Antibiotics 2022, 11(12), 1786; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121786 - 9 Dec 2022
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1384
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background: In the case of intra-abdominal infections (IAI) in beta-lactam (BL) allergic patients, empiric antimicrobial therapy without BL is recommended; however, data regarding the outcome with alternative regimens are scarce. This study aimed to compare the outcomes of BL allergic (BLA) patients with
[...] Read more.
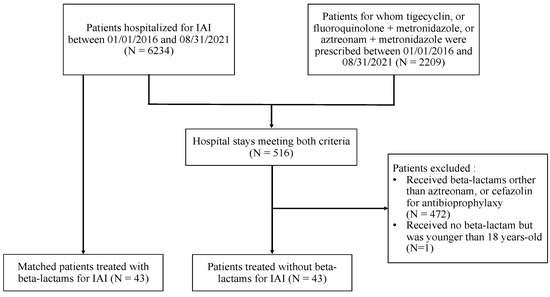
Background: In the case of intra-abdominal infections (IAI) in beta-lactam (BL) allergic patients, empiric antimicrobial therapy without BL is recommended; however, data regarding the outcome with alternative regimens are scarce. This study aimed to compare the outcomes of BL allergic (BLA) patients with IAI to those who were non-BLA (NBLA). Method: We conducted a case–control study in a French teaching hospital, between 1 January 2016 and 31 August 2021. BLA patients with IAI treated with fluoroquinolone or aztreonam and metronidazole were matched with controls treated with BL, on age, sex, disease severity, IAI localization, and healthcare-associated infection (HAI) status. We compared rates of therapeutic failures, adverse events, and HAI, and then assessed factors associated with therapeutic failure using a logistic regression model. Results: The therapeutic failure rate was 14% (p > 0.99) in both groups of 43 patients, and there was no significant difference in the adverse events rate (p > 0.99) and HAI rate (p = 0.154). Factors independently associated with therapeutic failure were higher BMI (OR 1.16; 95%CI [1.00–1.36]; p = 0.041), longer hospital length of stay (OR 1,20; 95%CI [1.08–1.41]; p = 0.006), and inadequate empiric antimicrobial therapy (OR 11.71; 95%CI [1.43–132.46]; p = 0.025). Conclusion: The outcomes of BLA patients with IAI treated without BL were the same as those for NBLA patients treated with BL.
Full article