Systematic Literature Review of Heuristic-Optimized Microgrids and Energy-Flexible Factories
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What optimization methods are currently used for:
- the optimal system sizing of microgrids (OSS);
- the optimization of electrical energy distribution to storage systems and consumers (EED); and
- the energy flexibilization of factories (EF)?
- What is the scope of the functionality of the models and optimization algorithms of the respective research approaches?
- To what extent do research approaches that integrate these three areas into a common use case already exist?
2. Foundations of Microgrids, Energy-Flexible Factories, and Optimization Concepts
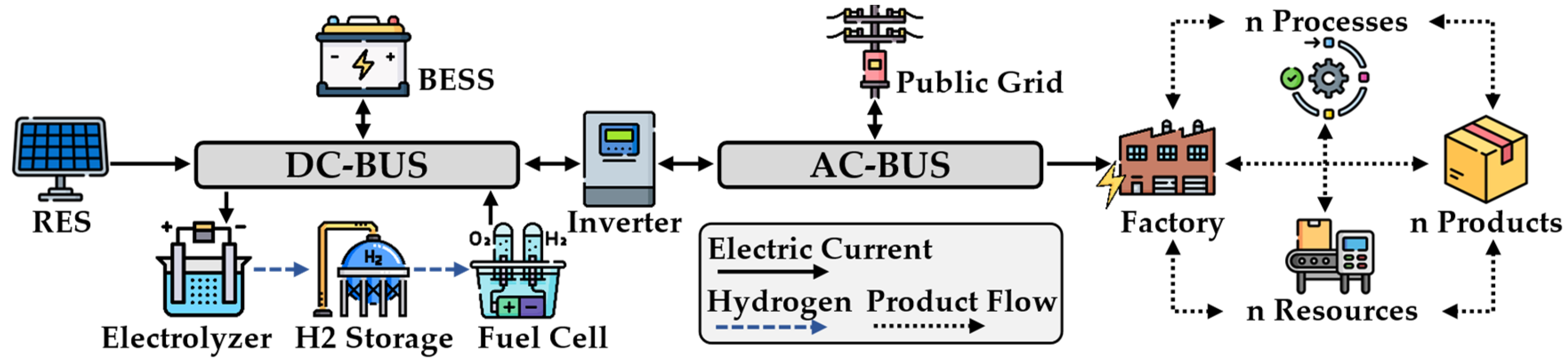
2.1. Introduction to Microgrids
2.2. Electrical Energy Distribution Strategies
2.3. Economic and Sustainable Optimization Objectives
2.4. Energy Flexible Factories
2.5. Basics of Simulation Models
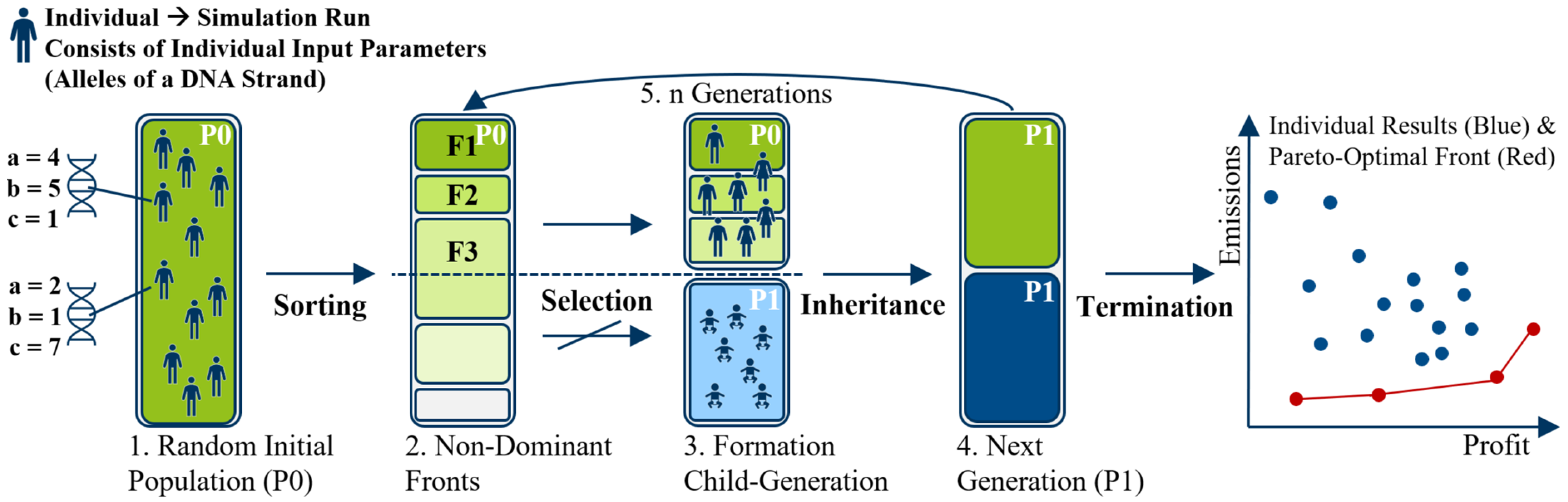
2.6. Introduction to Metaheuristic Optimization
3. Implementation of the Systematic Literature Review
3.1. Phase A—Comprehensive Collection of Literature
- For the SLR OSS search path, synonyms were chosen in the areas of hydrogen storage, decentralized energy supply, PV, BESS, and P2P systems, and methods for optimizing the MG component dimensions.
