Molecularly Imprinted Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Advanced Polymeric Membranes: Synthesis and Applications
2.1. Pharmaceutical and Food Applications
 ) chloramphenicol in the NMIM.
) chloramphenicol in the NMIM.
 ) chloramphenicol in the NMIM.
) chloramphenicol in the NMIM.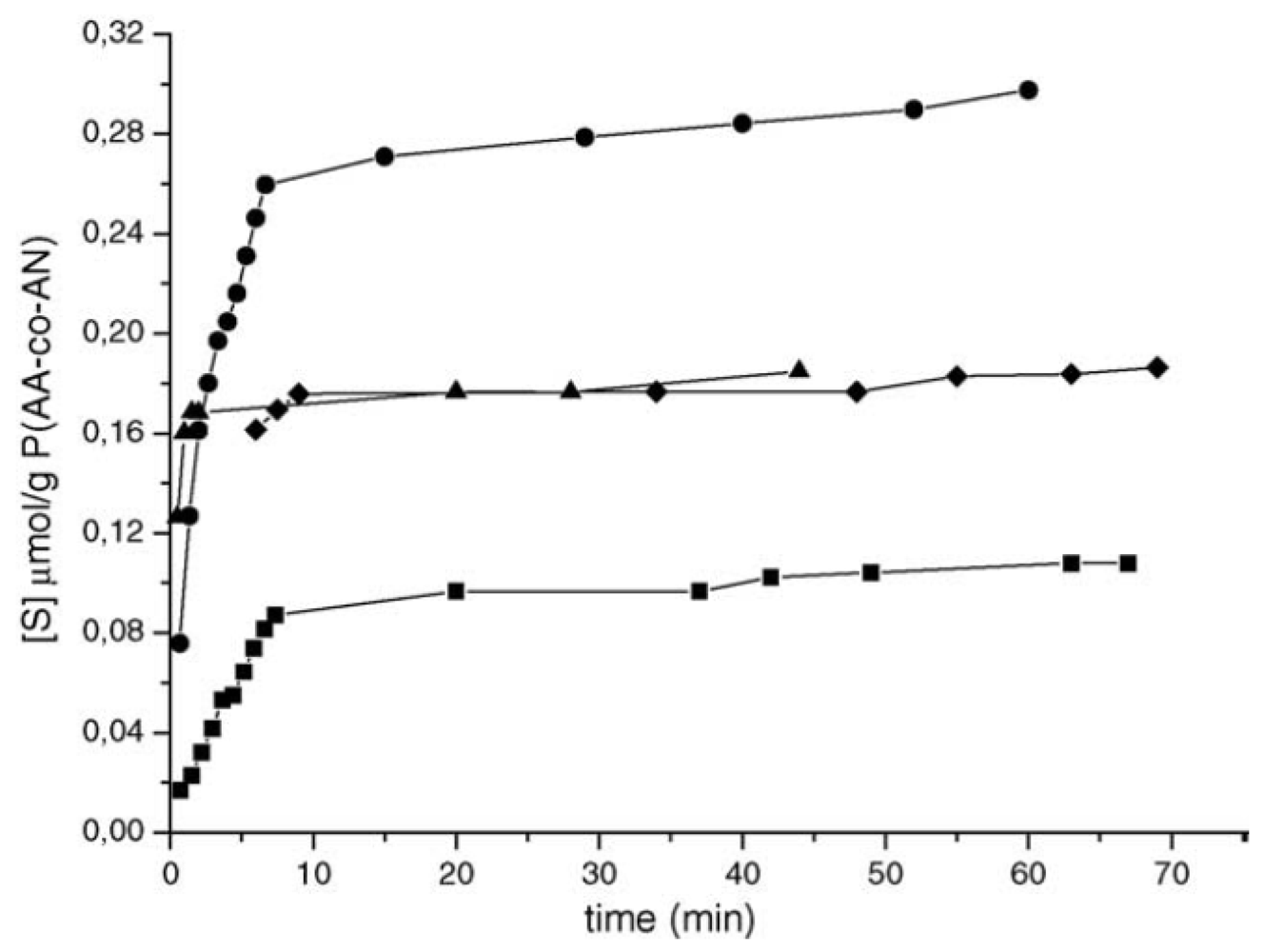
| TABLE (a) | % adsorbed in rebinding test | % adsorbed in competitive rebinding test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule | PC-imprinted membrane | Control membrane | PC-imprinted membrane | Control membrane |
| PC (template) | 78.05 | 6.09 | 68.22 | 4.11 |
| PS | 0.15 | 0.29 | 5.91 | 0.96 |
| PI | 0.10 | 0.16 | - | - |
| TABLE (b) | % adsorbed in rebinding test | % adsorbed in competitive rebinding test | ||
| Molecule | αA-imprinted membrane | Control membrane | αA-imprinted membrane | Control membrane |
| αA(template) | 43.46 | 12.21 | 39.55 | 9.33 |
| ALB | 8.30 | 6.12 | 6.71 | 6.89 |
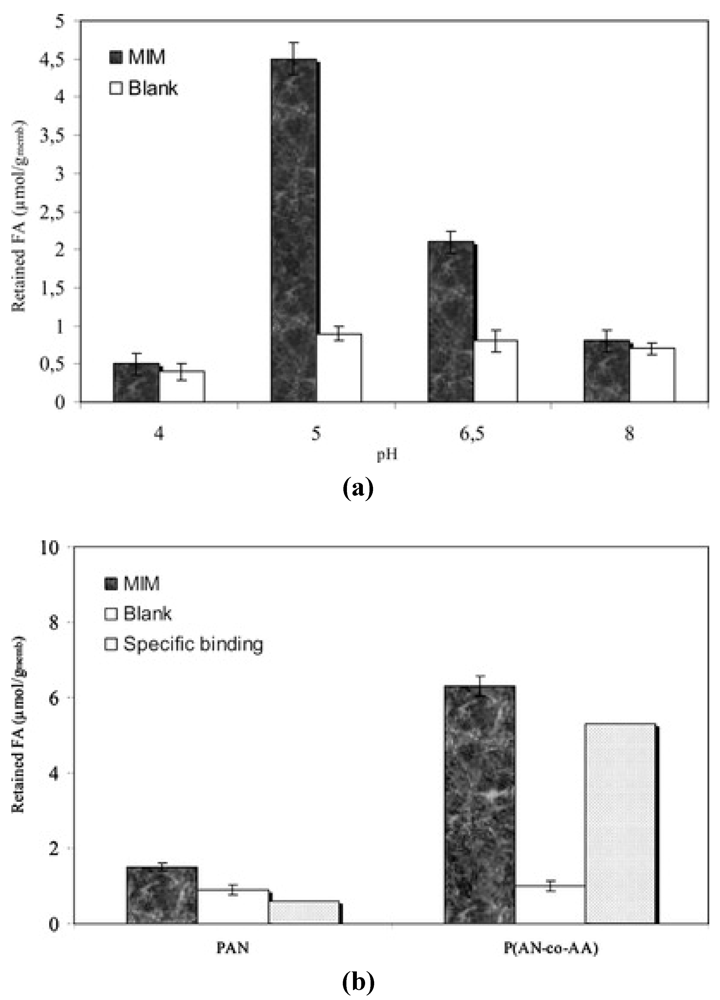
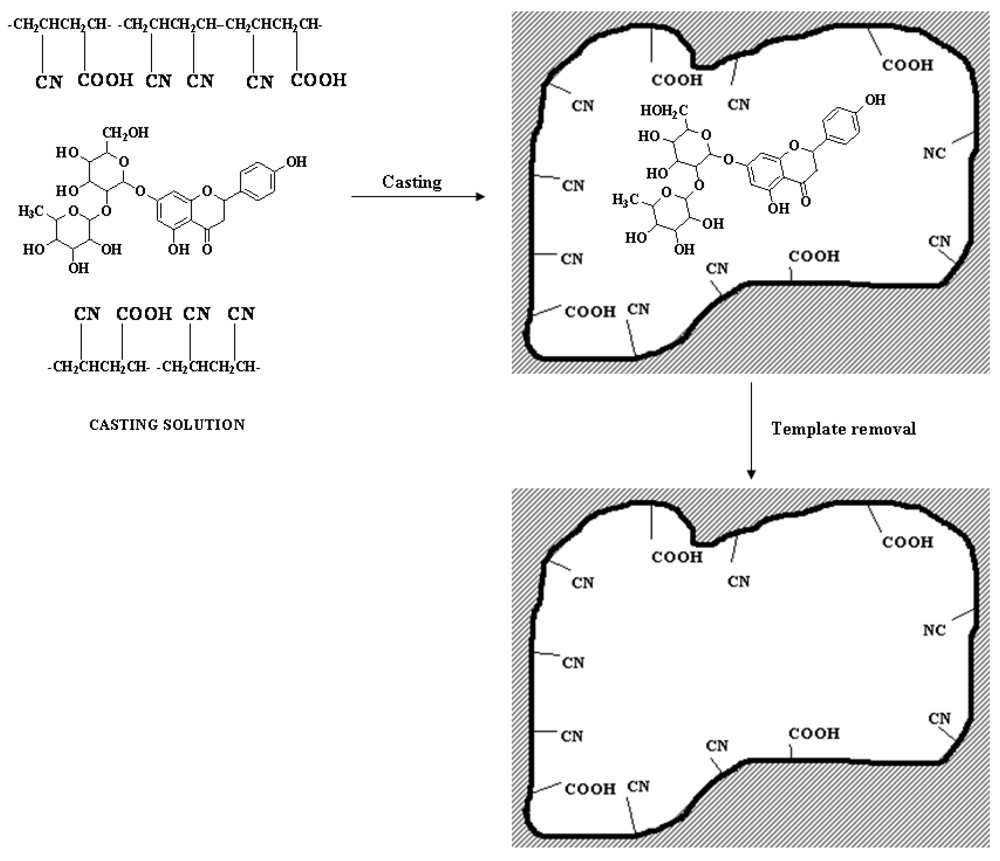
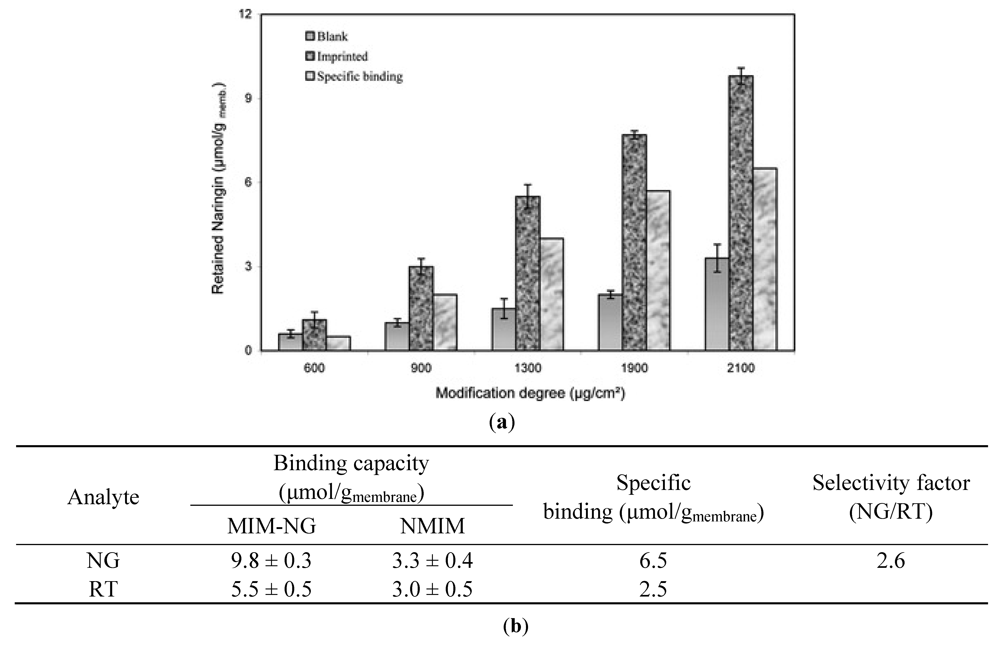
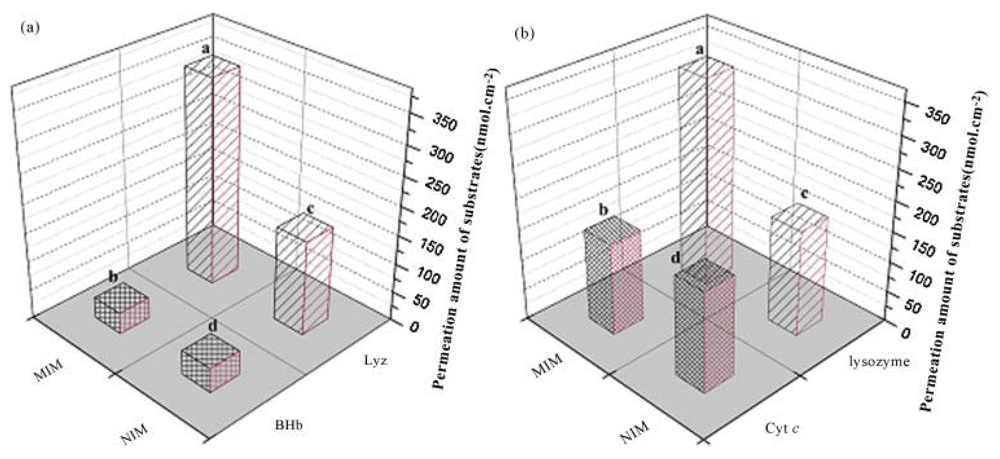
2.2. Polymer Membranes for Chiral Recognition of Amino Acids and Nucleic Acids
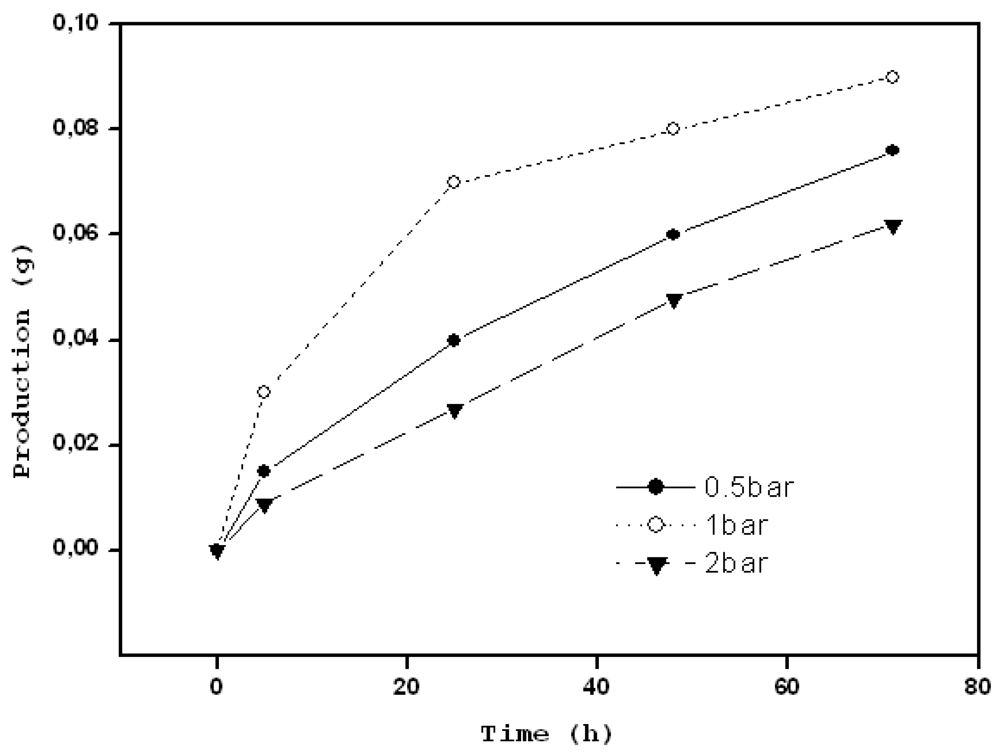
2.3. Metal Ions
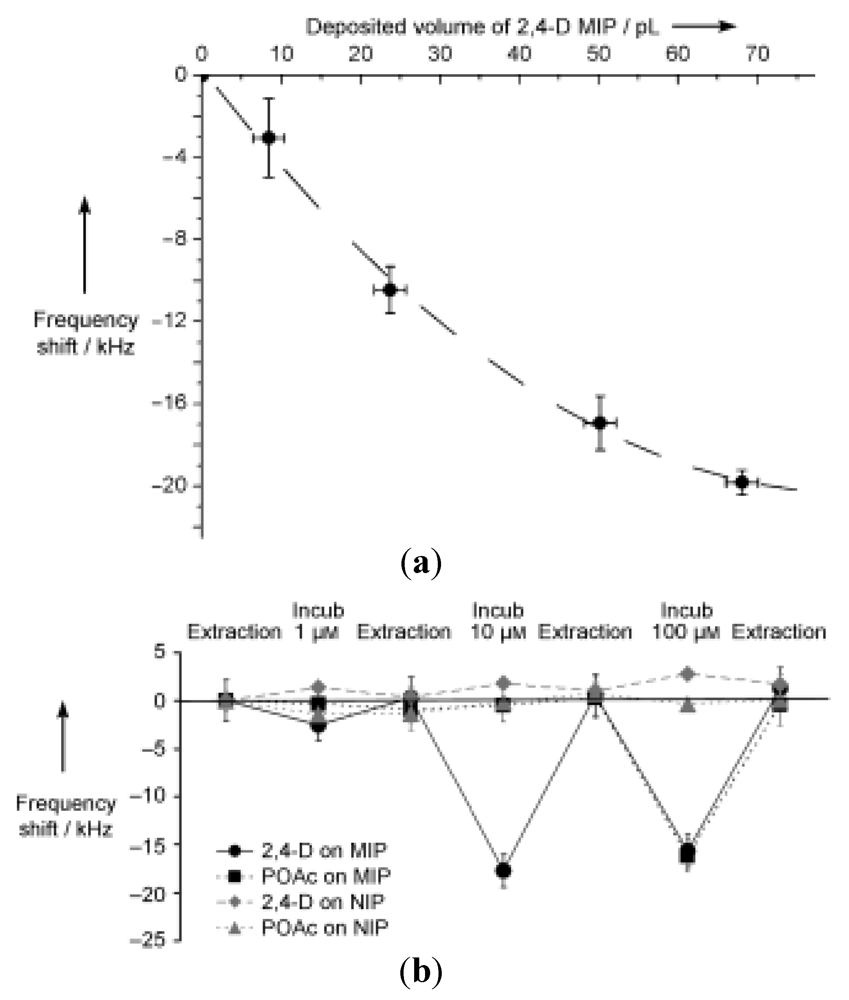
2.4. Herbicides, Pesticides, Organic Pollutants
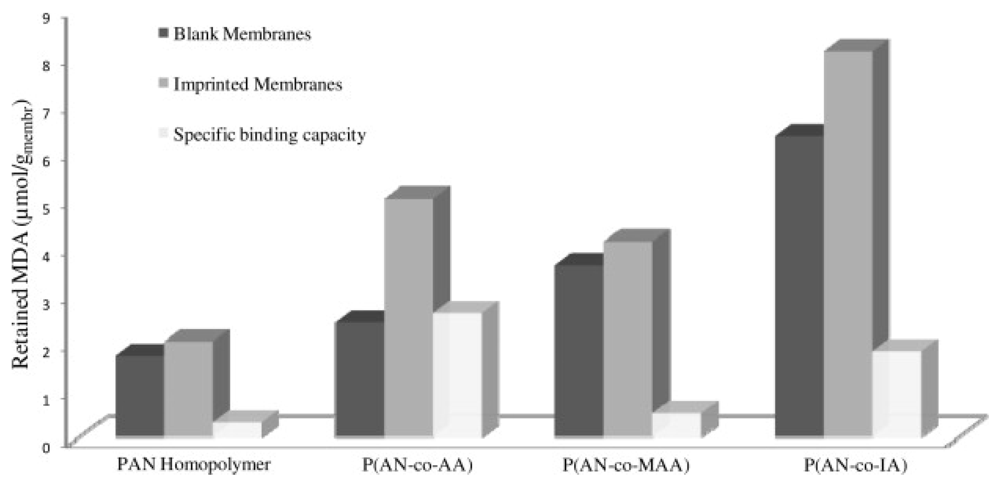
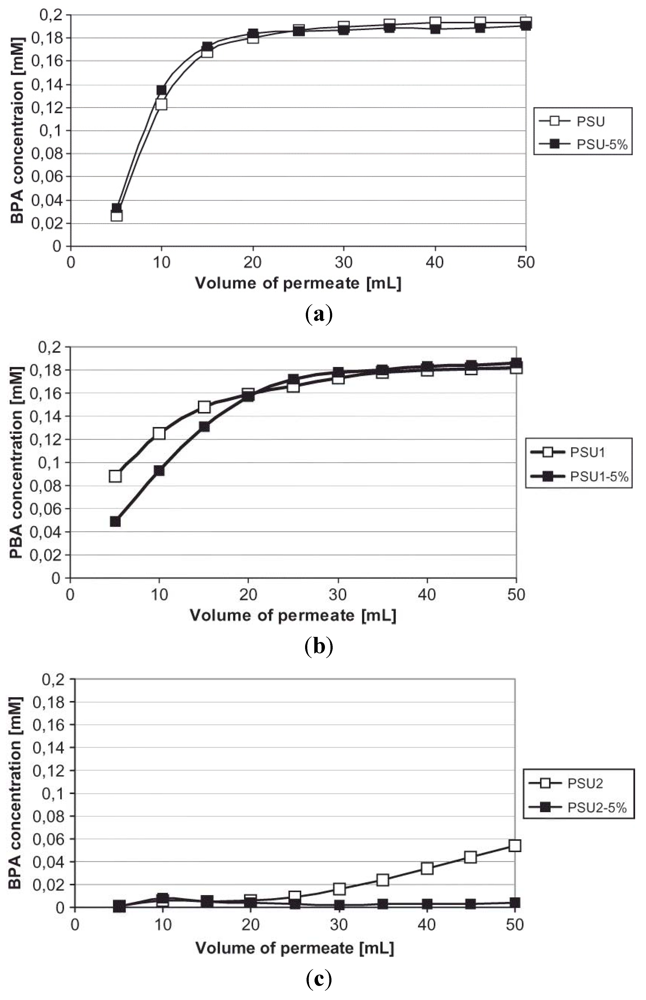
3. Summary
| Template | Author | Year | Monomer, Polymer Matrix And Support | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical And Food | ||||
| α-amylase | Silvestri et al. | 2006 | poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol), dextran blends | [43] |
| Silvestri et al. | 2007 | poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) | [44] | |
| α-tocopherol | Faizal et al. | 2008 | α-tocopherol methacrylate, acrylonitrile | [46] |
| Faizal et al. | 2008 | α-tocopherol methacrylate, divinylbenzene, polysulfone, cellulose acetate and nylon supports | [47] | |
| Faizal et al. | 2009 | polysulfone and calix[4]resorcarenes | [48] | |
| (S)-5-benzylhydantoin | Lu et al. | 2007 | poly(styrene-stat-acrylonitrile-stat-vinyl-2,4-diamino-1,3,5-triazine | [15] |
| BSA | Zhang et al. | 2010 | acrylamide, multi walled carbon nanotubes | [31] |
| cholesterol | Sreenivasan et al. | 1998 | hydroxyethyl methacrylate | [28] |
| cimetidine | Ceolin et al. | 2009 | methacrylic acid, hydroxyethyl methacrylate | [24] |
| enrofloxacin | Kamel et al. | 2011 | methacrylic acid, 2-vinylpyridine | [62] |
| folic acid | Donato et al. | 2010 | acrylonitrile, acrylamide | [49] |
| ibuprofen | Kochkodan et al. | 2010 | dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, trimethylopropane trimethacrylate | [90] |
| luteolin | Zhang et al. | 2009 | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane | [55] |
| lysozyme | Chen et al. | 2010 | acrylamide, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [58] |
| methyl orange | Takagishi et al. | 1972 | polyethyleneimine | [3] |
| naproxen | Ma et al. | 2010 | poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and poly(D,L-lactide) | [50] |
| naringin | Trotta et al. | 2002 | acrylic acid, acrylonitrile | [56] |
| Tasselli et al. | 2008 | acrylonitrile, itaconic acid, acrylic acid, acrylamide | [40] | |
| Ma et al. | 2011 | chitosan | [16] | |
| N-ethyl-o/p-toluensulfonamide | Gugliuzza et al. | 2007 | co-poly-(ether/amide) | [9] |
| De Luca et al. | 2009 | co-poly-(ether/amide) | [10] | |
| oleanolic acid | Zhang et al. | 2011 | polyamide-6, poly(styrene-co-maleic acid) | [53] |
| phosphatidylcoline | Silvestri et al. | 2007 | poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) | [44] |
| Pegoraro et al. | 2008 | poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) | [45] | |
| propanolol | Yoshimatsu et al. | 2008 | poly(ethylene terephthalate) | [19] |
| Jantarat et al. | 2008 | methacrylic acid | [17] | |
| Yoshimatsu et al. | 2008 | poly(ethylene terephthalate) | [19] | |
| Renkecz et al. | 2011 | methacrylic acid | [60] | |
| propofol | Petcu et al. | 2004 | 4-acetoxystytrene | [59] |
| puerarin | Quin et al. | 2011 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [52] |
| rhodamine b | Malaisamy et al. | 2004 | cellulose acetate, polysulfone | [38] |
| Ulbricht et al. | 2005 | cellulose acetate, sulfonated polysulfone | [36] | |
| rutin | Zeng et al. | 2012 | acrylamide, 2-vinylpyridine, divinylbenzene | [27] |
| sulfadiazine | Almeida et al. | 2011 | poly(vinyl chloride) | [64] |
| sulfamethoxazole | Almeida et al. | 2011 | poly(vinyl chloride) | [64] |
| tetracycline | Trotta et al. | 2005 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [42] |
| Guerreiro et al. | 2011 | methacrylic acid, acrylamide | [63] | |
| theophylline | Kobayashi et al. | 1995 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [32] |
| Wang et al. | 1996 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [5] | |
