Impact of the Ferroelectric Stack Lamination in Si Doped Hafnium Oxide (HSO) and Hafnium Zirconium Oxide (HZO) Based FeFETs: Toward High-Density Multi-Level Cell and Synaptic Storage
Abstract
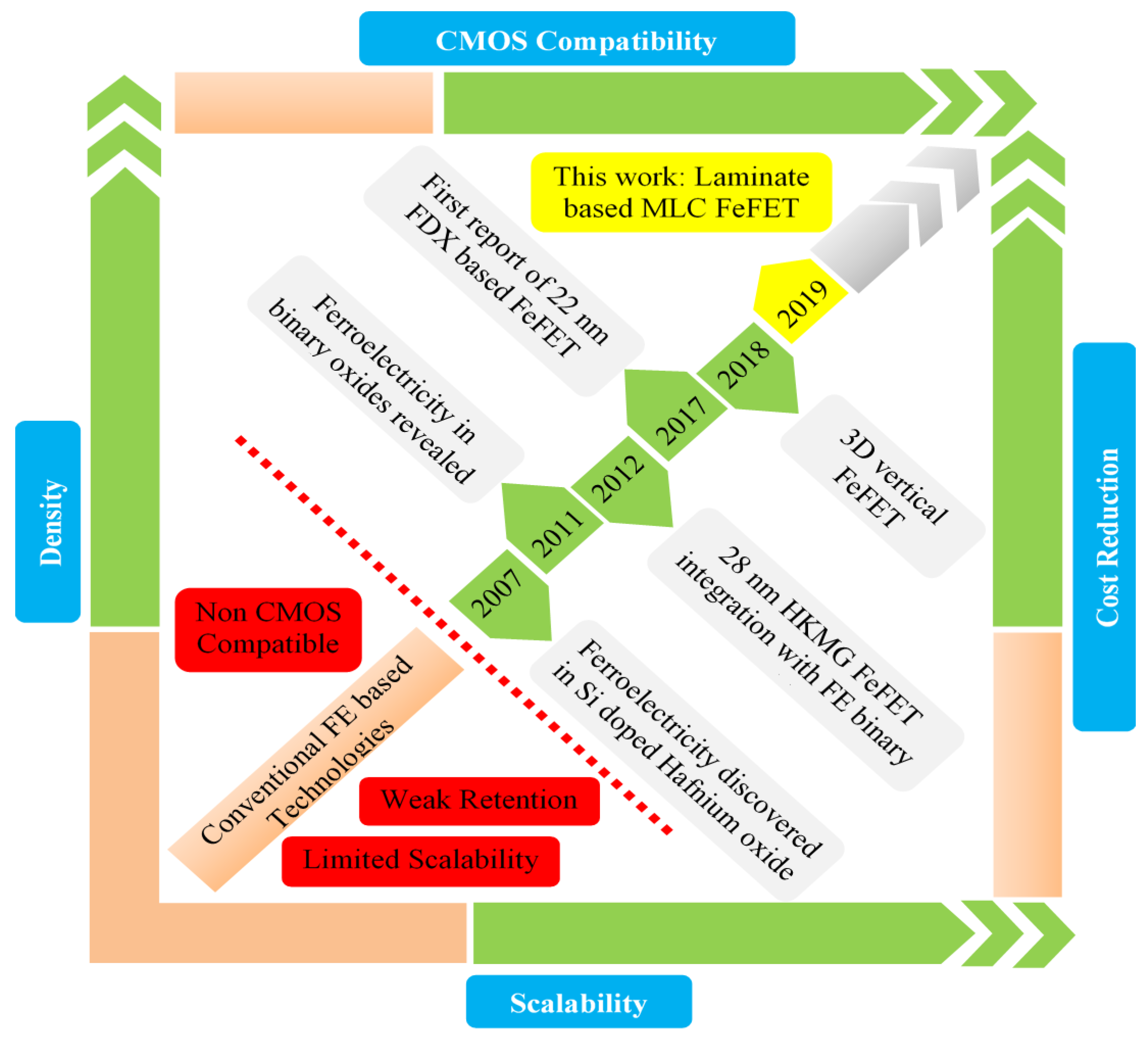
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
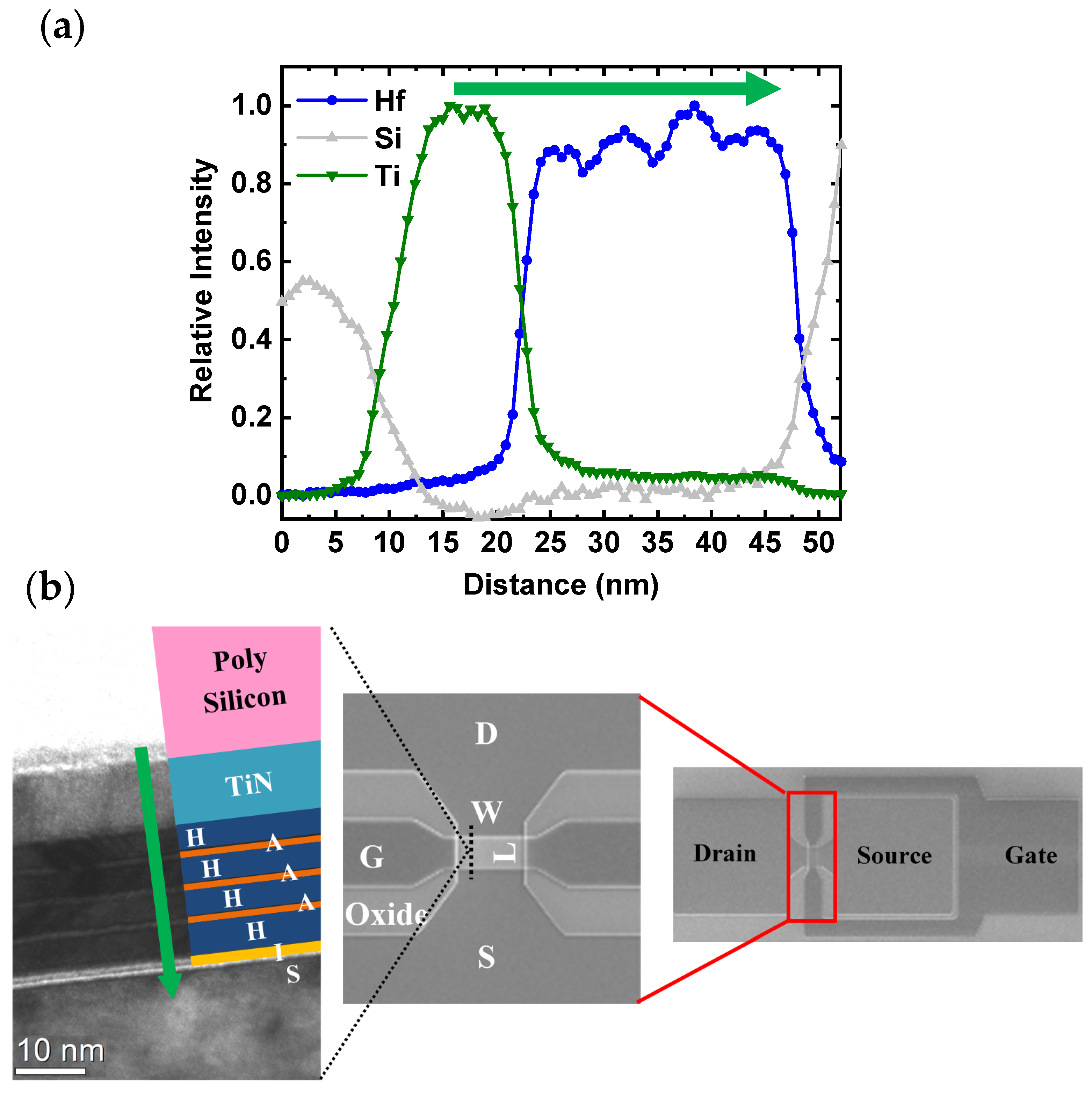
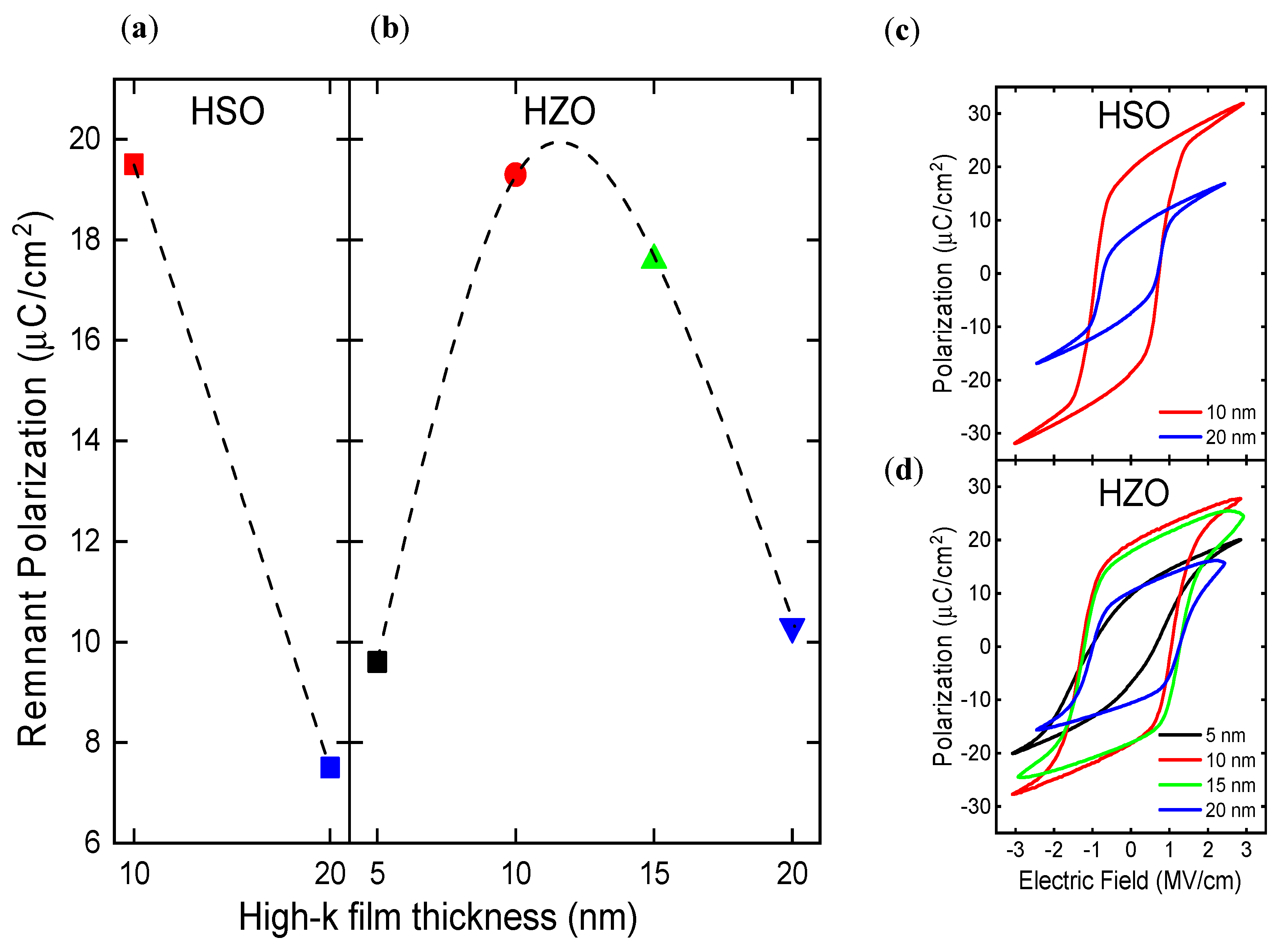
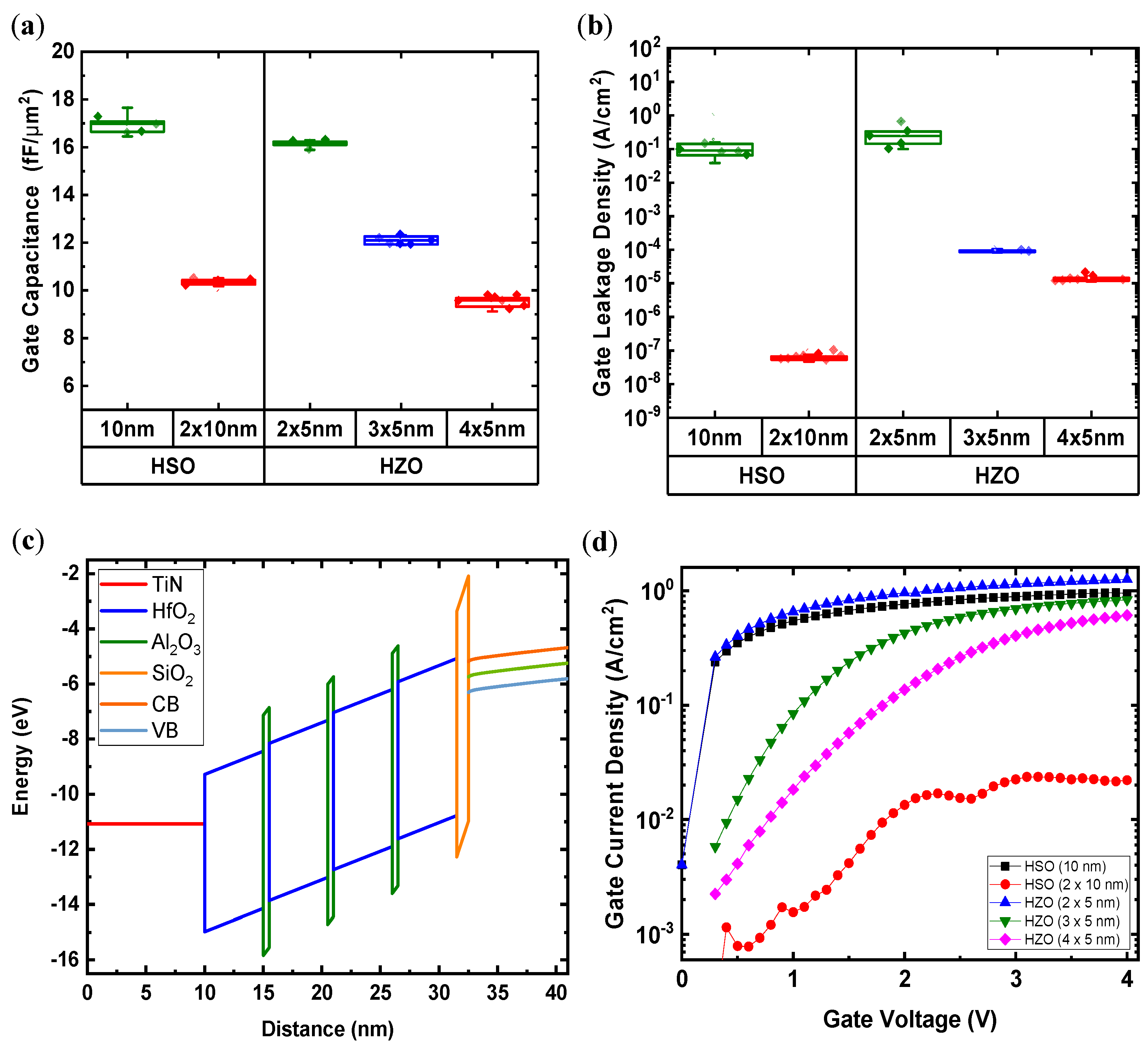
3.1. The Laminate MFM and Stack Characteristics
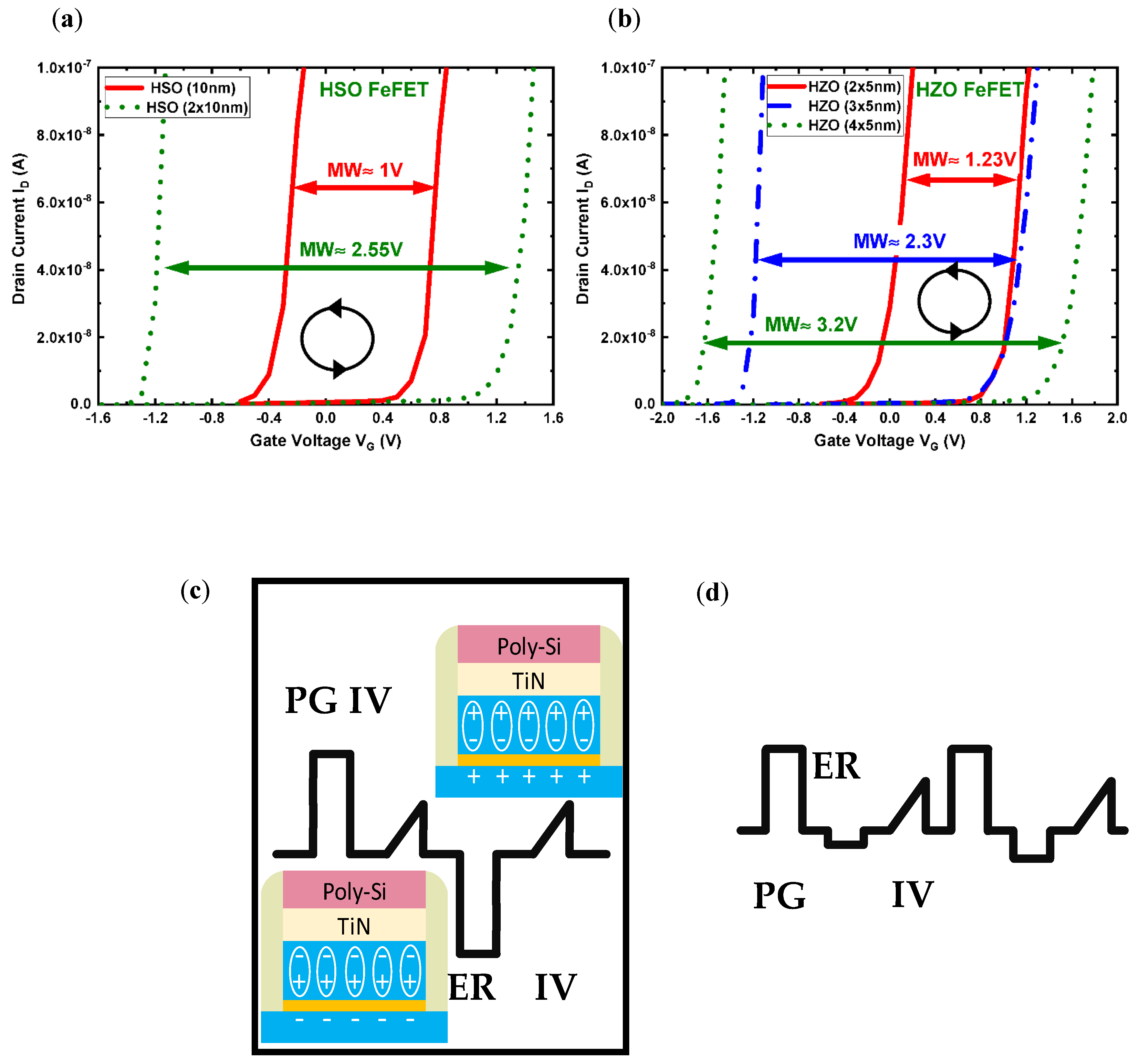
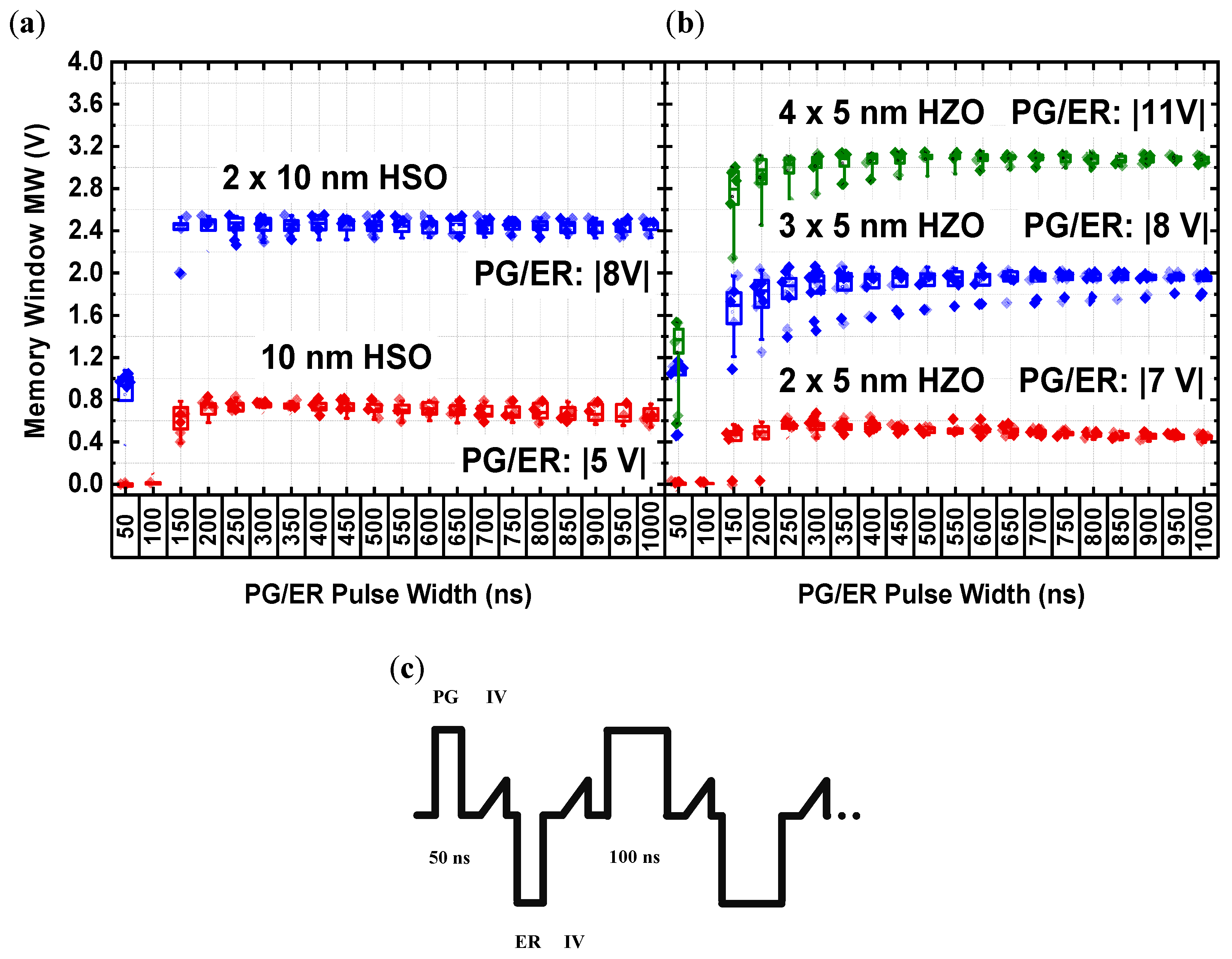
3.2. The Laminate FeFET Memory Switching
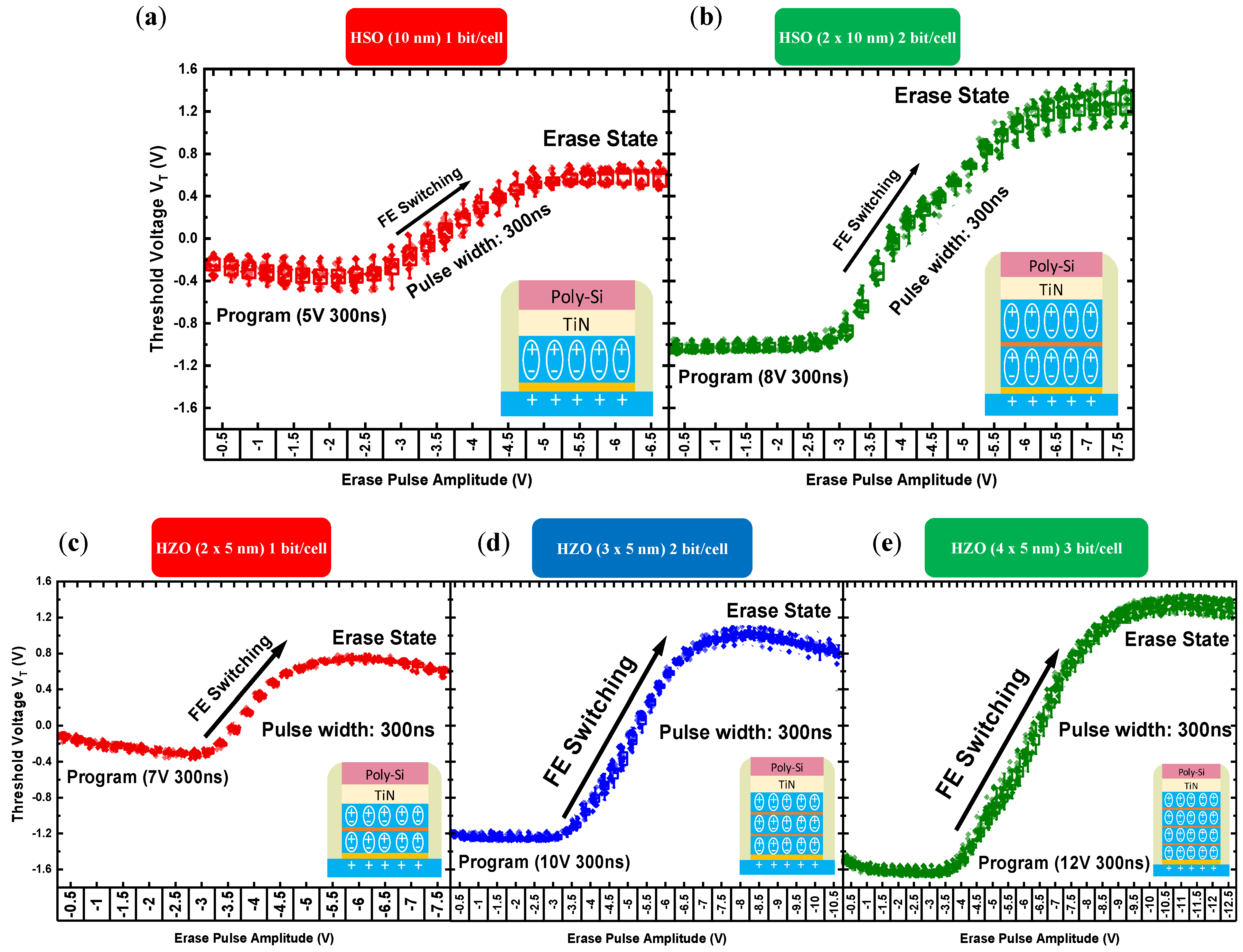
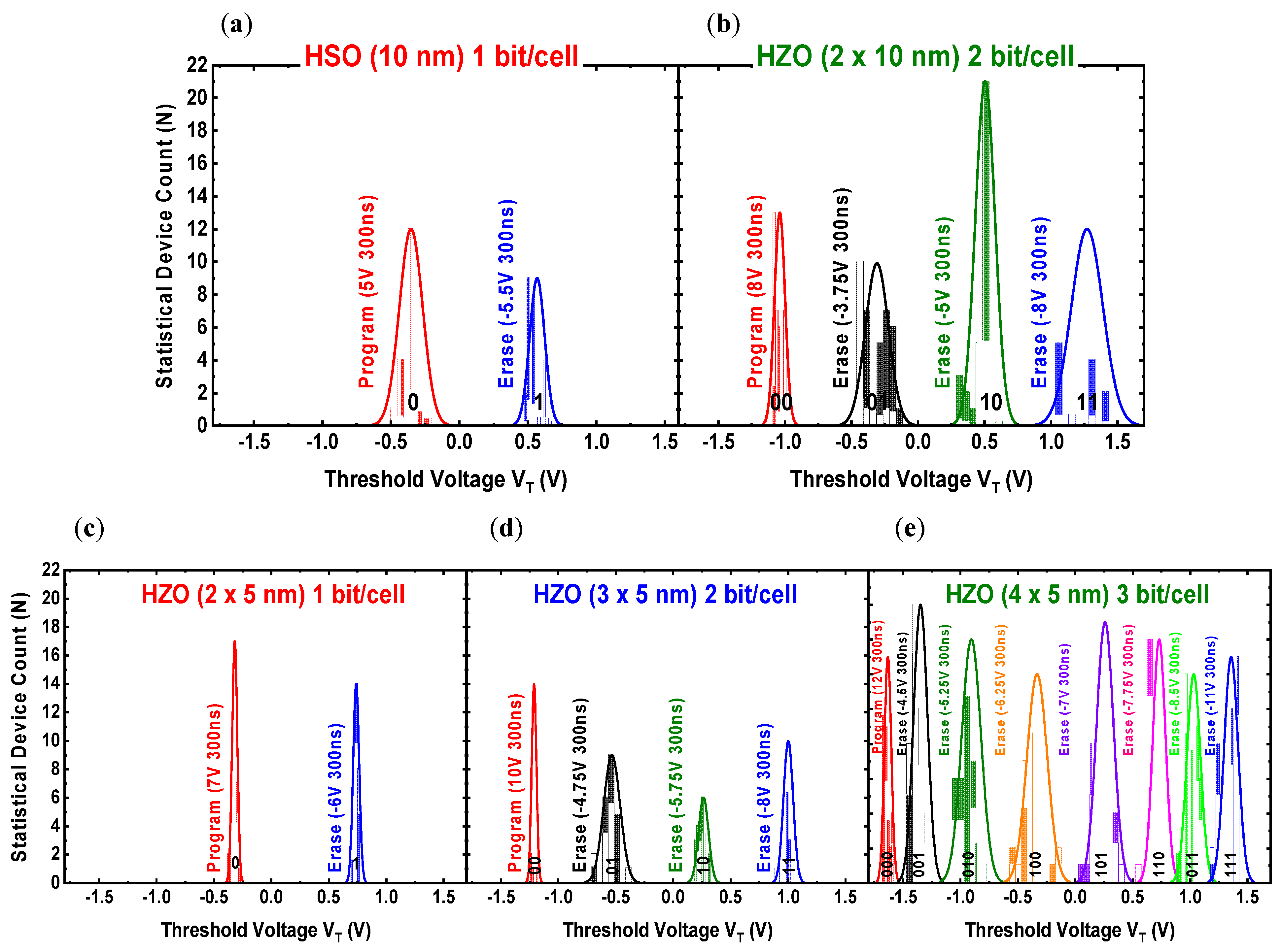
3.3. The Multi-Level Coding Operation (1 bit, 2 bit, 3 bit/cell)
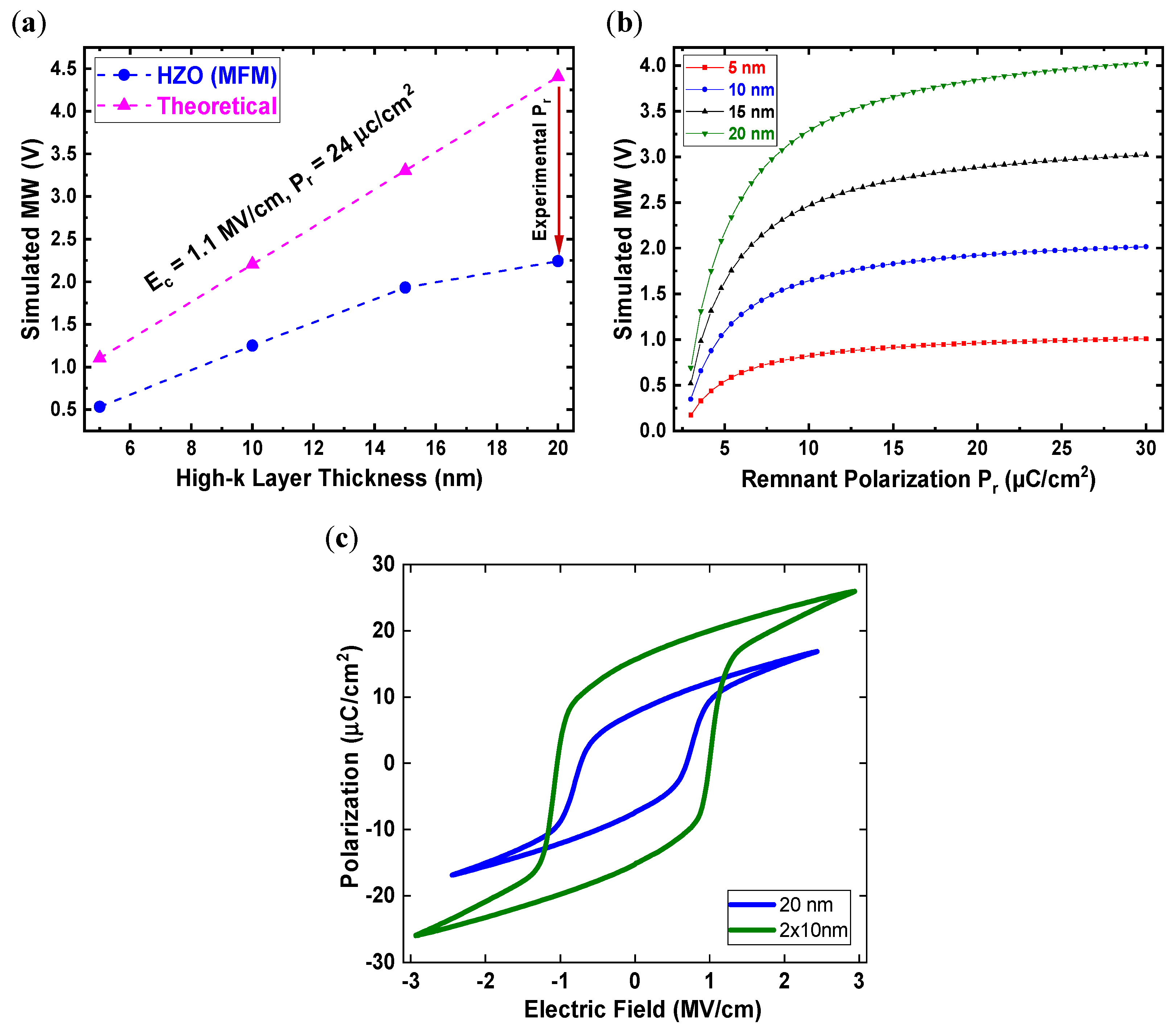
3.4. The Maximum MW Dependence on Ferroelectric Stack Thickness
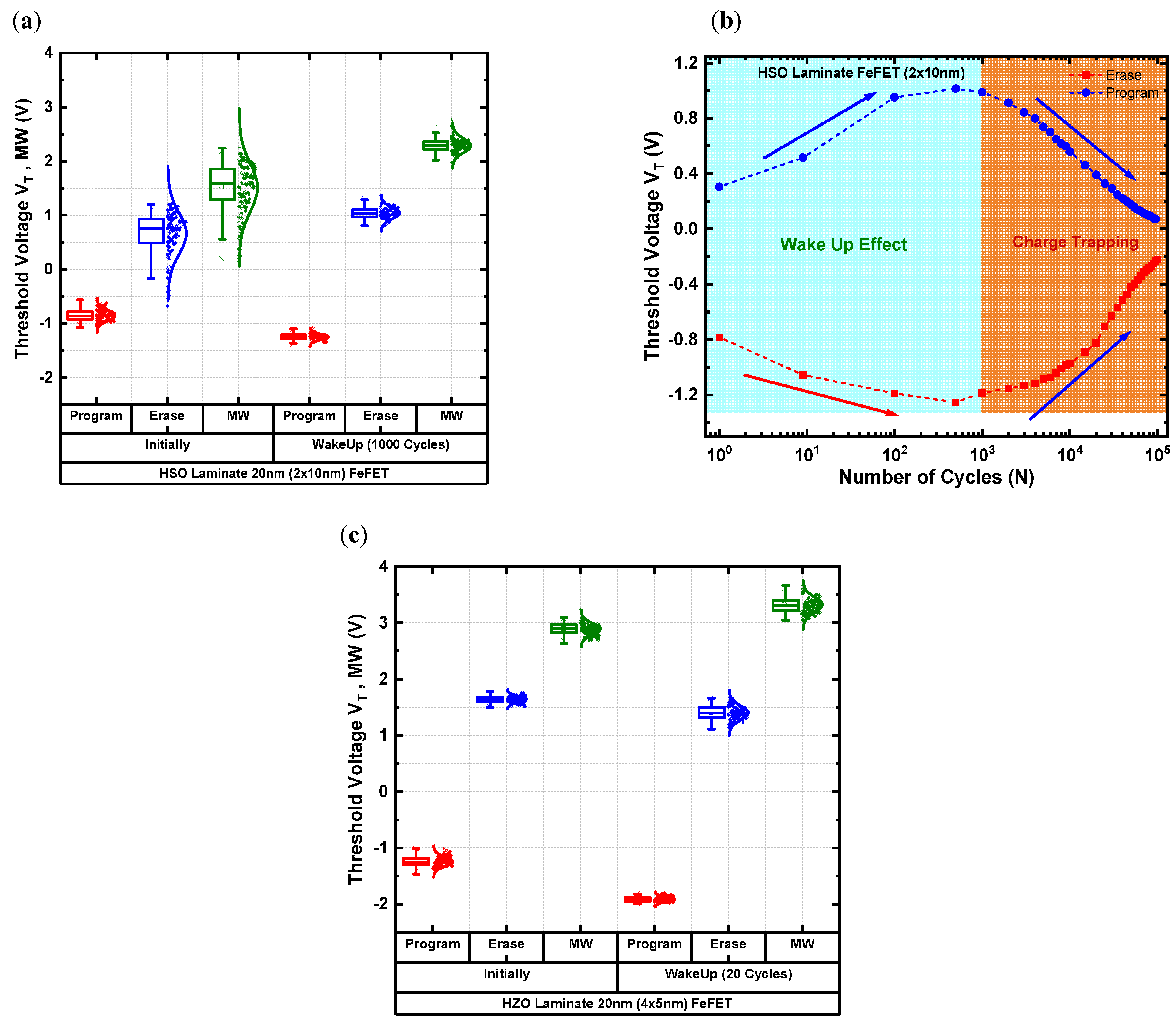
3.5. The Role of Wakeup and Charge Trapping
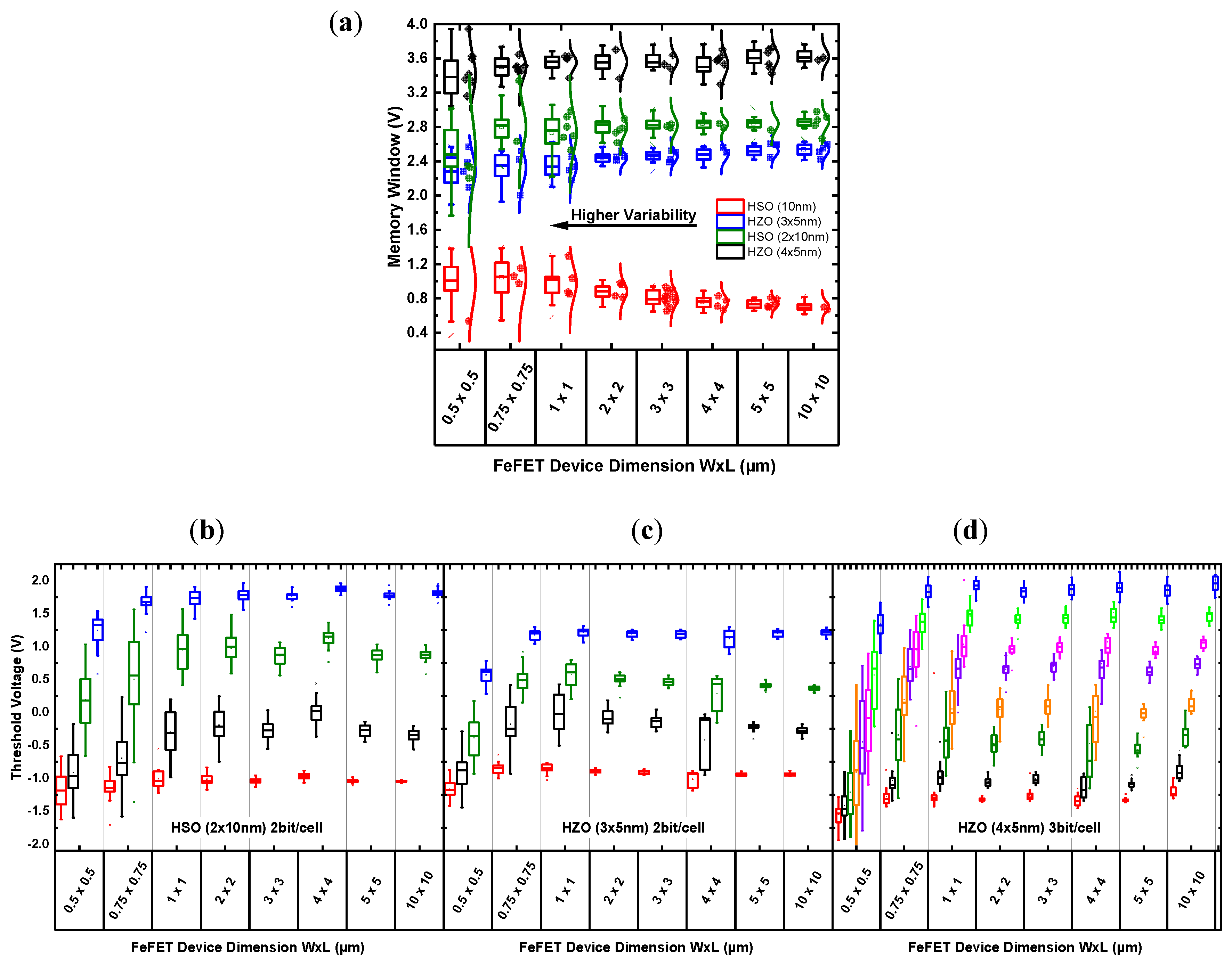
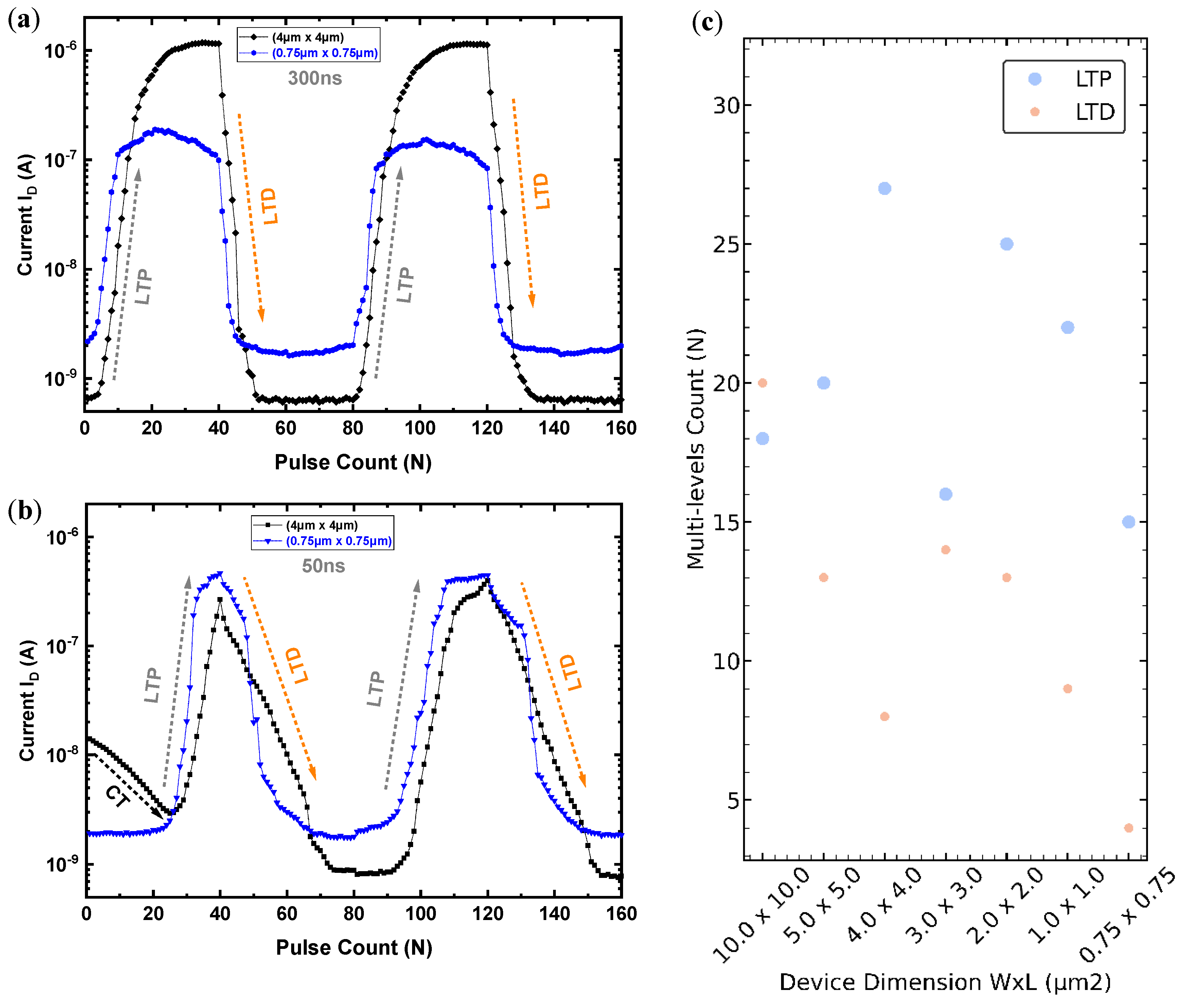
3.6. The MLC FeFET Area Dependence
3.7. The MLC Retention and Endurance
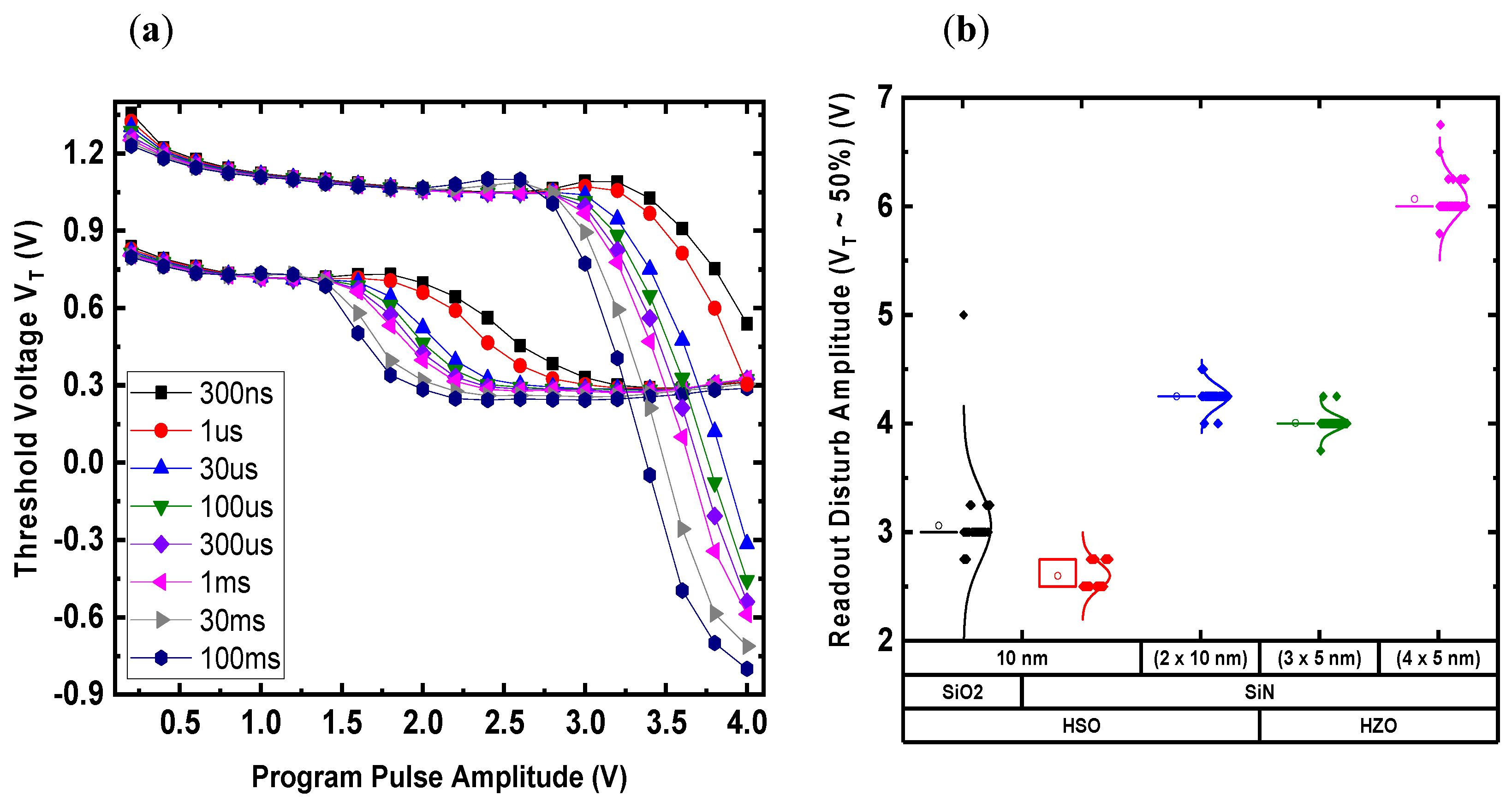
3.8. The Pass Voltage Disturb Effect
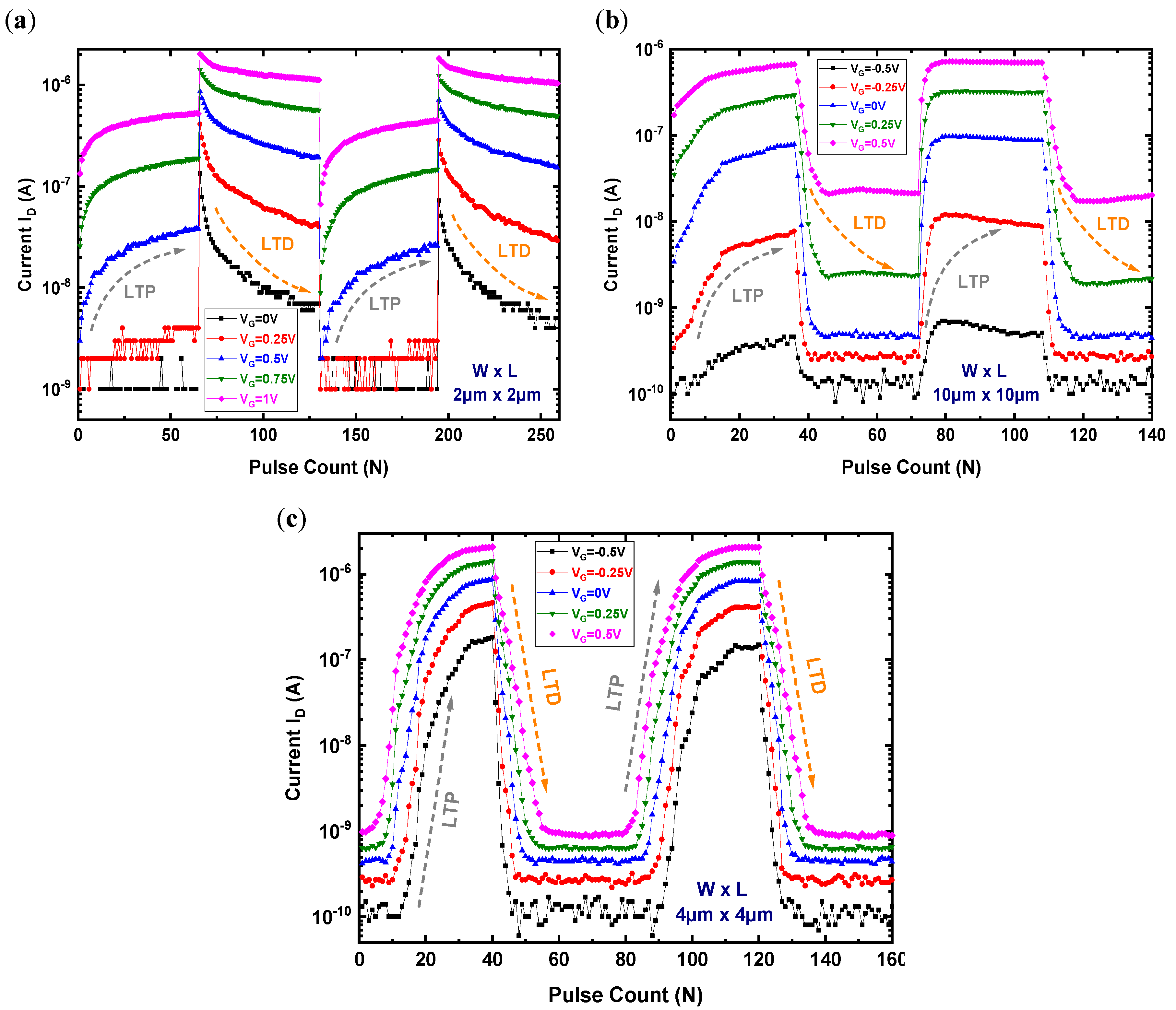
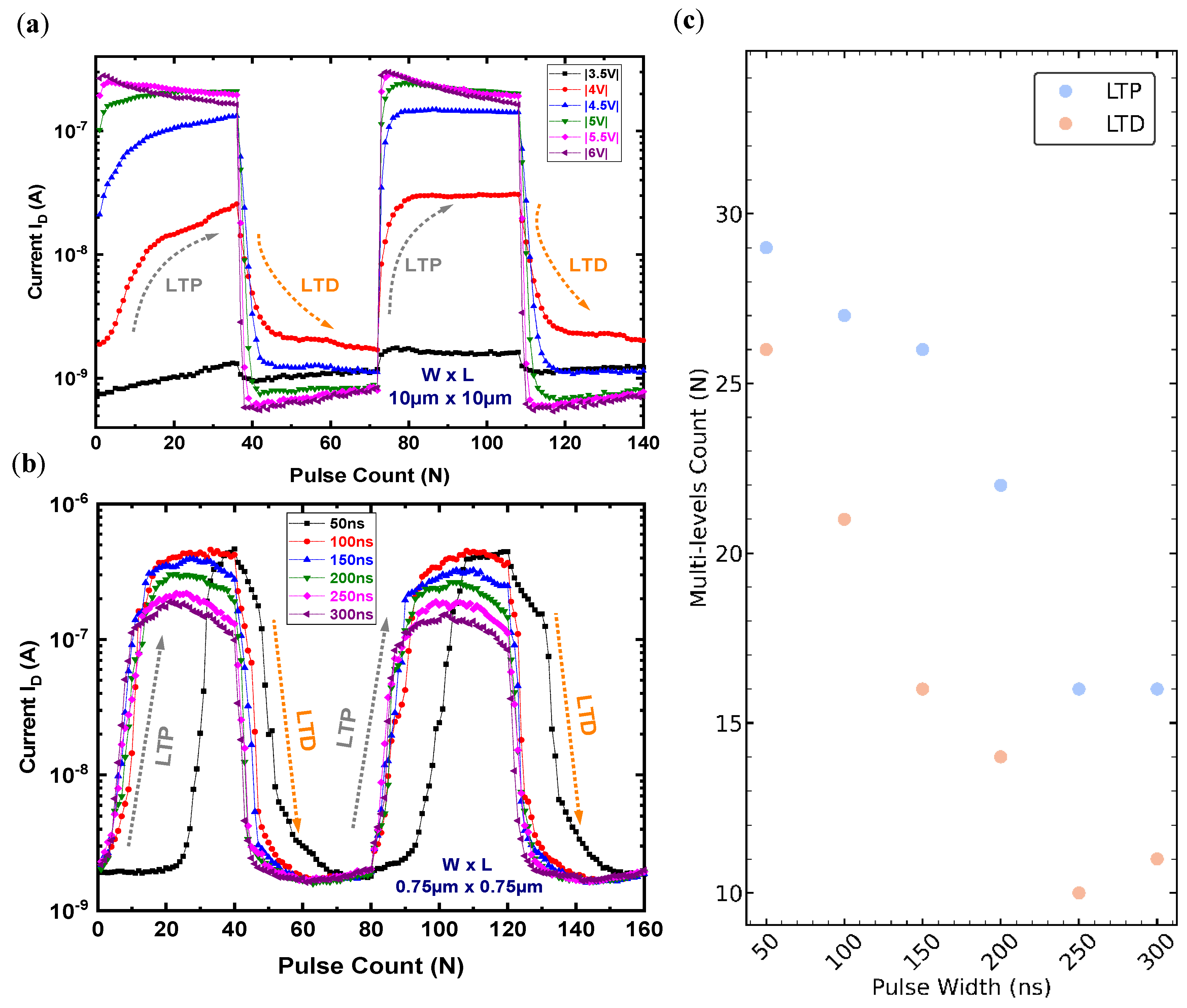
3.9. The Laminate FeFET-Based Synaptic Device
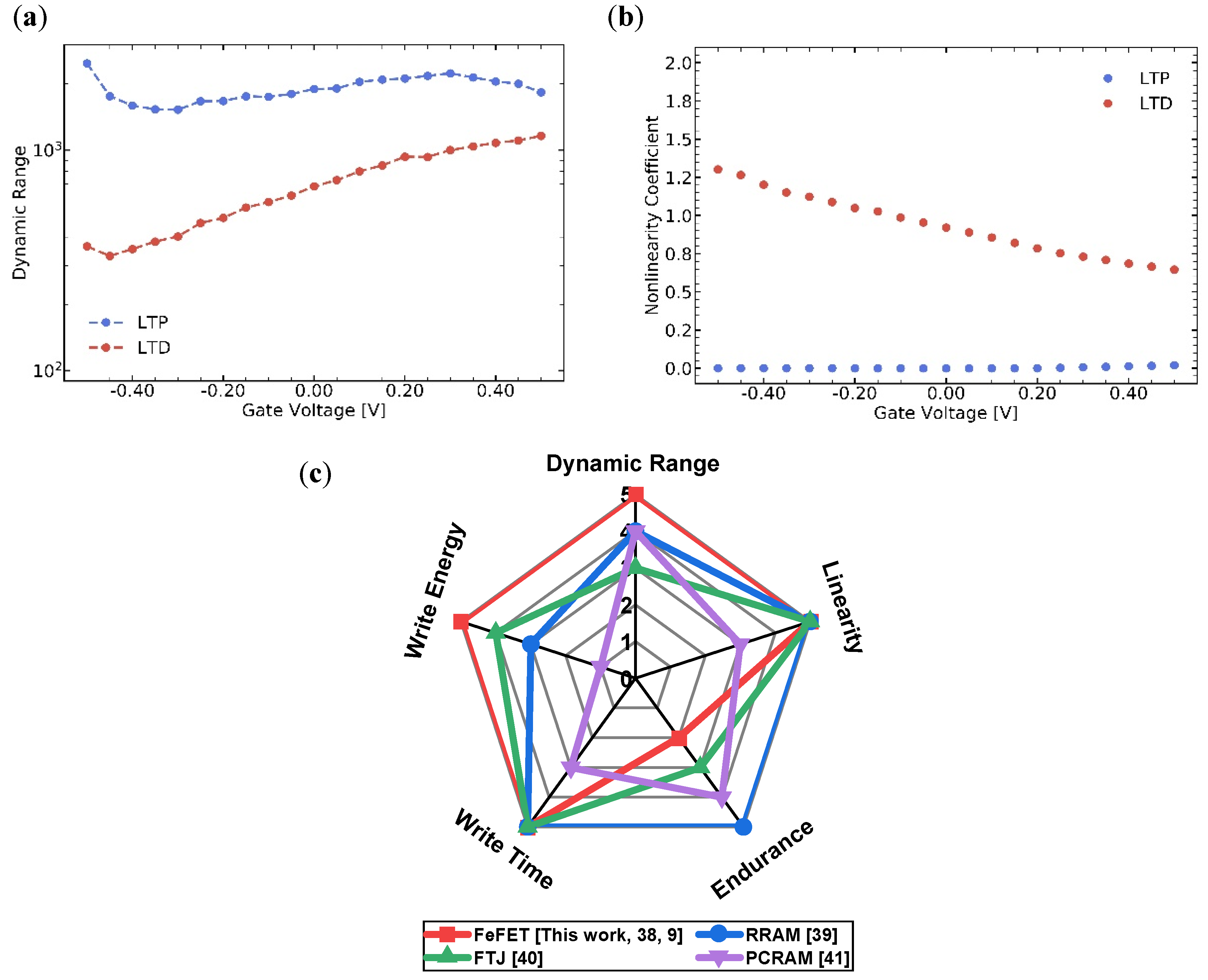
3.10. The Laminate FeFET Based Synaptic Metrics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfrey, M.; Hendry, D. The computer as von Neumann planned it. IEEE Ann. Hist. Comput. 