General Methods
All reactions were carried out under a positive pressure of argon, unless otherwise noted. All chemicals were purchased from commercial suppliers and used without further purification, unless otherwise noted. Molecular sieves were purchased from Wako Chemicals Inc. (Miyazaki, Japan) and dried at 300 °C for 2 h in a muffle furnace prior to use. Solvents as reaction media were dried over molecular sieves and used without purification. TLC analysis was performed on Merck TLC plates (silica gel 60F254 on glass plate). Compound detection was either by exposure to UV light (2536 Å) or by soak in a solution of 10% H2SO4 in ethanol followed by heating. Silica gel (80 mesh and 300 mesh) manufactured by Fuji Silysia Co. was used for flash column chromatography. Quantity of silica gel was usually estimated as 200 to 400-fold weight of sample to be charged. Solvent systems in chromatography were specified in v/v. Evaporation and concentration were carried out in vacuo. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded with JEOL ECA 400/500/600 and Bruker UltraShield Plus 500 spectrometers. Chemical shifts in 1H-NMR spectra are expressed in ppm (δ) relative to the signal of Me4Si, adjusted to δ 0.00 ppm. Data are presented as follow: Chemical shift, multiplicity (s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, dd = double of doublet, td = triple doublet, m = multiplet and/or multiple resonances), integration, coupling constant in Hertz (Hz), position of the corresponding proton. COSY methods were used to confirm the NMR peak assignments. High-resolution mass (ESI-TOF MS) spectra were run in a Bruker micrOTOF. Optical rotations were measured with a “Horiba SEPA-300” high-sensitive polarimeter.
Phenyl 4,6-O-anisylidene-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (
3). To the solution of
2 (20.0 g, 73.5 mmol) in the mixed solvent (CH
3CN–DMF 735 mL:200 mL) were added
p-anisaldehyde dimethyl acetal (25.0 mL, 147 mmol) and (±)-camphor-10-sulfonic acid (CSA) (680 mg, 2.94 mmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 2.5 h at room temperature as the reaction was monitored by TLC (10:1 CHCl
3–MeOH), the reaction was quenched by the addition of triethylamine. The reaction mixture was concentrated and diluted with EtOAc, of which solution was then added to separatory funnel. After addition of distilled water to the solution, the desired 4,6-
O-anisylidenated product was appeared as a pure crystalline material (26.0 g, 91%), the physical data of which was identical to those reported in the literature [
31]. To a solution of the 4,6-
O-anisylidenated product obtained (2.00 g, 5.13 mmol) in DMF (25.7 mL) was added sodium hydride (492 mg, 20.5 mmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 1 h at 0 °C,
p-methoxybenzyl chloride (2.8 mL, 20.5 mmol) was added to the mixture. After stirring for 17 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2.5 EtOAc–
n-hexane), the reaction was quenched by MeOH at 0 °C. Dilution of the mixture with EtOAc provided a solution, which was then washed with H
2O, satd aq NaHCO
3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na
2SO
4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:3 EtOAc–
n-hexane) to give
3 (2.94 g, 91%). [α]
D +3.3° (c 0.3, CHCl
3);
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ 7.54–6.82 (m, 17H, 4Ar), 5.54 (s, 1H, ArC
H), 4.85 (d, 1H,
Jgem = 10.9 Hz, ArC
H2), 4.78–4.70 (m, 4H, ArC
H2, H-1), 4.35 (dd, 1H,
J5,6 = 5.2 Hz,
Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-6), 3.81–3.76 (m, 11H, 3OCH
3, H-3, H-6'), 3.66 (t, 1H,
J3,4 =
J4,5 = 9.5 Hz, H-4), 3.45 (m, 2H, H-2, H-5);
13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl
3) δ 160.0, 159.4, 159.3, 133.1, 132.2, 130.5, 130.2, 129.9, 129.8, 129.0, 127.8, 127.3, 113.8, 113.6, 101.1, 88.3, 82.7, 81.4, 80.1, 75.5, 74.9, 70.2, 68.6, 55.3, 55.2. HRMS (ESI)
m/
z: found [M+Na]
+ 653.2180, C
36H
38O
8S calcd for [M+Na]
+ 653.2180.
Phenyl 2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (4). Compound 3 (2.60 g, 4.13 mmol) was dissolved in 80% AcOH aq (41.3 mL) and the solution was stirred for 1.5 h at 50 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (2:1 EtOAc–n-hexane). The reaction mixture was diluted with EtOAc and carefully washed with ice-cooled satd aq Na2CO3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 4 (2.11 g, quant.). [α]D −18.0° (c 0.4, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.52–6.87 (m, 13H, 3Ar), 4.90 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.3 Hz, ArCH2), 4.88 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.70 (m, 2H, ArCH2, H-1), 4.64 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 3.86 (m, 1H, H-6), 3.80 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.73 (m, 1H, H-6'), 3.55–3.43 (m, 3H, H-4, H-3, H-2), 3.32 (m, 1H, H-5), 2.28 (d, 1H, J4,OH = 2.5 Hz, OH), 2.08 (t, 1H, J6,OH = J6',OH = 6.6 Hz, OH); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 159.5, 159.5, 133.6, 131.7, 130.4, 130.0, 129.9, 129.7, 129.6, 129.0, 127.6, 114.1, 113.9, 87.7, 85.6, 80.6, 79.1, 75.0, 75.0, 70.4, 62.8, 55.3, 55.3. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 535.1758, C28H32O7S calcd for [M+Na]+ 535.1761.
(2S,3R,4E)-1-O-tert-Butyldimethylsilyl-3-O-(4-hydroxycarbonylbutanoate)-2-octadecanamido-4-octa-decene-1,3-diol (7). To a solution of 5 (25 mg, 36.8 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (368 µL) were added glutaric anhydride (21 mg, 184 µmol) and DBU (11 µL, 73.6 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 1 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (4:1 diethylether–n-hexane), the reaction was quenched by the addition of MeOH at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was evaporated. The crude residue obtained was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:3 diethylether–n-hexane) to give 7 (28 mg, 96%). [α]D +4.7° (c 0.3, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.76 (m, 2H, H-5, NH), 5.42 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.2 Hz, J4,5 = 15.3 Hz, H-4), 5.32 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 7.2 Hz, H-3), 4.28 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.72 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 3.1 Hz, Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-1), 3.59 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 4.4 Hz, H-1'), 2.46–2.36 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.17 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2Cer), 2.01 (m, 2H, H-6, H-6'), 1.95 (m, 2H, -CH2-), 1.59 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-Cer), 0.88 (m, 15H, t-Bu, 2-CH3Cer), 0.05-0.04 (2 s, 6H, Si(CH3)2); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 177.3, 173.3, 173.1, 171.1, 136.9, 124.6, 73.7, 61.6, 51.8, 51.6, 37.0, 33.4, 33.1, 33.0, 32.9, 32.4, 31.9, 30.0, 29.7, 29.7, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.4, 29.3, 29.2, 29.0, 25.8, 25.7, 22.7, 20.1, 19.9, 18.2, 14.1, −5.6, −5.6. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 816.6507, C47H91NO6Si calcd for [M+Na]+ 816.6508.