| Wang et al. | 1997 | N,N-diethylaminodithiocarbamoylmethylstyrene, acrylic acid | [33] | |
| Kobayashi et al. | 1998 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [34] | |
| Hattori et al. | 2004 | methacrylic acid, cellulose | [56] | |
| Silvestri et al. | 2006 | methyl methacrylate, methacrylic acid | [43] | |
| trimethoprim | Fan et al. | 2009 | methacrylic acid, polysulfone | [29] |
| Rebelo et al. | 2011 | methacrylic acid, 2-vinylpyridine | [61] | |
| uric acid | Silvestri et al. | 2006 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [43] |
| Aminoacids, Nucleotides And Sugars | ||||
| alanine | Yu et al. | 2000 | acrylic acid | [25] |
| AMP | Zayats et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, 3-(acrylamido)phenylboronic acid, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide, N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine | [23] |
| Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide-acrylamidephenylboronic acid copolymer | [79] | |
| 5-benzylhydantoin | Lu et al. | 2007 | poly(styrene-stat-acrylonitrile-stat-vinyl-2,4-diamino-1,3,5-triazine) | [15] |
| CMP | Zayats et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, 3-(acrylamido)phenylboronic acid, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide, N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine | [23] |
| Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide-acrylamidephenylboronic acid copolymer | [79] | |
| 9-ethyladenine | Yoshikawa et al. | 2001 | polystyrene resin, cellulose acetate, polysulfone | [78] |
| fructose | Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, acrylamidephenylboronic acid | [79] |
| galactose | Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, acrylamidephenylboronic acid | [79] |
| glucose | Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, acrylamidephenylboronic acid | [79] |
| glutamic acid | Yoshikawa et al. | 1998 | carboxylated polysulfone | [67] |
| Yoshikawa et al. | 1998 | chloromethylated polystyrene resin, divinylbenzene, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide | [66] | |
| Yu et al. | 2000 | methacrylic acid | [25] | |
| Yoshikawa et al. | 2007 | carboxylated polysulfone | [18] | |
| Yoshikawa et al. | 2007 | myrtenal polysulfone | [74] | |
| Sueyoshi et al. | 2010 | cellulose acetate | [76] | |
| Hatanaka et al. | 2011 | polyureas | [75] | |
| Sueyoshi et al. | 2012 | aldehydic polysulfone | [77] | |
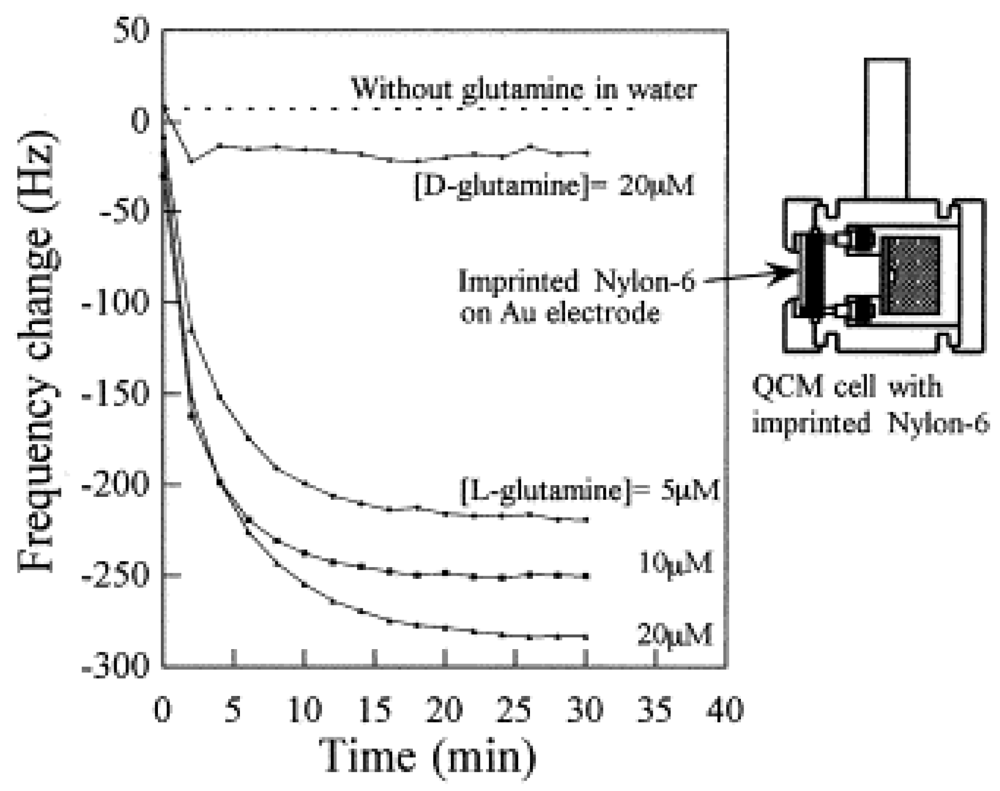
| glutamine | Yoshikawa et al. | 1998 | chloromethylated polystyrene resin, divinylbenzene, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide | [66] |
| Reddy et al. | 2002 | nylon-6 | [37] | |
| GMP | Zayats et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, 3-(acrylamido)phenylboronic acid, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide, N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine | [23] |
| Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide-acrylamidephenylboronic acid copolymer | [79] | |
| leucine | Yoshikawa et al. | 1998 | chloromethylated polystyrene resin, divinylbenzene, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide | [66] |
| lysine | Yoshikawa et al. | 1998 | chloromethylated polystyrene resin, divinylbenzene, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide | [66] |
| NAD+, NADP+, NADH, NADPH | Pogorelova et al. | 2003 | acrylamide-acrylamidophenylboronic acid | [80] |
| phenylalanine | Park et al. | 2002 | acrylic acid | [13] |
| Takeda et al. | 2005 | nylon-6, nylon-6,6, terephthalic phenylene polyamide | [70] | |
| Ul-Haq et al. | 2008 | carboxylated polysulfone | [72] | |
| Wu et al. | 2009 | sodium alginate, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane | [30] | |
| Ul-Haq et al. | 2010 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [73] | |
| serine | Son et al. | 2007 | polysulfone | [71] |
| tryptophan | Yoshikawa et al. | 1997 | DLDE derivative | [65] |
| Yu et al. | 2000 | acrylic acid, methacrylic acid | [25] | |
| Itou et al. | 2008 | polystyrene resin | [68] | |
| tyrosine | Dzgoev et al. | 1999 | 1,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)propane trimethacrylate, methacrylic acid | [69] |
| Yu et al. | 2000 | acrylic acid, methacrylic acid | [25] | |
| UMP | Sallacan et al. | 2002 | acrylamide-acrylamidephenylboronic acid copolymer | [79] |
| uracil | Wang et al. | 2004 | acrylonitrile, methacrylic acid | [39] |
| Kobayashi et al. | 2008 | poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride), poly(styrene-co-maleic acid) | [41] | |
| Metal Ions | ||||
| [Ni-dipyridyl]2+ complex | Wang et al. | 2008 | N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone | [83] |
| Ag+ | Shawky et al. | 2009 | chitosan | [86] |
| Wang et al. | 2009 | chitosan, poly(vinylalcohol) | [87] | |
| Cr(NO3)3·9H2O | Chen et al. | 2010 | sodium alginate, poly(vinylalcohol) | [84] |
| Cu2+ | Li et al. | 2007 | nitrocellulose, poly(vinyl alcohol) | [81] |