1993, 15, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C. The Gap between Processor and Memory Speeds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, Braga, Portugal, 11–15 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A. Emerging nonvolatile memory (NVM) technologies. In Proceedings of the 2015 45th European Solid State Device Research Conference (ESSDERC), Graz, Austria, 14–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Turvani, G.; Graziano, M. New Logic-In-Memory Paradigms: An Architectural and Technological Perspective. Micromachines 2019, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nandakumar, S.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Babu, A.V.; Rajendran, B. Building Brain-Inspired Computing Systems: Examining the Role of Nanoscale Devices. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2018, 12, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S. Neuro-Inspired Computing with Emerging Nonvolatile Memorys. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 260–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böscke, T.S.; Müller, J.; Bräuhaus, D.; Schröder, U.; Böttger, U. Ferroelectricity in hafnium oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 102903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Böscke, T.S.; Schröder, U.; Mueller, S.; Bräuhaus, D.; Böttger, U.; Mikolajick, T. Ferroelectricity in Simple Binary ZrO2 and HfO2. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4318–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Dunkel, S.; Trentzsch, M.; Muller, J.; Hellmich, A.; Utess, D.; Slesazeck, S. FeFET: A versatile CMOS compatible device with game-changing potential. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Memory Workshop (IMW), Dresden, Germany, 17–20 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentzsch, M.; Flachowsky, S.; Richter, R.; Paul, J.; Reimer, B.; Utess, D.; Rice, B. A 28nm HKMG super low power embedded NVM technology based on ferroelectric FETs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florent, K.; Pesic, M.; Subirats, A.; Banerjee, K.; Lavizzari, S.; Arreghini, A.; Houdt, J.V. Vertical Ferroelectric HfO2 FET based on 3-D NAND Architecture: Towards Dense Low-Power Memory. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajick, T.; Schroeder, U.; Slesazeck, S. The Past, the Present, and the Future of Ferroelectric Memories. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, H.; Wu, C.; Tseng, T. Device modeling of ferroelectric memory field-effect transistor (FeMFET). IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2002, 49, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Polakowski, P.; Buttner, T.; Kampfe, T.; Rudolph, M.; Patzold, B.; Seidel, K. Principles and Challenges for Binary Oxide Based Ferroelectric Memory FeFET. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 11th International Memory Workshop (IMW), Monterey, CA, USA, 12–15 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Polakowski, P.; Paul, J.; Riedel, S.; Hoffmann, R.; Drescher, M.; Kolodinski, S. (Invited) Integration Challenges of Ferroelectric Hafnium Oxide Based Embedded Memory. ECS Trans. 2015, 69, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, S.; Polakowski, P.; Müller, J. A thermally robust and thickness independent ferroelectric phase in laminated hafnium zirconium oxide. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 095123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Olivo, R.; Lederer, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Steinke, P.; Zimmermann, K.; Muller, F. A multilevel FeFET memory device based ON LAMINATED HSO and Hzo Ferroelectric layers for High-Density Storage. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulaosmanovic, H.; Chicca, E.; Bertele, M.; Mikolajick, T.; Slesazeck, S. Mimicking biological neurons with a nanoscale ferroelectric transistor. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21755–21763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Polakowski, P.; Riedel, S.; Buttner, T.; Kampfe, T.; Rudolph, M.; Muller, J. High Endurance Ferroelectric Hafnium Oxide-Based FeFET Memory without Retention Penalty. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehninger, D.; Olivo, R.; Ali, T.; Lederer, M.; Kämpfe, T.; Mart, C.; Seidel, K. Back-End-of-Line Compatible Low-Temperature Furnace Anneal for Ferroelectric Hafnium Zirconium Oxide Formation. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 2020, 217, 1900840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, J. Ferroelektrizität in HfO2-Basierten Dünnschichten und deren Anwendung in Nicht-Flüchtigen Halbleiterspeichern. Ph.D. Dissertation, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.L.; Mcwhorter, P.J. Physics of the ferroelectric nonvolatile memory field effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 5999–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, M. Ferroelektrische Feldeffekttransistoren: Modellierung und Anwendung. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität der Bundeswehr Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zagni, N.; Pavan, P.; Alam, M. A Memory Window Expression to Predict the Scaling Trends and Endurance of FeFETs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12743. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-M.; Park, E.-J.; Woo, J.-J.; Kwon, K.