Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- What are the BCT functionalities and features;
- (2)
- What are the prevailing and potential applications of BCT;
- (3)
- Identify the business benefits and impact of BCT in SCM.
2. Methodology
3. Literature Review and Analysis
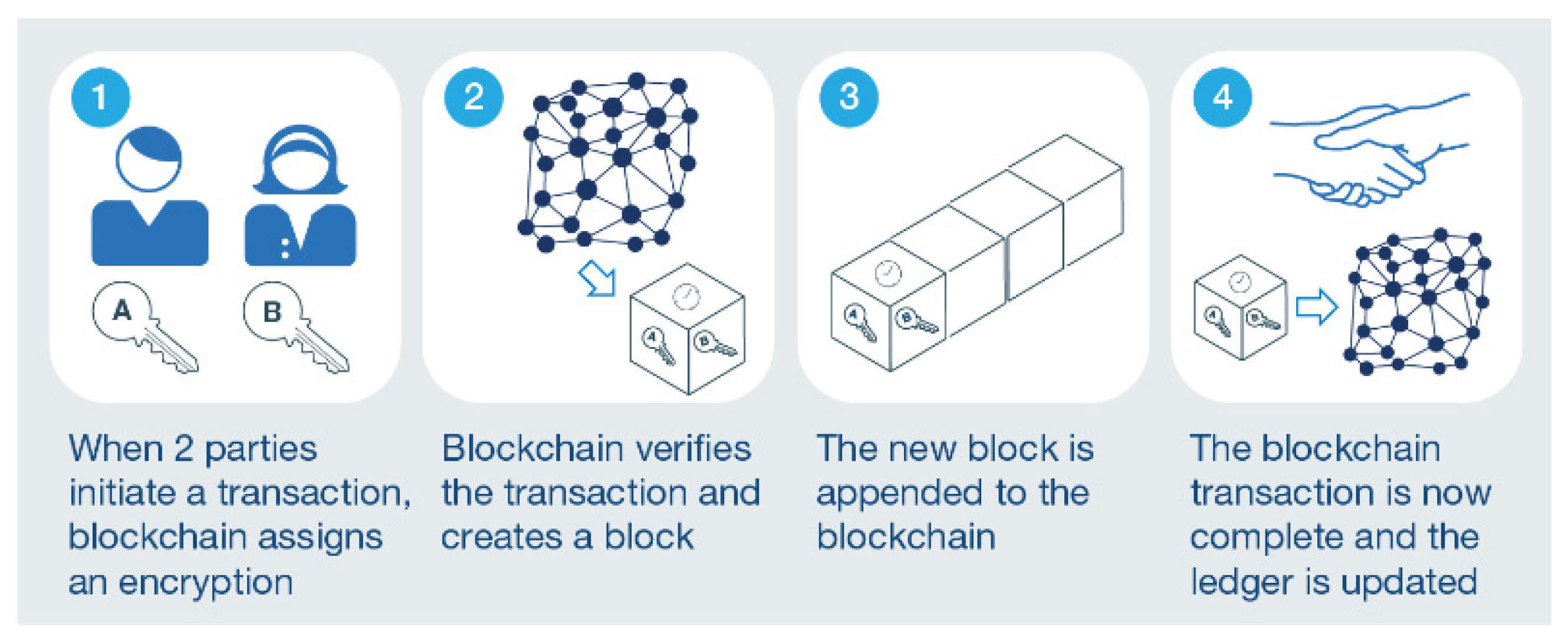
3.1. Blockchain Technology
3.2. Blockchain Technology and Supply Chain Management
3.3. Blockchain Technology and Metaverse
4. Results
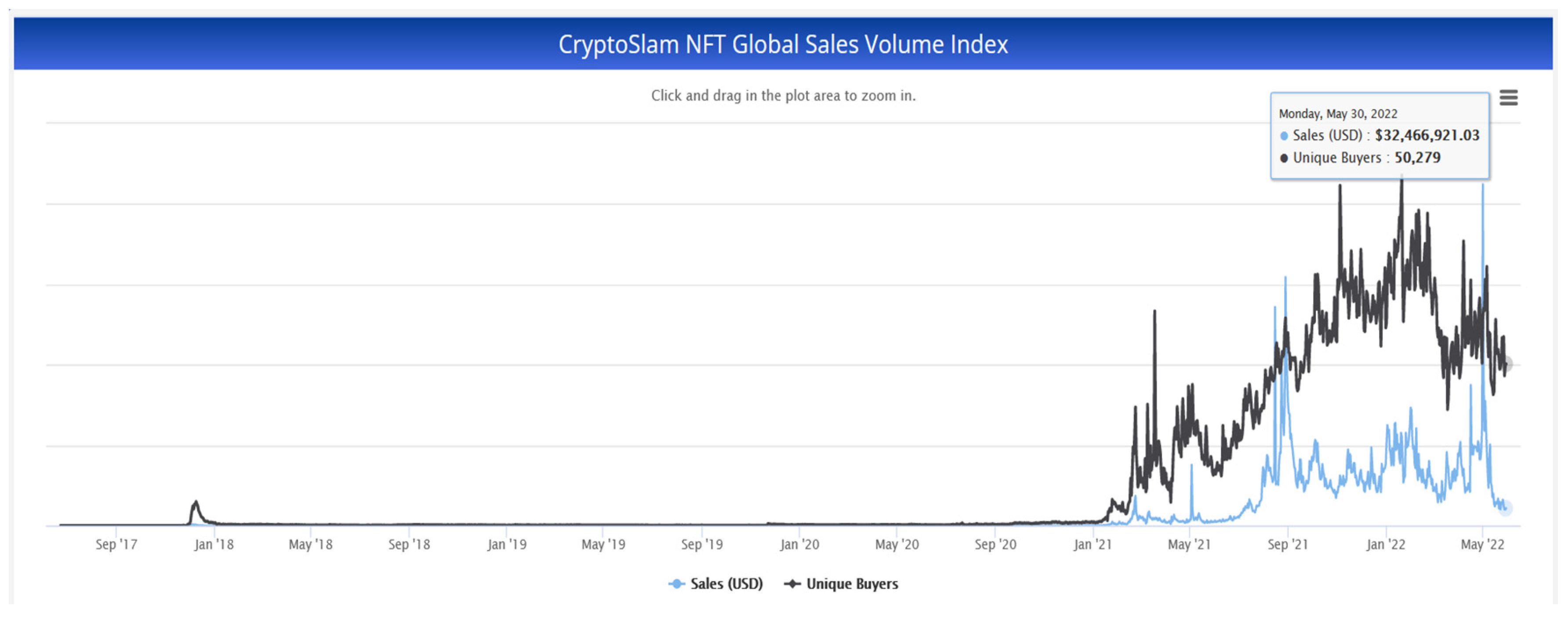
4.1. Blockchain between 1990–2022
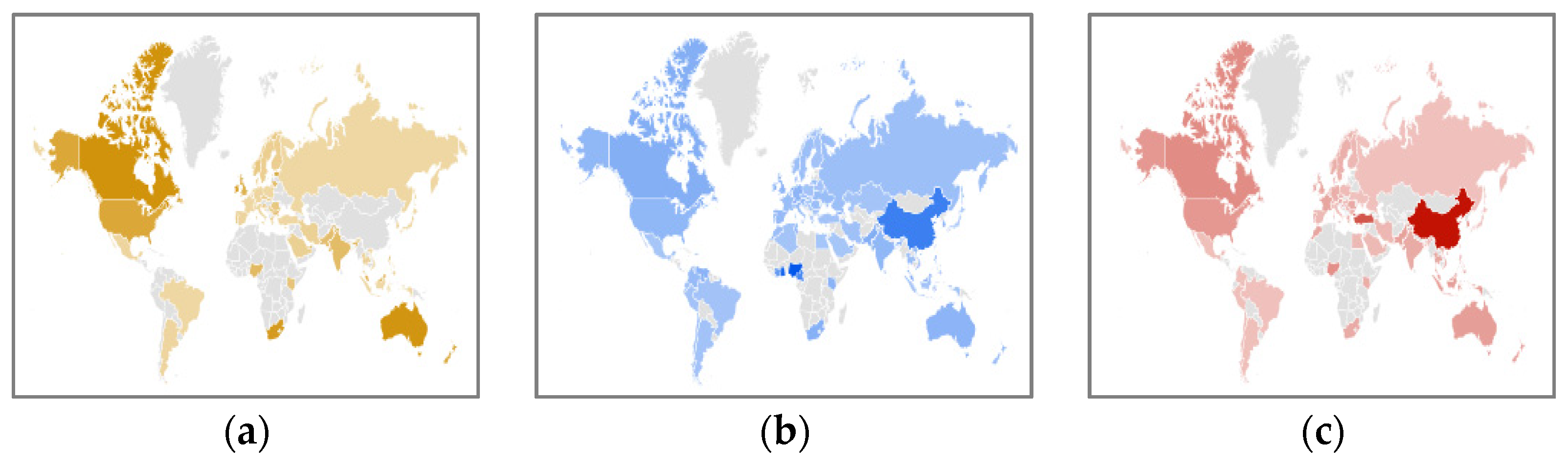
4.2. Top Countries with Interests in BCT, Bitcoin, and Metaverse
4.3. Network Analysis (BCT and SCM)
4.4. Blockchain Application Areas
5. Discussion and Limitations
6. Future Research Opportunities: Next Generation Blockchain
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puthal, D.; Malik, N.; Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E.; Das, G. Everything you wanted to know about the Blockchain: Its promise, components, processes, and problems. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2018, 7, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Macknisy and Company. Blockchain Technology for Supply Chains—A Must or a Maybe? 12 September 2017. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/ (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Klöckner, M.; Schmidt, C.G.; Wagner, S.M. When Blockchain Creates Shareholder Value: Empirical Evidence from Interna-tional Firm Announcements. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2021, 31, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougayar, W. A decision tree for blockchain applications: Problems, opportunities or capabilities. Startup Manag. 2015, 3, 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bitcoinist. Available online: https://bitcoinist.com/92-blockchain-projects-already-failed-average-lifespan-1-22-years/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Zerocoin Electric Coin Co. Available online: https://zerocoin.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Gaur, V. Bringing Blockchain, IoT, and Analytics to Supply Chains. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2021. Available online: https://hbr.org/2021/12/bringing-blockchain-iot-and-analytics-to-supply-chains (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- de Bem Machado, A.; Secinaro, S.; Calandra, D.; Lanzalonga, F. Knowledge management and digital transformation for In-dustry 4.0: A structured literature review. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2022, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuegbuzie, A.J.; Frels, R. Seven Steps to A Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach; Sage: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bartol, T.; Budimir, G.; Dekleva-Smrekar, D.; Pusnik, M.; Juznic, P. Assessment of research fields in Scopus and Web of Science in the view of national research evaluation in Slovenia. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, M. Blockchain: Blueprint for A New Economy; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, S.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J.; Shen, L. Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain man-agement. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 2117–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyperledger Building Enterprise Blockchain Ecosystems through Global, Open-Source Collaboration. Available online: www.hyperledger.org (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Crosby, M.; Pattanayak, P.; Verma, S.; Kalyanaraman, V. Blockchain technology: Beyond Bitcoin. Appl. Innov. 2016, 2, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.; Choi, T.M.; Somani, S.; Butala, R. Blockchain technology in supply chain operations: Applications, challenges, and research opportunities. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 142, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyratne, S.A.; Monfared, R.P. Blockchain ready manufacturing supply chain using distributed ledger. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F. An agri-food supply chain traceability system for China based on RFID & Blockchain technology. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), Kunming, China, 24–26 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, J.; Bakerm, J. Blockchain: The Solution for Transparency in Product Supply Chains. 2015. Available online: https://www.provenance.org (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R.; Del Vecchio, P.; Oropallo, E.; Secundo, G. Blockchain technology for bridging trust, traceability, and transparency in circular supply chain. Inf. Manag. 2021, 59, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhizadeh, M.; Saberi, S.; Sarkis, J. Blockchain technology and the sustainable supply chain: Theoretically exploring adoption barriers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Laskowski, M. Towards an Ontology-Driven Blockchain Design for Supply Chain Provenance 2016. Available online: CoRRabs/1610.02922 (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Kshetri, N. Blockchain and Supply Chain Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.C. Blockchain Adoption and Design for Supply Chain Management 2019. Ph.D. Thesis, Rutgers University-Graduate School-Newark, Newark, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.; Katehakis, M.N.; Shi, J.; Yan, Z. Blockchain-empowered Newsvendor optimization. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 238, 108144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Z.; Wang, S. A survey of supply chain operation and finance with Fintech: Research framework and managerial insights. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 108431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Fosso Wamba, S.; De Bourmont, M.; Telles, R. Blockchain adoption in operations and supply chain man-agement: Empirical evidence from an emerging economy. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 6087–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastig, G.M.; Sodhi, M.S. Blockchain for supply chain traceability: Business requirements and critical success factors. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossey, G.; Eisenhardt, J.; Hahn, G. Blockchain technology in supply chain management: An application perspective. Comput. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babich, V.; Hilary, G.O.M. Forum—Distributed ledgers and operations: What operations management researchers should know about blockchain technology. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2020, 22, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moosavi, J.; Naeni, L.M.