Dual RNA-Seq Reveals Temperature-Mediated Gene Reprogramming and Molecular Crosstalk between Grapevine and Lasiodiplodia theobromae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungus, Plant Materials and Culture Conditions
2.2. Pathogenicity Tests on Detached Green Shoots
2.3. Library Construction and Dual RNA-Seq
2.4. Gene Co-Transcribed Network between Grapevine and L. theobromae
2.5. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analyses
2.6. Real-Time qPCR Analyses
3. Results
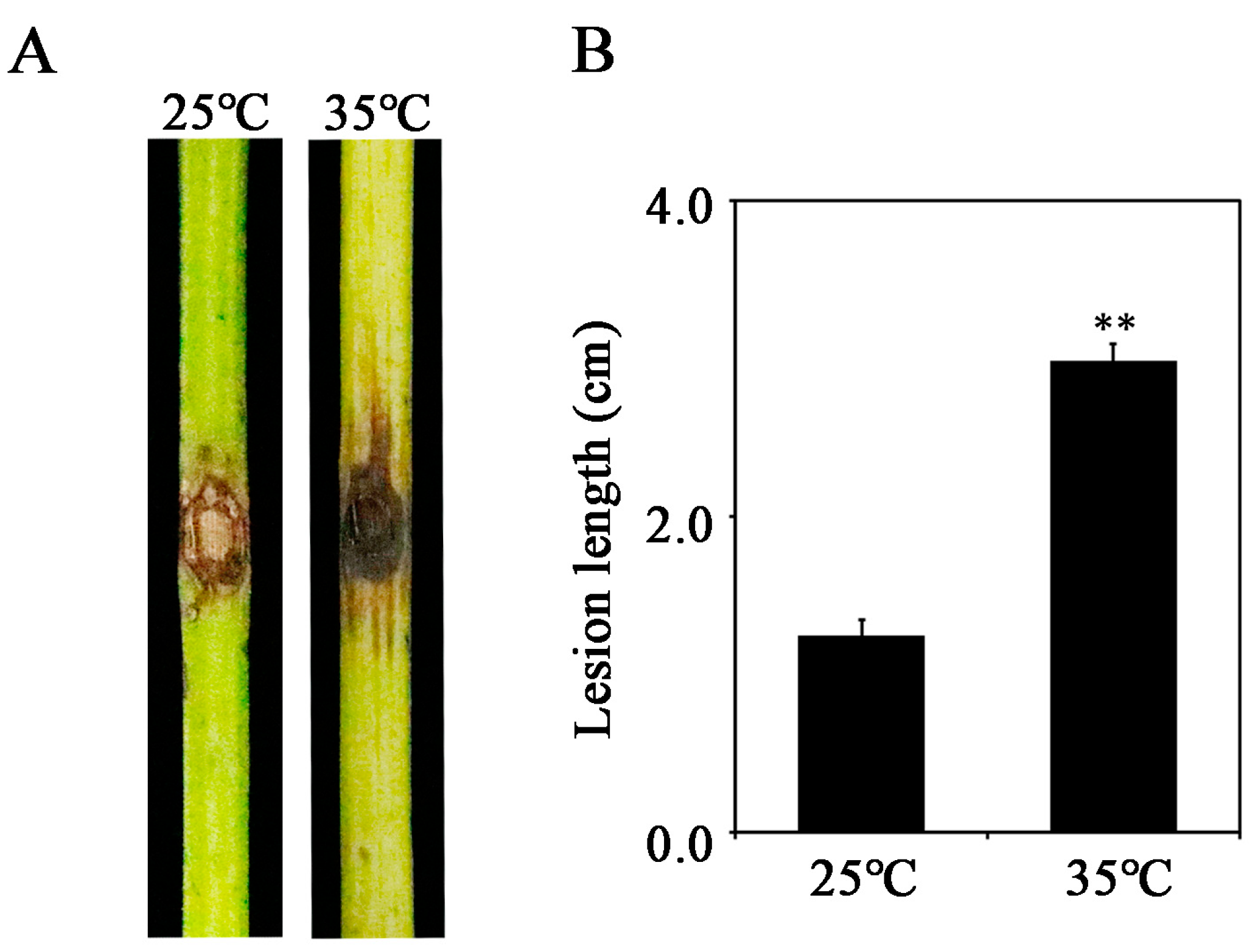
3.1. Disease Development under Different Temperatures
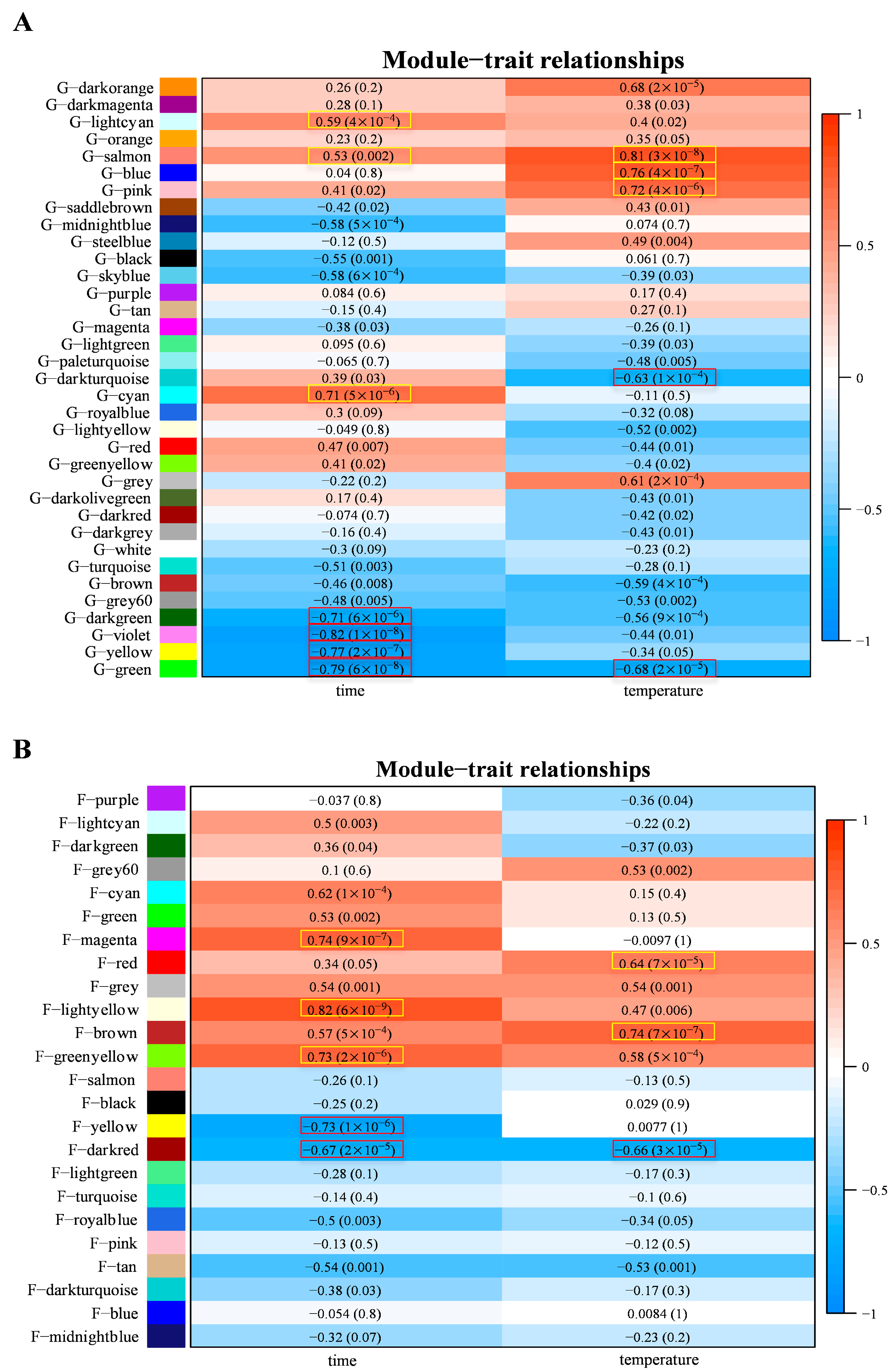
3.2. Identification of Grapevine and Fungal Gene Modules That Are Correlated with Infection Time and Temperature
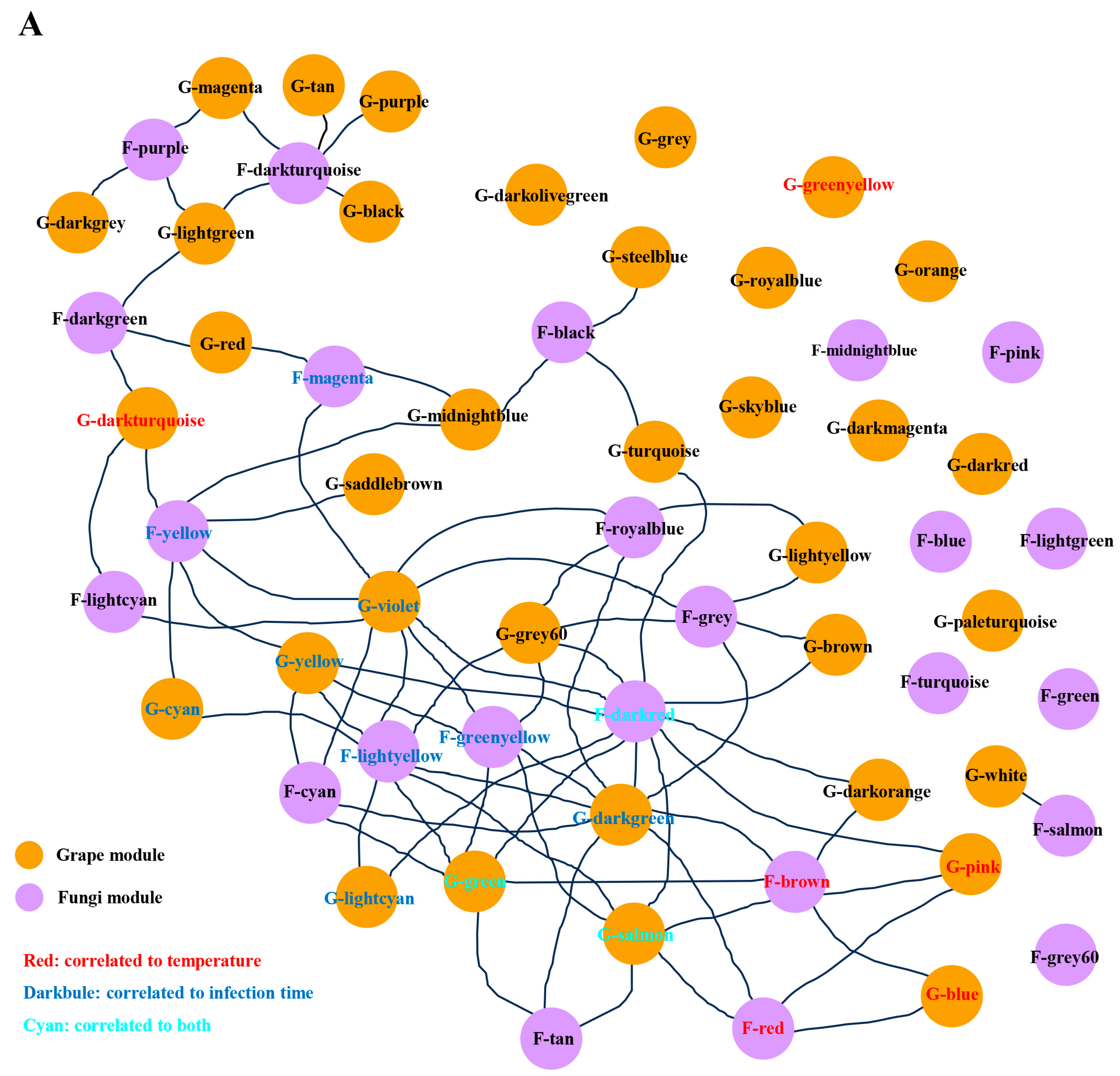
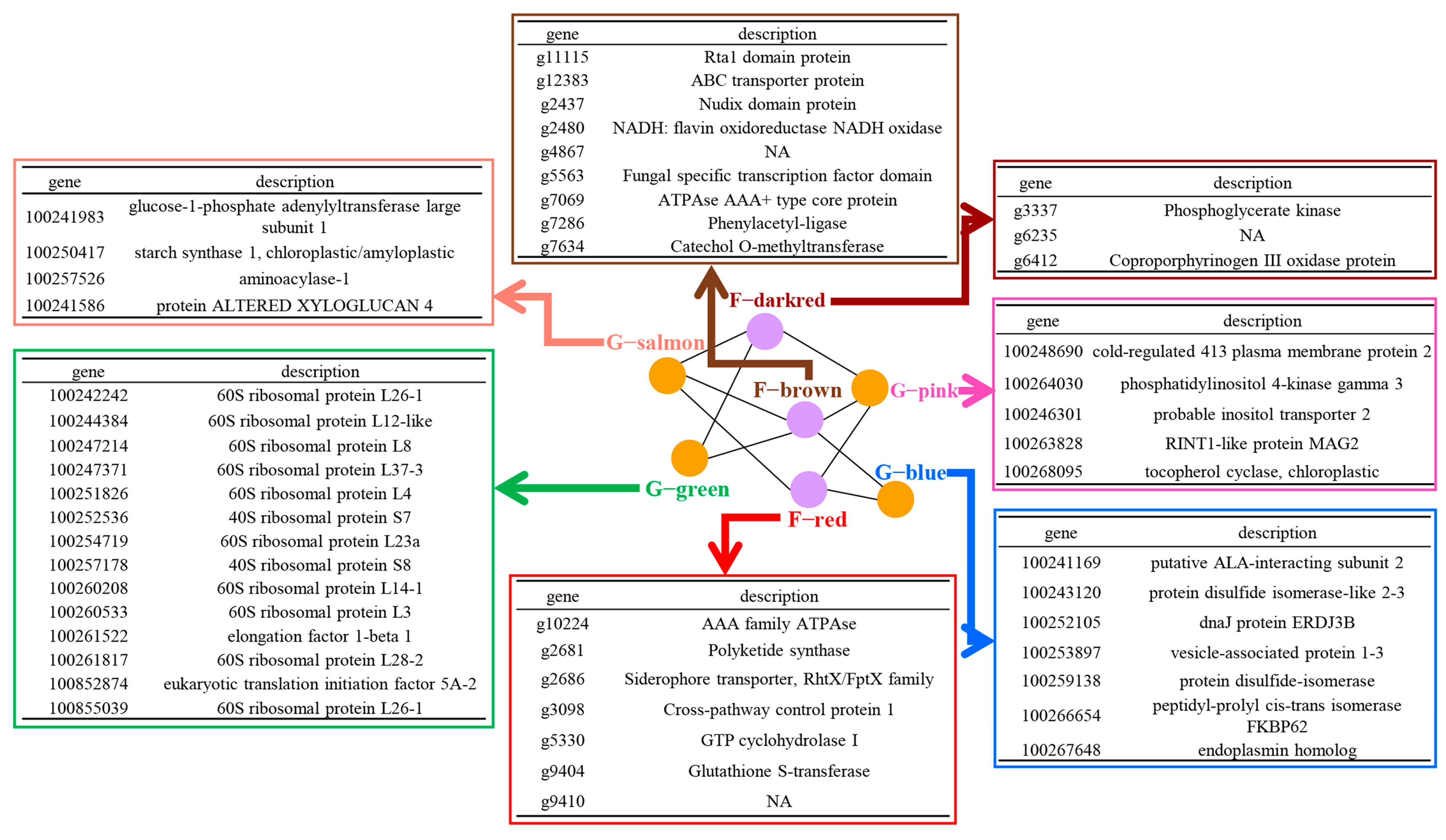
3.3. Gene Co-Transcribed Networks as an Efficient Tool to Decipher the Molecular Interactions between Grapevine and L. theobromae
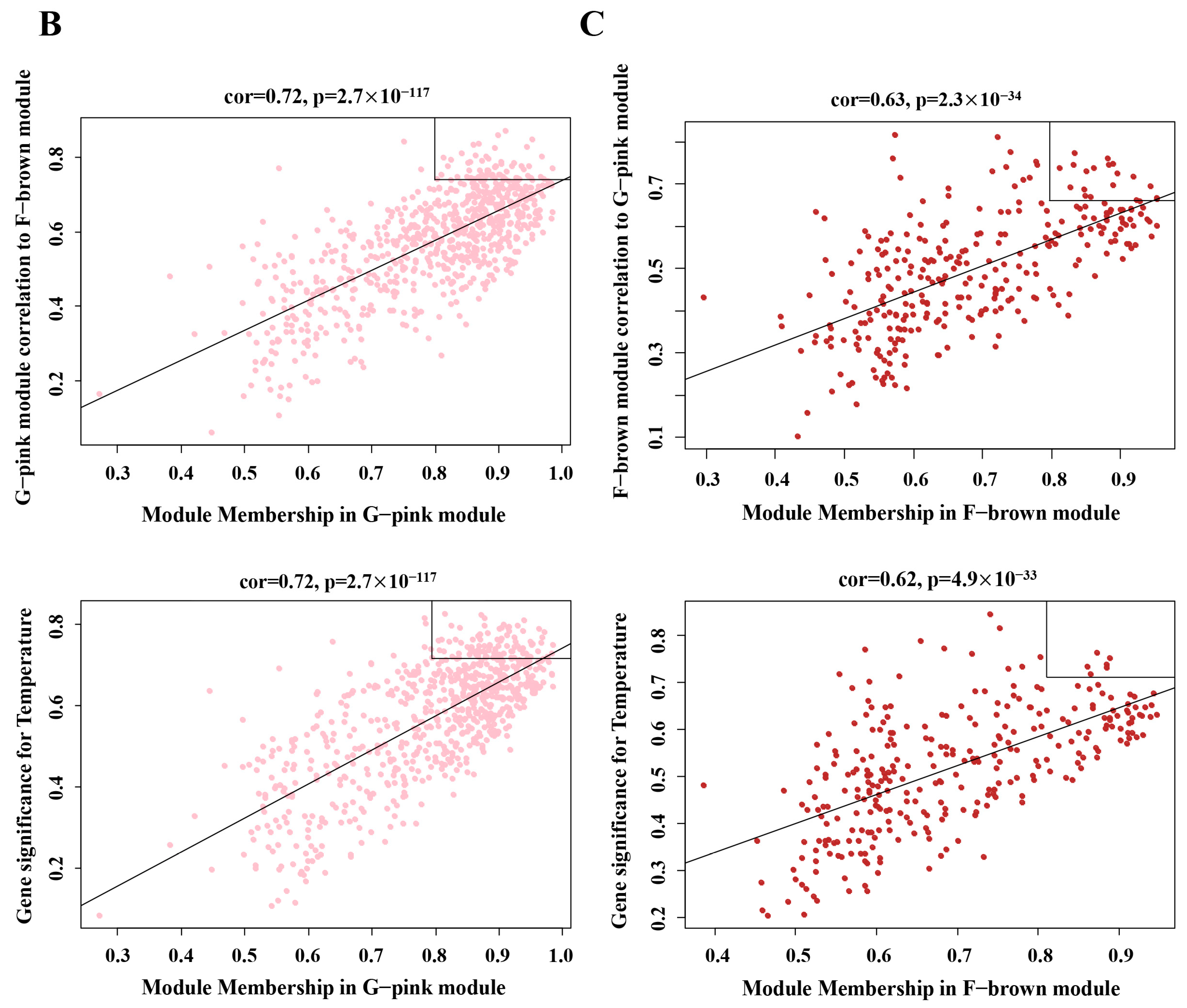
3.4. Grapevine and L. theobromae Gene Modules Correlated to Temperature
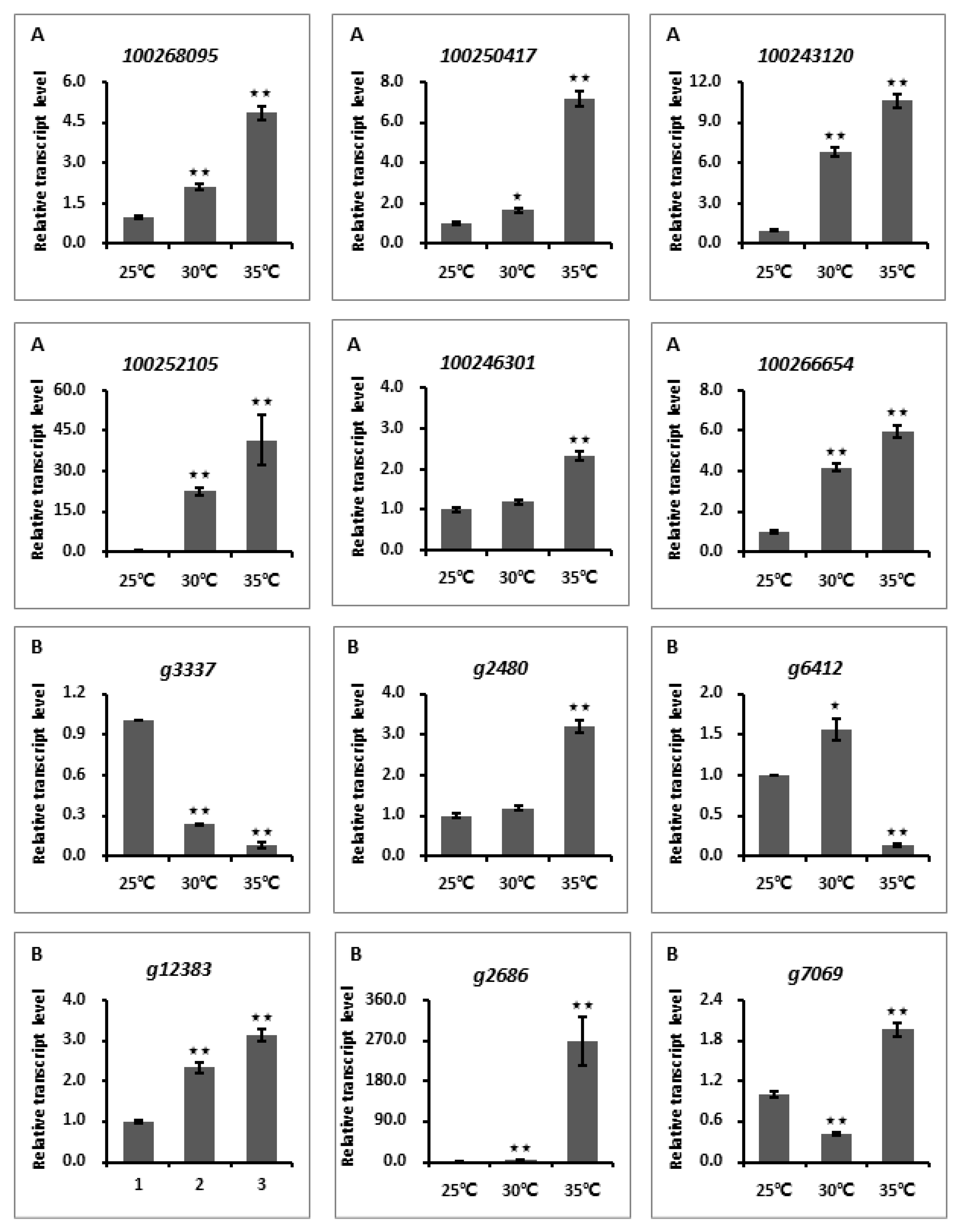
3.5. Transcription Analyses of Temperature-Responsive Genes within Grapevine and L. theobromae Gene Modules
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Úrbez-Torres, J.R.; Leavitt, G.M.; Guerrero, J.C.; Guevara, J.; Gubler, W.D. Identification and pathogenicity of Lasiodiplodia theobromae and Diplodia seriata, the causal agents of bot canker disease of grapevines in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Hsiang, T.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Lasiodiplodia theobromae-induced alteration in ROS metabolism and its relation to gummosis development in Prunus persica. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 154, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda-Shakirah, A.R.; Nor, N.M.I.M.; Zakaria, L.; Leong, Y.-H.; Mohd, M.H. Lasiodiplodia theobromae as a causal pathogen of leaf blight, stem canker, and pod rot of Theobroma cacao in Malaysia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanesh, B.N.; Arunakumar, G.S.; Tejaswi, A.; Supriya, M.; Manojkumar, H.B.; Devi, S.S. Characterization and pathogenicity of Lasiodiplodia theobromae causing black root rot and identification of novel sources of resistance in mulberry collections. Plant Pathol. J. 2022, 38, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, H.; Lin, M.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Shi, J. Lasiodiplodia theobromae (Pat.) Griff. & Maubl. reduced energy status and ATPase activity and its relation to disease development and pericarp browning of harvested longan fruit. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Leng, J.; Yu, L.; Bai, H.; Li, X.; Wisniewski, M.; Liu, J.; Sui, Y. Efficacy of the biocontrol agent Trichoderma hamatum against Lasiodiplodia theobromae on macadamia. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 994422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Asman, A.; Shao, J.; Balidion, J.F.; Strem, M.D.; Puig, A.S.; Meinhardt, L.W.; Bailey, B.A. Genome and transcriptome analysis of the latent pathogen Lasiodiplodia theobromae, an emerging threat to the cacao industry. Genome 2020, 63, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.-K.; Hyde, K.D.; Seem, R.C.; Zhang, G.-Z.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yao, S.-W.; et al. Species of Botryosphaeriaceae involved in grapevine dieback in China. Fungal Divers. 