-W. A Highly Linear Neuromorphic Synaptic Device Based on Regulated Charge Trap/Detrap. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 1848–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogio, S.; Ciocchini, N.; Laudato, M.; Milo, V.; Pirovano, A.; Fantini, P.; Ielmini, D. Unsupervised Learning by Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity in Phase Change Memory (PCM) Synapses. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, C.; Schenk, T.; Park, M.H.; Tscharntke, F.A.; Grimley, E.D.; LeBeau, J.M.; Zhou, C.; Fancher, C.M.; Jones, J.L.; Mikolajick, T.; et al. Si Doped Hafnium Oxide-A “Fragile” Ferroelectric System. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1700131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kuhnel, K.; Czernohorsky, M.; Rudolph, M.; Patzold, B.; Olivo, R.; Lehninger, D.; Mertens, K.; Muller, F.; Lederer, M.; et al. Impact of Ferroelectric Wakeup on Reliability of Laminate Based Si-Doped Hafnium Oxide (HSO) FeFET Memory Cells. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Dallas, TX, USA, 28 April–30 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lederer, M.; Kämpfe, T.; Vogel, N.; Utess, D.; Volkmann, B.; Ali, T.; Olivo, R.; Müller, J.; Beyer, S.; Trentzsch, M.; et al. Structural and Electrical Comparison of Si and Zr Doped Hafnium Oxide Thin Films and Integrated FeFETs Utilizing Transmission Kikuchi Diffraction. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulaosmanovic, H.; Ocker, J.; Müller, S.; Schroeder, U.; Müller, J.; Polakowski, P.; Flachowsky, S.; Bentum, R.V.; Mikolajick, T.; Slesazeck, S. Switching Kinetics in Nanoscale Hafnium Oxide Based Ferroelectric Field-Effect Transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, S.; Trentzsch, M.; Richter, R.; Moll, P.; Fuchs, C.; Gehring, O.; Majer, M.; Wittek, S.; Muller, B.; Melde, T.; et al. A FeFET Based Super-Low-Power Ultra-Fast Embedded NVM Technology for 22nm FDSOI and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Kido, M.; Yahashi, K.; Oomura, M.; Katsumata, R.; Kito, M.; Fukuzumi, Y.; Sato, M.; Nagata, Y.; Matsuoka, Y.; et al. Bit Cost Scalable Technology with Punch and Plug Process for Ultra High Density Flash Memory. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Kyoto, Japan, 12–14 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, K.; Wu, R.; Song, L.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Qian, H. Stacked 3D RRAM Array with Graphene/CNT as Edge Electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, J.D.; Kumar, S. The Building Blocks of a Brain-Inspired Computer. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerry, M.; Chen, P.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Sharma, P.; Ni, K.; Yu, S.; Datta, S. Ferroelectric FET Analog Synapse for Acceleration of Deep Neural Network Training. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mulaosmanovic, H.; Muller, F.; Lederer, M.; Ali, T.; Hoffmann, R.; Seidel, K.; Zhou, H.; Ocker, J.; Mueller, S.; Dunkel, S.; et al. Interplay Between Switching and Retention in HfO2-Based Ferroelectric FETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 3466–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, P.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Xia, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H. Scaling-up resistive synaptic arrays for neuro-inspired architecture: Challenges and prospect. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lederer, M.; Kampfe, T.; Ali, T.; Muller, F.; Olivo, R.; Hoffmann, R.; Laleni, N.; Seidel, K. Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistors as a Synapse for Neuromorphic Application. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, F.; Azni Zulkifli, T.Z.; Khanday, F.A. Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM): An Overview of Materials, Switching Mechanism, Performance, Multilevel Cell (mlc) Storage, Modeling, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhawat, A.; Walters, G.; Yang, N.; Guo, J.; Nishida, T.; Moghaddam, S. Data retention and low voltage operation of Al2O3/Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 based ferroelectric tunnel junctions. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 39LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Lee, S. Evolution of Phase-Change Memory for the Storage-Class Memory and Beyond. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 1394–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Performance Metric | Planar FeFET [31] | Vertical FeFET [11] | This work Laminate Based MLC FeFET | Flash NAND [32] | Vertical RRAM [33] |
| Program Voltage | 4.2 V | 10 V | 8 V (2b/cell), 10 V (3b/cell) | >11 V | 2.8 V (MLC) |
| Write Time | 10 ns | 100 ns | 300 ns | >100 µs | 100 ns |
| Endurance | 1E5 | 1E4 | 1E4 | 1E4 | >1E10 |
| Retention | 10 years @85 °C | 10 years @85 °C | 10 years @RT | 10 years @85 °C | >1E4sec @125 °C |
| Energy per Bit | <1 fJ | <1 fJ | <1 fJ | <1 nJ | 10 pJ |
