Bovine Lactoferrin-Induced CCL1 Expression Involves Distinct Receptors in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Monocyte Precursors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. bLF Up-Modulates CCL1 Expression in Mo and MoDCs


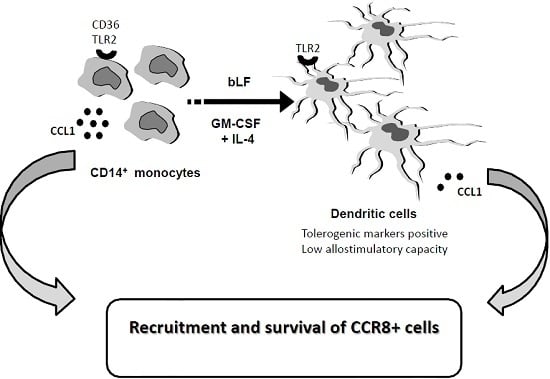
2.2. bLF-Mediated Up-Modulation of CCL1 Secretion Requires Different Receptors in Mo and MoDCs

3. Discussion

4. Experimental Section
4.1. Ethics Statements
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Cell Isolation and Culture
4.4. CCL1 mRNA and Protein Detection
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions

Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albar, A.H.; Almehdar, H.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Redwan, E.M. Structural heterogeneity and multifunctionality of lactoferrin. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 778–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Montoya, I.A.; Cendon, T.S.; Arevalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascon-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin a multiple bioactive protein: An overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueiros-Cendon, T.; Arevalo-Gallegos, S.; Iglesias-Figueroa, B.F.; Garcia-Montoya, I.A.; Salazar-Martinez, J.; Rascon-Cruz, Q. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, D.; Berlutti, F.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S.; Puddu, P. Lf immunomodulatory strategies: Mastering bacterial endotoxin. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, D. Lactoferrin, a key molecule in immune and inflammatory processes. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin on antigen presenting cells. Biochimie 2009, 91, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, G.; Haniffa, M. Human and mouse mononuclear phagocyte networks: A tale of two species? Front. Immunol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffray, C.; Sieweke, M.H.; Geissmann, F. Blood monocytes: Development, heterogeneity, and relationship with dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merad, M.; Sathe, P.; Helft, J.; Miller, J.; Mortha, A. The dendritic cell lineage: Ontogeny and function of dendritic cells and their subsets in the steady state and the inflamed setting. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 563–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombert, M.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Winterberg, F.; Bunemann, E.; Kubitza, R.C.; da Cunha, L.; Haahtela, A.; Lehtimaki, S.; Muller, A.; Rieker, J.; et al. CCL1-CCR8 interactions: An axis mediating the recruitment of T cells and langerhans-type dendritic cells to sites of atopic skin inflammation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5082–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaerli, P.; Ebert, L.; Willimann, K.; Blaser, A.; Roos, R.S.; Loetscher, P.; Moser, B. A skin-selective homing mechanism for human immune surveillance T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCully, M.L.; Moser, B. The human cutaneous chemokine system. Front. Immunol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingoni, A.; Soto, H.; Hedrick, J.A.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Sinigaglia, F.; D’Ambrosio, D.; O’Garra, A.; Robinson, D.; Rocchi, M.; et al. The chemokine receptor CCR8 is preferentially expressed in TH2 but not th1 cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chensue, S.W.; Lukacs, N.W.; Yang, T.Y.; Shang, X.; Frait, K.A.; Kunkel, S.L.; Kung, T.; Wiekowski, M.T.; Hedrick, J.A.; Cook, D.N.; et al. Aberrant in vivo T helper type 2 cell response and impaired eosinophil recruitment in CC chemokine receptor 8 knockout mice. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.A.; Chang, D.S.; Colvin, R.A.; Byrne, M.H.; McCully, M.L.; Moser, B.; Lira, S.A.; Charo, I.F.; Luster, A.D. Mouse CCL8, a CCR8 agonist, promotes atopic dermatitis by recruiting IL-5+ TH2 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, P.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Wilson, S.D.; Berman, M.; DeKruyff, R.; Billings, P.R.; Dorf, M.E. Cloning and characterization of a novel T cell activation gene. J. Immunol. 1987, 139, 3126–3131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.D.; Hata, S.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Krangel, M.S. A novel polypeptide secreted by activated human T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mira, E.; Leon, B.; Barber, D.F.; Jimenez-Baranda, S.; Goya, I.; Almonacid, L.; Marquez, G.; Zaballos, A.; Martinez, A.C.; Stein, J.V.; et al. Statins induce regulatory T cell recruitment via a CCL1 dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3524–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zen, Y.; Liberal, R.; Nakanuma, Y.; Heaton, N.; Portmann, B. Possible involvement of CCL1-CCR8 interaction in lymphocytic recruitment in IGG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.J.; Ornelles, D.A.; Mitchell, L.M.; Brzoza-Lewis, K.L.; Hiltbold, E.M. IL-12 produced by dendritic cells augments CD8+ T cell activation through the production of the chemokines CCL1 and CCL17. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo, J.A.; Qiu, Y.; Lora, J.M.; Al-Garawi, A.; Villeval, J.L.; Boyce, J.A.; Martinez, A.C.; Marquez, G.; Goya, I.; Hamid, Q.; et al. Coordinated involvement of mast cells and T cells in allergic mucosal inflammation: Critical role of the CC chemokine ligand 1:CCR8 axis. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Vizuet, R.; Vega-Miranda, A.; Valencia-Maqueda, E.; Negrete-Garcia, M.C.; Velasquez, J.R.; Teran, L.M. CC chemokine ligand 1 is released into the airways of atopic asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvan, R.S.; Zhou, L.J.; Krangel, M.S. Regulation of I-309 gene expression in human monocytes by endogenous interleukin-1. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sironi, M.; Martinez, F.O.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Gattorno, M.; Polentarutti, N.; Locati, M.; Gregorio, A.; Iellem, A.; Cassatella, M.A.; Van Damme, J.; et al. Differential regulation of chemokine production by fcgamma receptor engagement in human monocytes: Association of CCL1 with a distinct form of M2 monocyte activation (M2B, type 2). J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbatucci, M.; Purificato, C.; Fantuzzi, L.; Gessani, S. Toll-like receptor cross-talk in human monocytes regulates CC-chemokine production, antigen uptake and immune cell recruitment. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Latorre, D.; Carollo, M.; Catizone, A.; Ricci, G.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S. Bovine lactoferrin counteracts toll-like receptor mediated activation signals in antigen presenting cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, F.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Sanders, R.W.; Baldwin, C.E.; Sanchez-Hernandez, M.; Floris, R.; van Kooyk, Y.; de Jong, E.C.; Berkhout, B. Lactoferrin prevents dendritic cell-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission by blocking the DC-sign--GP120 interaction. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3009–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eda, S.; Eda, K.; Prudhomme, J.G.; Sherman, I.W. Inhibitory activity of human lactoferrin and its peptide on chondroitin sulfate A-, CD36-, and thrombospondin-mediated cytoadherence of plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Blood 1999, 94, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, L.; Borghi, P.; Ciolli, V.; Pavlakis, G.; Belardelli, F.; Gessani, S. Loss of CCR2 expression and functional response to monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP-1) during the differentiation of human monocytes: Role of secreted MCP-1 in the regulation of the chemotactic response. Blood 1999, 94, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, L.; Canini, I.; Belardelli, F.; Gessani, S. IFN-beta stimulates the production of beta-chemokines in human peripheral blood monocytes. Importance of macrophage differentiation. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2001, 12, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodenburg, R.J.; Brinkhuis, R.F.; Peek, R.; Westphal, J.R.; van Den Hoogen, F.H.; van Venrooij, W.J.; van de Putte, L.B. Expression of macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC) mrna in macrophages is enhanced by interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and lipopolysaccharide. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.A.; Wong, H.; Ashida, K.Y.; Schryvers, A.B.; Lonnerdal, B. The N1 domain of human lactoferrin is required for internalization by Caco-2 cells and targeting to the nucleus. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 10915–10920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Furmanski, P. Sequence specificity and transcriptional activation in the binding of lactoferrin to DNA. Nature 1995, 373, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, K.N.; Park, J.; Chung, C.K.; Chung, D.K.; Yu, D.Y.; Lee, K.K.; Kim, J. Human lactoferrin activates transcription of IL-1 beta gene in mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariller, C.; Benaissa, M.; Hardiville, S.; Breton, M.; Pradelle, G.; Mazurier, J.; Pierce, A. Human delta-lactoferrin is a transcription factor that enhances Skp1 (S-phase kinase-associated protein) gene expression. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 2038–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, D.; Pierce, A.; Elass, E.; Carpentier, M.; Mariller, C.; Mazurier, J. Lactoferrin structure and functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 606, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Latorre, D.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S. Immunoregulatory role of lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Biomet.: Int. J. Role Met. Ions Biol. Biochem. Med. 2010, 23, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elass-Rochard, E.; Legrand, D.; Salmon, V.; Roseanu, A.; Trif, M.; Tobias, P.S.; Mazurier, J.; Spik, G. Lactoferrin inhibits the endotoxin interaction with CD14 by competition with the lipopolysaccharide-binding protein. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spadaro, M.; Montone, M.; Arigoni, M.; Cantarella, D.; Forni, G.; Pericle, F.; Pascolo, S.; Calogero, R.A.; Cavallo, F. Recombinant human lactoferrin induces human and mouse dendritic cell maturation via toll-like receptors 2 and 4. FASEB J.: Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2014, 28, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Qin, Z.; Ye, Q.; Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Q.; Luo, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, W.; et al. Lactoferrin suppresses the epstein-barr virus-induced inflammatory response by interfering with pattern recognition of TLR2 and TLR9. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2014, 94, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Shindo, K.; Furusawa, T.; Fujino, T.; Kikugawa, K.; Nakano, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Akiyama, T.; et al. Human lactoferrin activates NF-kappab through the toll-like receptor 4 pathway while it interferes with the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated TLR4 signaling. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2051–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.D.; Ramos, R.A.; Tobias, P.S.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Mathison, J.C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 1990, 249, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, T.; Yasuda, M.; Fujita, M.; Kataoka, H.; Kiura, K.; Sano, H.; Shibata, K. CD14 directly binds to triacylated lipopeptides and facilitates recognition of the lipopeptides by the receptor complex of toll-like receptors 2 and 1 without binding to the complex. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkbacka, H. Multiple roles of toll-like receptor signaling in atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2006, 17, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoebe, K.; Georgel, P.; Rutschmann, S.; Du, X.; Mudd, S.; Crozat, K.; Sovath, S.; Shamel, L.; Hartung, T.; Zahringer, U.; et al. CD36 is a sensor of diacylglycerides. Nature 2005, 433, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed-Geaghan, E.G.; Savage, J.C.; Hise, A.G.; Landreth, G.E. CD14 and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are required for fibrillar a β stimulated microglial activation. J. Neurosci.: Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11982–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Carollo, M.G.; Belardelli, F.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S. Role of endogenous interferon and LPS in the immunomodulatory effects of bovine lactoferrin in murine peritoneal macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn-Siegrist, I.; Leger, O.; Daubeuf, B.; Poitevin, Y.; Depis, F.; Herren, S.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; Dean, Y.; Pugin, J.; Elson, G. Pivotal involvement of fcgamma receptor iia in the neutralization of lipopolysaccharide signaling via a potent novel anti-TLR4 monoclonal antibody 15C1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34817–34827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Rutz, M.; Schiemann, M.; Metzger, J.; Grabiec, A.; Schwandner, R.; Luppa, P.B.; Ebel, F.; Busch, D.H.; Bauer, S.; et al. Antagonistic antibody prevents toll-like receptor 2-driven lethal shock-like syndromes. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 113, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauzzi, M.C.; Purificato, C.; Donato, K.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Daniel, K.C.; Maghazachi, A.A.; Belardelli, F.; Adorini, L.; Gessani, S. Suppressive effect of 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on type I IFN-mediated monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells: Impairment of functional activities and chemotaxis. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Corno, M.; Michienzi, A.; Masotti, A.; da Sacco, L.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Belardelli, F.; Gessani, S. CC chemokine ligand 2 down-modulation by selected toll-like receptor agonist combinations contributes to T helper 1 polarization in human dendritic cells. Blood 2009, 114, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbatucci, M.; Covino, D.A.; Purificato, C.; Mallano, A.; Federico, M.; Lu, J.; Rinaldi, A.O.; Pellegrini, M.; Bona, R.; Michelini, Z.; et al. Endogenous CCL2 neutralization restricts HIV-1 replication in primary human macrophages by inhibiting viral DNA accumulation. Retrovirology 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latorre, D.; Pulvirenti, N.; Covino, D.A.; Varano, B.; Purificato, C.; Rainaldi, G.; Gauzzi, M.C.; Fantuzzi, L.; Conti, L.; Donninelli, G.; et al. Bovine Lactoferrin-Induced CCL1 Expression Involves Distinct Receptors in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Monocyte Precursors. Toxins 2015, 7, 5472-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124897
Latorre D, Pulvirenti N, Covino DA, Varano B, Purificato C, Rainaldi G, Gauzzi MC, Fantuzzi L, Conti L, Donninelli G, et al. Bovine Lactoferrin-Induced CCL1 Expression Involves Distinct Receptors in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Monocyte Precursors. Toxins. 2015; 7(12):5472-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124897
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatorre, Daniela, Nadia Pulvirenti, Daniela Angela Covino, Barbara Varano, Cristina Purificato, Gabriella Rainaldi, Maria Cristina Gauzzi, Laura Fantuzzi, Lucia Conti, Gloria Donninelli, and et al. 2015. "Bovine Lactoferrin-Induced CCL1 Expression Involves Distinct Receptors in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Monocyte Precursors" Toxins 7, no. 12: 5472-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124897
APA StyleLatorre, D., Pulvirenti, N., Covino, D. A., Varano, B., Purificato, C., Rainaldi, G., Gauzzi, M. C., Fantuzzi, L., Conti, L., Donninelli, G., Del Cornò, M., Sabbatucci, M., Gessani, S., & Puddu, P. (2015). Bovine Lactoferrin-Induced CCL1 Expression Involves Distinct Receptors in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Monocyte Precursors. Toxins, 7(12), 5472-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124897