Type 1 Diabetes and Addison’s Disease: When the Diagnosis Is Suggested by the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
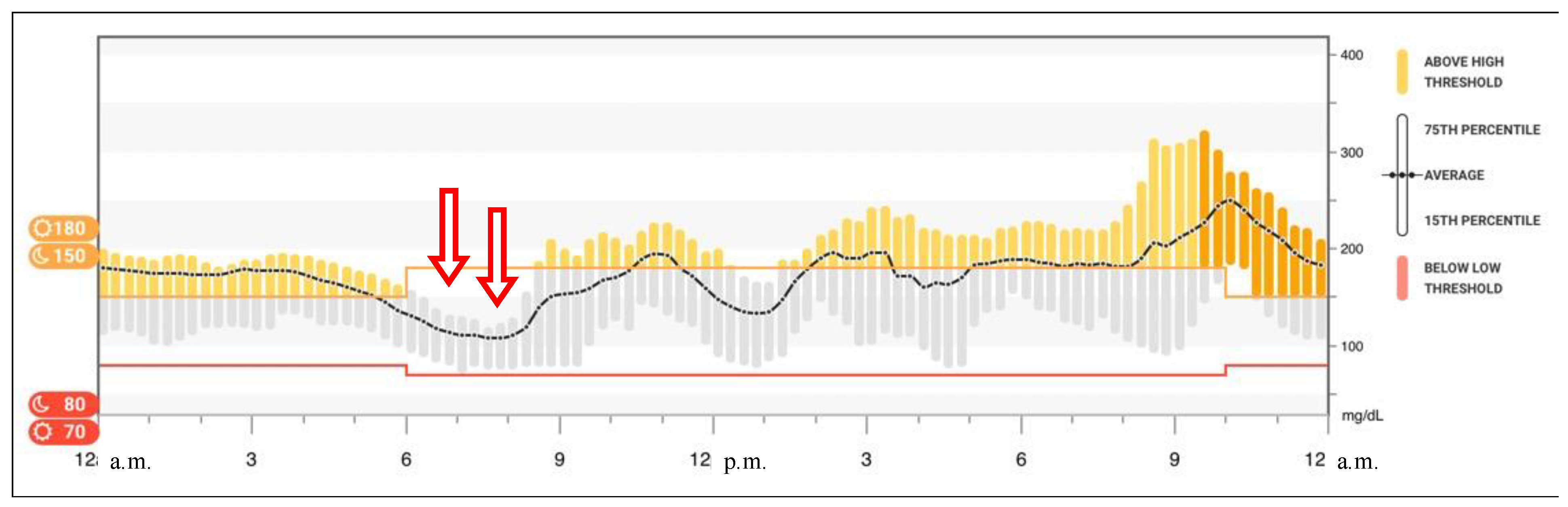
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prahalad, P.; Tanenbaum, M.; Hood, K.; Maahs, D.M. Diabetes technology: Improving care, improving patient-reported outcomes and preventing complications in young people with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassi, M.; Minuto, N.; Fichera, G.; Rebora, C.; Parodi, A.; Natoli, V.; Pontillo, L.; Buccianti, M.; D’Annunzio, G.; Maghnie, M. Practical Approach to Using Trend Arrows on Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Type 1 Diabetes Adolescents Living Camp Setting Treated With Multiple Daily Injection or Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Insulin Therapy. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szypowska, A.; Ramotowska, A.; Dzygalo, K.; Dzygalo, K.; Golicki, D. Beneficial 154 effect of real-time continuous glucose monitoring system on glycemic control in type 1 diabetic patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, F.J.; Northam, E.A.; Ryan, C.M. The effect of type 1 diabetes on the developing brain. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2019, 3, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaly, G.J.; Hansen, M.P. Type 1 diabetes associated autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäkimattila, S.; Harjutsalo, V.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.-H. Every Fifth Individual with Type 1 Diabetes Suffers From an Additional Autoimmune Disease: A Finnish Nationwide Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, G.; Hackemann, A.; Reusch, J.; Badenhoop, K. Nocturnal hypoglycemia identified by a continuous glucose monitoring system in patients with primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s Disease). Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uçar, A.; Baş, F.; Saka, N. Diagnosis and management of pediatric adrenal insufficiency. World J. Pediatr. 2016, 12, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warncke, K.; Fröhlich-Reiterer, E.E.; Thon, A.; Hofer, S.E.; Wiemann, D. Holl RW DPV Initiative of the German Working Group for Pediatric Diabetology; German BMBF Competence Network for Diabetes Mellitus. Polyendocrinopathy in children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes: A multicenter analysis of 28,671 patients from the German/Austrian DPV-Wiss database. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Libânio, D.; Marcos-Pinto, R.; Areia, M.; Leja, M.; Esposito, G.; Garrido, M.; Kikuste, I.; Megraud, F.; Matysiak-Budnik, T.; et al. Management of epithelial precancerous conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS II): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE), European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group (EHMSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and Sociedade Portuguesa de EndoscopiaDigestiva (SPED) guideline update 2019. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakleas, K.; Soldatou, A.; Karachaliou, F.; Karavanaki, K. Associated autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents with type 1 di-abetes mellitus (T1DM). Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passanisi, S.; Timpanaro, T.; Presti, D.L.; Caruso-Nicoletti, M. Recurrent hypoglycaemia in type-1 diabetes mellitus may unravel the association with Addison’s disease: A case report. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Lou, J.; Yu, J. A case of Metaplastic atrophic gastritis in immune Dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 13. Children and Adolescents: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl S1), S180–S199. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, F.H.; Elbarbary, N.S.; Fröhlich-Reiterer, E.; Holl, R.W.; Kordonouri, O.; Knip, M.; Simmons, K.; Craig, M.E. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Other complications and associated conditions in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 19, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E.S.; Anderson, M.S. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes: Clues to Type 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis. Immunity 2010, 32, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charmandari, E.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Chrousos, G.P. Adrenal Insufficiency. Lancet 2014, 383, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caturegli, P.; De Remigis, A.; Rose, N. Hashimoto thyroiditis: Clinical and diagnostic criteria. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banitt, P.F.; Munson, A.K. Addisonian crisis after thyroid replacement. Hosp. Pract. 1986, 21, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations from the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labhart, A. Adrenal cortex. In Clinical Endocrinology, Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; ; Labhart, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T. Comorbid Latent Adrenal Insufficiency with Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2015, 4, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinci, F.; d’Annunzio, G.; Napoli, F.; Bassi, M.; Montobbio, C.; Ferrando, G.; Minuto, N. Type 1 Diabetes and Addison’s Disease: When the Diagnosis Is Suggested by the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Children 2021, 8, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080702
Vinci F, d’Annunzio G, Napoli F, Bassi M, Montobbio C, Ferrando G, Minuto N. Type 1 Diabetes and Addison’s Disease: When the Diagnosis Is Suggested by the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Children. 2021; 8(8):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080702
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinci, Francesco, Giuseppe d’Annunzio, Flavia Napoli, Marta Bassi, Carolina Montobbio, Giulia Ferrando, and Nicola Minuto. 2021. "Type 1 Diabetes and Addison’s Disease: When the Diagnosis Is Suggested by the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System" Children 8, no. 8: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080702
APA StyleVinci, F., d’Annunzio, G., Napoli, F., Bassi, M., Montobbio, C., Ferrando, G., & Minuto, N. (2021). Type 1 Diabetes and Addison’s Disease: When the Diagnosis Is Suggested by the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Children, 8(8), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080702





