Coverage-Guaranteed Sensor Node Deployment Strategies for Wireless Sensor Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Network Model and Problem Description
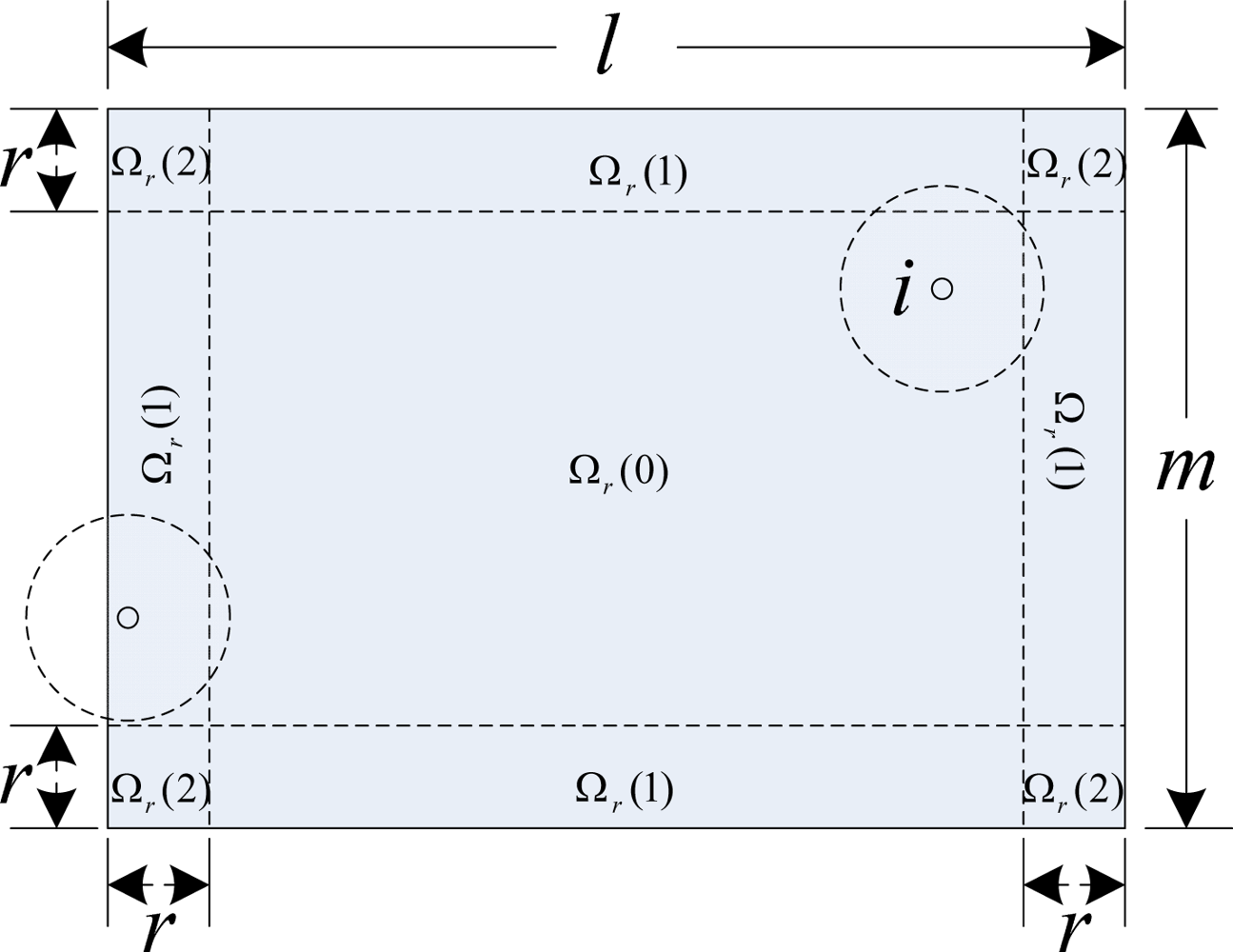
3.1. Network Model
