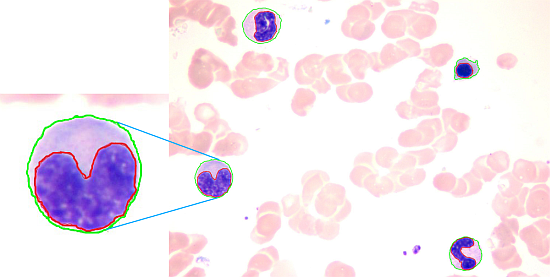
White Blood Cell Segmentation by Color-Space-Based K-Means Clustering
Abstract
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.-J.; Zhen, W.; Chang, J.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z. White Blood Cell Segmentation by Color-Space-Based K-Means Clustering. Sensors 2014, 14, 16128-16147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140916128
Zhang C, Xiao X, Li X, Chen Y-J, Zhen W, Chang J, Zheng C, Liu Z. White Blood Cell Segmentation by Color-Space-Based K-Means Clustering. Sensors. 2014; 14(9):16128-16147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140916128
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Congcong, Xiaoyan Xiao, Xiaomei Li, Ying-Jie Chen, Wu Zhen, Jun Chang, Chengyun Zheng, and Zhi Liu. 2014. "White Blood Cell Segmentation by Color-Space-Based K-Means Clustering" Sensors 14, no. 9: 16128-16147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140916128
APA StyleZhang, C., Xiao, X., Li, X., Chen, Y.-J., Zhen, W., Chang, J., Zheng, C., & Liu, Z. (2014). White Blood Cell Segmentation by Color-Space-Based K-Means Clustering. Sensors, 14(9), 16128-16147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140916128