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Fiore, U. Blockchain in supply chain management: A review, bibliometric, and network analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muessigmann, B.; von der Gracht, H.; Hartmann, E. Blockchain technology in logistics and supply chain management—A bibliometric literature review from 2016 to January 2020. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 988–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. Blockchain Adoption for Supply Chain Finance. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on PBFEAM, Newark, NJ, USA, 3–4 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Secinaro, S.; Dal Mas, F.; Brescia, V.; Calandra, D. Blockchain in the accounting, auditing and accountability fields: A bibli-ometric and coding analysis. Account. Audit. Account. J. 2021. Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/AAAJ-10-2020-4987/full/html (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Shi, J.; Chang, A. Blockchain Technology for Agricultural Value Chain. In Proceedings of the POMS Annual Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 21–25 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J. Blockchain Adoption for Agricultural Supply Chain. In Proceedings of the Institute for Operations Research & Man-agement Sciences (INFORMS) Annual Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 24 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Blockchain Solutions: Where Blockchain for Business Comes to Life. Available online: www.ibm.com/Blockchain (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Sousa, M.J.; Dal Mas, F.; Gonçalves, S.P.; Calandra, D. AI and Blockchain as New Triggers in the Education Arena. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2022, 12, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, R.; Massaro, M.; Iacuzzi, S. Blockchain for value creation in the healthcare sector. Technovation 2021, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Simske, S.; Treiblmaier, H. Blockchain Technologies in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: A Bib-liometric Review. Logistics 2021, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.H.; Braud, T.; Zhou, P.; Wang, L.; Xu, D.; Lin, Z.; Kumar, A.; Bermejo, C.; Hui, P. All one needs to know about Metaverse: A complete survey on technological singularity, virtual ecosystem, and research agenda. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.05352. [Google Scholar]
- Cryptoslam. Available online: https://cryptoslam.io/nftglobal (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Gadekallu, T.R.; Huynh-The, T.; Wang, W.; Yenduri, G.; Ranaweera, P.; Pham, Q.V.; da Costa, D.B.; Liyanage, M. Blockchain for the Metaverse: A Review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.09738. [Google Scholar]
- Which Blockchains are Behind the Top Metaverse Platforms? XR Today. Available online: https://www.xrtoday.com (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Hwang, T.; Rao, T.R.N. Secret error-correcting codes (SECC). In Proceedings of the Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptography, Davos, Switzerland, 25–27 May 1988; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 540–563. [Google Scholar]