- For the SLR EED search path, functionalities related to load shifting, demand management, flexibility, dynamic pricing, and optimization were included.
- For the SLR EF search path, keywords were formulated in the areas of flexibility, resource scheduling, production planning, energy management, and factory decarbonization.
3.2. Phase B—Selection of Sources
4. Results
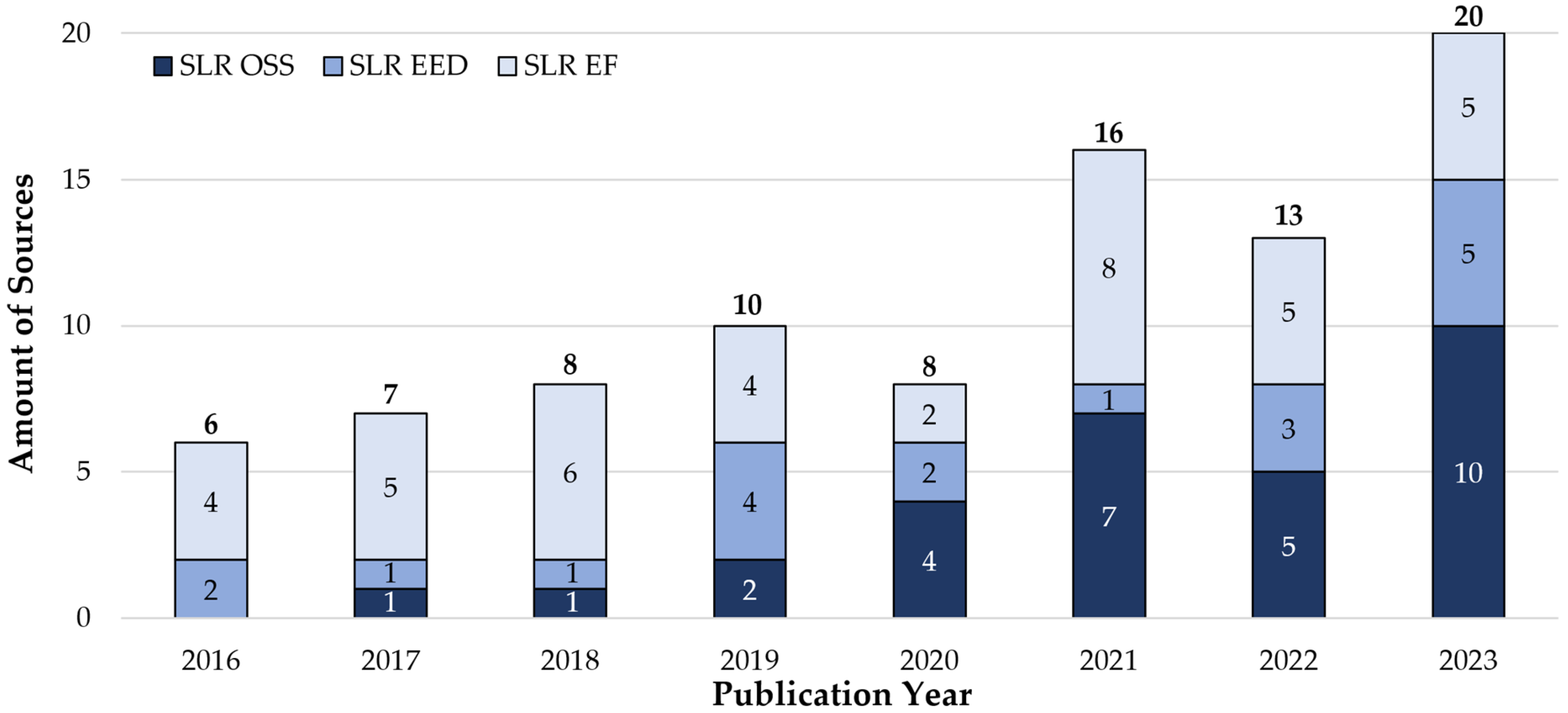
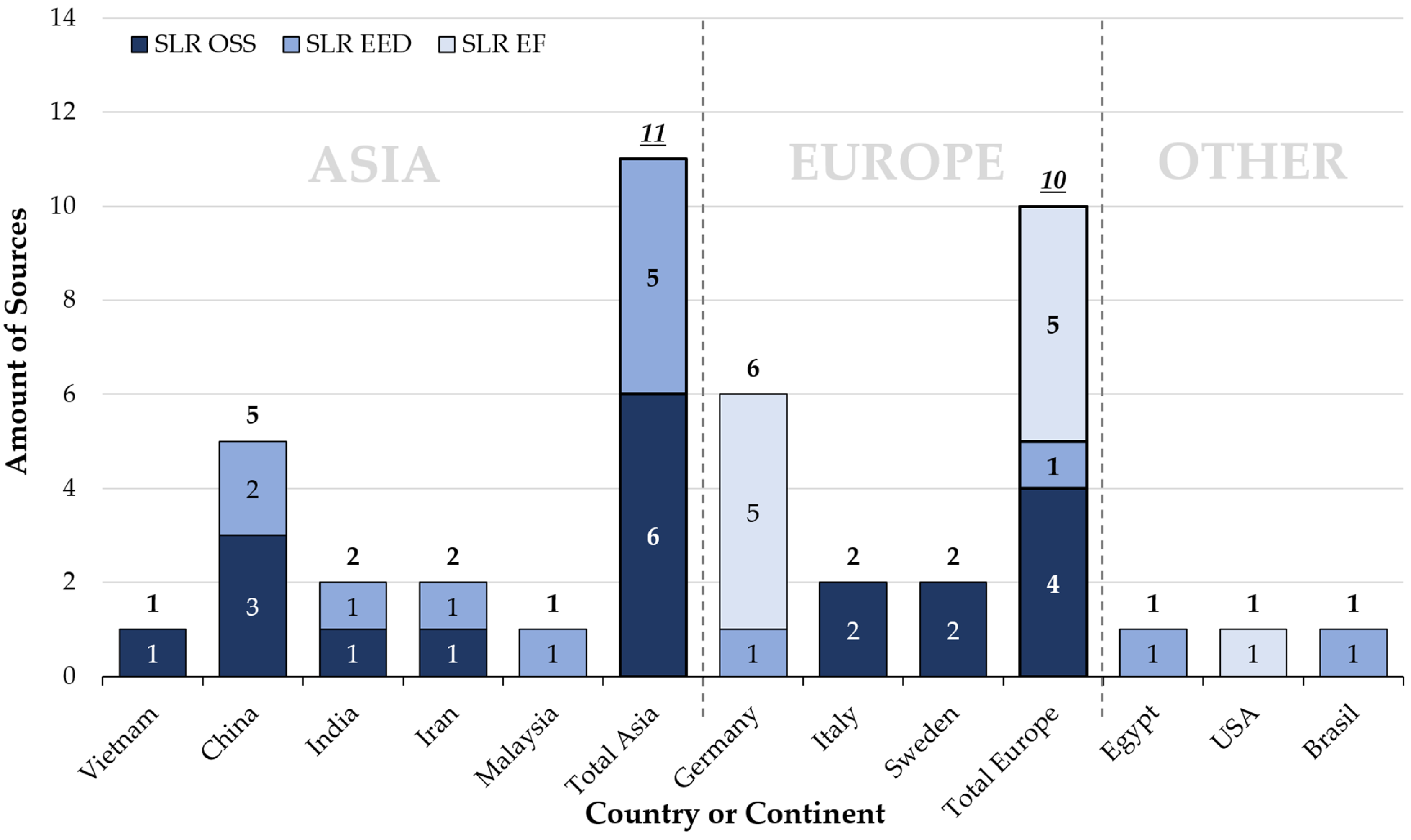
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
4.2. Individual Analysis
4.2.1. Analysis of the Research Area of the Optimal System Sizing of Microgrids
| Source | Ya. Zhang et al. [48] | Ya. Zhang [21] | Akhavan Shams et al. [43] | Singh et al. [44] | Yi. Zhang et al. [45] | Crespi et al. [51] | Crespi et al. [49] | Chen et al. [46] | Xing et al. [47] | Le et al. [50] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSS/EED/EF | ●/◑/○ | ●/◑/◑ | ●/○/○ | ●/○/○ | ●/○/○ | ●/◑/○ | ●/○/○ | ●/○/○ | ●/◑/○ | |
| GRID/PV/WT | ●/●/○ | ●/●/● | ●/●/○ | ●/●/● | ●/●/○ | ●/●/● | ●/●/● | ●/●/○ | ||
| BESS/P2P | ●/● | ●/● | ●/● | ●/● | ●/● | ○/● | ●/● | ●/● | ●/● | |
| Model Type | Dynamic | Deterministic | Dynamic | Stochastic | Deterministic | Deterministic | Deterministic | Dynamic | ||
| Steps; Period | 1 h; 25 a | 1 h; 20 a | 1 h; 20 a | 1 h; 1 a | 1 h; 1 a | 1 h; 6 a | 1 h; 30 a | 1 h; 25 a | ||
| Stage | Design, Operation | Design | Design | Design | Design, Operation | Design, Operation | Design | Design, Operation | ||
| Cost Model | NPV | NPV | NPV | NPV | NPV | NPV | NPV | NPV | ||
| Electricity Model | ToU, DAM, Fees | Fixed | ○ | ToU (Buying) | ToU | ToU, DAM | Fixed | ○ | ToU | |
| Sustainability Model | SSR | Social Costs | CO2 per kWh | SSR | SSR | SSR | SSR | SSR | ||
| Simulation Functionalities | ○ | * CHP | ○ | ○ | ○ | Ramp-Up | H2 Sale | ○ | Degradation | |
| Stochastics | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| Metaheuristic | Genetic Algorithm | Genetic Algorithm [OSS] | ABC-PO [OSS] | NSGA-II [OSS] | ○ | MOPSO [OSS] | PSO and NSGA-II [OSS] | MOMFA [OSS/EED] | ||
| * [OSS/EED] | [OSS/EED/EF] | |||||||||
| Solver | MILP | ○ | ○ | ○ | MILP [OSS/EED] | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||
| [EED] | [EED/EF] | |||||||||
| Objectives | NPV, SSR, LLR | NPV, SSR | LCOE | NPV, SSR, LLR | LCOE | NPV, SSR, LLR | NPV, SSR, LLR | NPV, SSR, LLR | NPV, SSR | |
