Phylogeographic Relationships among Bombyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) Populations and Their Relationships to B. mori Inferred from Mitochondrial Genomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Sequencing
2.2. Mitochondrial Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Collection of Public Data
2.4. Sequence Alignments
2.5. Genetic Diversity
2.6. Population Structure and Gene Flow
2.7. Phylogenetic Relationships
2.8. Bayesian Skyline Plot Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mitochondrial Genome Composition and Organization
3.2. Genetic Diversity
3.3. Population Structure and Gene Flow
3.4. Genetic Distance
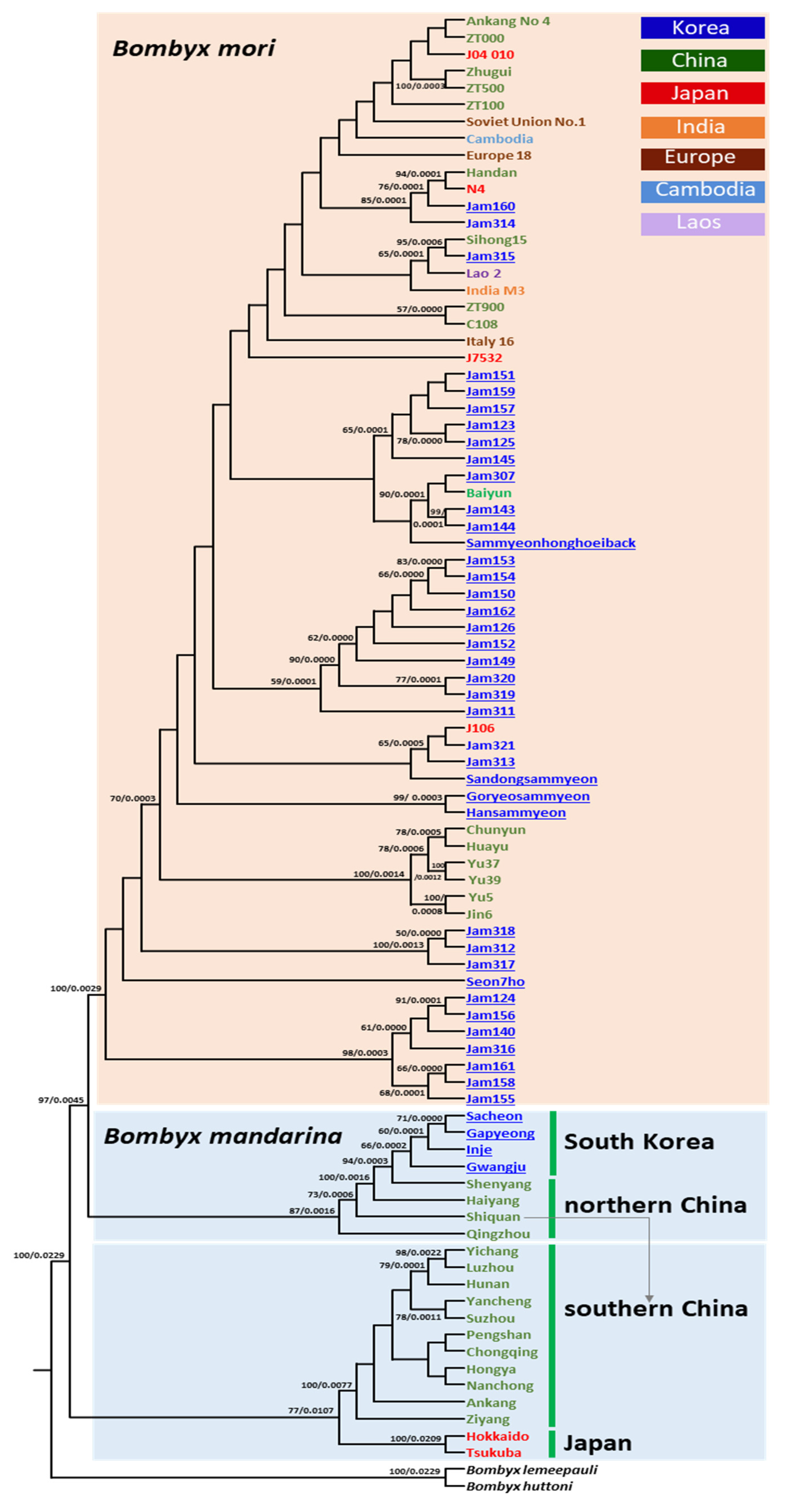
3.5. Phylogenetic Relationships
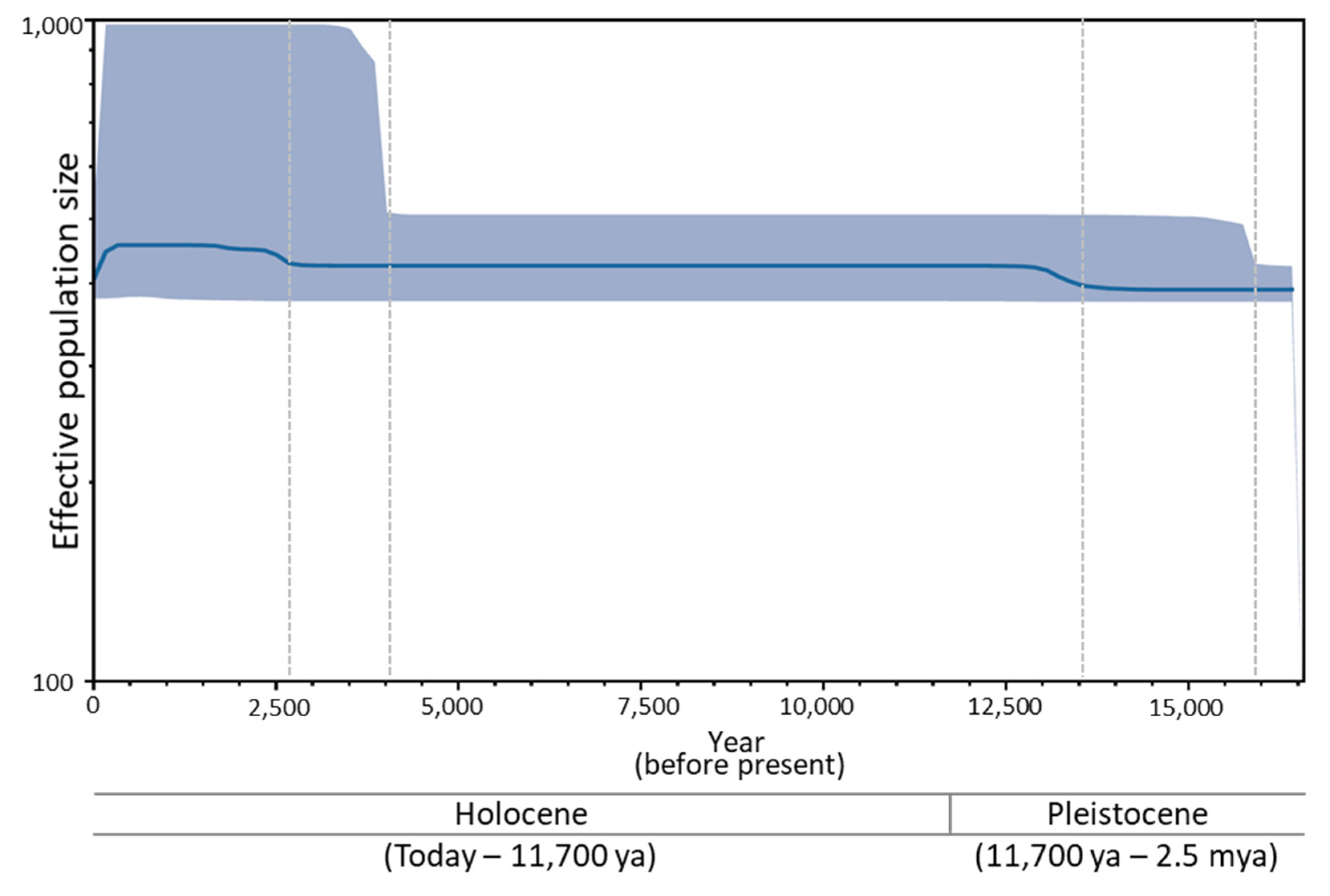
3.6. Historical Demography of B. mandarina
4. Discussion
4.1. The A + T-Rich Region
4.2. Genetic Diversity
4.3. Genetic Relationships of South Korea-Dwelling B. mandarina to Other Regional Populations
4.4. Genetic Relationships of Japan-Dwelling B. mandarina to Other Regional Populations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, W.C.; Kim, I. The strategy for the development of bio-resources utilizing sericultural products and insects. Int. J. Indust. Entomol. 2000, 1, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, K.S.; Kim, I.; Ahn, M.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, P. Functionality research on silkworm and sericultural products. Food. Sci. Indust. 2003, 36, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Lu, C.; Cheng, D.; Dai, F.; Li, B.; Zhao, P.; Zha, X.; Cheng, T.; Chai, C.; et al. A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 2004, 306, 1937–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, M.R.; Shimada, T.; Abe, H. The genetics and genomics of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 71–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Li, S.; Feng, Q. Advances in silkworm studies accelerated by the genome sequencing of Bombyx mori. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 513–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, S.-W.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, Y.L. Scalable and continuous nanomaterial integration with transgenic fibers for enhanced photoluminescence. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindroo, B.B.; Moorthy, S.M. Genetic divergence, implication of diversity, and conservation of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Int. J. Biodivers. 2014, 564850, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arunkumar, K.P.; Metta, M.; Nagaraju, J. Molecular phylogeny of silkmoths reveals the origin of domesticated silkmoth, Bombyx mori from Chinese Bombyx mandarina and paternal inheritance of Antheraea proylei mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yu, Q.; Xia, Y.; Dai, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, Z. Characterization of mitochondrial genome of Chinese wild mulberry silkworm, Bomyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Sci. China Life Sci. 2008, 51, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Shao, H.; Tellier, L.C.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Xia, Q. Genetic diversity, molecular phylogeny and selection evidence of the silkworm mitochondria implicated by complete resequencing of 41 genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.N.; Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, G.; Qian, H.; Xu, A.; et al. The evolutionary road from wild moth to domestic silkworm. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, Y.H.; Sun, W.; Kishino, H.; Xiang, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z. Nucleotide diversity and selection signature in the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori, and wild silkworm, Bombyx mandarina. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Underhill, A.P. Current issues in Chinese neolithic archaeology. J. World Prehistory. 1997, 11, 103–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, E. Zytrogishe Untersuchungen am Seidenspinner und seinen Verwandten. I. Gametogenese von Bombyx mori L. und B. mandarina M. und ihrer Bastarde. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1928, 7, 519–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astaurov, B.L.; Golisheva, M.D.; Roginskaya, I.S. Chromosome complex of Ussuri geographical race of Bombyx mandarina M. with special reference to the problem of the origin of the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Cytology 1959, 1, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Toyama, K. On the Spermatogenesis of the Silkworm; The Bulletin of the College of Agriculture: Tokyo, Japan, 1894; Volume 2, pp. 125–157. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Banno, Y.; Nakada, T.; Nho, S.-K.; Xu, M.K.; Ueda, K.; Kawarabata, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Koga, K. Geographic dimorphism of the wild silkworm, Bombyx mandarina, in the chromosome number and the occurrence of a retroposon-like insertion in the arylphorin gene. Genome 1999, 42, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banno, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Nagashima, E.; Fujii, H.; Doira, H. M chromosome of the wild silkworm, Bombyx mandarina (n = 27), corresponds to two chromosomes in the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori (n = 28). Genome 2004, 47, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. The number of chromosomes of wild mulberry silkworm, Bombyx mori, in Korea. Korean J. Seric. Sci. 1987, 29, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi, Y.; Banno, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Nho, S.-K.; Tu, Z.; Mita, K.; Tsuchida, K.; Takada, N.; Maekawa, H.; Nakajima1, Y. Method for rapid distinction of Bombyx mandarina (Japan) from B. mandarina (China) based on rDNA sequence differences. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2008, 77, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi, Y.; Takaishi, R.; Banno, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Nho, S.-K.; Maekawa, H.; Nakajima, Y. Sequence comparison of mariner-like elements among the populations of Bombyx mandarina inhabiting China, Korea and Japan. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2007, 76, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Yu, H.S.; Shen, Y.H.; Banno, Y.; Xiang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z. Phylogeny and evolutionary history of the silkworm. Sci. China Life Sci. 2012, 55, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.-B.; Zhang, R.-S.; Bian, H.-X.; Li, Q.; Xia, R.-X.; Li, Y.-P.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Lu, C. Comparative mitochondrial genomes provide new insights into the true wild progenitor and origin of domestic silkworm Bombyx mori. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, P.D.; Kim, S.G.; JIN, B.R.; Han, Y.S.; Kim, I. Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitochondrial genome of eri-silkworm, Samia cynthia ricini (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010; Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Jiang, H.; Lei, R.; Ding, S.W.; Zhu, S. Skewer: A fast and accurate adapter trimmer for next-generation sequencing paired-end reads. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, A.; Kalnis, P.; Solovyev, V. Karect: Accurate correction of substitution, insertion and deletion errors for next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3421–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, C.; Bachmann, L.; Chevreux, B. Reconstructing mitochondrial genomes directly from genomic next-generation sequencing reads-a baiting and iterative mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997v2. [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson, M.J.; Tesler, G. Mapping single molecule sequencing reads using basic local alignment with successive refinement (BLASR): Application and theory. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2016, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameron, S.L. How to sequence and annotate insect mitochondrial genomes for systematic and comparative genomics research. Syst. Entomol. 2014, 39, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Juhling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Putz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Zhu, X.; Meng, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx mori strain Baiyun (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 1652–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-M. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx mori strain Yu5 (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 4128–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-M. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx mori strain Jin6 (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 4168–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-M. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx mori strain Yu39 (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 3163–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Wu, A.-Q. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx mori strain Chunyun (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 4082–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhou, Q.-M. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx mori strain Huayu (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 2155–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the silkworm strain, Hukpyobeom Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae), that has a unique larval body marking. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2019, 4, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-W.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the silkworm strain, Chilseongjam Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae), with a unique larval body marking. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2019, 4, 2853–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, G.; Wang, R.; Chu, Q.; Peng, Y.; Liang, J.; Lin, J. Complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Bombyx mandarina strain Shiquan. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2019, 4, 3788–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yukuhiro, K.; Sezutsu, H.; Itoh, M.; Shimizu, K.; Banno, Y. Significant levels of sequence divergence and gene rearrangements have occurred between the mitochondrial genomes of the wild mulberry silkmoth, Bombyx mandarina, and its close relative, the domesticated silkmoth, Bombyx mori. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.L.; Cao, G.L.; Xue, R.Y.; Zheng, X.J.