Development of Optimal Digesting Conditions for Microplastic Analysis in Dried Seaweed Gracilaria fisheri
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Contamination Control
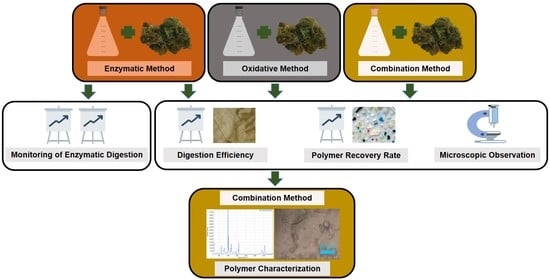
2.3. Optimization of Digestion Method
2.3.1. Enzymatic Method
2.3.2. Oxidative Method
2.3.3. Combination Method
2.4. Monitoring of Enzymatic Digestion
2.4.1. DNS Assay
2.4.2. TNBS Assay
2.5. Digestion Efficiency and Polymer Recovery Rate
2.6. Polymer Characterization
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enzymatic Method
3.2. Oxidative Method
3.3. Combination Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannah Ritchie, M.R. Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/plastic-pollution (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.; Hollman, P.; Mandoza-Hill, J. Microplastics in fisheries and aquaculture. FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Pap. 2017, 615, 127. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Bristow, K.; Filipović, V.; Lv, J.; He, H. Microplastics in Terrestrial Ecosystems: A Scientometric Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Park, J.; Md Din, M.F.; Mat Taib, S.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Kumar Yadav, K.; Kamyab, H. Microplastics pollution in different aquatic environments and biota: A review of recent studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-C.; Walther, B.A. Microplastic Contamination of Three Commonly Consumed Seafood Species from Taiwan: A Pilot Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Pham, T.D.; Tarafdar, A.; Hong, S.; Chun, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, D.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.B.; et al. Microplastics in Food: A Review on Analytical Methods and Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental development of a new protocol for extraction and characterization of microplastics in fish tissues: First observations in commercial species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, J.; Frias, J.; Nash, R. Quantification of microplastic ingestion by the decapod crustacean Nephrops norvegicus from Irish waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathalon, A.; Hill, P. Microplastic fibers in the intertidal ecosystem surrounding Halifax Harbor, Nova Scotia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Piazza, V.; Lavorano, S.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F.; Gambardella, C. Trophic Transfer of Microplastics from Copepods to Jellyfish in the Marine Environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannilli, V.; Pasquali, V.; Setini, A.; Corami, F. First evidence of microplastics ingestion in benthic amphipods from Svalbard. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelms, S.E.; Galloway, T.S.; Godley, B.J.; Jarvis, D.S.; Lindeque, P.K. Investigating microplastic trophic transfer in marine top predators. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan Alexander, M.B.; Cottrill, B.; Grasl-Kraupp, B. Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osseiran, N.; Lindmeier, C. WHO Calls for More Research into Microplastics and a Crackdown on Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/22-08-2019-who-calls-for-more-research-into-microplastics-and-a-crackdown-on-plastic-pollution (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Schwabl, P.; Koppel, S.; Konigshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Various Microplastics in Human Stool: A Prospective Case Series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usman, S.; Abdull Razis, A.F.; Shaari, K.; Amal, M.N.A.; Saad, M.Z.; Mat Isa, N.; Nazarudin, M.F.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Sutra, J.; Ibrahim, M.A. Microplastics Pollution as an Invisible Potential Threat to Food Safety and Security, Policy Challenges and the Way Forward. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; Romano, N.; Ho, Y.B.; Salamatinia, B. A high-performance protocol for extraction of microplastics in fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; Welden, N.A.; Sobral, P.; Cole, M. Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiele, C.J.; Hudson, M.D.; Russell, A.E. Evaluation of existing methods to extract microplastics from bivalve tissue: Adapted KOH digestion protocol improves filtration at single-digit pore size. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokhun, N.; Somparn, A. Microplastic Contaminations in Buffet Food from Local Markets. Naresuan Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Catarino, A.I.; Thompson, R.; Sanderson, W.; Henry, T.B. Development and optimization of a standard method for extraction of microplastics in mussels by enzyme digestion of soft tissues. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Murphy, F.; Gary, S.F.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Optimisation of enzymatic digestion and validation of specimen preservation methods for the analysis of ingested microplastics. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Friesen, L.W.; Granberg, M.E.; Hassellov, M.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Magnusson, K. An efficient and gentle enzymatic digestion protocol for the extraction of microplastics from bivalve tissue. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, S.; Brinker, A. Rapid and Efficient Method for the Detection of Microplastic in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Fishes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4522–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri Conti, G.; Ferrante, M.; Banni, M.; Favara, C.; Nicolosi, I.; Cristaldi, A.; Fiore, M.; Zuccarello, P. Micro- and nano-plastics in edible fruit and vegetables. The first diet risks assessment for the general population. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Shi, H. Microplastics in the commercial seaweed nori. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 388, 122060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, M.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vandegehuchte, M.B.; Janssen, C.R. New techniques for the detection of microplastics in sediments and field collected organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, F.; Fischer, E.K. Various Digestion Protocols Within Microplastic Sample Processing—Evaluating the Resistance of Different Synthetic Polymers and the Efficiency of Biogenic Organic Matter Destruction. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuelle, M.T.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Lusher, A.L.; Olsen, M.; Nizzetto, L. Validation of a Method for Extracting Microplastics from Complex, Organic-Rich, Environmental Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7409–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phi, T.N. Cultivation Characteristics and Biological Responses of Agarophytic Seaweed, Gracilaria fisheri (Rhodophyta), in Southern Thailand. Ph.D. Thesis, Prince of Songkla University, Pattani Campus, Pattani, Thailand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sae-Lao, T.; Luplertlop, N.; Janvilisri, T.; Tohtong, R.; Bates, D.O.; Wongprasert, K. Sulfated galactans from the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri exerts anti-migration effect on cholangiocarcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2017, 36, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongprasert, K.; Rudtanatip, T.; Praiboon, J. Immunostimulatory activity of sulfated galactans isolated from the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri and development of resistance against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjama, O.; Masniyom, P. Biochemical composition and physicochemical properties of two red seaweeds (Gracilaria fisheri and G. tenuistipitata) from the Pattani Bay in Southern Thailand. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 34, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Arranz, K.; Urrutxurtu, I.; Prieto, D.; Ibarrola, I.; Urrutia, M.B.; Navarro, E. Methods for assessment of body tissue composition as an indication of the energetic status in bivalve populations: A comparison of biochemical and elemental analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutow, L.; Eckerlebe, A.; Gimenez, L.; Saborowski, R. Experimental Evaluation of Seaweeds as a Vector for Microplastics into Marine Food Webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.N.; Lee, S.J.; Sung, H.J. A lubricant-infused slip surface for drag reduction. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 091901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beine, R.L. Plants. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; Latimer, G.W., Ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dehaut, A.; Hermabessiere, L.; Duflos, G. Current frontiers and recommendations for the study of microplastics in seafood. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Morrissey, M.T. Protein Hydrolysates from Pacific Whiting Solid Wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaut, A.; Cassone, A.L.; Frere, L.; Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Rinnert, E.; Riviere, G.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P.; Huvet, A.; et al. Microplastics in seafood: Benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Azzawi, M.S.M.; Kefer, S.; Weißer, J.; Reichel, J.; Schwaller, C.; Glas, K.; Knoop, O.; Drewes, J.E. Validation of Sample Preparation Methods for Microplastic Analysis in Wastewater Matrices—Reproducibility and Standardization. Water 2020, 12, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Sayas, T.; Bucki, P.; Brown-Miyara, S.; Kleiman, M. Real-Time Visualization of Cellulase Activity by Microorganisms on Surface. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; Munno, K.; Hermabessiere, L.; Carr, S. Isolation and Extraction of Microplastics from Environmental Samples: An Evaluation of Practical Approaches and Recommendations for Further Harmonization. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunraksa, N.; Rattanasansri, S.; Praiboon, J.; Chirapart, A. Proximate composition and the production of fermentable sugars, levulinic acid, and HMF from Gracilaria fisheri and Gracilaria tenuistipitata cultivated in earthen ponds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 31, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zimmermann, W. Microbial enzymes for the recycling of recalcitrant petroleum-based plastics: How far are we? Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Railo, S.; Talvitie, J.; Setala, O.; Koistinen, A.; Lehtiniemi, M. Application of an enzyme digestion method reveals microlitter in Mytilus trossulus at a wastewater discharge area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Girao, A.V.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Identifying a quick and efficient method of removing organic matter without damaging microplastic samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, B.E.; Proudfoot, A.T.; Vale, J.A. Hydrogen Peroxide Poisoning. Toxicol. Rev. 2004, 23, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck Millipore Home Page. Available online: https://www.merckmillipore.com/TH/en/product/Hydrogen-peroxide-300-0,MDA_CHEM-107209 (accessed on 24 August 2021).