| Zhuqing et al. | 2010 | N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl]ethylenediamine | [20] | |
| metallothionein | Cai et al. | 2008 | TiO2 | [21] |
| Ni(II) | Vatanpour et al. | 2011 | methacrylic acid | [85] |
| Zn(II)-(2,2'-bipyridyl) | Zhai et al. | 2008 | 4-vinylpyridine | [82] |
| Herbicides, Pesticides And Pollutants | ||||
| ametrex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| atranex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| atrazine | Sergeyeva et al. | 2008 | methacrylic acid, itaconic acid, acrylamide | [98] |
| Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid, | [91] | |
| bisphenol A | Bryjak et al. | 2011 | polysulfone | [100] |
| chlorpyrifos | Xie et al. | 2010 | polyaminothiophenol | [22] |
| Cu(II)–catechol–urocanic | Sergeyeva et al. | 2010 | (tri)ethyleneglycoldimethacrylate and oligourethaneacrylate | [102] |
| 2,4-D | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid | [91] |
| desmetryn | Kochkodan et al. | 2001 | 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [97] |
| Kochkodan et al. | 2010 | 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [90] | |
| diazinon | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid, | [91] |
| dibenzofuran | Kobayashi et al. | 2002 | polysulfone | [35] |
| 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid | Ayela et al. | 2007 | 4-vinylpyridine, trimethylacrylate | [96] |
| Xie et al. | 2010 | polypyrrole polymers | [95] | |
| dichlorovos | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid | [91] |
| dimethoate | Donato et al. | 2011 | acrylonitrile, methacrylic acid, acrylamide | [89] |
| disulfoton | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid | [91] |
| ethion | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid | [91] |
| haloacetic acids | Suedee et al. | 2004 | 4-vinylpyridine | [94] |
| 4,4'-methylenedianiline | De Luca et al. | 2011 | acrylonitrile, acrylic acid | [11] |
| Del Blanco et al. | 2012 | acrylonitrile, itaconic acid, acrylic acid, methacrylic acid | [99] | |
| monocrotophos | Zhu et al. | 2006 | methacrylic acid, Nylon-6 | [88] |
| N-benzyl-isopropylamine | Kalim et al. | 2005 | poly(vinyl alcohol), cellulose acetate | [101] |
| parathion | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid, | [91] |
| phorate | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid, | [91] |
| pinacolyl methylphosphonate | Vishnuvardhan et al. | 2007 | methylmethacrylic acid | [92] |
| prometrex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| prozinex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| simanex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| terbutex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| 1,3,5-triazine | Kochkodan et al. | 2001 | 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [97] |
| 2,4,6-trichlorophenol | Feng et al. | 2008 | 4-vinylpyridine, methyacrylic acid | [26] |
| tyllanex | Pogorelova et al. | 2002 | acrylamide, sodium methacrylate, N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide | [93] |
| 2,4,5-twere | Prasad et al. | 2007 | methacrylic acid | [91] |
4. Conclusions
Nomenclature
| AA | acrylic acid |
| AAm | acrylamide |
| AIBN | 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile |
| AMP | adenosine 5'-monophosphate |
| AN | acrylonitrile |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| α-TMA | α-tocopherol methacrylate |
| Boc- | N-α-tert-butoxycarbonyl protection |
| Bzl | benzyl protection |
| CA | cellulose acetate |
| CMP | cytosine 5'-monophosphate |
| CS | chitosan |
| DLDE | H-Asp(OcHex)-Leu-Asp(OcHex)-Glu(OBzl)-CH2- |
| DMF | N,N'-dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | dimethylsulfoxide |
| EGDMA | ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| ESD | electrospray deposition |
| EVA | poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) |
| Gln | glutamine |
| Glu | glutamic acid |
| Gly | glycine |
| GMP | guanosine 5'-monophosphate |
| IA | itaconic acid |
| iniferter | initiator-transfer agent-terminator |
| IPN | interpenetrating polymer |
| ISFET | ion sensitive field-effect transistor |
| Leu | leucine |
| Lys | lysine |
| MAA | methacrylic acid |
| MBAA | N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide |
| MIM | molecularly imprinted membrane |
| MIP | molecularly imprinted polymer |
| MIPCM | molecular imprinted polymer composite membrane |
| MMA | methylmethacrylic acid |
| NAD+/NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide/reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NADP+/NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate/reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NG | naringin |
| NHD | neohesperidin |
| NMIM | non molecularly imprinted membrane |
| NMIP | non molecularly imprinted particle |
| NMP | N,N-methylpyrrolidone |
| Ny | nylon |
| P(AN-co-AA) | poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid) |
| P(AN-co-AAm) | poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylamide) |