| Bit/Cell | 1 | 1 | Up to 3 | Up to 4 | Up to 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, T.; Kühnel, K.; Olivo, R.; Lehninger, D.; Müller, F.; Lederer, M.; Rudolph, M.; Oehler, S.; Mertens, K.; Hoffmann, R.; et al. Impact of the Ferroelectric Stack Lamination in Si Doped Hafnium Oxide (HSO) and Hafnium Zirconium Oxide (HZO) Based FeFETs: Toward High-Density Multi-Level Cell and Synaptic Storage. Electron. Mater. 2021, 2, 344-369. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2030024
Ali T, Kühnel K, Olivo R, Lehninger D, Müller F, Lederer M, Rudolph M, Oehler S, Mertens K, Hoffmann R, et al. Impact of the Ferroelectric Stack Lamination in Si Doped Hafnium Oxide (HSO) and Hafnium Zirconium Oxide (HZO) Based FeFETs: Toward High-Density Multi-Level Cell and Synaptic Storage. Electronic Materials. 2021; 2(3):344-369. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Tarek, Kati Kühnel, Ricardo Olivo, David Lehninger, Franz Müller, Maximilian Lederer, Matthias Rudolph, Sebastian Oehler, Konstantin Mertens, Raik Hoffmann, and et al. 2021. "Impact of the Ferroelectric Stack Lamination in Si Doped Hafnium Oxide (HSO) and Hafnium Zirconium Oxide (HZO) Based FeFETs: Toward High-Density Multi-Level Cell and Synaptic Storage" Electronic Materials 2, no. 3: 344-369. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2030024
APA StyleAli, T., Kühnel, K., Olivo, R., Lehninger, D., Müller, F., Lederer, M., Rudolph, M., Oehler, S., Mertens, K., Hoffmann, R., Zimmermann, K., Schramm, P., Metzger, J., Binder, R., Czernohorsky, M., Kämpfe, T., Seidel, K., Müller, J., Van Houdt, J., & Eng, L. M. (2021). Impact of the Ferroelectric Stack Lamination in Si Doped Hafnium Oxide (HSO) and Hafnium Zirconium Oxide (HZO) Based FeFETs: Toward High-Density Multi-Level Cell and Synaptic Storage. Electronic Materials, 2(3), 344-369. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2030024