(2S,3R,4E)-1-O-tert-Butyldimethylsilyl-3-O-(2-hydroxycarbonylisobutanoate)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol (8). To a solution of 5 (47 mg, 69.2 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (1.4 mL) were added dimethylmalonyl dichloride (92 µL, 692 µmol) and triethylamine (96 µL, 692 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 3 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 diethylether–n-hexane), the reaction was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with H2O and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:4 diethylether–n-hexane) to give 8 (17 mg, 31%). [α]D +4.4° (c 0.8, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.44 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.0 Hz, NH), 5.77 (m, 1H, H-5), 5.41 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.4 Hz, J4,5 = 15.3 Hz, H-4), 5.32 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 7.4 Hz, H-3), 4.20 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.76 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 2.7 Hz, Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-1), 3.62 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 4.2 Hz, H-1'), 2.28 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.00 (m, 2H, H-6, H-6'), 1.60 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.49 (s, 6H, CH3CCH3), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.89 (m, 15H, t-Bu, 2-CH3Cer), 0.05 (2 s, 6H, Si(CH3)2). LRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M−H]− 792.6438, C47H91NO6Si calcd for [M−H]− 792.6543.
(2S,3R,4E)-1-O-tert-Butyldimethylsilyl-3-O-(o-hydroxycarbonylbenzoate)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol (9). To a solution of 5 (1.00 g, 1.47 mmol) in pyridine (7.4 mL) were added phthalic anhydride (327 mg, 2.21 mmol), DMAP (18 mg, 147 µmol) and triethylamine (612 µL, 4.41 mmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 23 h at 40 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (4:1 diethylether–n-hexane), the solvent was removed by co-evaporation with toluene, and then the residue was diluted with CHCl3, washed with H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:2 diethylether–n-hexane) to give 9 (1.22 g, quant.). [α]D +58.3° (c 0.3, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.80–7.52 (m, 4H, Ar), 6.07 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 10.3 Hz, NH), 5.81 (m, 1H, H-5), 5.71 (t, 1H, J2,3 = J3,4 = 6.9 Hz, H-3), 5.54 (dd, 1H, J4,5 = 15.5 Hz, H-4), 4.44 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.76 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 4.1 Hz, Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-1), 3.64 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 5.5 Hz, H-1'), 2.27 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.03 (m, 2H, H-6, H-6'), 1.63 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.33 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 15H, t-Bu, 2-CH3), 0.05 (2 s, 6H, Si(CH3)2); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 174.7, 169.8, 166.4, 136.9, 132.7, 131.4, 131.2, 130.8, 129.5, 128.8, 123.7, 75.3, 62.1, 52.3, 37.0, 32.4, 31.9, 29.7, 29.7, 29.5, 29.4, 29.4, 29.3, 29.3, 29.0, 25.8, 25.7, 22.7, 18.1, 14.1, −5.5, −5.6. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 850.6351, C51H91NO5Si calcd for [M+Na]+ 850.6351.
Phenyl 6-O-{3-[(2S,3R,4E)-1-O-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylpropanoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (10). To a solution of 4 (124 mg, 242 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (4.8 mL) were added 6 (200 mg, 242 µmol), EDC·HCl (51 mg, 266 µmol) and DMAP (3.0 mg, 24.2 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 2.5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 10 (215 mg, 70%). [α]D −7.7° (c 0.3, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.56–7.24 (m, 5H, Ph), 7.54–6.85 (m, 8H, 2Ar), 5.74 (m, 2H, H-5Cer, NHCer), 5.43 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.2 Hz, J4,5 = 15.2 Hz, H-4Cer), 5.36 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 7.2 Hz, H-3Cer), 4.84 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.83 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.77 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.68 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.65 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 9.2 Hz, H-1a), 4.39 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 4.6 Hz, Jgem = 12.0 Hz, H-6a), 4.33 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 2.0 Hz, H-6'a), 4.23 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.80–3.79 (2 s, 6H, 2 OCH3), 3.69 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 9.7 Hz, Jgem = 10.4 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.57 (m, 2H, H-1'Cer, H-4a), 3.50 (t, 1H, J2,3 = J3,4 = 9.2 Hz, H-3a), 3.44 (m, 3H, H-2a, H-5a, OHa), 2.66–2.60 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.15 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2Cer), 2.01 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.57 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.30 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 15H, t-Bu, 2-CH3Cer), 0.04 (2 s, 6H, Si(CH3)2); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.8, 172.5, 170.7, 159.4, 159.3, 136.7, 133.7, 131.9, 130.6, 130.2, 129.9, 129.6, 128.8, 127.5, 124.6, 113.9, 113.8, 87.7, 85.6, 80.2, 77.5, 75.2, 75.0, 74.0, 69.8, 63.6, 61.6, 55.2, 55.2, 51.9, 36.9, 32.3, 31.9, 30.0, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.2, 29.0, 29.0, 25.8, 25.8, 22.6, 18.1, 14.2, 14.1, −5.5, −5.6. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1296.8116, C74H119NO12SSi calcd for [M+Na]+ 1296.8114.
Phenyl 6-O-{3-[(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylpropanoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (11). To a solution of 10 (183 mg, 144 µmol) in THF (1.4 mL) were added AcOH (26 µL, 432 µmol) and TBAF (432 µL, 432 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with satd. aq. NaHCO3. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:1.5 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 11 (159 mg, 95%). [α]D −12.0° (c 0.3, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.55–7.25 (m, 5H, Ph), 7.35–6.86 (m, 8H, 2Ar), 6.05 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.0 Hz, NHCer), 5.76 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.42 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.3 Hz, J4,5 = 15.2 Hz, H-4Cer), 5.35 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 7.3 Hz, H-3Cer), 4.85 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.9 Hz, ArCH2), 4.84 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.4 Hz, ArCH2), 4.72 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.68 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.66 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 9.6 Hz, H-1a), 4.45 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 4.6 Hz, Jgem = 11.9 Hz, H-6a), 4.29 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 1.6 Hz, H-6'a), 4.15 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.80–3.79 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.66 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 4.2 Hz, Jgem = 11.6 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.60 (near dd, 1H, H-1'Cer), 3.54–3.42 (m, 4H, H-3a, H-5a, H-4a, H-2a), 3.27 (br s, 1H, OHa), 2.83 (br s, 1H, OHCer), 2.72–2.62 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.16 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2Cer), 2.11 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.58 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.30 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.6, 172.7, 171.5, 159.4, 137.2, 133.7, 131.8, 130.4, 130.1, 129.9, 129.7, 128.9, 127.5, 124.5, 114.0, 113.8, 87.8, 85.6, 80.2, 77.3, 75.3, 75.0, 74.6, 69.6, 63.7, 61.6, 55.3, 55.2, 52.9, 36.7, 32.3, 31.9, 29.7, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.3, 29.2, 29.1, 28.9, 25.7, 22.7, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1182.7250, C68H105NO12S calcd for [M+Na]+ 1182.7250.
Phenyl 6-O-{4-[(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylbutanoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (12). To a solution of 4 (90 mg, 175 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (3.5 mL) were added 7 (139 mg, 175 µmol), EDC·HCl (37 mg, 193 µmol) and DMAP (2.1 mg, 17.5 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 1.5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give the crude mixture mainly containing 12. The crude mixture was exposed to high vacuum for 15 h and then dissolved in THF (1.8 mL). AcOH (31 µL, 525 µmol) and TBAF (525 µL, 525 µmol) were added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 4 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:2 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 13 (96 mg, 47% in two steps). [α]D −22.5° (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.55–7.25 (m, 5H, Ph), 7.36–6.87 (m, 8H, 2Ar), 6.00 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.6 Hz, NHCer), 5.76 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.44 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.4 Hz, J4,5 = 15.4 Hz, H-4Cer), 5.28 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 7.4 Hz, H-3Cer), 4.87 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.1 Hz, ArCH2), 4.85 (d, 1H, Jgem = 9.9 Hz, ArCH2), 4.69 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.68 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.65 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 9.4 Hz, H-1a), 4.34 (near s, 2H, H-6a, H-6'a), 4.12 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.81–3.80 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.66 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 3.8 Hz, Jgem = 11.7 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.60 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 2.7 Hz, H-1'Cer), 3.50–3.42 (m, 4H, H-2a, H-3a, H-4a, H-5a), 2.85 (br s, 1H, OHCer), 2.75 (s, 1H, OHa), 2.43–2.39 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.16 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2Cer), 2.01 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.96 (m, 2H, -CH2-), 1.58 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.29 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-Cer), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.4, 173.1, 172.7, 159.5, 159.4, 137.4, 133.7, 131.9, 130.4, 130.0, 129.9, 129.7, 128.9, 127.6, 124.7, 114.1, 113.9, 87.7, 85.5, 80.3, 77.6, 75.2, 75.0, 74.3, 69.9, 63.6, 61.7, 55.3, 55.2, 53.1, 36.8, 33.4, 33.0, 32.3, 31.9, 30.0, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.3, 29.2, 28.9, 25.7, 22.7, 20.0, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1196.7404, C69H107NO12S calcd for [M+Na]+ 1196.7406.