| P(AN-co-DTCS) | poly(acrylonitrile-co-N,N'-diethylaminodithiocarbamoylmethylstyrene) |
| P(AN-co-IA) | poly(acrylonitrile-co-itaconic acid) |
| P(AN-co-MAA) | poly(acrylonitrile-co-methacrylic acid) |
| PA6 | polyamide-6 |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| PC | phosphatidylcoline |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| PET | poly(ethylene terephthalate) |
| Phe | phenylalanine |
| PP | poly(propylene) |
| PSf | polysulfone |
| PSMA | poly(styrene-co-maleic acid) |
| PTFE | polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PU | polyurethane |
| PVA | poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PVC | poly(vinyl chloride) |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF_phil: hydrophilized polyvinylidene fluoride; PVDF_phob: unmodified hydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride) |
| QCM | quartz crystal microbalance |
| RT | rutin |
| SA | sodium alginate |
| ScCO2 | supercritical carbon dioxide |
| Ser | serine |
| TCH | tetracycline hydrochloride |
| TEOS | tetraethoxysilane |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| TMP | trimethoprim |
| Trp | tryptophan |
| Tyr | tyrosine |
| UMP | uridine 5'-monophosphate |
| VP | vinylpyridine |
Acknowledgments
References
- Polyakov, M.V. Adsorption properties and structure of silica gel. Zhurnal fizicheskoi khimii 2 S. 1931, 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A. Über die Anwendung von Enzymanalog Gebauten Polymeren zur Racemattrennung. Angew. Chem. 1972, 84, 364–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagishi, T.; Klotz, I.M. Macromolecule-small interactions: Introduction of additional binding sites in polyethyleneimine by disulfide cross-linkages. Biopolymers 1972, 11, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Present and future prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sc. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprint membranes prepared by the phase inversion precipitation technique. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4850–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, V.K. Molecularly imprinted polymers: The way forward. Organic Chem. Current Res. 2012, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Row, K.H. Characteristic and synthetic approach of molecularly imprinted polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; De Luca, G.; Tocci, E.; De Lorenzo, L.; Drioli, E. Intermolecular Interactions as Controlling Factor for Water Sorption into Polymer Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 8868–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.; Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. Competitive hydrogen-bonding interactions in modified polymer membranes: A density functional theory investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.; Donato, L.; García Del Blanco, S.; Tasselli, F.; Drioli, E. On the cause of controlling affinity to small molecules of imprinted polymeric membranes prepared by noncovalent approach: A computational and experimental investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9345–9351. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, A.; Ulbricht, M. Effect of surface modification on the synthesis of pore-filling polymeric monoliths in microfiltration membranes made from poly(propylene) and poly(ethylene terephthalate). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Seo, J.I. Characteristics of Phe imprinted membrane prepared by the wet phase inversion method. KoreanJ. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widawski, G.; Rawiso, B.; François, B. Self-organized honeycomb morphology of star-polymer polystyrene films. Nature 1994, 369, 387–389. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Ren, Y.; Xiao, G.; Wang, X.; Li, C. Water-assisted formation of novel molecularly imprinted polymer membranes with ordered porous structure. Polymer 2007, 48, 6205–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, R.; Zheng, X.; Youn, H.; Chen, Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted CS membrane for recognizing naringin in aqueous media. Polym. Bull. 2011, 66, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantarat, C.; Tangthong, N.; Songkro, S.; Martin, G.P.; Suedee, R. S-propranolol imprinted polymer nanoparticle-on-microsphere composite porous cellulose membrane for the enantioselectively controlled delivery of racemic propranolol. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Nakai, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Tanioka, A.; Guiver, M.D.; Robertson, G.P. Molecularly imprinted nanofiber membranes from carboxylated polysulfone by electrospray deposition. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, K.; Ye, L.; Lindberg, J.; Chronakis, I.S. Selective molecular adsorption using electrospun nanofiber affinity membranes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuqing, W.; Min, W.; Genhua, W.; Yuyong, S.; Chiyang, H. Ion imprinted sol-gel nanotubes membrane for selective separation of copper ion from aqueous solution. Microchim. Acta 2010, 169, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.F.; Dai, H.J.; Si, S.H.; Ren, F.L. Molecular imprinting and adsorption of metallothionein on nanocrystalline titania membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 4457–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Gao, S.; Guo, Q.; Xu, K. Electrochemical sensor for 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid using molecularly imprinted polypyrrole membrane as recognition element. Microchim. Acta 2010, 169, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayats, M.; Lahav, M.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Willner, I. Imprinting of specific molecular recognition sites in inorganic and organic thin layer membranes associated with ion-sensitive field-effect transistors. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceolin, G.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Horvai, G.; Horvath, V. Accelerated development procedure for molecularly imprinted polymers using membrane filterplates. J. Comb. Chem. 2009, 11, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Mosbach, K. Influence of mobile phase composition and cross-linking density on the enantiomeric recognition properties of molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 888, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.Z.; Zhao, L.X.; Chu, B.L.; Yan, W.; Lin, J.M. Synthesis and binding site characteristics of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol-imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Kong, J.; Nie, C. Preparation of molecular imprinted polymers using bi-functional monomer and bi-crosslinker for solid-phase extraction of rutin. Talanta 2012, 93, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, K. Synthesis and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polyurethane-poly(HEMA) semi-interpenetrating polymer networks as membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Wang, B. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer membrane with blending trimethoprim-MIP and polysulfone and its transport properties Korean. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, M.; Jiang, Z. Molecularly imprinted organic-inorganic hybrid membranes for selective separation of Phe isomers and its analogue. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Yu, P.; Chen, X. Preparation and characteristics of protein molecularly imprinted membranes on the surface of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Talanta 2010, 81, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprinting of theophylline in acrylonitrile-acrylic acid copolymer membrane. Chem. Lett. 1995, 24, 927–928. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujii, N. Surface molecular imprinting on photosensitive dithiocarbamoyl polyacrylonitrile membranes using photograft polymerization. J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol. 1997, 70, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprint membranes of polyacrylonitrile copolymers with different acrylic acid segments. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 365, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Reddy, P.S.; Ohta, M.; Abe, M.; Fujii, N. Molecularly imprinted polysulfone membranes having acceptor sites for donor dibenzofuran as novel membrane adsorbents: Charge transfer interaction as recognition origin. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M.; Malaisamy, R. Insights into the mechanism of molecular imprinting by immersion precipitation phase inversion of polymer blends via a detailed morphology analysis of porous membranes. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Kobayashi, T.; Abe, M.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprinted Nylon-6 as a recognition material of amino acids. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisamy, R.; Ulbricht, M. Evaluation of molecularly imprinted polymer blend filtration membranes under solid phase extraction conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 39, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Xia, S.L.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.K.; Cao, S.K.; Kobayashi, T. Molecularly imprinted copolymer membranes functionalized by phase inversion imprinting for uracil recognition and permselective binding. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 804, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasselli, F.; Donato, L.; Drioli, E. Evaluation of molecularly imprinted membranes based on different acrylic copolymers. J. Membrane Sci. 2008, 320, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Leong, S.S.; Zhang, Q. Using polystyrene-co-maleic acid for molecularly imprinted membranes prepared in supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Baggiani, C.; Luda, M.P.; Drioli, E.; Massari, T. A molecular imprinted membrane for molecular discrimination of tetracycline hydrochloride. J. Membrane Sci. 2005, 254, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, D.; Barbani, N.; Cristallini, C.; Giusti, P.; Ciardelli, G. Molecularly imprinted membranes for an improved recognition of biomolecules in aqueous medium. J. Membrane Sci. 2006, 282, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, D.; Barbani, N.; Coluccio, M.L.; Pegoraro, C.; Giusti, P.; Cristallini, C.; Ciardelli, G. poly(Ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) membranes with specific adsorption properties for potential clinical application. Separ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 2829–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, C.; Silvestri, D.; Ciardelli, G.; Cristallini, C.; Barbani, N. Molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) membranes for the specific recognition of phospholipids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, C.K.M.; Hoshina, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Scaffold membranes for selective adsorption of α-tocopherol by phase inversion covalently imprinting technique. J. Membrane Sci. 2008, 322, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, C.K.M.; Kobayashi, T. Tocopherol-targeted membrane adsorbents prepared by hybrid molecular imprinting. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, C.K.M.; Kikuchic, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Molecular imprinting targeted for α-tocopherol by calix[4]resorcarenes derivative in membrane scaffold prepared by phase inversion. J. Membrane Sci. 2009, 334, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, L.; Tasselli, F.; Drioli, E. Molecularly imprinted membranes with affinity properties for folic acid. Separ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; McHugh, A.J. The interplay of membrane formation and drug release in solution-cast films of polylactide polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljoughi, E.; Amirilargani, M.; Mohammadi, T. Asymmetric cellulose acetate dialysis membranes: Synthesis, characterization, and performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar]
- Quin, P.; Jie, Y.; Kairm, M.N. Characterization and selectivity studies of molecular imprinted membranes of puerarin using scanning electron microscopy. Scanning 2011, 33, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z. Preparation and adsorption properties of PA6/PSMA-OA molecularly imprinted composite membranes in supercritical CO2. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3348–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Hiwatari, M.; Iiyama, C.; Yoshimi, Y.; Kohori, F.; Sakai, K.; Piletsky, A.A. Gate effect of theophylline-imprinted polymers grafted to the cellulose by living radical polymerization. J. Membrane Sci. 2004, 233, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X. Study on preparation of composite membrane with molecular recognizing property and its selective permeance mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Drioli, E.; Baggiani, C.; Lacopo, D. Molecular imprinted polymeric membrane for naringin recognition. J. Membrane Sci. 2002, 201, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, L.; Chiappetta, G.; Drioli, E. Surface functionalization of PVDF membrane with a naringin-imprinted polymer layer using photo-polymerization method. Separ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.R.; Qin, L.; Jia, M.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y. Novel surface modified molecularly imprinted membrane prepared with iniferter for permselective separation of lysozyme. J. Membrane Sci. 2010, 363, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcu, M.; Schaare, P.N.; Cook, C.J. Propofol-imprinted membranes with potential application in biosensors. Analy. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkecz, T.; Ceolin, G.; Horvàth, V. Selective solid phase extraction of propranolol on multiwell membrane filter plates modified with molecularly imprinted polymer. Analyst 2011, 136, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, T.S.C.R.; Almeida, S.A.A.; Guerreiro, J.R.L.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M.; Sales, M.G.F. Trimethoprim-selective electrodes with molecularly imprinted polymers acting as ionophores and potentiometric transduction on graphite solid-contact. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Rebelo, T.S.C.R.; Sales, M.G.F. Molecularly-imprinted materials for potentiometric transduction: Application to the antibiotic enrofloxacin. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 2107–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, J.R.L.; Freitas, V.; Sales, M.G.F. New sensing materials of molecularly-imprinted polymers for the selective recognition of chlortetracycline. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.A.A.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Heitor, A.M.