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.R.; Gong, C.L. The complete mitogenome and phylogenetic analysis of Bombyx mandarina strain Qingzhou. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, F.; Chen, J. Complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Bombyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2019, 4, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, X.Y.; Zhou, P.; Qiang, Y.; Qian, Z.Q. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx huttoni (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 4112–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Q.; Gu, X.S.; Wang, X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Bombyx lemeepauli (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) and its phylogenetic relationship. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2017, 2, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Asimenos, G.; Toh, H. Multiple alignment of DNA sequences with MAFFT, Methods. Mol. Biol. 2009, 537, 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wernersson, R.; Pedersen, A.G. RevTrans—Constructing alignments of coding DNA from aligned amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3537–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.L.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Con-catenation software for the fast assembly of multigene datasets withcharacter set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s laser gene sequence analysis software. In Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols; Misener, S., Krawets, S.A., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Messeguer, X.; Rozas, R. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2496–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Genetic variation within species. In Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Nei, M., Ed.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Chapter 8; pp. 176–207. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP * 4.0: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods), Version 4b2; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Corander, J.; Tang, J. Bayesian analysis of population structure based on linked molecular information. Math. Biosci. 2007, 205, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlóci, L. Multivariate Analysis in Vegetation Research, 2nd ed.; Springer: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the 9th Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), IEEE, New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Shapiro, B.; Pybus, O.G. Bayesian coalescent inference of past population dynamics from molecular sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, P.; Alshamali, F.; Pereira, J.B.; Fernandes, V.; Silva, N.; Afonso, C.; Costa, M.D.; Musilova, E.; Macaulay, V.; Richards, M.B. The Expansion of mtDNA haplogroup L3 within and out of Africa. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.J.; Wan, X.; Kim, K.-G.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, I. Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of the endangered Eumenis autonoe (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 735–754. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of Saturnia jonasii (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae): Genomic comparisons and phylogenetic inference among Bombycoidea. Genomics 2018, 110, 174–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameron, S.L. Insect mitochondrial genomics: Implications for evolution and phylogeny. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hale, M.L.; Burg, T.M.; Steeves, T.E. Sampling for microsatellite-based population genetic studies: 25 to 30 individuals per population is enough to accurately estimate allele frequencies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.; Shen, G. Molecular phylogeny of the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori, based on the sequences of mitochondrial cytochrome b genes. J. Genet. 2005, 84, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.Y.; Lee, E.M.; Jo, Y.H.; Park, H.C.; Kim, S.R.; Hwang, J.S.; Jin, B.R.; Kang, P.D.; Kim, K.-G.; Han, Y.S.; et al. Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of the silk moth Caligula boisduvalii (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) and comparison with other lepidopteran insects. Gene 2008, 413, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, M.; Dai, F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, C.; Xiang, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Chineseoak silkmoth, Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.J.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the lappet moth, Kunugia undans (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae): Genomic comparisons among macroheteroceran superfamilies. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.R.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the wild silkmoth, Saturnia boisduvalii (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Entomol. Res. 2017, 47, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Tamura, K.; Aotsuka, T. Replication origin of mitochondrial DNA in insects. Genetics 2005, 171, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muir, W.M.; Wong, G.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Groenen, M.A.; Crooijmans, R.P.; Megens, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Okimoto, R.; Vereijken, A.; et al. Genome-wide assessment of worldwide chicken SNP genetic diversity indicates significant absence of rare alleles in commercial breeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17312–17317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, J.M.; Carneiro, M.; Afonso, S.; Lopes, S.; Garreau, H.; Boucher, S.; Allain, D.; Queney, G.; Esteves, P.J.; Bolet, G.; et al. Levels and patterns of genetic diversity and population structure in domestic rabbits. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahammi, F.Z.; Gaouar, S.B.S.; Laloë, D.; Faugeras, R.; Tabet-Aoul, N.; Rognon, X.; Tixier-Boichard, M.; Saidi-Mehtar, N. A molecular analysis of the patterns of genetic diversity in local chickens from western Algeria in comparison with commercial lines and wild jungle fowls. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2016, 133, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharzinova, V.R.; Dotsev, A.V.; Deniskova, T.E.; Solovieva, A.D.; Fedorov, V.I.; Layshev, K.A.; Romanenko, T.M.; Okhlopkov, I.M.; Wimmers, K.; Reyer, H.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of domestic and wild reindeer (Rangifer tarandus L. 1758): A novel approach using BovineHD BeadChip. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aramburu, O.; Ceballos, F.; Casanova, A.; Le Moan, A.; Hemmer-Hansen, J.; Bekkevold, D.; Bouza, C.; Martínez, P. Genomic signatures after five generations of intensive selective breeding: Runs of homozygosity and genetic diversity in representative domestic and wild populations of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukuhiro, K.; Sezutsu, H.; Tamura, T.; Kosegawa, E.; Iwata, K.; Ajimura, M.; Gu, S.