- Islam, M.; Sarkar, P.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Suzauddula, M. Optimization of fermentation condition for cellulase enzyme production from Bacillus sp. Malays. J. Halal Res. 2019, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razzaq, A.; Shamsi, S.; Ali, A.; Ali, Q.; Sajjad, M.; Malik, A.; Ashraf, M. Microbial Proteases Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdulhameed, S.; Pandey, A. Purification and Characterization of Tannin Acyl Hydrolase from Aspergillus niger ATCC 16620. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 43, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Loder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamoah, B.O.; Uurasjarvi, E.; Raty, J.; Koistinen, A.; Roussey, M.; Peiponen, K.E. Towards the Development of Portable and In Situ Optical Devices for Detection of Micro and Nanoplastics in Water: A Review on the Current Status. Polymers 2021, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappler, A.; Fischer, D.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Schernewski, G.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Voit, B. Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8377–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loder, M.G.J.; Imhof, H.K.; Ladehoff, M.; Loschel, L.A.; Lorenz, C.; Mintenig, S.; Piehl, S.; Primpke, S.; Schrank, I.; Laforsch, C.; et al. Enzymatic Purification of Microplastics in Environmental Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14283–14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbachu, O.; Jenkins, G.; Pratt, C.; Kaparaju, P. Enzymatic purification of microplastics in soil. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Digestion Condition | Digestion Efficiency (%) | Polymer Recovery Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1% (v/v) cellulase and 5% (v/v) protease | 59.3 ± 2.0 a | 98.9 ± 0.5 b |
| 3% (v/v) cellulase and 5% (v/v) protease | 61.6 ± 1.3 b | 95.3 ± 1.3 a |
| 5% (v/v) cellulase and 5% (v/v) protease | 63.7 ± 1.2 c | 94.7 ± 0.8 a |
| Sample | Digestion Time (h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | |
| Digestion Efficiency (%) | ||||||
| OD50 | 93.0 ± 0.3 aA | 93.5 ± 0.4 aAB | 93.9 ± 0.7 aB | 95.0 ± 0.2 aC | 95.2 ± 0.3 aC | 94.1 ± 0.3 aB |
| OD100 | 93.4 ± 0.3 aA | 93.8 ± 0.3 aAB | 95.3 ± 0.5 bC | 95.8 ± 0.3 bCD | 96.3 ± 0.2 bD | 94.2 ± 0.8 aB |
| Polymer Recovery Rate (%) | ||||||
| Positive control | 98.7 ± 0.9 A | 99.1 ± 2.9 A | 98.9 ± 10.8 A | 98.6 ± 0.6 A | 98.3 ± 3.1 A | 97.6 ± 3.6 A |
| Digestion Method | Digestion Efficiency (%) | Polymer Recovery Rate (%) | Digestion Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic method 1% (v/v) cellulase and 5% (v/v) protease | 59.3 ± 2.0 a | 98.8 ± 0.5 a | 30 |
| Oxidative method OD100 | 96.3 ± 0.2 b | 98.3 ± 3.1 a | 72 |
| Combination method | 97.4 ± 0.5 b | 99.7 ± 0.1 a | 38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prihandari, R.; Karnpanit, W.; Kittibunchakul, S.; Kemsawasd, V. Development of Optimal Digesting Conditions for Microplastic Analysis in Dried Seaweed Gracilaria fisheri. Foods 2021, 10, 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092118
Prihandari R, Karnpanit W, Kittibunchakul S, Kemsawasd V. Development of Optimal Digesting Conditions for Microplastic Analysis in Dried Seaweed Gracilaria fisheri. Foods. 2021; 10(9):2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092118
Chicago/Turabian StylePrihandari, Rizky, Weeraya Karnpanit, Suwapat Kittibunchakul, and Varongsiri Kemsawasd. 2021. "Development of Optimal Digesting Conditions for Microplastic Analysis in Dried Seaweed Gracilaria fisheri" Foods 10, no. 9: 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092118
APA StylePrihandari, R., Karnpanit, W., Kittibunchakul, S., & Kemsawasd, V. (2021). Development of Optimal Digesting Conditions for Microplastic Analysis in Dried Seaweed Gracilaria fisheri. Foods, 10(9), 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092118