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M.; Aguilar, G.G.; Sales, M.G.F. Sulphonamide-imprinted sol-gel materials as ionophores in potentiometric transduction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Izumi, J.; Kitao, T.; Sakamoto, S. Alternative molecularly imprinted polymeric membranes from a tetrapeptide residue consisting of D- or L-amino acids. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1997, 18, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Izumi, J.; Kitao, T.; Sakamoto, S. Molecularly imprinted polymeric membranes involving tetrapeptide EQKL derivatives as chiral-recognition sites toward amino acids. Anal.Chim. Acta 1998, 365, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Izumi, J.; Ooi, T.; Kitao, T.; Guiver, M.D.; Robertson, G.P. Carboxylated polysulfone membranes having a chiral recognition site induced by an alternative molecular imprinting technique. Polym. Bull. 1998, 40, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, Y.; Nakano, M.; Yoshikawa, M. Optical resolution of racemic amino acid derivatives with molecularly imprinted membranes from tetrapetide consisting of glycinyl residues. J. Membrane Sci. 2008, 325, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzgoev, A.; Haupt, K. Enantioselective molecularly imprinted polymer membranes. Chirality 1999, 11, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Abe, M.; Kobayashi, T. Molecular-imprinted nylon membranes for the permselective binding of phe as optical- resolution membrane adsorbents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.H.; Jegal, J. Chiral Separation of D,L-serine racemate using a molecularly imprinted polymer composite membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Haq, N.; Khan, T.; Park, J.K. Enantioseparation with D-Phe- and L-Phe-imprinted PAN-based membranes by ultrafiltration. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Haq, N.; Park, J.K. Chiral resolution of Phe by D-Phe imprinted membrane considering rejection property. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakoshi, K.; Kogita, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Guiver, M.D.; Robertson, G.P. Chiral separation membranes from modified polysulfone having myrtenal-derived terpenoid side groups. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, M.; Nishioka, Y.; Yoshikawa, M. Polyurea with L-lysinyl residues as components: Application to membrane separation of enantiomers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Fukushima, C.; Yoshikawa, M. Molecularly imprinted nanofiber membranes from cellulose acetate aimed for chiral separation. J. Membrane Sci. 2010, 357, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, Y.; Utsunomiya, A.; Yoshikawa, M.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D. Chiral separation with molecularly imprinted polysulfone-aldehyde derivatized nanofiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Izumi, J.; Guiver, M.D.; Robertson, G.P. Recognition and selective transport of nucleic acid components through molecularly imprinted polymeric membranes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallacan, N.; Zayats, M.; Bourenko, T.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Willner, I. Imprinting of nucleotide and monosaccharide recognition sites in acrylamidephenylboronic acid-AAm copolymer membranes associated with electronic transducers. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 702–712. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorelova, S.P.; Zayats, M.; Bourenko, T.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Lioubashevski, O.; Katz, E.; Willner, I. Analysis of NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H cofactors by imprinted polymer membranes associated with ion-sensitive field-effect transistor devices and Au–quartz crystals. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.M.; Liu, J.M.; Liu, Z.B.; Liu, Q.Y.; Lin, X.; Li, F.M.; Yang, M.L.; Zhu, G.H.; Huang, X.M. Preparation for nitrocellulose membrane-poly (vinyl alcohol)-ionic imprinting and its application to determine trace copper by room temperature phosphorimetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 589, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Ruan, X.; Liu, J. Metal ion-small molecule complex imprinted polymer membranes: Preparation and separation characteristics. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Xu, Z.L.; Bing, N.C.; Yang, Z.G. Preparation and characterization of metal-complex imprinted PVDF hollow fiber membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Li, G.P.; Liu, Q.L.; Ni, J.C.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, J.M. Cr(III) ionic imprinted polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate (PVA/SA) porous composite membranes for selective adsorption of Cr(III) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 465–473. [Google Scholar]