| Optimizer Functionalities | MILP Integrated | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | Hyperparameter Tuning | ○ | ||
| EED Strategy | Conventional, Peak Shaving | Conventional | Conventional | Conventional, Grid Charging | Conventional, Grid Charging | Conventional | Conventional | Conventional, Grid Charging | ||
| EF Strategy | ○ | Load Shifting | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| Case Study | Multi-Apartment Building | University Building | University Building | ○ | 1 MW Load | Factory | Port | Community | Warehouse | |
| Location | Sweden | Iran | India | China | Italy | China | China | Vietnam | ||
4.2.2. Analysis of the Research Area for the Optimization of Electrical Energy Distribution to Storage Systems and Consumers
| Source | Jaramillo et al. [54] | Khan et al. [59] | Shahryari et al. [55] | Ruiming [57] | Mosa et al. [56] | Cambambi et al. [61] | Vaish et al. [60] | Guo et al. [58] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSS/EED/EF | ○/●/◑ | ○/●/○ | ○/●/◑ | ○/●/○ | ○/●/○ | ○/●/○ | ○/●/○ | ○/●/○ |
| GRID/PV/WT | ●/●/○ | ●/●/● | ●/●/● | ●/●/● | ●/●/○ | ●/●/● | ●/●/● | ●/●/● |
| BESS/P2P | ○/● | ●/● | ●/● | ○/● | ●/● | ●/● | ●/● | ●/● |
| Model Type | Deterministic | Dynamic | Stochastic | Dynamic | Dynamic | Deterministic | Deterministic | Dynamic |
| Steps; Period | 15 min; 2 wk | 1 h; 1 d | 1 h; 1 d | 1 h; 1 d | 1 h; 1 d | 1 h; 1 d | 1 h; 1 d | 1 h; 1 a |
| Stage | Operation | Operation | Operation | Operation | Operation | Operation | Operation | Operation |
| Cost Model | O&M, Peak Load Fees, | O&M | O&M | O&M | O&M, CaPex, Load Loss | O&M | O&M | NPV |
| Electricity Model | ToU, DAM | ToU | ToU (buying), DAM | ToU | ToU | ToU | ToU | ToU |
| Sustainability Model | CO2 per kWh | CO2, NOX, SO2 per kWh | CO2, NOX, SO2 per kWh | CO2 per kWh | CO2, NOX, SO2 per kWh | ○ | ○ | CO2 per kWh |
| Simulation Functionalities | Standard Load Profile, Ramp-Up | Multi-Agent Approach | DAM | Degradation, Ramp-Up | DAM, PV Load Forecast, Ramp-Up | Degradation | CHP, Ramp-Up | SOC Forecast |
| Stochastics | ○ | ○ | RES, ToU, Loads | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Metaheuristic | ○ | ○ | MOGSO [EED/EF] | NSGA-II [EED] | ○ | ○ | Physic-Based [EED] | Rolling Horizon [EED] |
| Solver | MILP [EED/EF] | ○ | ○ | ○ | BARON [EED] | MILP [EED] | ○ | MILP [EED] |
| Objectives | OpEx, Peak Loads, Emissions | ○ | OpEx, Emissions | OpEx, Emissions | OpEx | OpEx | LCOE | NPV, SSR |