2013, 61, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, A.; Cibelli, F.; Lops, F.; Raimondo, M.L. Characterization of Botryosphaeriaceae species as causal agents of trunk diseases on grapevines. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Pierron, R.; Larignon, P.; Lecomte, P.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Farine, S.; Bertsch, C.; Jacques, A.; Trotel-Aziz, P.; Rego, C.; et al. Vitis methods to understand and develop strategies for diagnosis and sustainable control of grapevine trunk diseases. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethana, K.W.T.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Hyde, K.D.; Yan, J. Trail of decryption of molecular research on Botryosphaeriaceae in woody plants. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2016, 55, 147–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; He, S.Y. Plant-microbe interactions facing environmental challenge. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Leach, J.E. High temperature-induced plant disease susceptibility: More than the sum of its parts. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 56, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Qian, W.; Hua, J. Temperature modulates plant defense responses through NB-LRR proteins. PLOS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, A.; Li, H.; Weingart, H.; Aufhammer, S.; Burse, A.; Finis, K.; Schenk, A.; Ullrich, M.S. Thermoregulated expression of virulence factors in plant-associated bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2001, 176, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Hua, J.; Hu, Y.; Tao, F.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Analysis of temperature modulation of plant defense against biotrophic microbes. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez, A.C.; Castroverde, C.D.M.; He, S.Y. Plant-pathogen warfare under changing climate conditions. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R619–R634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Chatterjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. Elevated temperature enhances virulence of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora strain EC153 to plants and stimulates production of the quorum sensing signal, N-acyl homoserine lactone, and extracellular proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4655–4663. [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, K.; Fouts, D.E.; Rehm, A.H.; Hill, A.R.; Collmer, A.; Alfano, J.R. The Avr (effector) proteins HrmA (HopPsyA) and AvrPto are secreted in culture from Pseudomonas syringae pathovars via the Hrp (type III) protein secretion system in a temperature- and pH-sensitive manner. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingart, H.; Stubner, S.; Schenk, A.; Ullrich, M.S. Impact of temperature on in planta expression of genes involved in synthesis of the Pseudomonas syringae phytotoxin coronatine. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 2004, 17, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang, H.-G.; Qian, W.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, J.; Kang, H.-G.; Klessig, D.F.; Hua, J. Abscisic acid deficiency antagonizes high-temperature inhibition of disease resistance through enhancing nuclear accumulation of resistance proteins SNC1 and RPS4 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, K.M.; Oña, I.; Bai, J.; Garrett, K.A.; Mew, T.; Vera Cruz, C.M.; Leach, J.E. A benefit of high temperature: Increased effectiveness of a rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene. New Phytol. 