Phenyl 6-O-{2-[(2S,3R,4E)-1-O-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylisobutanoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (14). To a solution of 4 (55 mg, 107 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (2.1 mL) were added 8 (85 mg, 107 µmol), EDC·HCl (23 mg, 118 µmol) and DMAP (1.3 mg, 10.7 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (2:1 diethylether–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 14 (70 mg, 51%). 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.54–6.85 (m, 13H, 3Ar), 6.70 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.0 Hz, NHCer), 5.75 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.37 (m, 2H, H-4Cer, H-3Cer), 4.84 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.82 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.72 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.66 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.63 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 9.6 Hz, H-1a), 4.40 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 4.0 Hz, Jgem = 11.9 Hz, H-6a), 4.34 (near dd, 1H, H-6'a), 4.15 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.81–3.80 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.68 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 3.3 Hz, Jgem = 10.4 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.57 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 4.3 Hz, H-1'Cer), 3.50–3.47 (m, 3H, H-3a, H-4a, H-5a), 3.40 (m, 1H, H-2a), 2.87 (br s, 1H, OHa), 2.28 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 1.99 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.59 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.45 (s, 6H, CH3CCH3), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 15H, t-Bu, 2-CH3Cer), 0.05 (2 s, 6H, Si(CH3)2).
Phenyl 6-O-{2-[(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylisobutanoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (15). To a solution of 14 (62 mg, 48.1 µmol) in THF (481 µL) were added AcOH (8.6 µL, 144 µmol) and TBAF (144 µL, 144 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 3.5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:3 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 15 (51 mg, 91%). 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.54–6.86 (m, 13H, 3Ar), 6.71 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.6 Hz, NHCer), 5.75 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.41 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.4 Hz, J4,5 = 15.4 Hz, H-4Cer), 5.29 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 7.4 Hz, H-3Cer), 4.83 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.8 Hz, ArCH2), 4,82 (d, 1H, Jgem = 9.9 Hz, ArCH2), 4.72 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.66 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.64 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 9.2 Hz, H-1a), 4.39 (near d, 2H, H-6a, H-6'a), 4.08 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.81–3.80 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.55–3.46 (m, 5H, H-1Cer, H-1'Cer, H-3a, H-4a, H-5a), 3.40 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 9.2 Hz, H-2a), 3.32 (d, 1H, J4,OH = 3.4 Hz, OHa), 2.83 (br s, 1H, OHCer), 2.30 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.01 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.60 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.45 (2 s, 6H, CH3CCH3), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer). HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1196.7487, C69H107NO12S calcd for [M+Na]+ 1196.7406.
Phenyl 6-O-{[(2S,3R,4E)-1-O-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylbenzoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (16). To a solution of 4 (87 mg, 169 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (3.4 mL) were added 9 (140 mg, 169 µmol), EDC∙HCl (36 mg, 186 µmol) and DMAP (2.1 mg, 16.9 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 5.5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:3 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 16 (71 mg, 32%). [α]D +4.5° (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.77–6.83 (m, 17H, 4Ar), 5.93 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.6 Hz, NHCer), 5.77 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.61 (t, 1H, J2,3 = J3,4 = 6.9 Hz, H-3Cer), 5.54 (dd, 1H, J4,5 = 15.4 Hz, H-4Cer), 4.82 (s, 2H, ArCH2), 4.79 (d, 1H, Jgem = 9.9 Hz, ArCH2), 4.68 (m, 3H, ArCH2, H-1a, H-6a), 4.57 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 1.9 Hz, Jgem = 12.0 Hz, H-6'a), 4.39 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 4.11 (br s, 1H, OHa), 3.81–3.79 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.71 (m, 2H, H-1Cer, H-4a), 3.63 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 5.1 Hz, Jgem = 10.5 Hz, H-1'Cer), 3.57 (m, 2H, H-3a, H-5a), 3.45 (t, 1H, J1,2 = J2,3 = 9.2 Hz, H-2a), 2.15 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.03 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.55 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 15H, t-Bu, 2-CH3Cer), 0.04–0.03 (2 s, 6H, Si(CH3)2); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.1, 166.9, 166.8, 159.4, 159.3, 136.2, 133.5, 133.1, 132.2, 131.8, 131.5, 131.0, 130.8, 130.7, 130.3, 129.8, 129.6, 129.2, 128.8, 127.5, 124.4, 113.9, 113.9, 113.8, 87.4, 85.8, 79.9, 77.8, 77.6, 75.8, 75.3, 75.0, 69.9, 64.3, 62.0, 55.3, 55.2, 52.0, 36.9, 32.4, 31.9, 29.7, 29.7, 29.5, 29.4, 29.4, 29.3, 29.2, 29.1, 25.8, 25.7, 22.7, 18.2, 14.1, −5.4, −5.6. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1344.8116, C78H119NO12SSi calcd for [M+Na]+ 1344.8114.
Phenyl 6-O-{[(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-3-yloxy-1,3-diol]carbonylbenzoyl}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-1-thio-β-d-glucopyranoside (17). To a solution of 16 (190 mg, 144 µmol) in THF (1.4 mL) were added AcOH (26 µL, 432 µmol) and TBAF (432 µL, 432 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 4 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 EtOAc–n-hexane), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:2 EtOAc–n-hexane) to give 17 (156 mg, 90%). [α]D +3.3° (c 0.3, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85–6.84 (m, 17H, 4Ar), 6.41 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.2 Hz, NHCer), 5.82 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.61 (t, 1H, J2,3 = J3,4 = 6.6 Hz, H-3Cer), 5.47 (dd, 1H, J4,5 = 15.4 Hz, H-4Cer), 4.87–4.80 (m, 3H, ArCH2, H-6a), 4.73 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.7 Hz, ArCH2), 4.68 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 9.2 Hz, H-1a), 4.65 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.48 (near d, 1H, H-6'a), 4.27 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.80–3.78 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.74 (br d, 1H, H-1Cer), 3.69 (s, 1H, OHa), 3.57–3.51 (m, 4H, H-4a, H-5a, H-3a, H-1'Cer), 3.42 (t, 1H, J2,3 = 9.2 Hz, H-2a), 2.85 (br s, 1H, OHCer), 2.21 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.03 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.62 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.30 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.6, 167.3, 167.1, 159.4, 137.3, 133.5, 132.8, 132.0, 131.1, 130.4, 130.3, 130.1, 129.9, 129.8, 129.8, 129.7, 129.0, 128.9, 127.5, 124.3, 114.0, 113.9, 113.9, 87.6, 85.8, 80.0, 77.6, 77.4, 76.2, 75.5, 75.0, 69.2, 64.1, 61.6, 55.3, 55.2, 52.5, 36.7, 32.3, 31.9, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.3, 29.2, 28.9, 25.7, 22.7, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1230.7250, C72H105NO12S calcd for [M+Na]+ 1230.7250.
