Recent Advances in BLV Research
Abstract
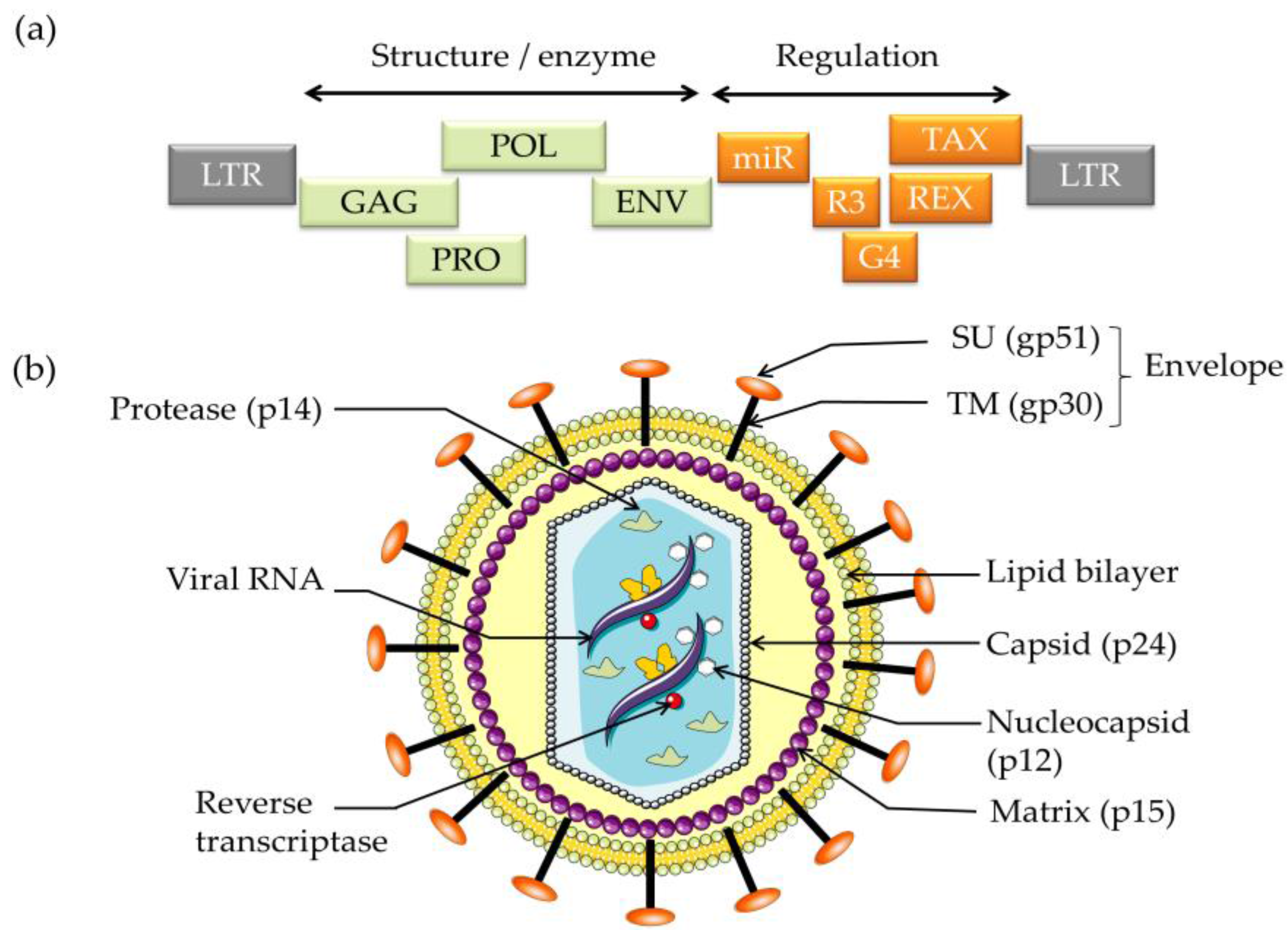
:1. Introduction
2. Viral Oncogenes Drive Proliferation
3. Reverse Genetics Reveals the Significance of Viral Sequences in Infection and Replication
4. A Mutation that Increases Pathogenicity: Potential Hyperpathogenic Strain
5. In Vivo Kinetics Indicates that BLV-Infected Cells Undergo High Turnover during Chronic Infection of Sheep
6. Massive Depletion of Clones Located in Genomic Transcriptionally Active Sites during Infection
7. Tight Control of Virus-Positive Cells by the Immune Response
8. A Therapy Based on Activation of Viral Expression
9. Towards an Efficient Vaccine
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, L.C.; Scarratt, W.K.; Buehring, G.C.; Saunders, G.K. Bovine leukemia virus infection in a juvenile alpaca with multicentric lymphoma. Can. Vet. J. 2012, 53, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meas, S.; Ohashi, K.; Tum, S.; Chhin, M.; Te, K.; Miura, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Onuma, M. Seroprevalence of bovine immunodeficiency virus and bovine leukemia virus in draught animals in Cambodia. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2000, 62, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, S.M.; Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; de Brogniez, A.; Sanchez-Alcaraz, M.T.; Boxus, M.; Boulanger, F.; Gutierrez, G.; Trono, K.; Alvarez, I.; et al. Preventive and therapeutic strategies for bovine leukemia virus: Lessons for HTLV. Viruses 2011, 3, 1210–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, N.; Florins, A.; Boxus, M.; Burteau, C.; Nigro, A.; Vandermeers, F.; Balon, H.; Bouzar, A.B.; Defoiche, J.; Burny, A.; et al. Mechanisms of leukemogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus: Prospects for novel anti-retroviral therapies in human. Retrovirology 2007, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lairmore, M.D. Animal models of bovine leukemia virus and human T-lymphotrophic virus type-1: Insights in transmission and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, P.C.; Norby, B.; Byrem, T.M.; Parmelee, A.; Ledergerber, J.T.; Erskine, R.J. Bovine leukemia virus and cow longevity in Michigan dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, G.; Rodriguez, S.M.; de Brogniez, A.; Gillet, N.; Golime, R.; Burny, A.; Jaworski, J.P.; Alvarez, I.; Vagnoni, L.; Trono, K.; et al. Vaccination against delta-retroviruses: The bovine leukemia virus paradigm. Viruses 2014, 6, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Tsutsui, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayama, Y.; Muroga, N.; Konishi, M.; Kameyama, K.; Murakami, K. The role of neighboring infected cattle in bovine leukemia virus transmission risk. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxus, M.; Willems, L. Mechanisms of HTLV-1 persistence and transformation. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehring, G.C.; Shen, H.M.; Jensen, H.M.; Jin, D.L.; Hudes, M.; Block, G. Exposure to bovine leukemia virus is associated with breast cancer: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derse, D. trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mRNA processing. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kerkhofs, P.; Heremans, H.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. In vitro and in vivo oncogenic potential of bovine leukemia virus G4 protein. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2554–2559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willems, L.; Grimonpont, C.; Heremans, H.; Rebeyrotte, N.; Chen, G.; Portetelle, D.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R. Mutations in the bovine leukemia virus Tax protein can abrogate the long terminal repeat-directed transactivating activity without concomitant loss of transforming potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, E.; Kerkhofs, P.; Mammerickx, M.