3.2. Problem Description
4. Random Deployment Strategies
4.1. Expected-Area Coverage Deployment Strategy
4.2. Boundary Assistant Deployment Strategy
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Performance of Three Deployment Strategies
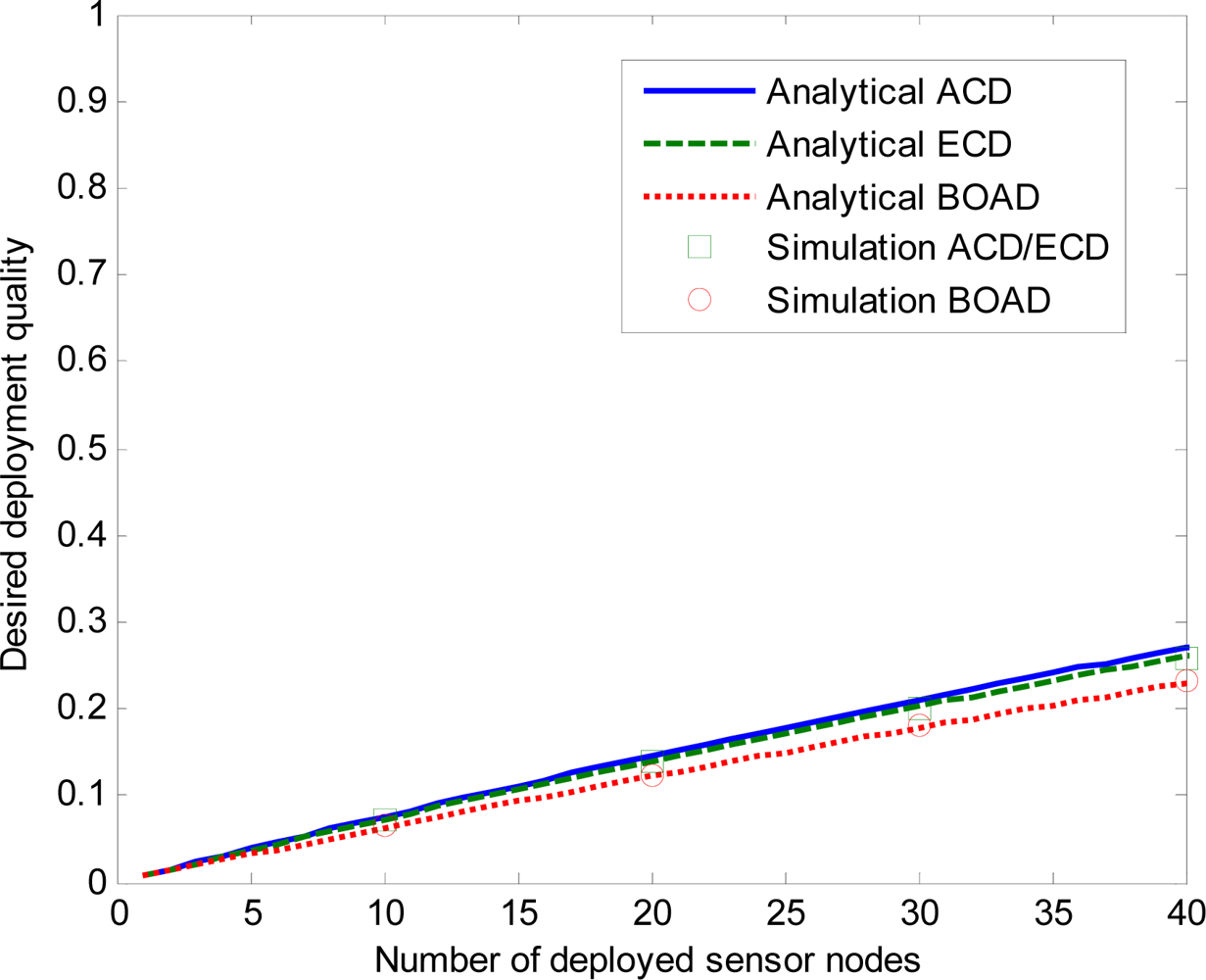
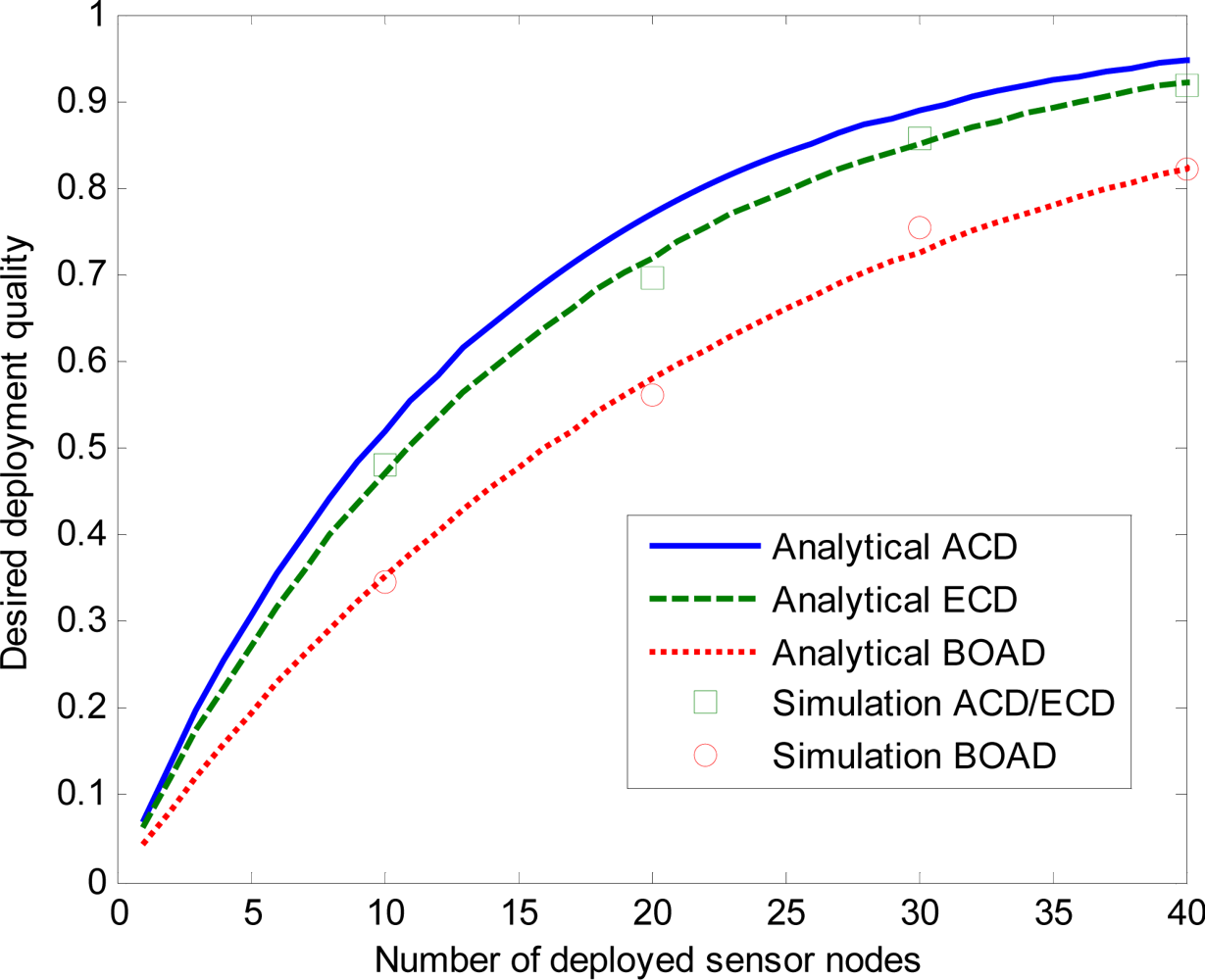
- The minimum number of deployed sensor nodes: a measure of deployment cost to achieve the desired deployment quality.