(2,3-Di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-β-d-glucopyranosyl)-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol-3,6'-succinate (18β). Condition A: To a mixture of 11 (32 mg, 27.6 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (5.5 mL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (64 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (45 mg, 82.8 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 18 (19 mg, 67%, α:β = 1:1.7). Condition B: To a mixture of 11 (47 mg, 40.5 µmol) in acetonitrile/CH2Cl2 (2:1 8.1 mL) was added 3 Å molecular sieves (95 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (65 mg, 121 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 18 (33 mg, 77%, α:β = 1:8.2). 18β: [α]D −10.4° (c 0.5, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27–6.86 (m, 8H, 2Ar), 5.93 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.2 Hz, NHCer), 5.77 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.55 (t, 1H, J2,3 = J3,4 = 6.3 Hz, H-3Cer), 5.30 (dd, 1H, J4,5 = 15.5 Hz, H-4Cer), 4.87 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.4 Hz, ArCH2), 4.78 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.8 Hz, ArCH2), 4.67–4.59 (m, 2H, H-6a, ArCH2), 4.55 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.40 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 4.34 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.0 Hz, H-1a), 4.09 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 2.1 Hz, Jgem = 11.6 Hz, H-6'a), 3.97 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 4.72 Hz, Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.80 (s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.77 (near d, 1H, H-1'Cer), 3.44 (td, 1H, J4,5 = 2.1 Hz, H-5a), 3.38–3.29 (m, 3H, H-2a, H-3a, H-4a), 2.79–2.61 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.19 (d, 1H, J4,OH = 1.8 Hz, OHa), 2.17 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2Cer), 1.99 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.61 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.1, 172.6, 169.9, 159.4, 159.3, 136.5, 130.4, 130.1, 129.8, 129.6, 124.1, 114.0, 113.8, 102.8, 83.2, 81.0, 74.7, 74.1, 73.7, 73.4, 70.8, 65.0, 63.7, 55.2, 50.4, 36.8, 32.2, 31.9, 29.7, 29.7, 29.7, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.2, 29.0, 28.8, 25.7, 22.6, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1072.7060, C62H99NO12 calcd for [M+Na]+ 1072.7059.
(2,3-Di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-d-glucopyranosyl)-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol-3,6´-glutarate (19). Condition A: To a mixture of 13 (27 mg, 23.0 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (4.6 mL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (55 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (37 mg, 69.0 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 3 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 19 (8.3 mg, 34%, α:β = 1:2.0). Condition B: To a mixture of 13 (29 mg, 24.7 µmol) in acetonitrile/CH2Cl2 (2:1 4.9 mL) was added 3 Å molecular sieves (60 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (40 mg, 74.1 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 20 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 19 (10.4 mg, 40%, α:β = 1:7.7). 19β: 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.29–6.86 (m, 8H, 2Ar), 5.79 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.73 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.7 Hz, NHCer), 5.32 (m, 2H, H-4Cer, H-3Cer), 4.89 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.3 Hz, ArCH2), 4.79 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.9 Hz, ArCH2), 4.68 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.58 (m, 2H, H-6a, ArCH2), 4.37 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.3 Hz, H-1a), 4.27 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 4.02 (dd, 1H, J5,6´ = 4.5 Hz, Jgem = 11.8 Hz, H-6´a), 3.96 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 4.6 Hz, Jgem = 9.9 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.80 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.69 (dd, 1H, J1',2 = 3.0 Hz, H-1'Cer), 3.44 (m, 2H, H-4a, H-5a), 3.37 (m, 2H, H-2a, H-3a), 2.57–2.29 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.13 (s, 1H, OHa), 2.09–1.85 (m, 6H, C(=O)CH2Cer, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer, -CH2-), 1.54 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.23 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-Cer), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.9, 172.7, 171.3, 159.5, 159.4, 137.2, 130.4, 130.3, 129.6, 129.5, 125.1, 114.1, 114.0, 113.9, 102.7, 83.2, 81.7, 77.6, 74.8, 74.5, 72.6, 72.4, 69.9, 67.0, 62.5, 55.3, 55.2, 50.9, 36.8, 33.0, 32.5, 32.3, 31.9, 30.0, 29.7, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.4, 29.4, 29.2, 28.9, 25.7, 22.7, 19.6, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1086.7216, C63H101NO12 calcd for [M+Na]+ 1086.7216.
(2,3-Di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-d-glucopyranosyl)-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol-3,6´-(2,2-dimethylmalonate) (20). Condition A: To a mixture of 15 (24 mg, 20.4 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (4.1 mL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (50 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (33 mg, 61.2 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 20 (16 mg, 75%, α:β = 1:2.4). Condition B: To a mixture of 15 (26 mg, 22.2 µmol) in acetonitrile/CH2Cl2 (2:1 4.5 mL) was added 3 Å molecular sieves (55 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (36 mg, 66.6 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 20 (18 mg, 76%, α:β = 1:9.1). 20β: 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.24–6.85 (m, 8H, 2Ar), 6.55 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 7.0 Hz, NHCer), 5.75 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.59 (t, 1H, J2,3 = J3,4 = 6.4 Hz, H-3Cer), 5.33 (dd, 1H, J4,5 = 15.4 Hz, H-4Cer), 4.81 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.5 Hz, ArCH2), 4.66 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, ArCH2), 4.59 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 5.2 Hz, Jgem = 11.7 Hz, H-6a), 4.55 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.54 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.44 (m, 2H, H-1a, H-6'a), 4.56 (dd, 1H, Jgem = 11.9 Hz, J1,2 = 2.1 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.89 (m, 1H, H-2Cer), 3.59 (m, 2H, H-1'Cer, H-5a), 3.48 (t, 1H, J3,4 = J4,5 = 7.3 Hz, H-4a), 3.44 (t, 1H, J1,2 = J2,3 = 7.3 Hz, H-2a), 3.36 (t, 1H, H-3a), 2.44 (s, 1H, OHa), 2.30 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.00 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.60 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.41–1.40 (2 s, 6H, CH3CCH3), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 175.0, 172.4, 170.7, 159.5, 159.4, 136.2, 130.3, 130.1, 129.7, 129.7, 129.6, 129.5, 129.0, 127.6, 127.1, 124.6, 114.2, 114.0, 114.0, 113.9, 103.6, 82.2, 80.5, 74.1, 73.3, 72.8, 72.2, 70.4, 69.8, 62.7, 55.3, 54.6, 50.8, 50.7, 34.5, 32.3, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.3, 29.3, 29.2, 29.2, 29.0, 28.9, 25.0, 23.7, 22.7, 21.8, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1086.7217, C63H101NO12 calcd for [M+Na]+ 1086.7216.