| Optimizer Functionalities | ○ | ○ | Stochastic Modeling | Interactive Search | ○ | ○ | ○ | Data-Driven Scheduling |
| EED Strategy | Optimizer, Peak Shaving, Grid Charging | Conventional | Optimizer | Optimizer | Optimizer | Optimizer | Optimizer | Optimizer |
| EF Strategy | E-Charging | ○ | Load Shifting | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Case Study | University Building | Community | Generic | Generic | Multi-Apartment Building | Generic | Generic | Generic |
| Location | Germany | Malaysia | Iran | China | Egypt | Brazil | India | China |
4.2.3. Analysis of the Research Area of the Energy Flexibilization of Factories
4.3. Research Gap Analysis
- Although energy pricing incorporated granular dynamic ToU prices, emissions were not considered in similar detail. A ToU consideration of emissions per kWh of electricity could shift focus from predominantly economic to sustainability considerations. Databases, such as [69], have already provided time- and location-dependent emissions of electricity.
- A holistic multi-agent simulation and optimization model covering all three research areas could not be identified. It is advisable to develop an overarching optimization algorithm that integrates various metaheuristics, thereby combining their respective advantages.
- The increasing complexity of optimization models, arising from the integration of numerous sub-models and functionalities into the optimization calculations, should not be underestimated. There is a risk of becoming trapped in local optima during the optimization process. However, the accumulation of experiential knowledge and the precise tuning of hyperparameters for various metaheuristics in relation to the specific application can enhance the results and improve the robustness of the methodology and models.
- Various functionalities have been introduced; however, an approach that implements all functionalities cannot be found. It is crucial to emphasize that not all functionalities can be applied within a single simulation and optimization model because of the potential complexity that could outweigh the benefits.
- Studies analyzing all functionalities through sensitivity analyses to determine their criticality are lacking, particularly for EED and EF strategies. Furthermore, an analysis should be conducted to determine which functionalities and model characteristics are better suited for the design and operation stages.
