tmRNA Has a Protective Effect against Fluoroquinolones in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acebo, P.; Herranz, C.; Espenberger, L.B.; Gómez-Sanz, A.; Terrón, M.C.; Luque, D.; Amblar, M. A Small Non-Coding RNA Modulates Expression of Pilus-1 Type in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Boto, D.; Acebo, P.; García-Peña, F.J.; Abad, J.C.; Echeita, M.A.; Amblar, M. Isolation of a Point Mutation Associated with Altered Expression of the CmeABC Efflux Pump in a Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter jejuni Population of Poultry Origin. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015, 3, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Strain | MIC (µg/mL) 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVX | LVX + Res | CPX | CPX + Res | |
| R6 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| SPN1852 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| A1 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| A3 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| A4 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| A5 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| H4 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| B9 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| D1 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 0.5 |
| Name | Sequence | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PatBFup | CGCATGCAGACTTGGTTGCCA | PCR4 and sequencing | [32] |
| PatARACE2 | CCAATCAACCAAGCCCCGATAC | PCR6 and sequencing | [32] |
| HexAF757 | CCAAGATTGCTGGCTTGCCAGC | PCRs 6, 7, 9, 10, 11 and sequencing | [32] |
| PatBRDown | ATGGACAAGAAAAAGCTGCCC | PCRs 4, 5, 7 and sequencing | [32] |
| patBR3 | CTCGTTGGTCGACTCTGCAATC | PCRs 9, 12 and sequencing | This study |
| patBR2 | TGCCAAAAAAATTGAACTGTCTTC | PCRs 10, 13 and sequencing | This study |
| PatARDown | TGGCAACCAAGTCTGCATGCG | PCRs 3, 11 and sequencing | [32] |
| PatAF17 | GATGACAGGCTTGATGGTTGC | PCRs 3, 5, 12, 13 and sequencing | [32] |
| PatARTR | AACGACTAGATTTCCCGCAT | Sequencing and qRT-PCR | [32] |
| PatAF1 | GCTAGAATAACATCACACAAACAG | sequencing | This study |
| PatAF2 | AAGCCAGATTATCTTTACCATTG | sequencing | This study |
| PatAF3 | GTGAATTCATTCATCGTATGGAG | sequencing | This study |
| PatAR1 | CATTGGATAGGTAAAGGTCAC | sequencing | This study |
| PatAR2 | AACAATCACCCACCACAGAG | sequencing | This study |
| PatBF2 | AACGTAGATACGGTGACAGAAAGC | sequencing | This study |
| PatBRTR | GCACGCGCTCATTTTGTTCA | sequencing | [32] |
| PatBRTF | GCACCCCATTGGCTTTCCTTA | sequencing | [32] |
| PatARTF2 | GCTTGGTTGATTGGTGTGGC | qRT-PCR | This studty |
| patBRTF2 | AATACACCAACCTCCAGCAG | qRT-PCR | This studty |
| 16SF | AGCGTTGTCCGGATTTATTG | qRT-PCR | [49] |
| 16SR | CATTTCACCGCTACACATGG | qRT-PCR | [49] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amblar, M.; Zaballos, Á.; de la Campa, A.G. Role of PatAB Transporter in Efflux of Levofloxacin in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121837
Amblar M, Zaballos Á, de la Campa AG. Role of PatAB Transporter in Efflux of Levofloxacin in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(12):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121837
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmblar, Mónica, Ángel Zaballos, and Adela G de la Campa. 2022. "Role of PatAB Transporter in Efflux of Levofloxacin in Streptococcus pneumoniae" Antibiotics 11, no. 12: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121837
APA StyleAmblar, M., Zaballos, Á., & de la Campa, A. G. (2022). Role of PatAB Transporter in Efflux of Levofloxacin in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics, 11(12), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121837