(2,3-Di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-d-glucopyranosyl)-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol-3,6'-phthalate (21). Condition A: To a mixture of 17 (50 mg, 41.4 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (8.3 mL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (100 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (67 mg, 124 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 1 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 21 (24 mg, 53%, α:β = 1:2.0). Condition B: To a mixture of 17 (45 mg, 37.3 µmol) in acetonitrile/CH2Cl2 (2:1 11.3 mL) was added 3 Å molecular sieves (90 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. DMTST (60 mg, 112 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 1 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:2 acetone–n-hexane), the solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and H2O. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:5 acetone–n-hexane) to give 21 (29 mg, 71%, α:β = 1:5.2). 21β: 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–6.86 (m, 12H, 3Ar), 6.18 (br d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.8 Hz, NHCer), 5.88 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.67 (m, 1H, H-3Cer), 5.41 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.8 Hz, J4,5 = 15.3 Hz, H-4Cer), 4.90 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.4 Hz, ArCH2), 4.81 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.7 Hz, ArCH2), 4.64 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.56 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.53–4.47 (m, 3H, H-6a, H-6'a, H-2Cer), 4.33 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.4 Hz, H-1a), 3.97 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 4.4 Hz, Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-1Cer), 3.90 (near dd, 1H, J1',2 = 5.4 Hz, H-1'Cer), 3.82–3.78 (m, 7H, H-4a, 2OCH3), 3.50 (m, 1H, H-5a), 3.43–3.36 (m, 2H, H-2a, H-3a), 2.22 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.16 (s, 1H, OHa), 2.00 (m, 2H, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.64 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.8, 159.5, 159.4, 131.5, 130.9, 130.4, 130.2, 129.8, 129.7, 129.6, 129.0, 124.4, 124.1, 114.1, 114.1, 114.0, 113.9, 103.1, 83.4, 81.3, 77.6, 75.1, 74.8, 74.3, 70.9, 55.3, 51.8, 50.2, 37.0, 32.3, 31.9, 29.7, 29.7, 29.7, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.2, 28.8, 25.9, 25.6, 22.7, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1120.7060, C66H99NO12 calcd for [M+Na]+ 1120.7059.
4-Methoxyphenyl 3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-2-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxycarbamoyl)-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (24). To a mixture of 22 (80 mg, 144 µmol) and 23 (82 mg, 144 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (1.4 mL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (320 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. NIS (49 mg, 216 µmol) and TfOH (1.9 µL, 21.6 µmol) were then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (4:1 toluene–EtOAc), the reaction was quenched by the addition of satd aq NaHCO3. The solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq Na2S2O3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (10:1 toluene–EtOAc) to give 24 (126 mg, 86%). [α]D −5.6° (c 0.8, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39–7.26 (m, 15H, 3 Ph), 7.04–6.79 (m, 4H, Ar), 5.65 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 6.9 Hz, NHc), 5.27 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.8 Hz, H-4c), 5.04 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, PhCH2), 4.96 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, PhCH2), 4.91 (d, 1H, Jgem = 12.4 Hz, PhCH2), 4.84 (d, 2H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1b, PhCH2), 4.70 (m, 2H, H-3c, H-1c), 4.64 (d, 1H, PhCH2), 4.55 (q, 2H, Jgem = 11.7 Hz, OCH2CCl3), 4.41 (d, 1H, PhCH2), 4.10 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 7.6 Hz, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, H-6c), 4.06 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.8 Hz, H-4b), 4.04 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 6.2 Hz, H-6'c), 3.92 (m, 2H, H-2b, H-2c), 3.80 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 5.8 Hz, Jgem = 10.0 Hz, H-6b), 3.77 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.76–3.71 (m, 2H, H-6'b, H-5c), 3.66 (m, 2H, H-3b, H-5b), 2.14–1.94 (3 s, 9H, 3Ac); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.3, 170.2, 155.3, 154.3, 151.4, 138.2, 138.1, 137.2, 129.0, 128.7, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 128.0, 127.8, 127.7, 127.6, 125.3, 118.6, 114.5, 102.9, 101.9, 95.8, 81.6, 79.6, 75.7, 75.3, 74.6, 74.3, 73.6, 73.5, 71.7, 70.9, 69.1, 66.5, 61.1, 55.6, 52.7, 20.6, 20.5. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 1040.2402, C49H54Cl3NO16 calcd for [M+Na]+ 1040.2400.
4-Methoxyphenyl 3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (25). To a solution of 24 (100 mg, 98.3 µmol) in acetonitrile/AcOH (4:1, 3.3 mL) was added Zn (500 mg) at rt. After stirring for 30 min at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 toluene–EtOAc), the solution was diluted with EtOAc and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq Na2CO3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1.5:1 toluene–EtOAc) to give 25 (81 mg, 98%). [α]D −12.3° (c 0.4, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36–7.24 (m, 15H, 3Ph), 7.06–6.78 (m, 4H, Ar), 5.29 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.1 Hz, H-4c), 5.01 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, PhCH2), 4.87 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1b), 4.83 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.7 Hz, PhCH2), 4.82 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.6 Hz, PhCH2), 4.69 (d, 1H, PhCH2), 4.66 (dd, 1H, J2,3 = 10.7 Hz, H-3c), 4.55 (s, 2H, PhCH2), 4.49 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 8.2 Hz, H-1c), 4.08 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 7.6 Hz, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, H-6c), 4.04 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.8 Hz, H-4b), 4.02 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 6.2 Hz, H-6'c), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, J2,3 = 9.6 Hz, H-2b), 3.80 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 4.8 Hz, Jgem = 10.3 Hz, H-6b), 3.76 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.76–3.73 (m, 2H, H-6'b, H-5c), 3.66 (m, 1H, H-5b), 3.59 (dd, 1H, H-3b), 3.15 (dd, 1H, H-2c), 2.09–2.01 (3 s, 9H, 3Ac); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.4, 170.3, 170.2, 155.2, 151.5, 138.2, 138.1, 137.9, 129.0, 128.6, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 127.5, 125.3, 118.3, 114.5, 105.1, 102.9, 81.0, 78.8, 75.2, 74.8, 74.1, 73.9, 73.6, 73.6, 70.5, 69.8, 66.3, 61.5, 55.6, 51.9, 21.4, 20.8, 20.7, 20.6. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 866.3358, C46H53NO14 calcd for [M+Na]+ 866.3358.
4-Methoxyphenyl 2-acetamido-4,6-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (26). Compound 25 (270 mg, 320 µmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane/AcOH (4:1, 32 mL) and the solution was stirred for 50 h at 60 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1.5 toluene–EtOAc). Dilution of the mixture with CHCl3 provided a solution, which was then washed with satd aq Na2CO3. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (2:1 toluene–EtOAc) to give 26 (218 mg, 81%). [α]D −3.5° (c 0.6, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.24 (m, 15H, 3Ph), 7.17 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 3.4 Hz, NHc), 7.05–6.78 (m, 4H, Ar), 5.91 (d, 1H, J3,OH = 1.4 Hz, OHc), 5.27 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 3.4 Hz, H-4c), 5.12 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, PhCH2), 4.88 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1b), 4.87 (d, 1H, Jgem = 9.6 Hz, PhCH2), 4.73 (d, 2H, PhCH2), 4.56 (q, 2H, Jgem = 11.7 Hz, PhCH2), 4.46 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 8.2 Hz, H-1c), 4.15 (dd, 1H, J5,6 = 6.5 Hz, Jgem = 11.3 Hz, H-6c), 4.05 (m, 2H, H-6'c, H-4b), 3.89–3.83 (m, 3H, H-2b, H-2c, H-6b), 3.77 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.76–3.69 (m, 4H, H-6'b, H-3b, H-5b, H-5c), 3.53 (br d, 1H, H-3c), 2.14–1.61 (3 s, 9H, 3Ac); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 173.9, 170.5, 170.3, 155.4, 151.2, 138.1, 138.0, 136.4, 129.1, 129.0, 128.8, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 128.0, 127.9, 127.7, 127.5, 118.5, 114.5, 102.9, 102.7, 81.6, 79.9, 75.7, 75.3, 74.3, 73.6, 71.3, 69.3, 67.9, 61.9, 55.8, 55.6, 29.7, 22.3, 20.8, 20.7. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 866.3358, C46H53NO14 calcd for [M+Na]+ 866.3358.