- A user-friendly modeling approach specifically tailored for factories, particularly a holistic implementation methodology with template-based generic sub-models designed for SMEs, is currently lacking.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsche Bundesregierung. Klimaschutzgesetz. 2023. Available online: https://www.bundesregierung.de/breg-de/themen/klimaschutz/klimaschutzgesetz-2021-1913672 (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Deutsche Bundesregierung. Wo Steht Deutschland Bei Der Energiewende|Anteil der Erneuerbaren Energien Steigt Weiter. 2022. Available online: https://www.bundesregierung.de/breg-de/themen/klimaschutz/faq-energiewende-2067498 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Umweltbundesamt. Emissionsvermeidung Durch Erneuerbare Energieträger. 2022. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/themen/klima-energie/erneuerbare-energien/emissionsvermeidung-durch-erneuerbare#Emissionsbilanz (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Bundesnetzagentur. Bericht zu Stand und Entwicklung der Versorgungssicherheit im Bereich der Versorgung mit Elektrizität. 2023. Available online: https://www.bmwk.de/Redaktion/DE/Downloads/V/versorgungssicherheitsbericht-strom.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=4 (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Interconnector GmbH. Direktvermarktung Strom: Zuverlässig & Transparent. 2023. Available online: https://www.interconnector.de/direktvermarktung-strom/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Tischkov, S. Windparkbetreiber Kämpfen mit Strompreis und Überkapazitäten. 2023. Available online: https://www.tagesschau.de/wirtschaft/windkraft-probleme-101.html (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Claußner, M.; Huneke, F.; Brinkhaus, M.; Peper, D.; Kost, C.; Fluri, V. Potentiale und Rahmenbedingungen Für den Ausbau des Prosuming; Bundesverband der Energie- und Wasserwirtschaft (BDEW): Berlin/Freiburg, Germany, 2022; Available online: https://www.bdew.de/service/publikationen/potentiale-und-rahmenbedingungen-fuer-den-ausbau-des-prosuming/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- BDEW. Industriestrompreise (Inklusive Stromsteuer) in Deutschland in den Jahren 1998 bis 2024. 2024. Available online: https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/252029/umfrage/industriestrompreise-inkl-stromsteuer-in-deutschland/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Bundesministerium Für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz. Aktionsplan, Mittelstand, Klimaschutz und Transformation. 2023. Available online: https://www.bmwk.de/Redaktion/DE/Dossier/politik-fuer-den-mittelstand.html (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Peiseler, F.; Runkel, M.; Wettingfeld, M.; Mensinger, L. Nachhaltige Soziale Marktwirtschaft. 2023. Available online: https://www.bertelsmann-stiftung.de/de/publikationen/publikation/did/steuerpolitik-fuer-eine-nachhaltige-transformation-des-mittelstands (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Amoussou, I.; Tanyi, E.; Fatma, L.; Agajie, T.F.; Boulkaibet, I.; Khezami, N.; Ali, A.; Khan, B. The Optimal Design of a Hybrid Solar PV/Wind/Hydrogen/Lithium Battery for the Replacement of a Heavy Fuel Oil Thermal Power Plant. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnemann, J.; Prior, J.; Kuhlenkötter, B. Skalierbare Elektrolyseurmontage. Z. Für Wirtsch. Fabr. 2021, 116, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaschning, V. Regenerative Energiesysteme: Technologie—Berechnung—Klimaschutz, 11th ed.; Hanser: München, Germany, 2021; ISBN 9783446472068. [Google Scholar]
- Eiselt, H.A. Operations Research: A Model-Based Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-97161-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, J.; Scharmer, V.M.; Zaeh, M.F. Energy self-sufficient manufacturing systems—Integration of renewable and decentralized energy generation systems. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 43, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, R.S.; Zaeh, M.F. Determination of the Technical Energy Flexibility of Production Systems. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1018, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazitabar, M.; Abdi, H.; Nourianfar, H.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Hatziargyriou, N. An Introduction to Microgrids, Concepts, Definition, and Classifications. In Microgrids: Advances in Operation, Control, and Protection; Hatziargyriou, N., Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B., Abdi, H., Anvari-Moghaddam, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 3–16. ISBN 978-3-030-59749-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tafarte, P.; Geiger, C.; Lehmann, P. Quantifying the opportunity cost of land use restrictions and their impact on the energy transition—A case study for Germany’s onshore wind power. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on the European Energy Market, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 13–15 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleipen, M.; Drath, R. Three-view-concept for modeling process or manufacturing plants with AutomationML. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation, Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 22–25 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Integration of Distributed Renewable Energy and Energy Storages in Buildings; KTH Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019; ISBN 978-91-7873-193-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tiemann, P.H.; Bensmann, A.; Stuke, V.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Electrical energy storage for industrial grid fee reduction—A large scale analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 208, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, M. Net Present Value and Risk Modelling for Projects; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781315248172. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesnetzagentur. SMARD. 2023. Available online: https://www.smard.de/home/downloadcenter/download-marktdaten/ (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Umweltbundesamt. Strom- und Wärmeversorgung in Zahlen. 2024. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/themen/klima-energie/energieversorgung/strom-waermeversorgung-in-zahlen#Strommix (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- electricitymaps. 