Can Introns Stabilize Gene Duplication?
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
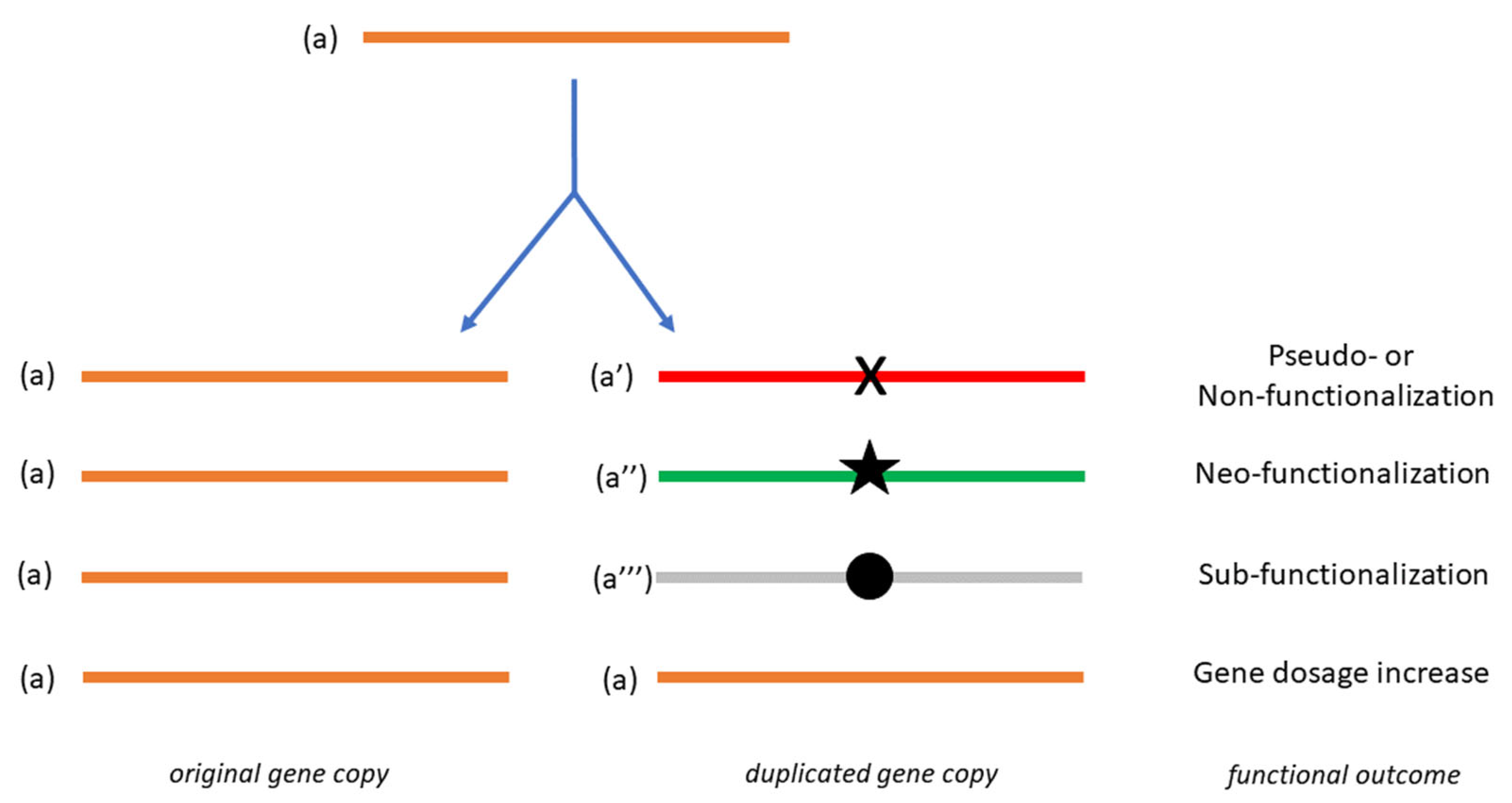
1. Essential Aspects of Gene Duplication
2. Genomes and Non-Coding DNA Content
3. Introns
4. Hypothesis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vosseberg, J.; van Hooff, J.J.E.; Marcet-Houben, M.; van Vlimmeren, A.; van Wijk, L.M.; Gabaldón, T.; Snel, B. Timing the origin of eukaryotic cellular complexity with ancient duplications. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.M.B.; Zhang, F.; Lupski, J.R. Genomic disorders: A window into human gene and genome evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuzmin, E.; Taylor, J.S.; Boone, C. Retention of duplicated genes in evolution. Trends Genet. 2021, 38, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The Evolutionary Fate and Consequences of Duplicate Genes. Science 2000, 290, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, S. Evolution by Gene Duplication; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, S. Gene duplication and the uniqueness of vertebrate genomes circa 1970–1999. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 10, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashov, F.A.; Kondrashov, A.S. Role of selection in fixation of gene duplications. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 239, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, B.; Antonarakis, S.E. Gene Duplication: A Drive for Phenotypic Diversity and Cause of Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2007, 8, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innan, H. Population genetic models of duplicated genes. Genetica 2009, 137, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; King, J.L. Fixation of a deleterious allele at one of two “duplicate” loci by mutation pressure and random drift. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 2858–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.H. Rate of gene silencing at duplicate loci: A theoretical study and interpretation of data from tetraploid fishes. Genetics 1980, 95, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Pavelitz, T.; Kidd, J.R.; Kidd, K.K.; Weiner, A.M. Concerted evolution of the tandemly repeated genes encoding human U2 snRNA (the RNU2 locus) involves rapid intrachromosomal homogenization and rare interchromosomal gene conversion. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondrashov, F.A.; Rogozin, I.B.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Selection in the evolution of gene duplications. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0008.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Innan, H.; Kondrashov, F. The evolution of gene duplications: Classifying and distinguishing between models. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.H.; Woods, P.S.; Hughes, W.L. The Organization and Duplication of Chromosomes as Revealed by Autoradiographic Studies Using Tritium-Labeled Thymidinee. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1957, 43, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smithies, O. Chromosomal Rearrangements and Protein Structure. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1964, 29, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszul, R.; Caburet, S.; Dujon, B.; Fischer, G. Eucaryotic genome evolution through the spontaneous duplication of large chromosomal segments. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellis, M.; Birren, B.W.; Lander, E.S. Proof and evolutionary analysis of ancient genome duplication in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 2004, 428, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Shields, D.C. Molecular evidence for an ancient duplication of the entire yeast genome. Nature 1997, 387, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L.; Friedman, R.; Ekollu, V.; Rose, J.R. Non-random association of transposable elements with duplicated genomic blocks in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdobnov, E.M.; von Mering, C.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Consistency of genome-based methods in measuring Metazoan evolution. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3355–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrne, K.P.; Wolfe, K.H. The Yeast Gene Order Browser: Combining curated homology and syntenic context reveals gene fate in polyploid species. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.-M.; Noel, B.; Policriti, A.; Clepet, C.; Casagrande, A.; Choisne, N.; Aubourg, S.; Vitulo, N.; Jubin, C.; et al. The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 2007, 449, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuskan, G.A.; Difazio, S.; Jansson, S.; Bohlmann, J.; Grigoriev, I.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; Ralph, S.; Rombauts, S.; Salamov, A.; et al. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 2006, 313, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sémon, M.; Wolfe, K.H. Preferential subfunctionalization of slow-evolving genes after allopolyploidization in Xenopus laevis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8333–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papp, B.; Pál, C.; Hurst, L.D. Dosage sensitivity and the evolution of gene families in yeast. Nature 2003, 424, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.A. The genetic organization of chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1971, 5, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Nuclear volume control by nucleoskeletal DNA, selection for cell volume and cell growth rate, and the solution of the DNA c-value paradox. J. Cell Sci. 1978, 34, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, K.; Egan, E. Non-coding RNA: More uses for genomic junk. Nature 2017, 543, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, G. The Genomic Code: A Pervasive Encoding/Molding of Chromatin Structures and a Solution of the “Non-Coding DNA” Mystery. Bioessays 2019, 41, e1900106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolondi, A.; Caldarelli, F.; Di Felice, F.; Durano, D.; Germani, G.; Michetti, L.; Tramutolo, A.; Micheli, G.; Camilloni, G. What is a Gene? A Two Sided View. Evol. Biol. 2017, 44, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beadle, G.W.; Tatum, E.L. Neurospora. II. Methods of Producing and Detecting Mutations Concerned with Nutritional Requirements. Am. J. Bot. 1945, 32, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berget, S.M.; Moore, C.; Sharp, P.A. Spliced segments at the 5’ terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 3171–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, L.T.; Gelinas, R.E.; Broker, T.R.; Roberts, R.J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5’ ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell 1977, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, M.; Roy, S.W. Origin of Spliceosomal Introns and Alternative Splicing. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.A.; Stajich, J.E.; Field, D.J.; Olive, J.E.; DeAbreu, D.M. The low information content of Neurospora splicing signals: Implications for RNA splicing and intron origin. RNA 2015, 21, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Intron phylogeny: A new hypothesis. Trends Genet. 1991, 7, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Selfish DNA and the origin of introns. Nature 1985, 315, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A.M.; Zimmerly, S. Group II introns: Mobile ribozymes that invade DNA. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V. The origin of introns and their role in eukaryogenesis: A compromise solution to the introns-early versus introns-late debate? Biol. Direct 2006, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabut, M.; Samavarchi-Tehrani, P.; Wang, X.; Slobodeniuc, V.; O’Hanlon, D.; Sung, H.-K.; Alvarez, M.; Talukder, S.; Pan, Q.; Mazzoni, E.O.; et al. An alternative splicing switch regulates embryonic stem cell pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell 2011, 147, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, A.J. Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: Developmental consequences and mechanisms of regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1998, 32, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, P.M.; Chou, T.B.; Mims, I.; Zachar, Z. On/off regulation of gene expression at the level of splicing. Trends Genet. 1988, 4, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.; Lim, Z.Q.; Khandelia, P.; Friedman, B.; Makeyev, E.V. Coordinated regulation of neuronal mRNA steady-state levels through developmentally controlled intron retention. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, W. Why genes in pieces? Nature 1978, 271, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamary, J.-V.; Hurst, L.D. Similar rates but different modes of sequence evolution in introns and at exonic silent sites in rodents: Evidence for selectively driven codon usage. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Micheli, G.; Camilloni, G. Can Introns Stabilize Gene Duplication? Biology 2022, 11, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060941
Micheli G, Camilloni G. Can Introns Stabilize Gene Duplication? Biology. 2022; 11(6):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060941
Chicago/Turabian StyleMicheli, Gioacchino, and Giorgio Camilloni. 2022. "Can Introns Stabilize Gene Duplication?" Biology 11, no. 6: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060941
APA StyleMicheli, G., & Camilloni, G. (2022). Can Introns Stabilize Gene Duplication? Biology, 11(6), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060941