4-Methoxyphenyl 2-acetamido-3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-{[methyl 5-acetamido-4,7,8,9-tetra-O-acetyl-3,5-dideoxy-d-glycero-α-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosylonate]-(2→3)}-2,6-di-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2-acetamido-4,6-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (29). To a mixture of 28 (180 mg, 135 µmol) and 26 (114 mg, 135 µmol) in CH2Cl2 (4.5 mL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (300 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. TMSOTf (2.4 µL, 13.5 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1:1 CHCl3–acetone), the reaction was quenched by the addition of satd aq NaHCO3. The solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (40:1 CHCl3–MeOH) to give 29 (203 mg, 75%). [α]D −7.7° (c 0.2, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.00–7.19 (m, 25H, 5Ph), 7.57 (d, 1H, J5,NH = 8.9 Hz, NHe), 7.20 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.2 Hz, NHc), 6.96–6.78 (m, 4H, Ar), 6.78 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 6.9 Hz, NHf), 5.32 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 3.5 Hz, H-4c), 5.29–5.25 (m, 2H, H-8e, H-3f), 5.23 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.7 Hz, H-4f), 5.14–5.09 (m, 2H, H-2d, H-7e), 4.90 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1d), 4.85 (d, 2H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1b, H-1f), 4.78 (m, 1H, H-4e), 4.74 (d, 1H, Jgem = 11.7 Hz, PhCH2), 4.68 (m, 2H, H-1c, PhCH2), 4.59 (m, 2H, H-3d, PhCH2), 4.52 (d, 1H, Jgem = 12.4 Hz, PhCH2), 4.47 (m, 2H, H-6d, PhCH2), 4.41 (d, 1H, Jgem = 12.4 Hz, PhCH2), 4.28 (m, 1H, H-3c), 4.25 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 5.5 Hz, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, H-6'd), 4.08–4.00 (m, 3H, H-6c, H-6f, H-9e), 3.98–3.91 (m, 4H, H-6'c, H-6'f, H-9'e, H-5d), 3.86–3.72 (m, 8H, H-4d, H-5c, H-5f, H-2c, H-2f, H-6e, H-6b, H-5e), 3.75–3.68 (2 s, 6H, 2OCH3), 3.66 (near t, 1H, H-2b), 3.59–3.53 (m, 4H, H-3b, H-4b, H-5b, H-6'b), 2.30 (dd, 1H, J3eq,4 = 4.8 Hz, Jgem = 13.1 Hz, H-3eeq), 1.80 (near t, 1H, H-3eax), 2.08–1.64 (12 s, 36H, 12 Ac); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.3, 170.7, 170.6, 170.5, 170.4, 170.4, 170.2, 169.9, 169.8, 168.1, 166.0, 164.3, 155.1, 151.5, 138.4, 137.9, 133.2, 133.1, 130.0, 129.5, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.0, 127.7, 127.5, 118.3, 114.4, 102.8, 100.7, 100.5, 100.0, 98.3, 80.7, 79.2, 75.3, 74.9, 74.1, 74.0, 73.8, 73.5, 73.2, 72.1, 72.0, 70.8, 70.3, 70.1, 70.0, 69.3, 68.7, 67.4, 66.9, 66.5, 63.7, 62.7, 62.1, 61.4, 55.6, 54.2, 53.1, 51.8, 49.2, 36.1, 31.9, 29.7, 29.3, 23.4, 23.1, 22.7, 21.1, 20.8, 20.7, 20.7, 20.7, 20.5, 20.4, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 2038.7055, C100H117N3O41 calcd for [M+Na]+ 2038.7055.
4-Methoxyphenyl 2-acetamido-3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-{[methyl 5-acetamido-4,7,8,9-tetra-O-acetyl-3,5-dideoxy-d-glycero-α-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosylonate]-(2→3)}-2,6-di-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2-acetamido-4,6-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (30). To a solution of 29 (215 mg, 107 µmol) in EtOH (10.7 mL) was added Pd(OH)2/C (20%, 215 mg). After stirring for 16 h at rt under a hydrogen atmosphere as the reaction was monitored by TLC (10:1 CHCl3–MeOH), the mixture was filtered through Celite. The filtrate was concentrated and the crude residue obtained was exposed to high vacuum for 3 h. The resulting residue was then dissolved in pyridine (535 µL). Benzoic anhydride (145 mg, 642 µmol) and DMAP (7.8 mg, 64.2 µmol) were added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 40 min at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (15:1 CHCl3–MeOH), the reaction was quenched by the addition of MeOH at 0 °C. The mixture was co-evaporated with toluene and the residue was then diluted with CHCl3, and washed with 2 M HCl, H2O and satd aq NaHCO3. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The resulting residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (25:1 CHCl3–MeOH) to give 30 (180 mg, 82%). [α]D +6.3° (c 0.4, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.01–7.35 (m, 26H, 5Ph, NHe), 7.11 (br d, 1H, J2,NH = 5.5 Hz, NHc), 7.01 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.2 Hz, NHf), 6.85–6.62 (m, 4H, Ar), 5.60 (t, 1H, J1,2 = J2,3 = 7.6 Hz, H-2b), 5.52 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 2.8 Hz, H-3b), 5.39 (d, 1H, H-1b), 5.30 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.7 Hz, H-4c), 5.25 (m, 3H, H-3f, H-8e, H-4f), 5.12 (m, 2H, H-2d, H-7e), 4.87 (m, 2H, H-1d, H-1f), 4.81 (m, 1H, H-4e), 4.74 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 8.3 Hz, H-1c), 4.59 (d, 1H, J2,3 = 10.3 Hz, H-3d), 4.49–4.41 (m, 5H, H-6b, H-4b, H-6'b, H-6d, H-5b), 4.29 (br dd, 1H, J2,3 = 10.3 Hz, H-3c), 4.24 (dd, 1H, J5,6' = 5.5 Hz, Jgem = 11.0 Hz, H-6'd), 4.06 (m, 2H, H-6f, H-9e), 3.98–3.93 (m, 3H, H-6'f, H-9'e, H-6c), 3.90–3.72 (m, 7H, H-4d, H-5d, H-5f, H-2f, H-6e, H-5e, H-6'c), 3.75 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.67 (m, 1H, H-5c), 3.62 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.60 (m, 1H, H-2c), 2.26 (near dd, 1H, H-3eeq), 2.09–1.75 (m, 37H, H-3eax, 12Ac); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.1, 170.6, 170.5, 170.5, 170.5, 170.3, 170.2, 169.9, 169.7, 168.1, 166.3, 166.1, 166.0, 165.3, 164.3, 155.5, 151.2, 133.6, 133.4, 133.1, 132.9, 130.1, 130.0, 130.0, 129.8, 129.7, 129.6, 129.5, 129.4, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 118.7, 114.3, 100.9, 100.8, 100.4, 98.2, 97.8, 74.7, 74.0, 73.4, 72.7, 72.0, 71.9, 71.2, 70.6, 70.1, 70.0, 69.7, 69.4, 68.8, 67.3, 67.0, 66.5, 63.7, 63.5, 62.8, 62.3, 61.4, 55.5, 53.1, 52.1, 52.0, 49.3, 36.3, 29.7, 23.4, 23.2, 21.1, 20.9, 20.8, 20.8, 20.7, 20.5, 20.4. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 2080.6434, C100H111N3O44 calcd for [M+Na]+ 2080.6433.