- Bellare, M.; Kilian, J.; Rogaway, P. The security of cipher block chaining. In Annual International Cryptology Conference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 341–358. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Dong, C.; Minner, S. Combating copycats in the supply chain with permissioned Blockchain technology. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Telles, R.; Bonilla, S.H. Blockchain and supply chain management integration: A systematic review of the literature. Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 25, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/home (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Norman, A.T. Blockchain Technology Explained: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide about Blockchain Wallet, Mining, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Zcash, Monero, Ripple, Dash, IOTA and Smart Contracts; Amazon Distribution: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, P.; Pradhan, C. Blockchain 1.0 to Blockchain 4.0—The Evolutionary Transformation of Blockchain Technology. In Blockchain Technology: Applications and Challenges; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.; Wu, C.H.; Tsang, Y.P.; Chen, Q. An End-to-End Bidirectional Authentication System for Pallet Pooling Management Through Blockchain Internet of Things (BIoT). J. Organ. End User Comput. 2021, 33, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Tsang, Y.-P.; Lee, C.K.-M.; Ching, W.-K. A Blockchain-IoT Platform for the Smart Pallet Pooling Management. Sensors 2021, 21, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Katehakis, M.N.; Melamed, B.; Shi, J. Blockchain Technology and its Applications. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 38, 173–180. [Google Scholar]







| Blockchain Features | Links | Occurrences | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traceability | 201 | 210 | 1329 |
| Security | 132 | 79 | 789 |
| Transparency | 126 | 126 | 527 |
| Efficiency | 88 | 32 | 216 |
| Confidentiality | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Immutability | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BCT 1.0 Bitcoin—“The Mother of All Blockchain.” | BCT 2.0 Ethereum | BCT 3.0 Hyperledger | BCT 4.0 Industry 4.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Based on | Distributed Ledger Technology, proof of work [50] | Smart contracts, proof of work consensus mechanisms [51] | Smart contract + decentralized Apps (dApps), proof of stack, proof of authority [51] | BCT + A.I. Proof of integrity [51] |
| Speed | 7 transactions/sec. | 30 transactions/sec. | Thousands of transactions/sec. | 1 Million Transaction/sec. |
| Pros |
|
|
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
|
|
| Cost Level | $$$$$$ | $$$$ | $$ | $ |
| Well-known Applications | Financial Applications. | Electronic voting, trading, and real estate. | Business platform. | Business-usable platform. Industry 4.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, A.; El-Rayes, N.; Shi, J. Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review. FinTech 2022, 1, 191-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech1020015
Chang A, El-Rayes N, Shi J. Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review. FinTech. 2022; 1(2):191-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech1020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Aichih (Jasmine), Nesreen El-Rayes, and Jim Shi. 2022. "Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review" FinTech 1, no. 2: 191-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech1020015
APA StyleChang, A., El-Rayes, N., & Shi, J. (2022). Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review. FinTech, 1(2), 191-205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech1020015