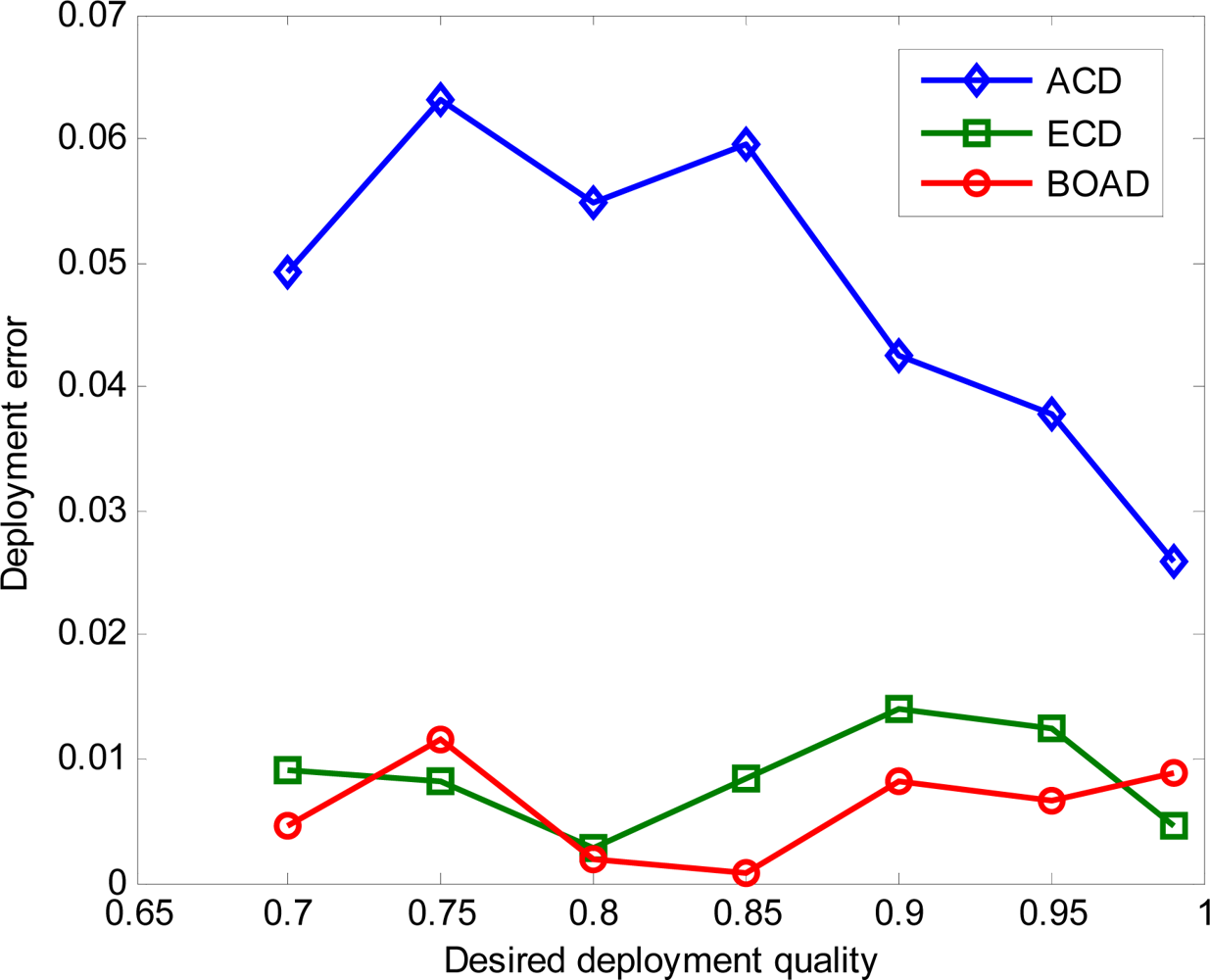
- Deployment quality achieved and deployment errors: a measure of efficiency for deployment quality.
5.2. Detection Application
5.3. Effects of Network Parameters
- Both BOAD and ECD can efficiently alleviate the coverage overestimation in terms of the desired deployment quality, which can ensure the surveillance quality.
- Both BOAD and ECD reduce the average intrusion distance compared to ACD in intrusion detection applications. Furthermore, BOAD, which uses a boundary assistant region, has the best performance in terms of the average intrusion distance when the invasion of intruder is from the boundary of a monitored region. ECD has the best performance in terms of the average intrusion distance when the invasion of intruder is from the inside of monitored region.
