Design of Self-Oscillating Gels and Application to Biomimetic Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design of Self-Oscillating Gel
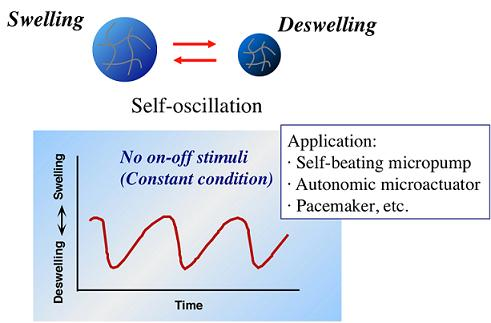
3. Self-Oscillating Motion of Miniature Bulk Gel: Homogeneous Swelling-Deswelling Oscillation
4. Worm-Like Peristaltic Motion of Gel
5. Design of Biomimetic Actuator Using Self-Oscillating Gel
5.1. Self-Walking Gel
5.2. Mass Transport Surface Utilizing Peristaltic Motion of Gel
5.3. Ciliary Motion Actuator (Artificial Cilia)
5.4. Control of Chemical Wave Propagation in Self-Oscillating Gel Array
6. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Yoshida, R. Design of functional polymer gels and their application to biomimetic materials. Curr. Org. Chem 2005, 9, 1617–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Dusek, K. (Ed.) Responsive gels: Volume transitions II; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1993.
- Ashley, S. Artificial muscles. Sci. Am 2003, 289, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Osada, Y.; Okuzaki, H.; Hori, H. A polymer gel with electrically driven motility. Nature 1992, 355, 242–244. [Google Scholar]
- Kokufuta, E.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tanaka, T. Biochemo-mechanical function of urease-loaded gels. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Edn 1994, 6, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, T.; Nemoto, H.; Hirai, M.; Hayashi, S. Electrostriction of highly swollen polymer gel: possible application for gel actuator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 1994, 53, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, T.; Asaka, K.; Kosaka, A.; Aida, T. Fully plastic actuator through layer-by-layer casting with ionic-liquid-based bucky gel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2005, 44, 2410–2413. [Google Scholar]
- Asaka, K.; Oguro, K. Bending of polyelectrolyte membrane platinum composites by electric stimuli Part II. Response kinetics. J. Electroanal. Chem 2000, 480, 186–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zrinyi, M.; Szabo, D.; Filipcsei, G.; Feher, J. Polymer Gels and Networks; Osada, Y, Khokhlov, A.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 309–355. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ichijo, H. Self-oscillating gel. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1996, 118, 5134–5135. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ichijo, H. Self-oscillating gels. Adv. Mater 1997, 9, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R. Self-oscillating polymer and gels as novel biomimetic materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 2008, 81, 676–688. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Sakai, T.; Hara, Y.; Maeda, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Suzuki, D.; Murase, Y. Self-oscillating gel as novel biomimetic materials. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Field, R.J.; Burger, M. (Eds.) Oscillations and Traveling Waves in Chemical Systems; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1985.
- Epstein, I.R.; Pojman, J.A. An Introduction to Nonlinear Chemical Dynamics: Oscillations, Waves, Patterns, and Chaos; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Tanaka, M.; Onodera, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kokufuta, E. In-phase synchronization of chemical and mechanical oscillations in self-oscillating gels. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 7549–7555. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Takei, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Self-beating motion of gels and modulation of oscillation rhythm synchronized with organic acid. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 1759–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y.; Nogawa, M.; Yoshida, R. Temperature control of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction using a thermo-responsive polymer. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9577–9579. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Otoshi, G.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kokufuta, E. Traveling chemical waves for measuring solute diffusivity in thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 3667–3672. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Kokufuta, E.; Yamaguchi, T. Beating polymer gels coupled with a nonlinear chemcial reaction. Chaos 1999, 9, 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kokufuta, E. Molecular design of self-oscillating polymer gels and their dynamic swelling-deswelling behaviors. J. Intel. Mat. Syst. Struct 1999, 10, 451–457. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Hashimoto, S. Peristaltic motion of polymer gels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 6690–6693. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, S.; Koga, S.; Yoshida, R.; Yamaguchi, T. Mechanical oscillation coupled with the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction in gel. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5595–5600. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, R.; Enoki, M.; Yoshida, R. Measurement of elastic properties of self-oscillating gel. Key Eng. Mater 2006, 321–323, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Amemiya, T.; Ohmori, T.; Yamaguchi, T. An Oregonator-class model for photoinduced behavior in the Ru(bpy)32+-catalyzed Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction. J. Phys. Chem 2000, 104, 336–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Sakai, T.; Tabata, O.; Yamaguchi, T. Design of novel biomimetic polymer gels with self-oscillating function. Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater 2002, 3, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Takeoka, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yoshida, R. Self-sustaining peristaltic motion on the surface of a porous gel. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 13320–13321. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, S.; Seki, T.; Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R.; Takeoka, Y. Chemical and optical control of peristaltic actuator based on self-oscillating porous gel. Chem. Commun 2008, 4735–4737. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, S.; Seki, T.; Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R.; Takeoka, Y. Photoregulated wormlike motion of a gel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 9039–9043. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R.; Hashimoto, S. Self-walking gel. Adv. Mater 2007, 19, 3480–3484. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Hashimoto, S. Control of dynamic motion of a gel actuator driven by the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction. Macromol. Rapid Commun 2008, 29, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Murase, Y.; Maeda, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Yoshida, R. Design of a mass transport surface utilizing peristaltic motion of a self-oscillating gel. Langmuir 2009, 25, 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Murase, Y.; Takeshima, R.; Yoshida, R. Design of mass transport surface using self-oscillating gel. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn 2009, 34, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Tabata, O.; Hirasawa, H.; Aoki, S.; Yoshida, R.; Kokufuta, E. Ciliary motion actuator using self-oscillating gel. Sens. Actuat. A 2002, 95, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tabata, O.; Kojima, H.; Kasatani, T.; Isono, Y.; Yoshida, R. Ciliary motion actuator using self-oscillating gel. Proceedings of the International Conference on MEMS 2003, Shiga, Japan; 2003; pp. 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Yoshida, R. Design of chemo-mechanical actuator using self-oscillating gel. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO 2004), Tokyo, Japan, 2004; p. 313.
- Tateyama, S.; Shibuta, Y.; Yoshida, R. Direction control of chemical wave propagation in self-oscillating gel array. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Sakai, T.; Ito, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Self-oscillation of polymer chains with rhythmical soluble-insoluble changes. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 124, 8095–8098. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R. Self-oscillating nanogel particles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, D.; Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R. Self-flocculating/self-dispersing oscillation of microgels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 917–920. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, D.; Yoshida, R. Temporal control of self-oscillation for microgels by cross-linking network structure. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5830–5838. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, D.; Yoshida, R. Effect of initial substrate concentration of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction on self-oscillation for microgel system. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 12618–12624. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, D.; Taniguchi, H.; Yoshida, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 12058–12059.
- Ito, Y.; Hara, Y.; Uetsuka, H.; Hasuda, H.; Onishi, H.; Arakawa, H.; Ikai, A.; Yoshida, R. AFM observation of immobilized self-oscillating polymer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5170–5173. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, T.; Takeoka, Y.; Seki, T.; Yoshida, R. Organized monolayer of thermosensitive microgel beads prepared by double-templete polymerization. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8651–8654. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, Y.; Yoshida, R. Self-oscillation of polymer chains induced by the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction under acid-free conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 9451–9454. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, Y.; Yoshida, R. Control of oscillating behavior for the self-oscillating polymer with pH-control site. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9773–9776. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, Y.; Sakai, T.; Maeda, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Yoshida, R. Self-oscillating soluble-insoluble changes of polymer chain including an oxidizing agent induced by the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23316–23319. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, Y.; Yoshida, R. Self-oscillating polymer fueled by organic acid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 8427–8429. [Google Scholar]








© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshida, R. Design of Self-Oscillating Gels and Application to Biomimetic Actuators. Sensors 2010, 10, 1810-1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301810
Yoshida R. Design of Self-Oscillating Gels and Application to Biomimetic Actuators. Sensors. 2010; 10(3):1810-1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301810
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshida, Ryo. 2010. "Design of Self-Oscillating Gels and Application to Biomimetic Actuators" Sensors 10, no. 3: 1810-1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301810
APA StyleYoshida, R. (2010). Design of Self-Oscillating Gels and Application to Biomimetic Actuators. Sensors, 10(3), 1810-1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100301810