2024. Available online: https://app.electricitymaps.com/map (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Siemon, L.; Blume, C.; Mennenga, M.; Herrmann, C. Multi-scale Simulation for Energy Flexible Factories and Factory Networks: A System of Systems Perspective. Procedia CIRP 2022, 105, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolato, A.; Faria, P.; Vale, Z. Probabilistic Determination of Consumers Response and Consumption Management Strategies in Demand Response Programs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition (T&D), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.; Hünecke, P.; Neureiter, C.; Lüder, A. Towards flexible production systems engineering according to RAMI 4.0 by utilizing PPR notation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 21st International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Lemgo, Germany, 18–20 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz. RAMI 4.0—Ein Orientierungsrahmen für die Digitalisierung. 2018. Available online: https://www.plattform-i40.de/IP/Redaktion/DE/Downloads/Publikation/rami40-eine-einfuehrung.html (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Fazli Khalaf, A.; Wang, Y. Energy-cost-aware flow shop scheduling considering intermittent renewables, energy storage, and real-time electricity pricing. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 3928–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, E.; Ercan, F.; Kuhlenkötter, B.; Herzog, M. Modeling and Simulation for the Operative Service Delivery Planning in the Context of Product-Service Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2023 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–13 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coakley, D.; Raftery, P.; Keane, M. A review of methods to match building energy simulation models to measured data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, J.; Hypki, A.; Kuhlenkötter, B. Heuristische Optimierung von P2G2P Speichern: Ein Template basierter Ansatz zur Evaluierung von Speicherstrategien und Optimierungsalgorithmen. In Erfolg Durch Nachhaltiges Energie- und Ressourcenmanagement; Posch, W., Vorbach, S., Zsifkovits, H., Feichtinger, G., Eds.; Nomos: Baden-Baden, Germany, 2023; pp. 193–207. ISBN 978-3-98542-056-8. [Google Scholar]
- Spong, M.W. Introduction to Modeling and Simulation: A Systems Approach, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; ISBN 9781119982906. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.; Mahanand, B.S. Chapter 9—Affordable energy-intensive routing using metaheuristics. In Cognitive Big Data Intelligence with a Metaheuristic Approach; Mishra, S., Tripathy, H.K., Mallick, P.K., Sangaiah, A.K., Chae, G.-S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 193–210. ISBN 978-0-323-85117-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Vale, Z.A. (Eds.) Applications of Modern Heuristic Optimization Methods in Power and Energy Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781119602293. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Computat. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier. Scopus: Umfassende, Multidisziplinäre Abstract- und Quellenangaben-Datenbank. 2023. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/de-de/products/scopus (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Catalogue of the German National Library. Available online: https://www.dnb.de/DE/Home/home_node.html (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Landing Page. 2024. Available online: https://www.fraunhofer.de/en.html (accessed on 13 February 2024).
- Akhavan Shams, S.; Ahmadi, R. Dynamic optimization of solar-wind hybrid system connected to electrical battery or hydrogen as an energy storage system. Int J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 10630–10654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, N.; Gupta, A. System sizing of hybrid solar-fuel cell battery energy system using artificial bee colony algorithm with predator effect. Int J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 5847–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Tan, J.; Li, Z.; Hou, W.; Guo, Y. Capacity configuration optimization of multi-energy system integrating wind turbine/photovoltaic/hydrogen/battery. Energy 2022, 252, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yan, X.; Yuan, Y. Capacity configuration optimization of port multi-energy system integrating wind turbine/photovoltaic/battery/hydrogen. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Xi’an, China, 4–6 August 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Liu, Y. An Optimization Capacity Design Method of Wind/Photovoltaic/Hydrogen Storage Power System Based on PSO-NSGA-II. Energy Eng. 2023, 120, 1023–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Campana, P.E.; Lundblad, A.; Yan, J. Comparative study of hydrogen storage and battery storage in grid connected photovoltaic system: Storage sizing and rule-based operation. Appl. Energy 2017, 201, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, E.; Colbertaldo, P.; Guandalini, G.; Campanari, S. Energy storage with Power-to-Power systems relying on photovoltaic and hydrogen: Modelling the operation with secondary reserve provision. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.S.; Nguyen, T.N.; Bui, D.-K.; Ngo, T.D. Optimal sizing of renewable energy storage: A techno-economic analysis of hydrogen, battery and hybrid systems considering degradation and seasonal storage. Appl. Energy 2023, 336, 120817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, E.; Colbertaldo, P.; Guandalini, G.; Campanari, S. Design of hybrid power-to-power systems for continuous clean PV-based energy supply. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13691–13708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YALMIP. GUROBI. 2016. Available online: https://yalmip.github.io/solver/gurobi/ (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- HOMER. Hybrid Renewable and Distributed Generation System Design Software. 2024. Available online: https://homerenergy.com/ (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Jaramillo, L.B.; Weidlich, A. Optimal microgrid scheduling with peak load reduction involving an electrolyzer and flexible loads. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahryari, E.; Shayeghi, H.; Mohammadi-ivatloo, B.; Moradzadeh, M. A copula-based method to consider uncertainties for multi-objective energy management of microgrid in presence of demand response. Energy 2019, 175, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, M.A.; Ali, A.A. Energy management system of low voltage dc microgrid using mixed-integer nonlinear programing and a global optimization technique. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 192, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiming, F. Multi-objective optimized operation of integrated energy system with hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29409–29417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wei, W.; Bai, J.; Mei, S. Long-term operation of isolated microgrids with renewables and hybrid seasonal-battery storage. Appl. Energy 2023, 349, 121628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.W.; Wang, J.; Xiong, L.; Ma, M. Modelling and optimal management of distributed microgrid using multi-agent systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaish, J.; Tiwari, A.K.; Siddiqui, K.M. Optimization of micro grid with distributed energy resources using physics based meta heuristic techniques. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambambi, C.A.C.; Lautert, R.R.; Rangel, C.A.S.; Milani, I.; Canha, L.N. Model for Cooperative Operation of Li-ion Batteries and Hydrogen Storage Systems in Microgrids Considering Cycling Costs and Dynamic Prices. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDEW-Lastprofile. 1999. Available online: https://www.bdew.de/media/documents/1999_Repraesentative-VDEW-Lastprofile.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Küster, T.; Rayling, P.; Wiersig, R.; Pardo, F.D.P. Multi-objective optimization of energy-efficient production schedules using genetic algorithms. Optim. Eng. 2021, 24, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro-Ruiz, C.; Lombardi, P.; Richter, M.; Pelzer, A.; Komarnicki, P.; Pavas, A.; Mojica-Nava, E. Coordination of optimal sizing of energy storage systems and production buffer stocks in a net zero energy factory. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.; Komarnicki, P.; Zhu, R.; Liserre, M. Flexibility options identification within Net Zero Energy Factories. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanapinit, N.; Thomsen, J.; Kost, C.; Weidlich, A. An MILP model for evaluating the optimal operation and flexibility potential of end-users. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, J.; Thiede, S.; Herrmann, C. Energy flexibility of manufacturing systems for variable renewable energy supply integration: Real-time control method and simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlach, K.; Westkämper, E. Energiewertstrom: Der Weg zur Energieeffizienten Fabrik; Fraunhofer Verl.: Stuttgart, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9783839600108. [Google Scholar]
- Open Weather. Current Weather and Forecast. 2024. Available online: https://openweathermap.org/ (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Agajie, T.F.; Ali, A.; Fopah-Lele, A.; Amoussou, I.; Khan, B.; Velasco, C.L.R.; Tanyi, E. A Comprehensive Review on Techno-Economic Analysis and Optimal Sizing of Hybrid Renewable Energy Sources with Energy Storage Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsad, A.Z.; Hannan, M.A.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Mansur, M.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Dong, Z.Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Hydrogen energy storage integrated hybrid renewable energy systems: A review analysis for future research directions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 17285–17312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.M.R.C.; Homayouni, S.M.; Fontes, D.B.M.M. Energy-Efficient Scheduling in Job Shop Manufacturing Systems: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Yu, M.; Waseem, M. Review on recent optimization strategies for hybrid renewable energy system with hydrogen technologies: State of the art, trends and future directions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 25155–25201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, A.A.; Subramanian, B. Scrutiny of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems for Control, Power Management, Optimization and Sizing: Challenges and Future Possibilities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bänsch, K.; Busse, J.; Meisel, F.; Rieck, J.; Scholz, S.; Volling, T.; Wichmann, M.G. Energy-aware decision support models in production environments: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 159, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, C.; Vennemann, P. Modeling and optimization of multi-energy systems in mixed-use districts: A review of existing methods and approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangu, S.K.; Lolla, P.R.; Dhenuvakonda, K.R.; Singh, A.R. Recent trends in power management strategies for optimal operation of distributed energy resources in microgrids: A comprehensive review. Int J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 9889–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; Glock, C.H. Energy management for stationary electric energy storage systems: A systematic literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 264, 582–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.F.; Elbouchikhi, E.; Benbouzid, M. Microgrids energy management systems: A critical review on methods, solutions, and prospects. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büsch, L.; Jakschik, M.; Syniawa, D.; Masuhr, C.; Christ, L.; Schachtsiek, J.; Haalck, K.; Nerlich, L.; Frömsdorf, E.; Schirmack, N.; et al. HyPLANT100: Industrialization from Assembly to the Construction Site for Gigawatt Electrolysis. Hydrogen 2024, 5, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dena. Studie: Geschäftsmodelle für Dezentrale Wasserstoffkonzepte—Zeit zum Nachsteuern. 2023. Available online: https://www.dena.de/fileadmin/dena/Publikationen/PDFs/2023/STUDIE_Geschaeftsmodelle_fuer_dezentrale_Wasserstoffkonzepte_-_Zeit_zum_Nachsteuern.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2024).
- eur-lex.europa.eu. Green Deal. 2024. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/DE/TXT/HTML/?uri=PI_COM:C(2021)2800&from=EN (accessed on 13 March 2024).