- Achieved desired deployment quality increases when the number of sensor nodes or radius increases. BOAD achieves the lower desired deployment quality compared to ECD under the same number of sensor nodes and sensing radius, the analysis and simulations have slight discrepancy which efficiently alleviate coverage overestimation.
6. Practical Discussion
6.1. General Monitored Region
6.2. Probabilistic Sensing Model
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
References
- Krysander, M.; Frisk, E. Sensor placement for fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. A Syst. Humans 2008, 38, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, F.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Chen, J.L. A smart sensor network for object detection, classification and recognition. International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications (WOCC), Newark, NJ, USA, April 22–23, 2005; p. 70.
- Lazos, L.; Poovendran, R. Coverage in heterogeneous sensor networks. The Fourth International Symposium on Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc and Wireless Networks(WiOpt 2006), Boston, MA, USA, April 3–6, 2006; pp. 1–10.
- Onur, E.; Ersoy, C.; Delic, H. How many sensors for an acceptable breach detection probability? Comput. Commun 2006, 29, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, P.J.; Yi, C.W. Coverage by randomly deployed wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theo 2006, 52, 2658–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Meguerdichian, S.; Koushanfar, F.; Potkonjak, M.; Srivastava, M.B. Coverage problems in wireless ad-hoc sensor networks. Proceedings of Twentieth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications(INFOCOM 2001), Anchorage, AK, USA, April 22–26, 2001; pp. 1380–1387.
- Zou, Y.; Krishnendu, C. Sensor deployment and target localization based on virtual forces. Proceedings of Twenty-Second Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications(INFOCOM 2003), San Franciso, CA, USA, March 30–April 3, 2003; pp. 1293–1303.
- Hoffmann, F.; Kaufmann, M.; Kriegel, K. The Art Gallery theorem for polygons with holes. Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, San Juan, Puerto Rico, October 1–4, 1991; pp. 39–48.
- Shakkottai, S.; Srikant, R.; Shroff, N. Unreliable sensor grids: coverage, connectivity and diameter. Proceedings of Twenty-Second Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications(INFOCOM 2003), San Franciso, CA, USA, March 30–April 3, 2003; pp. 1073–1083.
- Hall, P. Introduction to the Theory of Coverage Processes; John Wiley & Sons Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Brass, P.; Dousse, O.; Nain, P.; Towsley, D. Mobility improves coverage of sensor networks. Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Symposium on Mobile ad hoc Networking and Computing (ACM MobiHoc 2005), Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA, May 25–28, 2005; pp. 300–308.
- Liu, B.; Towsley, D. A study of the coverage of large-scale sensor networks. 2004 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Systems, Piscataway, NJ, USA, October 25–27, 2004; pp. 475–483.
- Tsai, Y.R. Sensing Coverage for Randomly Distributed wireless sensor networks in shadowed environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol 2008, 57, 556–564. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A. Estimating Coverage Holes and Enhancing Coverage in Mixed Sensor Networks. Proceedings of the 29th Annual IEEE International Conference on Local Computer Networks, Washington, DC, USA, November 16–18, 2004; pp. 68–76.
- Adlakha, S.; Srivastava, M. Critical density thresholds for coverage in wireless sensor networks. 2003 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking (WCNC), New Orleans, LA, USA, March 16–20, 2003; pp. 1615–1620.
- Balister, P.; Kumar, S. Random vs. Deterministic Deployment of Sensors in the Presence of Failures and Placement Errors. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2009, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, April 19–25, 2009; pp. 2896–2900.
- Liu, C.; Wu, K.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, B. Random coverage with guaranteed connectivity: joint scheduling for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst 2006, 17, 562–575. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Li, F.; Wen, J.; W, G.F.; Zhang, H.Y. Random scheduling for wireless sensor networks. IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing with Applications, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, August 10–12, 2009; pp. 324–332.