2010, 185, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Liu, H.; Argueso, C.T.; Pereira, A.; Cruz, C.V.; Verdier, V.; Leach, J.E. RNA-Seq analysis reveals insight into enhanced rice Xa7-mediated bacterial blight resistance at high temperature. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huot, B.; Castroverde, C.D.M.; Velásquez, A.C.; Hubbard, E.; Pulman, J.A.; Yao, J.; Childs, K.L.; Tsuda, K.; Montgomery, B.L.; He, S.Y. Dual impact of elevated temperature on plant defence and bacterial virulence in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, X.; Feng, B.; Sheen, J.; Shan, L.; He, P. Plant immune response to pathogens differs with changing temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, Y.; Loo, E.P. Plant immunity in signal integration between biotic and abiotic stress responses. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.-F.; Kvitko, B.; He, S.Y. Pseudomonas syringae: What it takes to be a pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songy, A.; Fernandez, O.; Clément, C.; Larignon, P.; Fontaine, F. Grapevine trunk diseases under thermal and water stresses. Planta 2019, 249, 1655–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, C.; Meneses, R.; Gonçalves, M.F.M.; Tilleman, L.; Duarte, A.S.; Jorrín-Novo, J.V.; Van de Peer, Y.; Deforce, D.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Esteves, A.C.; et al. A multi-omics analysis of the grapevine pathogen Lasiodiplodia theobromae reveals that temperature affects the expression of virulence- and pathogenicity-related genes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, I.D.; Masclaux, F.G.; Aletti, C.; Rojas, E.C.; Savary, R.; Dupuis, C.; Sanders, I.R. Dual RNA-seq reveals large-scale non-conserved genotype × genotype-specific genetic reprograming and molecular crosstalk in the mycorrhizal symbiosis. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, A.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Genome Sequence Archive Family: Toward explosive data growth and diverse data types. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners. Database Resources of the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation in 2022. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, D27–D38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.Y.; Zhao, W.S.; Chen, Z.; Xing, Q.K.; Zhang, W.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Xue, M.F.; Xu, J.P.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Comparative genome and transcriptome analyses reveal adaptations to opportunistic infections in woody plant degrading pathogens of Botryosphaeriaceae. DNA Res. 2018, 25, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.F.M.; Nunes, R.B.; Tilleman, L.; Van de Peer, Y.; Deforce, D.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Esteves, A.C.; Alves, A. Dual RNA sequencing of Vitis vinifera during Lasiodiplodia theobromae infection unveils host-pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Xing, Q.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Zhao, W. Transcriptional response of grapevine to infection with the fungal pathogen Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Acero, F.J.; Colby, T.; Harzen, A.; Cantoral, J.M.; Schmidt, J. Proteomic analysis of the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea during cellulose degradation. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2892–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobos, R.; Barreiro, C.; Mateos, R.M.; Coque, J.J. Cytoplasmic- and extracellular-proteome analysis of Diplodia seriata: A phytopathogenic fungus involved in grapevine decline. Proteome Sci. 2010, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolinelli-Alfonso, M.; Villalobos-Escobedo, J.M.; Rolshausen, P.; Herrera-Estrella, A.; Galindo-Sánchez, C.; López-Hernández, J.F.; Hernandez-Martinez, R. Global transcriptional analysis suggests Lasiodiplodia theobromae pathogenicity factors involved in modulation of grapevine defensive response. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.B. Cultural practices in disease control. In Plant Pathology: An Advanced Treatise, Volume III: The Diseases Population Epidemics and Control; Horsfall, J.G., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK, 1960; pp. 357–429. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; Shi, H.; Naqvi, N.I.; Qian, Q.; Liang, Y.; Kou, Y. Warm temperature compromises JA-regulated basal resistance to enhance Magnaporthe oryzae infection in rice. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.F.; Bhakta, A.V.; Truesdell, G.M.; Pudlo, W.M.; Williamson, V.M. Evidence for a role of the N terminus and leucine-rich repeat region of the Mi gene product in regulation of localized cell death. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluthmuhandiram, J.V.S.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Zhang, W.; Peng, J.; Zhao, E.; Li, X.H.; N, S.; Yan, J. Impact of temperature variation on the phytotoxic secondary metabolite production by Lasiodiplodia theobromae. J. Phytopathol. 2021, 169, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstad, S.; Le Nguyen, A.