2-Acetamido-3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-{[methyl 5-acetamido-4,7,8,9-tetra-O-acetyl-3,5-dideoxy-d-glycero-α-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosylonate]-(2→3)}-2,6-di-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2-acetamido-4,6-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzoyl-α-d-galactopyranosyl trichloroacetimidate (31). To a solution of 30 (115 mg, 55.9 µmol) in acetonitrile/toluene/H2O (6:5:3, 1.1 mL) was added CAN (245 mg, 447 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C as the reaction was monitored by TLC (10:1 CHCl3–MeOH), the mixture was diluted with CHCl3. The solution was then washed with H2O, satd aq NaHCO3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was roughly purified by silica gel column chromatography (30:1 CHCl3–MeOH). The product obtained was exposed to high vacuum for 20 h and then dissolved in CH2Cl2 (502 µL). CCl3CN (101 µL, 1.00 mmol) and DBU (9.0 µL, 60.2 µmol) were added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 30 min at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (15:1 CHCl3–MeOH), the reaction mixture was evaporated. The crude residue obtained was purified by silica gel column chromatography (40:1 CHCl3–MeOH) to give 31 (94 mg, 81%). [α]D +14.0° (c 0.6, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.65 (br s, 1H, C(=NH)), 8.01–7.37 (m, 26H, 5Ph, NHe), 7.21 (br s, 1H, NHc), 6.98 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.2 Hz, NHf), 6.57 (br s, 1H, H-1b), 5.77 (br d, 1H, H-2b), 5.64 (near dd, 1H, H-3b), 5.31 (s, 1H, H-4c), 5.23 (m, 3H, H-3f, H-8e, H-4f), 5.10 (m, 2H, H-2d, H-7e), 4.89 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1d), 4.86–4.81 (m, 3H, H-1f, H-1c, H-4e), 4.62 (m, 2H, H-4b, H-5b), 4.56 (br d, 1H, H-3d), 4.48 (m, 2H, H-6b, H-6d), 4.38 (near dd, 1H, H-6'b), 4.31 (br d, 1H, H-3c), 4.25 (near dd, 1H, H-6'd), 4.06 (m, 2H, H-6f, H-9e), 3.98–3.84 (m, 8H, H-6'f, H-9'e, H-6c, H-4d, H-5d, H-5f, H-2f, H-6'c), 3.81–3.69 (m, 6H, H-6e, OCH3, H-5e, H-5c), 3.62 (m, 1H, H-2c), 2.26 (near dd, 1H, H-3eeq), 2.09–1.66 (m, 37H, H-3eax, 12Ac); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.0, 170.8, 170.4, 170.4, 170.4, 170.3, 170.2, 169.8, 169.7, 166.1, 165.9, 165.3, 164.2, 160.4, 133.5, 133.3, 133.1, 133.0, 129.9, 129.8, 129.7, 129.6, 129.5, 128.7, 128.4, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 100.7, 100.5, 98.2, 98.0, 93.4, 90.8, 74.8, 73.5, 73.1, 71.9, 71.9, 71.4, 71.3, 70.9, 70.4, 70.1, 70.0, 69.5, 68.7, 67.2, 66.9, 66.4, 63.8, 63.5, 62.8, 62.2, 61.4, 55.3, 53.0, 51.2, 49.1, 36.1, 29.6, 23.3, 23.1, 22.9, 22.6, 21.0, 20.8, 20.8, 20.7, 20.6, 20.4, 20.3, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M+Na]+ 2117.5111, C95H105Cl3N4O43 calcd for [M+Na]+ 2117.5110.
4-O-{2-Acetamido-3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-[(methyl 5-acetamido-4,7,8,9-tetra-O-acetyl-3,5-dideoxy-d-glycero-α-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosylonate)-(2→3)]-2,6-di-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2-acetamido-4,6-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)}-2,3-di-O-p-methoxybenzyl-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol-3,6'-succinate (32). To a mixture of 31 (59 mg, 28.2 µmol) and 18β (30 mg, 28.2 µmol) in CHCl3 (940 µL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (100 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. TMSOTf (0.5 µL, 2.82 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 1.5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (1.5:1 acetone–n-hexane), the reaction was quenched by the addition of satd aq NaHCO3. The solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:1 acetone–n-hexane) to give 32 (22 mg, 26%). [α]D +7.8° (c 0.4, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.08–6.80 (m, 33H, 7Ar), 6.77 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 7.9 Hz, NHc), 5.73 (m, 2H, J2,NH = 8.9 Hz, H-5Cer, NHCer), 5.58–5.53 (m, 2H, H-3b, H-2d), 5.47–5.35 (m, 3H, NHf, H-3Cer, H-8e), 5.33 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 3.1 Hz, H-4c), 5.31–5.20 (m, 4H, H-4f, H-2b, H-4Cer, H-7e), 5.14 (d, 1H, J5,NH = 9.9 Hz, NHe), 5.09 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 8.1 Hz, H-1f), 5.05 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 8.4 Hz, H-1c), 4.99 (m, 1H, H-4e), 4.96 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.8 Hz, H-1d), 4.84–4.73 (m, 3H, 2 ArCH2, H-3f), 4.71 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.7 Hz, H-1b), 4.66 (d, 1H, Jgem = 10.8 Hz, ArCH2), 4.61 (m, 2H, H-6b, H-6d), 4.52 (d, 1H, ArCH2), 4.47 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 1.6 Hz, H-4d), 4.33–4.19 (m, 5H, H-6'b, H-2Cer, H-1a, H-6f, H-6c), 4.14–4.03 (m, 5H, H-6'd, H-6'f, H-3c, H-9e, H-9'e), 4.00–3.87 (m, 6H, H-4b, H-6'c, H-6a, H-2c, H-3d, H-5e), 3.85–3.72 (m, 8H, H-6'a, OCH3, H-5b, H-6e, H-5d, H-1Cer), 3.66–3.58 (m, 3H, H-1'Cer, H-3a, H-4a), 3.54 (m, 1H, H-5a), 3.48 (m, 2H, H-5c, H-5f), 3.33 (t, 1H, J1,2 = J2,3 = 7.2 Hz, H-2a), 3.16 (m, 1H, H-2f), 2.58–2.45 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.29 (dd, 1H, J3eq,4 = 4.8 Hz, Jgem = 13.4 Hz, H-3eeq), 2.18–1.55 (m, 43H, C(=O)CH2CH2Cer, H-3eax, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer, 12Ac), 1.26 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.8, 171.8, 171.2, 171.0, 170.6, 170.5, 170.4, 170.4, 170.2, 169.9, 169.8, 168.1, 166.2, 166.0, 165.6, 164.3, 159.3, 159.0, 137.1, 133.6, 133.3, 133.1, 130.5, 130.0, 130.0, 129.8, 129.8, 129.7, 129.6, 129.6, 129.6, 129.0, 128.8, 128.5, 128.4, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 125.6, 124.3, 120.2, 113.8, 113.7, 101.8, 100.9, 100.6, 98.3, 97.8, 81.8, 80.7, 78.5, 77.6, 75.0, 73.9, 73.7, 73.5, 73.3, 72.7, 72.2, 72.0, 71.2, 70.6, 70.4, 70.4, 70.1, 70.0, 69.5, 68.7, 67.3, 66.9, 66.5, 63.5, 62.8, 62.7, 62.2, 61.4, 55.3, 55.2, 55.1, 53.8, 53.1, 51.9, 49.2, 43.0, 38.7, 36.6, 36.2, 32.3, 31.9, 31.7, 30.3, 29.7, 29.7, 29.7, 29.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.3, 29.1, 29.0, 28.9, 28.8, 25.9, 25.6, 23.9, 23.8, 23.4, 23.1, 23.0, 22.9, 22.8, 22.7, 22.6, 21.1, 20.8, 20.8, 20.8, 20.6, 20.4, 20.4, 14.1, 14.1, 14.0, 11.0, 10.9. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [1/2M+Na]+ 1514.6482, C155H202N4O54 calcd for [1/2M+Na]+ 1514.6484.