- Zou, Y.; Chakrabarty, K. A distributed coverage- and connectivity-centric technique for selecting active nodes in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Comput 2005, 54, 978–991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.R.; Xing, G.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Lu, C.Y.; Pless, R.; Gill, C. Integrated coverage and connectivity configuration in wireless sensor networks. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, November 5–7, 2003; pp. 28–39.
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.D.; Xie, B.; Wang, D.M.; Agrawal, D.P. Intrusion detection in homogeneous and heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput 2008, 7, 698–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.H.; Hou, J. On deriving the upper bound of a-lifetime for large sensor networks. Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Symposium on Mobile ad hoc Networking and Computing(ACM MobiHoc 2004), Roppongi Hills, Tokyo, Japan, May 24–26, 2004; pp. 121–132.
- Younis, M.; Akkaya, K. Strategies and techniques for node placement in wireless sensor networks: a survey. Ad Hoc Netw 2008, 6, 621–655. [Google Scholar]
- Coskun, V. Relocating Sensor Nodes to Maximize Cumulative connected coverage in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2008, 8, 2792–2817. [Google Scholar]
- Takahara, G.; Xu, K.; Hassanein, H. How resilient is grid-based WSN coverage to deployment errors? IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC 2007), Hong Kong, March 11–15, 2007; pp. 2874–2879.
- Yan, T.; He, T.; Stankovic, J.A. Differentiated surveillance for sensor networks. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, November 5–7, 2003; pp. 51–62.
- Choi, W.; Das, S.K. Coverage-adaptive random sensor scheduling for application-aware data gathering in wireless sensor networks. Comput. Commun 2006, 29, 3467–3482. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Yan, T.; Stankovic, J.; Abdelzaher, T. Analysis of target detection performance for wireless sensor networks. Lect. Note. Comput. Sci 2005, 3560, 276–292. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Q.; Tian, Z. Minimum node degree and k-connectivity of a wireless multihop network in bounded area. Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM 2007, Washington, DC, USA, November 26–30, 2007; pp. 1296–1301.
- Santalo, L. Integral Geometry and Geometric Probability; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Reading, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Onur, E.; Ersoy, C.; Delic, H.; Akarun, L. Surveillance wireless sensor networks: deployment quality analysis. IEEE Netw 2007, 21, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Yen, L. Estimating the Number of Links in ad hoc Mobile Networks with Applications; Technical Report CHU-CSIE-TR-2003-002;. Department CSIE, Chung Hua University: Taiwan, July 2003. Available online: http://www.csie.chu.edu.tw/tech/tech_file/tech143630.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2009).
Appendix
Computing Er[1]

Computing Er[2]
- Case 1. The distance to the corner is less than r (Figure 14a).
- Case 2. The distance to the corner is larger than or equal to r (Figure 14b).









| Notation | Definition |
|---|---|
| Ω | the monitored region |
| D | the deployed region |
| B | the boundary assistant region |
| n | the number of deployed sensor nodes |
| nk | the lower bound number of deployed sensor nodes for strategy k |
| ri | the sensing radius of sensor i |
| A(x) | the circular area centered at given point x with radius r |
| d(i) | the distance to the boundary of monitored region of sensor i |
| Ef(d(i)) | the effective coverage area of sensor i |
| Er[j] | the expected area of sub-region j |
| Ωr(j) | the sub-region j of monitored region |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, G.; Wang, R.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Sha, C. Coverage-Guaranteed Sensor Node Deployment Strategies for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2010, 10, 2064-2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100302064
Fan G, Wang R, Huang H, Sun L, Sha C. Coverage-Guaranteed Sensor Node Deployment Strategies for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors. 2010; 10(3):2064-2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100302064
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Gaojuan, Ruchuan Wang, Haiping Huang, Lijuan Sun, and Chao Sha. 2010. "Coverage-Guaranteed Sensor Node Deployment Strategies for Wireless Sensor Networks" Sensors 10, no. 3: 2064-2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100302064
APA StyleFan, G., Wang, R., Huang, H., Sun, L., & Sha, C. (2010). Coverage-Guaranteed Sensor Node Deployment Strategies for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors, 10(3), 2064-2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100302064