-H.; Wang, M.; Xia, Q.; Mita, K.; et al. Little gene flow between domestic silkmoth Bombyx mori and its wild relative Bombyx mandarina in Japan, and possible artificial selection on the CAD gene of B. mori. Genes Genet. Syst. 2012, 87, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.S.; Shen, Y.H.; Yuan, G.X.; Hu, Y.G.; Xu, H.E.; Xiang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z. Evidence of selection at melanin synthesis pathway loci during silkworm domestication. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 1785–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Peng, X.; Liu, G.; Pan, H.; Dorn, S.; Chen, M. High genetic diversity and structured populations of the oriental fruit moth in its range of origin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.-S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jeong, J.S.; Park, J.; Kim, I. Geographic variation in the spotted wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae), based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L.; Ishikawa, T.; Kamitani, S.; Sota, T.; Song, F.; Tian, L.; Cai, W.; et al. Global phylogeography and invasion history of the spotted lanternfly revealed by mitochondrial phylogenomics. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jeong, J.S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Jeong, N.R.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, G.S.; Lee, W.; Kim, I. Tracing the invasion and expansion characteristics of the flatid planthopper, Metcalfa pruinosa (Hemiptera: Flatidae), in Korea using mitochondrial DNA sequences. Insects 2021, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, L.F.; Lenstra, J.A.; Eding, H.; Toro, M.A.; Scherf, B.; Pilling, D.; Negrini, R.; Finlay, E.K.; Jianlin, H.; Groeneveld, E.; et al. Genetic diversity in farm animals. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 6–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamo, T.; Ohtsuka, Y. Phylogenetic studies on the racial differentiation of the silkworm, Bombyx mori, on the basis of polymorphic genes in haemolymph proteins. Bull. Sericul. Exp. Sta. 1980, 28, 15–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yukuhiro, K.; Sakaguchi, H.; Komoto, N.; Tomita, S.; Itoh, M. Three single nucleotide polymorphisms indicate four distinctive distributions of Japanese Bombyx mandarina populations. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2017, 86, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C. Molecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Frankham, R. Relationship of genetic variation to population size in wildlife. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esaki, T. On the geographical distribution of insects in Japan, with some notes on its boundary lines. Zool. Sci. 1921, 33, 444–466. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, A. Insect fauna of Tsushima island. In Insect Geography in Japan—With Special Reference to Speciation and Variation; Kimoto, S., Ed.; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1986; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Xue, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Gong, C. Nuclear mitochondrial DNA pseudogenes in the genome of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. Res. 2011, 3, 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.D.; Xu, J.L. On the hearths of sericulture in China (in Chinese). J. Zhejiang Univ. Natl. 2003, 33, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Han, M.-J.; Kang, L.-F.; Li, Z.-W.; Shen, Y.-H.; Zhang, Z. Demographic history and gene flow during silkworm domestication. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iriondo, M.H.; Garcia, N.O. Climatic variations in the Argentine plains during the last 18,000 years. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1993, 101, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbø, C.L.; Fossheim, T.; Vøllestad, L.A.; Jakobsen, K.S. Genetic divergence and phylogeographic relationships among European perch (Perca fluviatilis) populations reflect glacial refugia and postglacial colonization. Mole. Ecol. 1999, 8, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Bae, J.-S.; Kim, I.; Suzuki, H.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, K.-Y.; Yang, W.-J.; Lee, S.-M.; Sohn, H.-D.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA sequence-based population genetic structure of the firefly, Pyrocoelia rufa (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Biochem. Genet. 2003, 41, 427–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.A. The change of sea level and climate during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene in the Yellow Sea region. Korean J. Quat. Res. 1992, 6, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.C.; Choi, C.S. Studies on the bionomies and analysis of damage of the rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis G. in South region of Korea. Rural Dev. Rev. 1984, 19, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kiritani, K. Colonizing insects: What prevented the brown planthopper from establishing itself in Japan? Insectarium 1984, 21, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Li, L.; Kim, M.J.; Park, H.C.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, I. DNA sequence variation of the tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), determined by mitochondrial A+T-rich region and nuclear ITS2 sequences. Biochem. Genet. 2011, 49, 760–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Li, J.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, T.H.; Jin, B.R.; Kim, I. Population genetic structure of the migratory rice leaf roller, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), inferred from the mitochondrial A+T-rich region and nuclear ITS2 sequences. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.-P.; Wu, M.-F.; Gao, B.-Y.; Liu, J.; Lee, G.-S.; Otuka, A.; Hu, G. High risk of the fall armyworm invading Japan and the Korean Peninsula via overseas migration. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 43, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.-J. Surveillance for Spodoptera frugiperda, fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in South Korea. EPPO Bull. 2020, 50, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Akintola, A.A.; Malekera, M.J.; Kamulegeya, P.; Nyakunga, K.B.; Mutimbu, M.K.; Shrestha, Y.K.; Hemayet, J.S.M.; Hoat, T.X.; Dao, H.T.; et al. Genetic relationship of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) populations that invaded Africa and Asia. Insects 2021, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakun, J.D.; Clark, P.U.; He, F.; Marcott, S.A.; Mix, A.C.; Liu, Z.; Bliesner, B.O.; Svhmittner, A.; Bard, E. Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation. Nature 2012, 484, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcott, S.A.; Shakun, J.D.; Clark, P.U.; Mix, A.C. A reconstruction of regional and global temperature for the past 11,300 years. Science 2013, 339, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.J.; Cho, Y.; Wang, A.R.; Kim, S.-S.