4-O-{2-Acetamido-3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-[(methyl 5-acetamido-4,7,8,9-tetra-O-acetyl-3,5-dideoxy-d-glycero-α-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosylonate)-(2→3)]-2,6-di-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2-acetamido-4,6-di-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-2,3,6-tri-O-benzoyl-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)}-2,3-di-O-acetyl-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol-3,6'-succinate (33). To a mixture of 31 (53 mg, 25.3 µmol) and 1 (23 mg, 25.3 µmol) in CHCl3 (843 µL) was added 4 Å molecular sieves (120 mg) at rt. After stirring for 1 h, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. TMSOTf (0.5 µL, 2.53 µmol) was then added to the mixture at 0 °C. After stirring for 2.5 h at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (4:3 acetone–n-hexane), the reaction was quenched by the addition of satd aq NaHCO3. The solution was diluted with CHCl3 and filtered through Celite. The filtrate was then washed with satd aq NaHCO3 and brine. The organic layer was subsequently dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (1:1 acetone–n-hexane) to give 33 (22 mg, 31%). The yields of 33 based on the use of 2.0 eq. and 3.0 eq. of 1 were 48% and 60%, respectively. [α]D +8.0° (c 0.5, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.11–7.31 (m, 25H, 5Ph), 6.31 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 8.2 Hz, NHc), 5.98 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 6.2 Hz, NHf), 5.77 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.59 (d, 1H, J2,NH = 9.6 Hz, NHCer), 5.52 (m, 2H, H-3b, H-2d), 5.38 (m, 1H, H-8e), 5.34–5.29 (m, 4H, H-4c, H-4f, H-2b, H-3Cer), 5.26–5.21 (m, 2H, H-4Cer, H-7e), 5.18–5.14 (m, 2H, H-3a, H-1f), 5.10 (d, 1H, J5,NH = 9.7 Hz, NHe), 5.04 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 8.3 Hz, H-1c), 5.00 (m, 1H, H-4e), 4.88 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 3.4 Hz, J2,3 = 11.0 Hz, H-3f), 4.83 (t, 1H, J1,2 = J2,3 = 7.2 Hz, H-2a), 4.75 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1b), 4.69 (d, 1H, J1,2 = 7.6 Hz, H-1d), 4.62 (m, 2H, H-6b, H-6d), 4.52 (d, 1H, J3,4 = 2.8 Hz, H-4d), 4.34 (m, 3H, H-1a, H-6'b, H-6'd), 4.25 (m, 2H, H-2Cer, H-6f), 4.19 (near dd, 1H, H-6c), 4.20–4.05 (m, 4H, H-6´f, H-3c, H-6´c, H-9e), 4.02–3.88 (m, 6H, H-9'e, H-4b, H-6a, H-2c, H-3d, H-5e), 3.85–3.75 (m, 8H, H-1Cer, OCH3, H-1'Cer, H-5b, H-5d, H-6e), 3.70 (m, 2H, H-4a, H-6'a), 3.60 (m, 2H, H-5c, H-5f), 3.50 (near t, 1H, H-5a), 3.12 (m, 1H, H-2f), 2.59–2.40 (m, 4H, 2C(=O)CH2), 2.29 (dd, 1H, Jgem = 13.0 Hz, J3eq,4 = 4.8 Hz, H-3eeq), 2.19–1.55 (m, 49H, C(=O)CH2CH2Cer, H-3eax, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer, 14Ac), 1.25 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.88 (m, 6H, 2-CH3Cer); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.7, 171.3, 171.2, 171.1, 170.5, 170.4, 170.3, 170.3, 169.9, 169.7, 169.3, 168.1, 166.1, 166.0, 165.9, 164.9, 164.3, 133.6, 133.3, 133.2, 130.4, 130.1, 130.0, 129.8, 129.7, 129.5, 129.4, 129.0, 128.8, 128.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 124.7, 101.0, 100.7, 100.4, 99.2, 98.3, 97.5, 76.5, 75.2, 74.0, 73.6, 73.3, 72.4, 72.1, 72.0, 72.0, 71.7, 71.3, 70.5, 70.4, 70.0, 69.6, 68.7, 67.3, 67.0, 66.5, 63.5, 63.0, 62.8, 62.2, 61.4, 53.1, 51.8, 50.0, 49.3, 36.8, 36.1, 32.3, 31.9, 29.7, 29.7, 29.5, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.3, 28.8, 25.6, 23.4, 23.2, 23.2, 23.1, 22.9, 22.8, 22.7, 22.6, 22.2, 22.0, 21.8, 21.1, 20.9, 20.8, 20.7, 20.6, 20.5, 20.4, 14.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [1/2M+Na]+ 1436.6014, C143H190N4O54 calcd for [1/2M+Na]+ 1436.6015.
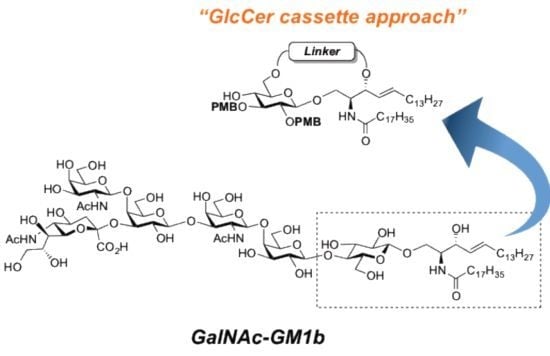
GalNAc-GM1b: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-[5-acetamido-3,5-dideoxy-d-glycero-α-d-galacto-2-nonulopyranosylonic acid-(2→3)]-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1'→1)-(2S,3R,4E)-2-octadecanamido-4-octadecene-1,3-diol. To a solution of 33 (15.0 mg, 5.31 µmol) in MeOH/THF (1:1, 532 µL) was added NaOMe (28% solution in MeOH, 102 µg, 0.531 µmol) at 0 °C. After stirring for 6 d at rt as the reaction was monitored by TLC (5:4:1 CHCl3–MeOH–10 mM aq ZnCl2), water (10 µL) was added to the mixture. After stirring for 8 d at rt, the reaction was neutralized with Dowex (H+) resin. The resin was filtered through cotton and the filtrate was then evaporated. The residue was purified by gel filtration column chromatography (LH-20) using CHCl3–MeOH as eluent followed by silica gel column chromatography (5:4:0.5 CHCl3–MeOH–H2O) to give the target GalNAc-GM1b (8.2 mg, 88%). [α]D +12.5° (c 0.2, 1:1 CHCl3–MeOH); 1H-NMR (600 MHz, 1:1 CDCl3–CD3OD) δ 5.70 (m, 1H, H-5Cer), 5.45 (dd, 1H, J3,4 = 7.6 Hz, J4,5 = 15.1 Hz, H-4Cer), 2.73 (br d, 1H, H-3eeq), 2.18 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2), 2.05–2.01 (m, 11H, 3Ac, H-6Cer, H-6'Cer), 1.85 (br t, 1H, H-3eax), 1.59 (m, 2H, C(=O)CH2CH2), 1.37–1.19 (m, 50H, 25-CH2-), 0.89 (m, 6H, 2-CH3); 13C-NMR (150 MHz, 1:1 CDCl3–CD3OD) δ 174.8, 174.6, 173.7, 173.4, 134.4, 129.7, 129.5, 128.0, 104.4, 103.8, 103.1, 102.0, 79.0, 76.2, 75.2, 75.0, 74.7, 74.5, 73.8, 73.6, 73.5, 72.1, 71.9, 71.3, 69.6, 69.5, 68.7, 68.6, 68.2, 64.6, 62.0, 61.5, 60.4, 60.2, 53.3, 53.1, 52.6, 51.8, 47.7, 36.4, 32.4, 32.0, 29.7, 29.6, 29.6, 29.6, 29.4, 29.3, 26.1, 22.7, 22.7, 22.0, 13.8. HRMS (ESI) m/z: found [M−H]− 1747.9487, C81H144N4O36 calcd for [M−H]− 1747.9488.