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. The CREB, ATF-1, and ATF-2 transcription factors from bovine leukemia virus-infected B lymphocytes activate viral expression. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willems, L.; Kettmann, R.; Chen, G.; Portetelle, D.; Burny, A.; Derse, D. A cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein (CREB2) is a cellular transactivator of the bovine leukemia virus long terminal repeat. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Twizere, J.C.; Kruys, V.; Lefebvre, L.; Vanderplasschen, A.; Collete, D.; Debacq, C.; Lai, W.S.; Jauniaux, J.C.; Bernstein, L.R.; Semmes, O.J.; et al. Interaction of retroviral Tax oncoproteins with tristetraprolin and regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, L.; Vanderplasschen, A.; Ciminale, V.; Heremans, H.; Dangoisse, O.; Jauniaux, J.C.; Toussaint, J.F.; Zelnik, V.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; et al. Oncoviral bovine leukemia virus G4 and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 p13(II) accessory proteins interact with farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. The interferon-inducible protein viperin inhibits influenza virus release by perturbing lipid rafts. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kincaid, R.P.; Burke, J.M.; Sullivan, C.S. RNA virus microRNA that mimics a B-cell oncomiR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosewick, N.; Momont, M.; Durkin, K.; Takeda, H.; Caiment, F.; Cleuter, Y.; Vernin, C.; Mortreux, F.; Wattel, E.; Burny, A.; et al. Deep sequencing reveals abundant noncanonical retroviral microRNAs in B-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2306–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, L.; Gatot, J.S.; Mammerickx, M.; Portetelle, D.; Burny, A.; Kerkhofs, P.; Kettmann, R. The YXXL signalling motifs of the bovine leukemia virus transmembrane protein are required for in vivo infection and maintenance of high viral loads. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4137–4141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willems, L.; Burny, A.; Collete, D.; Dangoisse, O.; Dequiedt, F.; Gatot, J.S.; Kerkhofs, P.; Lefebvre, L.; Merezak, C.; Peremans, T.; et al. Genetic determinants of bovine leukemia virus pathogenesis. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2000, 16, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, L.; Kerkhofs, P.; Dequiedt, F.; Portetelle, D.; Mammerickx, M.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R. Attenuation of bovine leukemia virus by deletion of R3 and G4 open reading frames. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11532–11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeri, V.W.; Hryniewicz, A.; Andresen, V.; Jones, K.; Fenizia, C.; Bialuk, I.; Chung, H.K.; Fukumoto, R.; Parks, R.W.; Ferrari, M.G.; et al. Requirement of the human T-cell leukemia virus p12 and p30 products for infectivity of human dendritic cells and macaques but not rabbits. Blood 2010, 116, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; Boxus, M.; Kerkhofs, P.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Even attenuated bovine leukemia virus proviruses can be pathogenic in sheep. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10195–10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatot, J.S.; Callebaut, I.; Mornon, J.P.; Portetelle, D.; Burny, A.; Kerkhofs, P.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Conservative mutations in the immunosuppressive region of the bovine leukemia virus transmembrane protein affect fusion but not infectivity in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12870–12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debacq, C.; Sanchez Alcaraz, M.T.; Mortreux, F.; Kerkhofs, P.