-V.; Johnsson, A. The temperature dependence of porphyrin production in Propionibacterium acnes after incubation with 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and its methyl ester (m-ALA). Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2006, 5, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harishchandra, D.L.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Chethana, K.W.T.; Hyde, K.D.; Brooks, S.; Yan, J.; Peng, J. A LysM domain-containing protein LtLysM1 is important for vegetative growth and pathogenesis in woody plant pathogen Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 36, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Xing, Q.; Huang, C.; Yan, J. Dual RNA-Seq Reveals Temperature-Mediated Gene Reprogramming and Molecular Crosstalk between Grapevine and Lasiodiplodia theobromae. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121197
Peng J, Li Y, Xing Q, Huang C, Yan J. Dual RNA-Seq Reveals Temperature-Mediated Gene Reprogramming and Molecular Crosstalk between Grapevine and Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(12):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121197
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Junbo, Yonghua Li, Qikai Xing, Caiping Huang, and Jiye Yan. 2023. "Dual RNA-Seq Reveals Temperature-Mediated Gene Reprogramming and Molecular Crosstalk between Grapevine and Lasiodiplodia theobromae" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 12: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121197
APA StylePeng, J., Li, Y., Xing, Q., Huang, C., & Yan, J. (2023). Dual RNA-Seq Reveals Temperature-Mediated Gene Reprogramming and Molecular Crosstalk between Grapevine and Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Journal of Fungi, 9(12), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9121197