- Vatanpour, V.; Madaeni, S.S.; Zinadini, S.; Rajabi, H.R. Development of ion imprinted technique for designing nickel ion selective membrane. J. Membrane Sci. 2011, 373, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, H.A. Synthesis of ion-imprinting chitosan/PVA crosslinked membrane for selective removal of Ag(I). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Song, R.; Hou, H.; Li, D. Enrichment and separation of silver from waste solutions by metal ion imprinted membrane. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 100, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Su, Q.; Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymer membranes for substance-selective solid-phase extraction from aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 4468–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, L.; Greco, M.C.; Drioli, E. Preparation of molecularly imprinted membranes and evaluation of their performance in the selective recognition of dimethoate. Desalination and Water Treatment 2011, 30, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N.; Melnik, V.; Kochkodan, O.; Vasilenko, O. Selective recognition of organic pollutants in aqueous solutions with composite imprinted membranes. Advan. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Prathish, K.P.; Gladis, J.M.; Naidu, G.R.; Rao, T.P. Design and development of imprinted polymer inclusion membrane-based field monitoring device for trace determination of phorate (O,O-Diethyl S-Ethyl Thiomethyl Phophorodithioate)in Natural Waters. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnuvardhan, V.; Prathish, K.P.; Naidu, G.R.K.; Prasada Rao, T. Fabrication and topographical analysis of non-covalently imprinted polymer inclusion membranes for the selective sensing of pinacolyl methylphosphonate—A simulant of soman. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 6922–6928. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorelova, S.P.; Bourenko, T.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Willner, I. Selective sensing of triazine herbicides in imprinted membranes using ion-sensitive field-effect transistors and microgravimetric quartz crystal microbalance measurements. Analyst 2002, 127, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suedee, R.; Srichana, T.; Sangpagai, C.; Tunthana, C.; Vanichapichat, P. Development of trichloroacetic acid sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer membrane for the screening of complex mixture of haloacetic acids in drinking water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z. Surface Molecular Self-assembly for organophosphate pesticide imprinting in electropolymerized poly(p-aminothiophenol) membranes on a gold nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ayela, C.; Vandevelde, F.; Lagrange, D.; Haupt, K.; Nicu, L. Combining resonant piezoelectric micromembranes with molecularly impronte polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9271–9274. [Google Scholar]
- Kochkodan, V.; Weigel, W.; Ulbricht, M. Thin layer molecularly imprinted microfiltration membranes by photofunctionalization using a coated a-cleavage photoinitiator. Analyst 2001, 126, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeyeva, T.A.; Piletska, O.V.; Piletsky, S.A.; Sergeeva, L.M.; Brovko, O.O.; El’ska, G.V. Data on the structure and recognition properties of the template-selective binding sites in semi-IPN-based molecularly imprinted polymer membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Blanco, S.G.; Donato, L.; Drioli, E. Development of molecularly impronte membranes for selective recognition of primary amines in organic medium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 87, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryjak, M.; Duraj, I. Molecularly imprinted membranes for removal of bisphenol A. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2011, 29, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalim, R.; Schomäcker, R.; Yüce, S.; Brüggemann, O. Catalysis of α-elimination applying membranes with incorporated molecularly imprinted polymer particles. Polym. Bull. 2005, 55, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeyeva, T.A.; Slinchenko, O.A.; Gorbach, L.A.; Matyushov, V.F.; Brovko, O.O.; Piletsky, S.A.; Sergeeva, L.M.; Elsk, G.V. Catalytic molecularly imprinted polymer membranes: Development of the biomimetic sensor for phenols detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Trotta, F.; Biasizzo, M.; Caldera, F. Molecularly Imprinted Membranes. Membranes 2012, 2, 440-477. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2030440
Trotta F, Biasizzo M, Caldera F. Molecularly Imprinted Membranes. Membranes. 2012; 2(3):440-477. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2030440
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrotta, Francesco, Miriam Biasizzo, and Fabrizio Caldera. 2012. "Molecularly Imprinted Membranes" Membranes 2, no. 3: 440-477. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2030440