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, I. Population genetic characterization of the black-veined white, Aporia crataegi (Lepidoptera: Pieridae), using novel microsatellite markers and mitochondrial DNA gene sequences. Conserv. Genet. 2020, 21, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, H.; Takada, N.; Mikitani, K.; Ogura, T.; Miyajima, N.; Fujiwara, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Ninaki, O. Nucleolus organizers in the wild silkworm Bombyx mandarina and the domesticated silkworm B. mori. Chromosoma 1988, 96, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, M. The last viaduct of Japan Islands. Earth Sci. 1966, 85, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
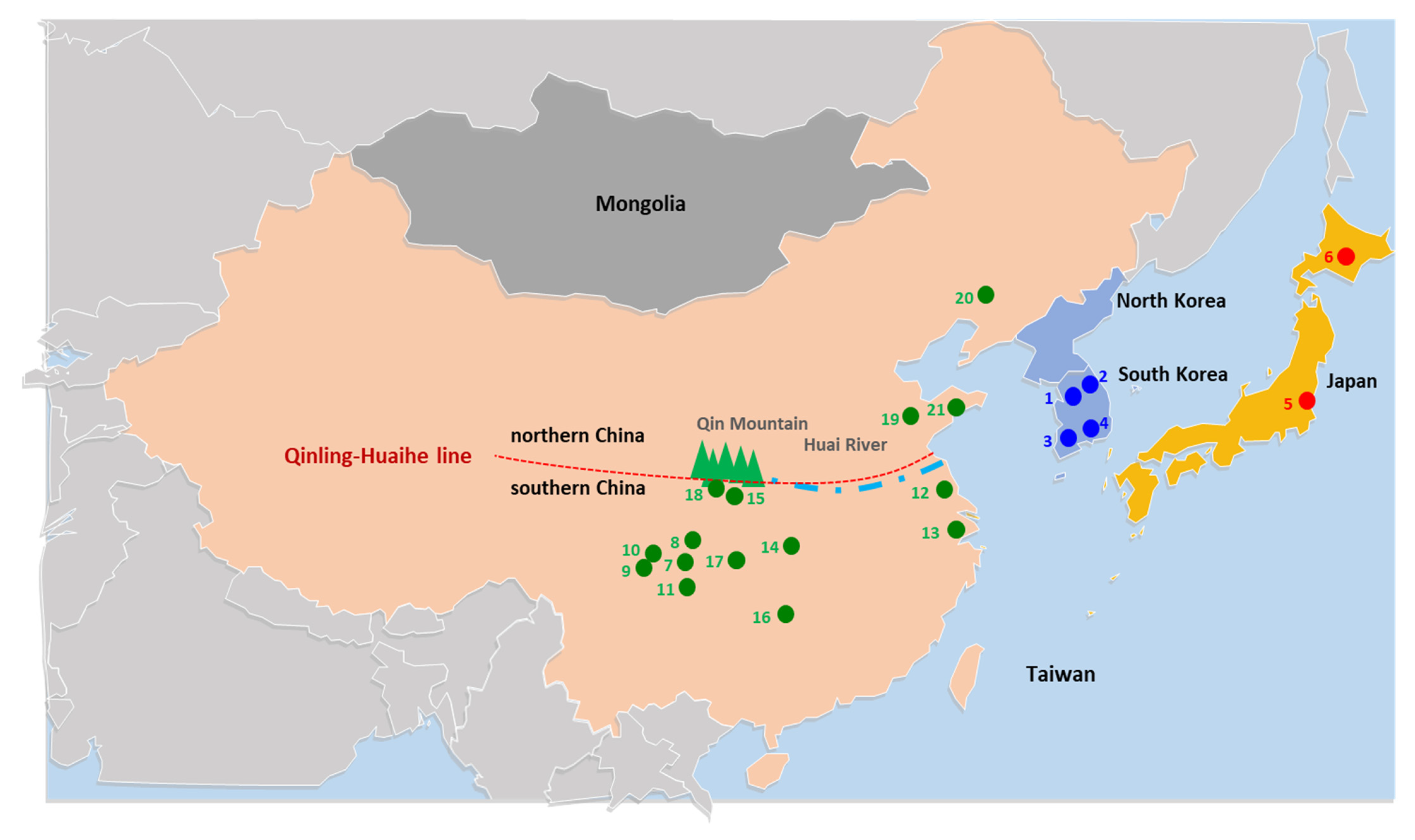

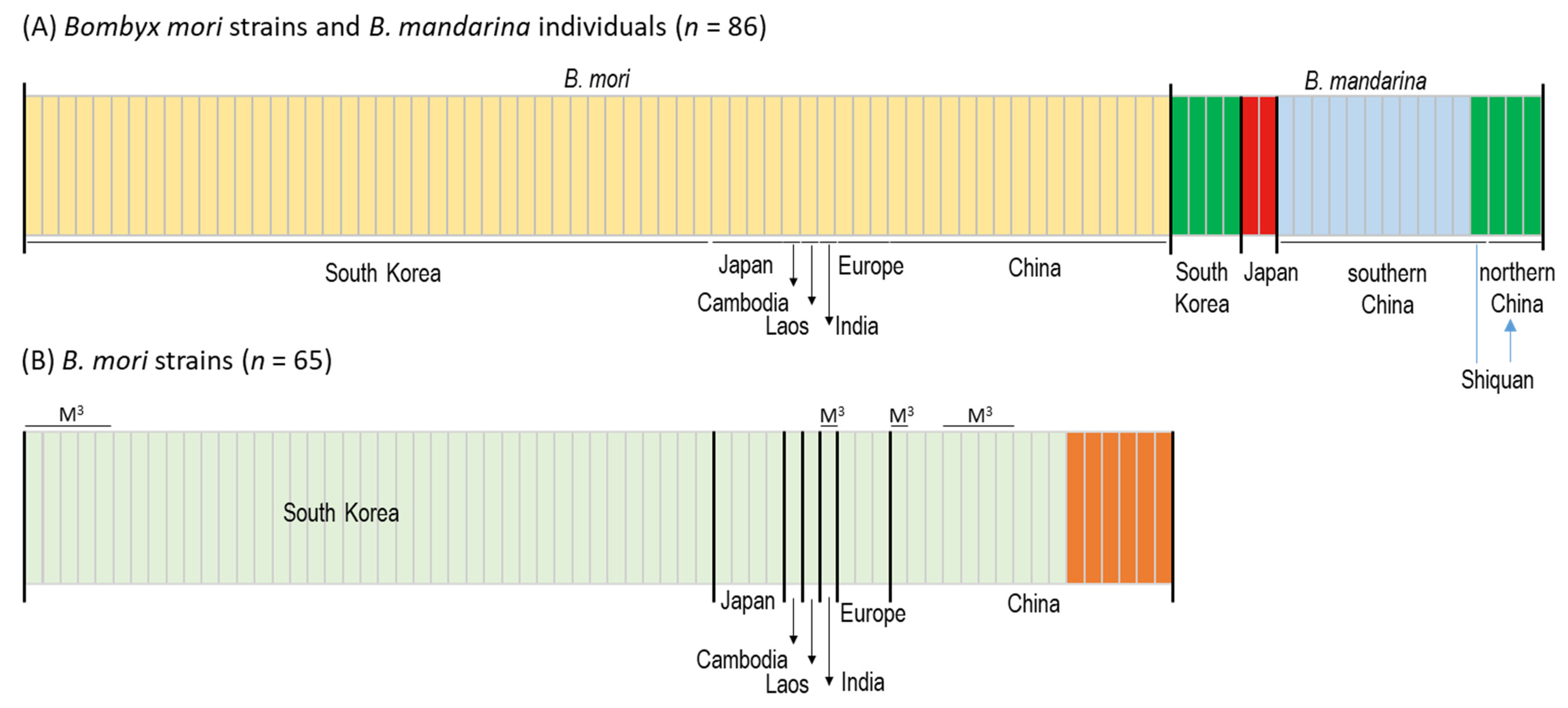
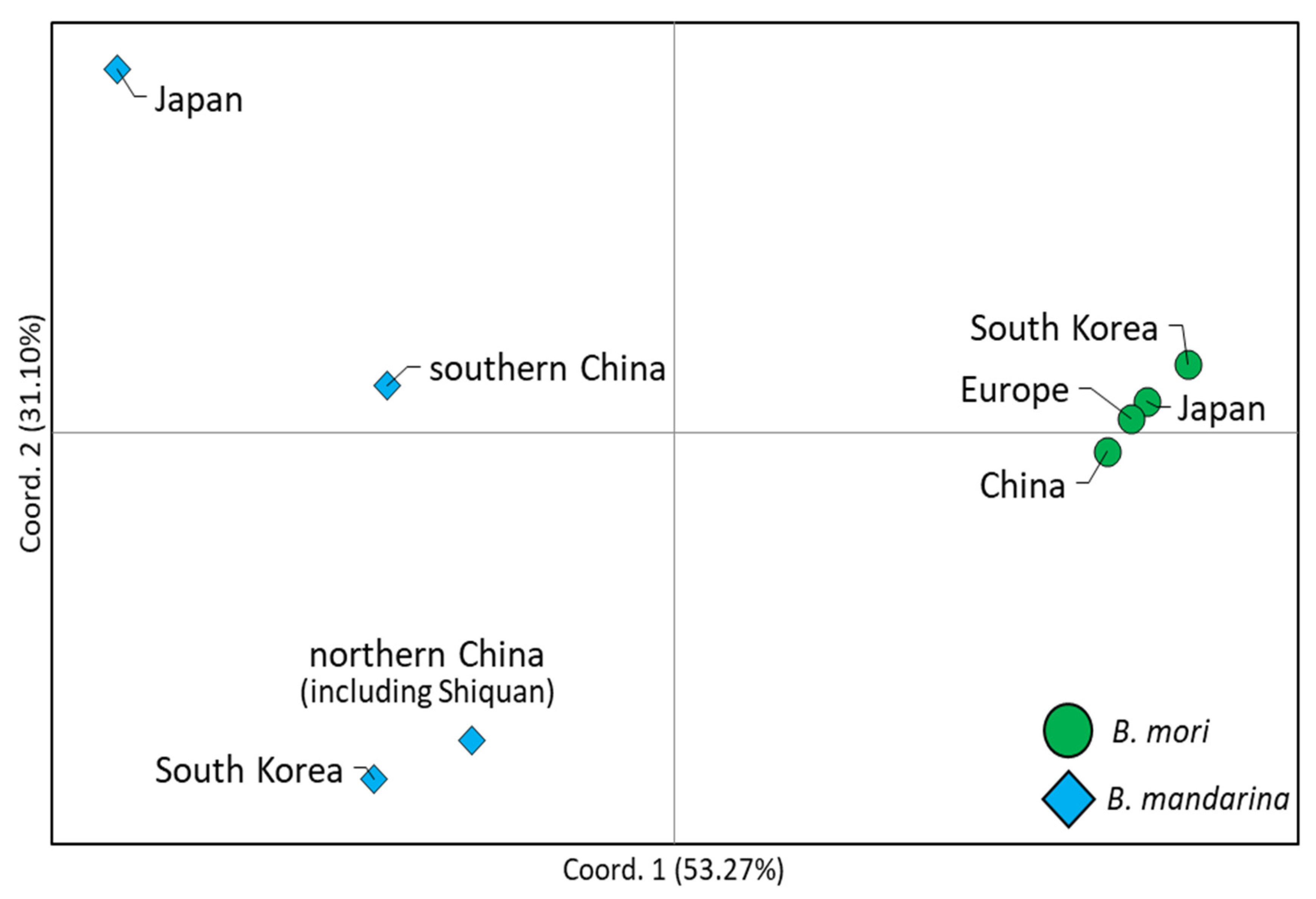
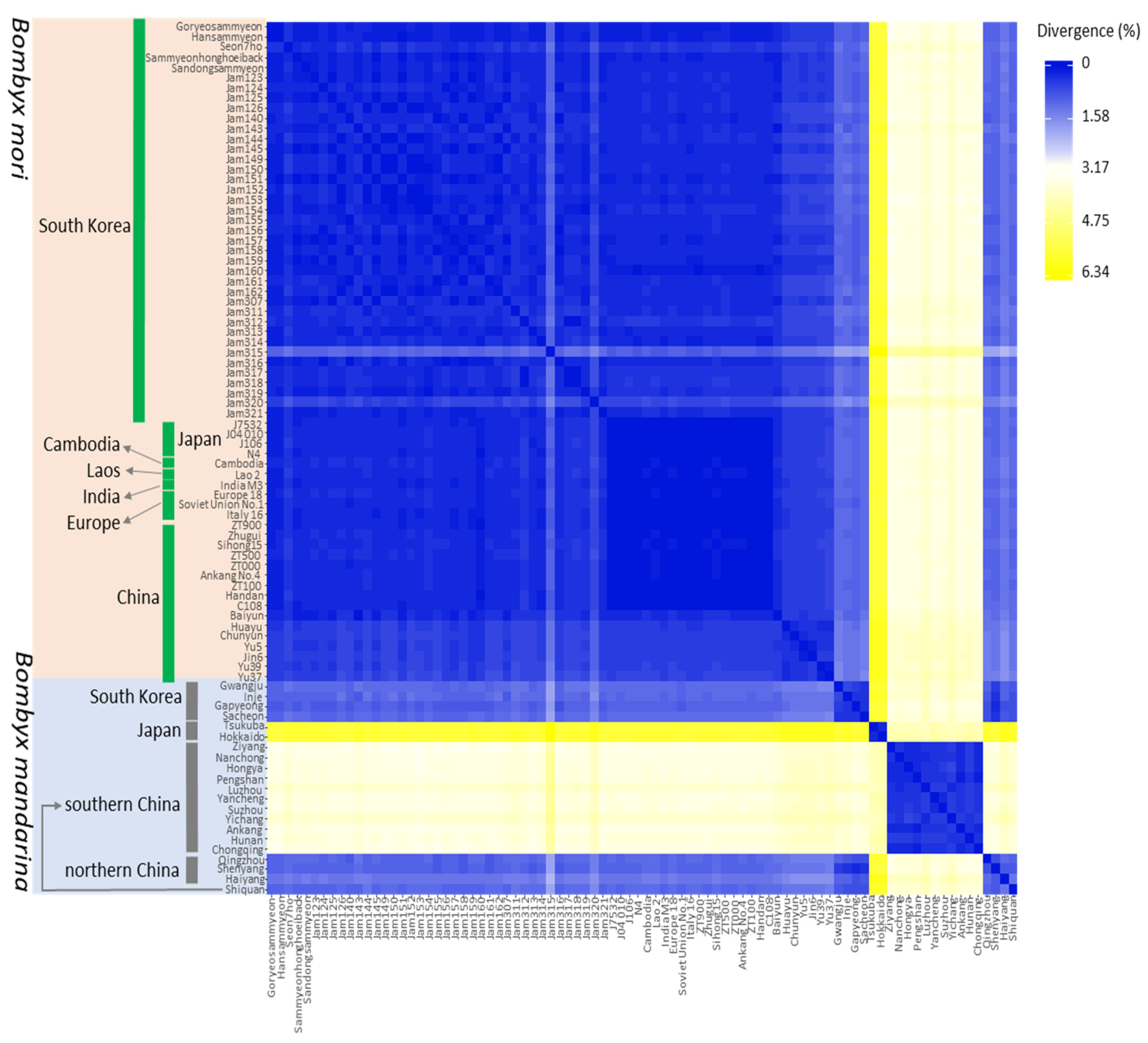
| Group | SS a | NH b | Hc | NP d | MPD e | π f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. B. mori plus B. mandarina | 86 | 86 | 1 ± 0.0018 | 1985 | 134.140959 ± 58.074825 | 0.008199 ± 0.003933 |
| 2. B. mori | 65 | 65 | 1 ± 0.0027 | 615 | 25.429197 ± 11.302211 | 0.001603 ± 0.000790 |
| a. South Korea | 39 | 39 | 1 ± 0.0058 | 452 | 16.744353 ± 7.615369 | 0.001056 ± 0.000534 |
| b. China | 16 | 16 | 1 ± 0.0221 | 238 | 41.835814 ± 19.178396 | 0.002668 ± 0.001370 |
| c. Japan | 4 | 4 | 1 ± 0.1768 | 23 | 11.841933 ± 6.819167 | 0.000756 ± 0.000520 |
| d. Europe | 3 | 3 | 1 ± 0.2722 | 19 | 12.674914 ± 7.925171 | 0.000810 ± 0.000631 |
| e. Cambodia | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| f. Laos | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| g. India | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| 3. B. mandarina | 21 | 21 | 1 ± 0.0147 | 1493 | 253.292065 ± 112.882473 | 0.015640 ± 0.007781 |
| a. South Korea | 4 | 4 | 1 ± 0.1768 | 160 | 30.249683 ± 16.885207 | 0.001923 ± 0.001282 |
| b. China | 15 | 15 | 1 ± 0.0243 | 963 | 185.321893 ± 84.149325 | 0.011620 ± 0.005916 |
| - southern China | 11 | 11 | 1 ± 0.0388 | 234 | 75.285248 ± 35.188128 | 0.004800± 0.002531 |
| - northern China | 4 | 4 | 1 ± 0.1768 | 333 | 74.1484056 ± 41.063087 | 0.004706± 0.003098 |
| c. Japan | 2 | 2 | 1 ± 0.5000 | 46 | 46.125073 ± 32.967009 | 0.002896 ± 0.002927 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kwak, W.; Kim, I. Phylogeographic Relationships among Bombyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) Populations and Their Relationships to B. mori Inferred from Mitochondrial Genomes. Biology 2022, 11, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010068
Kim M-J, Park J-S, Kim H, Kim S-R, Kim S-W, Kim K-Y, Kwak W, Kim I. Phylogeographic Relationships among Bombyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) Populations and Their Relationships to B. mori Inferred from Mitochondrial Genomes. Biology. 2022; 11(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Jee, Jeong-Sun Park, Hyeongmin Kim, Seong-Ryul Kim, Seong-Wan Kim, Kee-Young Kim, Woori Kwak, and Iksoo Kim. 2022. "Phylogeographic Relationships among Bombyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) Populations and Their Relationships to B. mori Inferred from Mitochondrial Genomes" Biology 11, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010068
APA StyleKim, M. -J., Park, J. -S., Kim, H., Kim, S. -R., Kim, S. -W., Kim, K. -Y., Kwak, W., & Kim, I. (2022). Phylogeographic Relationships among Bombyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) Populations and Their Relationships to B. mori Inferred from Mitochondrial Genomes. Biology, 11(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010068