| Source | Fazli Khalaf and Wang [31] | Caro-Ruiz et al. [64] | Lombardi et al. [65] | Beier et al. [67] | Wanapinit et al. [66] | Küster et al. [63] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSS/EED/EF | ○/◑/● | ◑/◑/● | ○/○/● | ◑/◑/● | ○/◑/● | |
| GRID/PV/WT | ●/●/● | ○/●/○ | ●/●/● | ●/●/● | ●/●/● | ●/●/○ |
| BESS/P2P | ●/○ | ●/○ | ●/● | ●/○ | ●/○ | ●/○ |
| Model Type | Stochastic | Deterministic | Dynamic | Dynamic | Deterministic | Dynamic |
| Steps; Period | 5 min; 1 d | 1 h; 1 a | 1 s; 1 h | 5 min; 1 wk | 1 s; 1 d | |
| Stage | Operation | Design and Operation | Operation | Design and Operation | Operation | |
| Cost Model | Electricity Costs | ○ | Electricity Costs | Electricity Costs | Electricity Costs | |
| Electricity Model | ToU, DAM | ○ | Peak Fees | ToU, DAM | ToU | |
| Sustainability Model | ○ | SSR | SSR; CO2 per kWh | ○ | SSR | |
| Simulation Functionalities | ○ | BESS/Buffer Sizing Methodology, PPR Modeling | Throughput times, PPR Modeling, Multi-Agents, CO2 per product | PPR Modeling, Flexibilization Analysis, CHP | PPR Modeling | |
| Stochastics | RES | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| Metaheuristic | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | Genetic Algorithm [EF] | |
| Solver | SMILP [EED/EF] | MILP [EED/EF] | ○ | ○ | MILP [EED/EF] | ○ |
| Objectives | Electricity Costs | SSR | ○ | SSR | Electricity Costs | Fitness Function |
| Optimizer Functionalities | 2 Stages: Deterministic and Stochastic | ○ | ○ | ○ | Scheduling Processes as Alleles | |
| EED Strategy | Optimizer | Optimizer | Conventional | Conventional | Optimizer | Conventional |
| EF Strategy | Flow-Shop | Flow-Shop | Flow-Shop | Flexible Job-Shop | Flexible Job-Shop | |
| Case Study | Factory | Factory | Factory | Factory | Factory | |
| Location | USA | Germany | Germany | Germany | Germany | |
| Group | Feature | SLR OSS | SLR EED | SLR EF | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metaheuristic/Solver | Evolutionary Based | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Swarm Based | 4 | 1 | - | 5 | |
| Linear Solver | 3 | 4 | 3 | 10 | |
| Objectives | Single-Objective | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| Multi-Objective | 8 | 4 | - | 12 | |
| Emissions-Related Objectives | 9 | 4 | 2 | 15 | |
| Costs-Related Objectives | 12 | 7 | 2 | 21 |
| Group | Feature | SLR OSS | SLR EED | SLR EF | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Size | s/min/h | -/-/10 | -/1/7 | 2/2/2 | 2/3/19 |
| Simulation Period | h/d/wk/a | -/-/-/10 | -/6/1/1 | 1/2/1/2 | 1/8/2/13 |
| Cost Model | Only Electricity Costs | - | - | 4 | 4 |
| CaPex | - | 1 | - | 1 | |
| OpEx | - | 8 | - | 8 | |
| NPV | 10 | 1 | - | 11 | |
| Electricity Model | DAM | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| ToU Buying/Selling | 5/3 | 7/6 | 3/3 | 15/12 | |
| Peak Fees | 2 | - | 1 | 3 | |
| Electricity Price Trend | 1 | - | - | 1 | |
| Sustainability model | CO2, NOX, SO2 Emissions | 1 | 6 | - | 7 |
| Social Costs | 1 | - | - | 1 | |
| SSR | 8 | - | 4 | 12 | |
| Simulation Model Functionalities | CHP | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Ramp-Up | 1 | 2 | - | 3 | |
| H2 Sale, Buying | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | |
| Degradation | 1 | 2 | - | 3 | |
| Standard Load Profile | - | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Multi-Agent | - | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Load Forecast | - | 1 | - | 1 | |
| RES Forecast | - | 1 | - | 1 | |
| SOC Forecast | - | 1 | - | 1 | |
| PPR Modeling | - | - | 4 | 4 | |
| Flexibilization Analysis | - | - | 2 | 2 | |
| KPIs per Product | 1 | 1 | |||
| Stochastics | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
| Optimization Model Functionalities | MILP Integrated | 2 | - | - | 2 |
| Hyperparameter Tuning | 1 | - | - | 1 | |
| Stochastic Modeling | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Interactive Search | - | 2 | - | 2 | |
| Data-Driven Scheduling | - | - | 1 | 1 | |
| Scheduling Process as Alleles | - | - | 1 | 1 | |
| EED Strategy | Conventional | 10 | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| Grid Charging | 7 | - | - | 7 | |
| Optimizer | - | 7 | 3 | 10 | |
| EF Strategy | Load Shifting | 1 | 2 | - | 3 |
| Flow-Shop | - | - | 4 | 4 | |
| Flexible Job-Shop | - | - | 2 | 2 | |
| Case Study | Factory/Building/Generic | 4/5/- | -/3/5 | 6/-/- | 10/8/5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prior, J.; Drees, T.; Miro, M.; Kuhlenkötter, B. Systematic Literature Review of Heuristic-Optimized Microgrids and Energy-Flexible Factories. Clean Technol. 2024, 6, 1114-1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030055
Prior J, Drees T, Miro M, Kuhlenkötter B. Systematic Literature Review of Heuristic-Optimized Microgrids and Energy-Flexible Factories. Clean Technologies. 2024; 6(3):1114-1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030055
Chicago/Turabian StylePrior, Johannes, Tobias Drees, Michael Miro, and Bernd Kuhlenkötter. 2024. "Systematic Literature Review of Heuristic-Optimized Microgrids and Energy-Flexible Factories" Clean Technologies 6, no. 3: 1114-1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030055
APA StylePrior, J., Drees, T., Miro, M., & Kuhlenkötter, B. (2024). Systematic Literature Review of Heuristic-Optimized Microgrids and Energy-Flexible Factories. Clean Technologies, 6(3), 1114-1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol6030055