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Reduced proviral loads during primo-infection of sheep by Bovine Leukemia virus attenuated mutants. Retrovirology 2004, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merezak, C.; Pierreux, C.; Adam, E.; Lemaigre, F.; Rousseau, G.G.; Calomme, C.; van Lint, C.; Christophe, D.; Kerkhofs, P.; Burny, A.; et al. Suboptimal enhancer sequences are required for efficient bovine leukemia virus propagation in vivo: Implications for viral latency. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6977–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Brogniez, A.; Bouzar, A.B.; Jacques, J.R.; Cosse, J.P.; Gillet, N.; Callebaut, I.; Reichert, M.; Willems, L. Mutation of a single envelope N-linked glycosylation site enhances the pathogenicity of bovine leukemia virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8945–8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debacq, C.; Asquith, B.; Kerkhofs, P.; Portetelle, D.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Increased cell proliferation, but not reduced cell death, induces lymphocytosis in bovine leukemia virus-infected sheep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10048–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, B.; Zhang, Y.; Mosley, A.J.; de Lara, C.M.; Wallace, D.L.; Worth, A.; Kaftantzi, L.; Meekings, K.; Griffin, G.E.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. In vivo T lymphocyte dynamics in humans and the impact of human T-lymphotropic virus 1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8035–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debacq, C.; Asquith, B.; Reichert, M.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Reduced cell turnover in bovine leukemia virus-infected, persistently lymphocytotic cattle. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13073–13083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoiche, J.; Debacq, C.; Asquith, B.; Zhang, Y.; Burny, A.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L.; Macallan, D.; Willems, L. Reduction of B cell turnover in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, B.; Debacq, C.; Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; Sanchez-Alcaraz, T.; Mosley, A.; Willems, L. Quantifying lymphocyte kinetics in vivo using carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE). Proc. Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; Asquith, B.; Boxus, M.; Burteau, C.; Twizere, J.C.; Urbain, P.; Vandermeers, F.; Debacq, C.; Sanchez-Alcaraz, M.T.; et al. Cell dynamics and immune response to BLV infection: A unifying model. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florins, A.; Reichert, M.; Asquith, B.; Bouzar, A.B.; Jean, G.; Francois, C.; Jasik, A.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Earlier onset of δ-retrovirus-induced leukemia after splenectomy. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, N.A.; Gutierrez, G.; Rodriguez, S.M.; de Brogniez, A.; Renotte, N.; Alvarez, I.; Trono, K.; Willems, L. Massive depletion of bovi ne leukemia virus proviral clones located in genomic transcriptionally active sites during primary infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, N.A.; Malani, N.; Melamed, A.; Gormley, N.; Carter, R.; Bentley, D.; Berry, C.; Bushman, F.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. The host genomic environment of the provirus determines the abundance of HTLV-1-infected T-cell clones. Blood 2011, 117, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florins, A.; de Brogniez, A.; Elemans, M.; Bouzar, A.B.; Francois, C.; Reichert, M.; Asquith, B.; Willems, L. Viral expression directs the fate of B cells in bovine leukemia virus-infected sheep. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achachi, A.; Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; Debacq, C.; Urbain, P.; Foutsop, G.M.; Vandermeers, F.; Jasik, A.; Reichert, M.; Kerkhofs, P.; et al. Valproate activates bovine leukemia virus gene expression, triggers apoptosis, and induces leukemia/lymphoma regression in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10309–10314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzar, A.B.; Boxus, M.; Defoiche, J.; Berchem, G.; Macallan, D.; Pettengell, R.; Willis, F.; Burny, A.; Lagneaux, L.; Bron, D.; et al. Valproate synergizes with purine nucleoside analogues to induce apoptosis of B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagneaux, L.; Gillet, N.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Delforge, A.; Dejeneffe, M.; Massy, M.; Meuleman, N.; Kentos, A.; Martiat, P.; Willems, L.; et al. Valproic acid induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through activation of the death receptor pathway and potentiates TRAIL response. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezin, A.; Gillet, N.; Olindo, S.; Signate, A.; Grandvaux, N.; Verlaeten, O.; Belrose, G.; Hiscott, J.; de Carvalho Bittencourt, M.; Asquith, B.; et al. Histone deacetylase mediated transcriptional activation reduces proviral loads in HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis patients. Blood 2007, 110, 3722–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olindo, S.; Belrose, G.; Gillet, N.; Rodriguez, S.; Boxus, M.; Verlaeten, O.; Asquith, B.; Bangham, C.; Signate, A.; Smadja, D.; et al. Safety of long-term treatment of HAM/TSP patients with valproic acid. Blood 2011, 118, 6306–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, P.V.; Mekaouche, M.; Mortreux, F.; Toulza, F.; Moriceau, A.; Wattel, E.; Gessain, A.; Bangham, C.R.; Dubreuil, G.; Plumelle, Y.; et al. Highly active antiretroviral treatment against STLV-1 infection combining reverse transcriptase and HDAC inhibitors. Blood 2010, 116, 3802–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toomey, N.; Barber, G.; Ramos, J.C. Preclinical efficacy of belinostat in combination with zidovudine in adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Retrovirology 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Response to scientific and technical information provided by an NGO on Xylella fastidiosa. EFSA J. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansky, L.M.; Temin, H.M. Lower mutation rate of bovine leukemia virus relative to that of spleen necrosis virus. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willems, L.; Thienpont, E.; Kerkhofs, P.; Burny, A.; Mammerickx, M.; Kettmann, R. Bovine leukemia virus, an animal model for the study of intrastrain variability. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barez, P.-Y.; De Brogniez, A.; Carpentier, A.; Gazon, H.; Gillet, N.; Gutiérrez, G.; Hamaidia, M.; Jacques, J.-R.; Perike, S.; Neelature Sriramareddy, S.; et al. Recent Advances in BLV Research. Viruses 2015, 7, 6080-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112929
Barez P-Y, De Brogniez A, Carpentier A, Gazon H, Gillet N, Gutiérrez G, Hamaidia M, Jacques J-R, Perike S, Neelature Sriramareddy S, et al. Recent Advances in BLV Research. Viruses. 2015; 7(11):6080-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112929
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarez, Pierre-Yves, Alix De Brogniez, Alexandre Carpentier, Hélène Gazon, Nicolas Gillet, Gerónimo Gutiérrez, Malik Hamaidia, Jean-Rock Jacques, Srikanth Perike, Sathya Neelature Sriramareddy, and et al. 2015. "Recent Advances in BLV Research" Viruses 7, no. 11: 6080-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112929
APA StyleBarez, P.-Y., De Brogniez, A., Carpentier, A., Gazon, H., Gillet, N., Gutiérrez, G., Hamaidia, M., Jacques, J.-R., Perike, S., Neelature Sriramareddy, S., Renotte, N., Staumont, B., Reichert, M., Trono, K., & Willems, L. (2015). Recent Advances in BLV Research. Viruses, 7(11), 6080-6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112929




